1.卷积层(以Conv2d为例)

注:输入的参数包括batchsize,通道数,图像宽度和高度,对于一般的图像通常只有宽度和高度两个参数,所以可以使用reshape函数改变尺寸。
例1:以张量为例
input = torch.Tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]
])
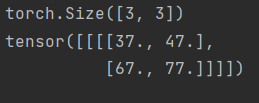
print(input.shape)
input = torch.reshape(input, [1, 1, 3, 3])
kernal = torch.Tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
kernal = torch.reshape(kernal, [1, 1, 2, 2])
output = torch.nn.functional.conv2d(input, kernal, stride=1, padding=0)
print(output)
输出:
例2 :单层神经网络
class model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(model, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 3, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
return x
2.池化层(以最大池化(下采样)为例)
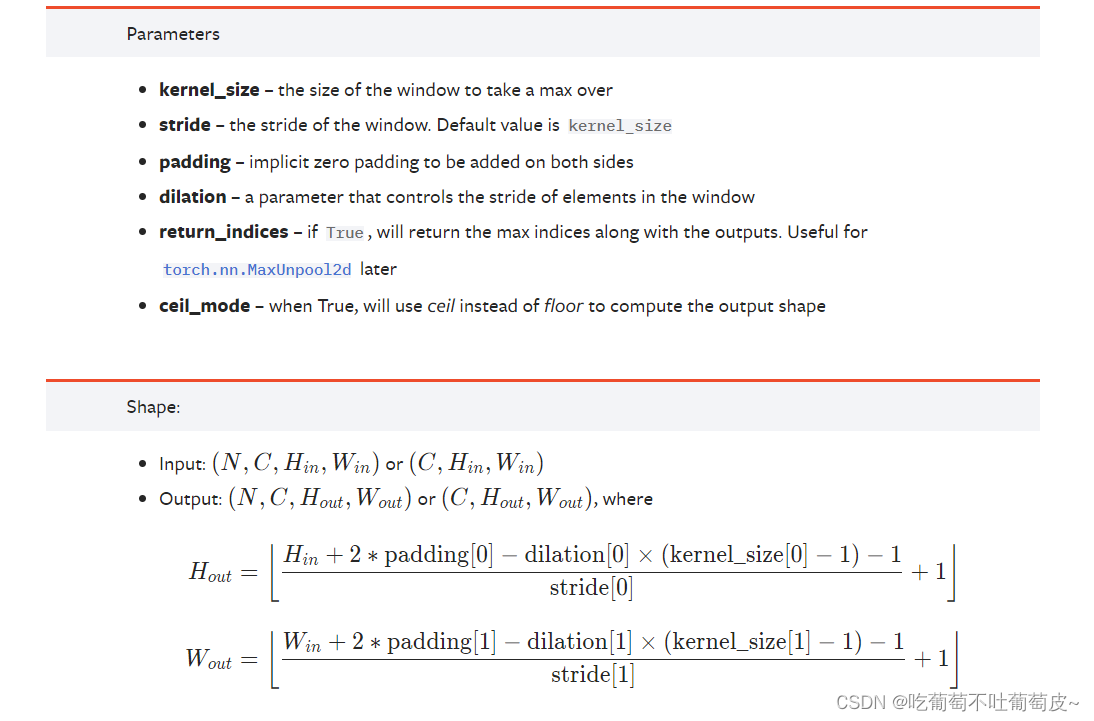
注:stride若不设置默认值为kernal的尺寸
例3 :以张量为例
input = torch.Tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]
])
print(input.shape)
input = torch.reshape(input, [1, 1, 3, 3])
kernal = torch.Tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
kernal = torch.reshape(kernal, [1, 1, 2, 2])
class model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(model, self).__init__()
self.maxpool1 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.maxpool1(x)
return x
model1 = model()
output = model1(input)
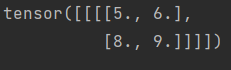
print(output)
输出:
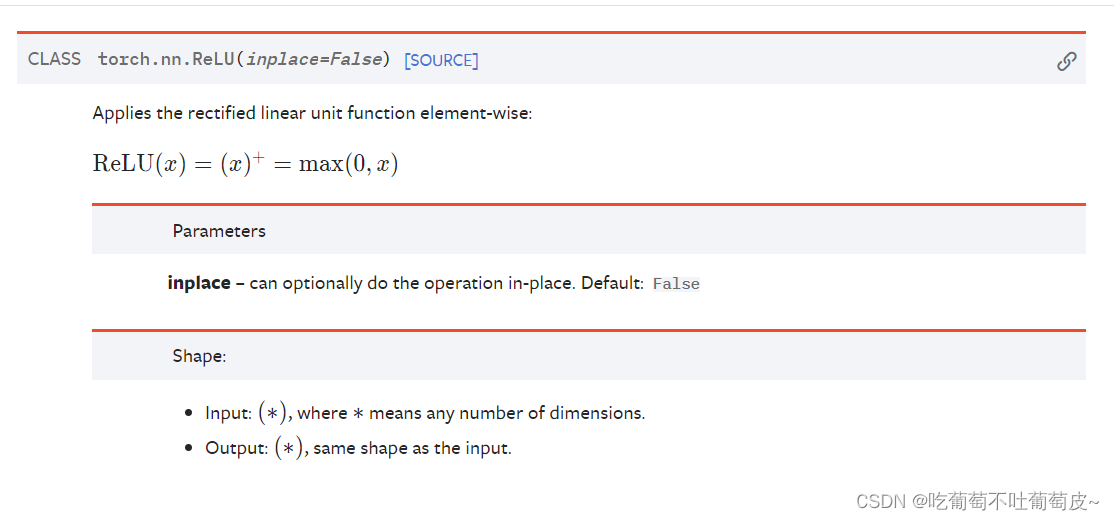
3.激活层(以ReLU为例)
4.实战
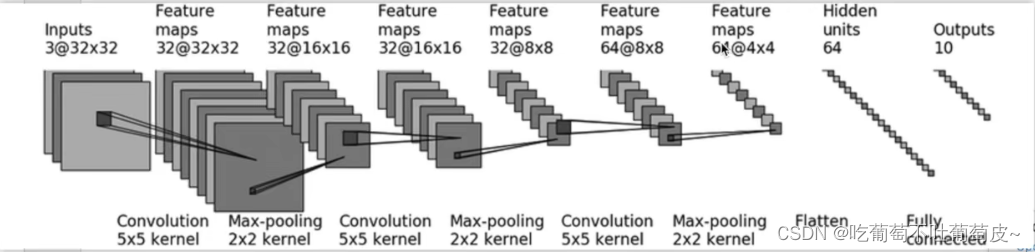
4.1 Model框架
class model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(model,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size = (5, 5), stride = (1, 1), padding=2)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, (5, 5), padding=2)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, (5, 5), padding=2)
self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.flatten1 = nn.Flatten()
self.linaer1 = nn.Linear(1024, 64)
self.linaer2 = nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, input):
input = self.conv1(input)
input = self.pool1(input)
input = self.conv2(input)
input = self.pool2(input)
input = self.conv3(input)
input = self.pool3(input)
input = self.flatten1(input)
input = self.linaer1(input)
input = self.linaer2(input)
return input
model1 = model()
input = torch.ones((64, 3, 32, 32))
output = model1(input)
print(output.shape)
输出:
torch.Size([64, 10])
4.2 Sequential框架
class model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(model,self).__init__()
self.model1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(32, 32, (5, 5), padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, (5, 5), padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(1024, 64),
nn.Linear(64, 10)
)
def forward(self, input):
input = self.model1(input)
return input
model1 = model()
input = torch.ones((64, 3, 32, 32))
output = model1(input)
print(output.shape)
输出:
torch.Size([64, 10])