YOLOX:pytorch实现网络结构
网络总体结构简介
YOLOX的网络主要由三个部分组成,分别是CSPDarkNet、FPN和YOLOXHead。
-
CSPDarkNet是YOLOX的主干特征提取网络,其输出为三个有效特征层
-
FPN是YOLOX的加强特征提取网络,其作用是将CSPDarkNet输出的三个有效特征层进行特征融合,将不同尺度的特征信息进行融合。
-
YOLOXHead是YOLOX的分类器和回归器,YOLOXHead通过FPN输出的三个特征图来判断特征点是否有物体与其对应,之前的YOLOHead是分类和回归在一个卷积里实现的,YOLOXHead则将分类和回归分开实现最后再整合在一起
主干网络CSPDarkNet的Pytorch实现
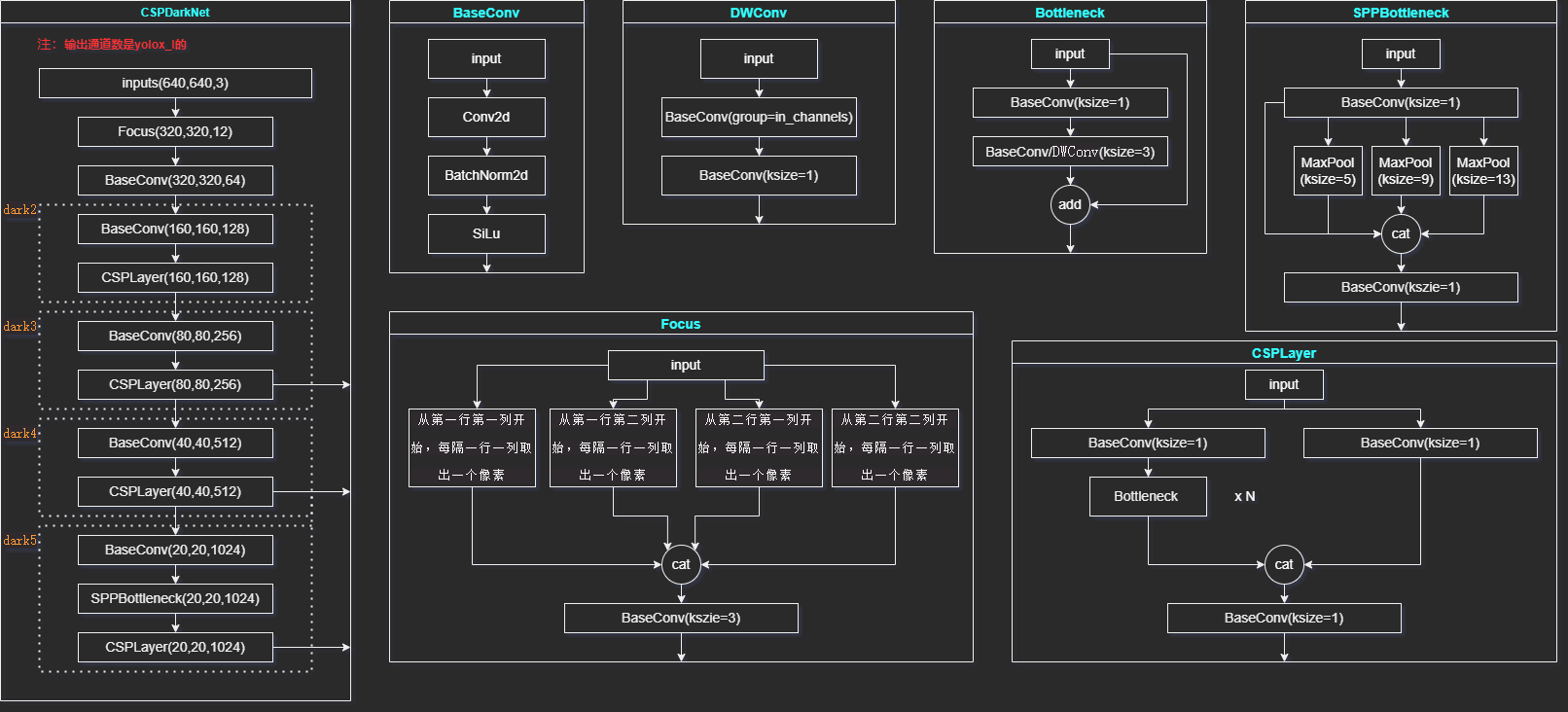
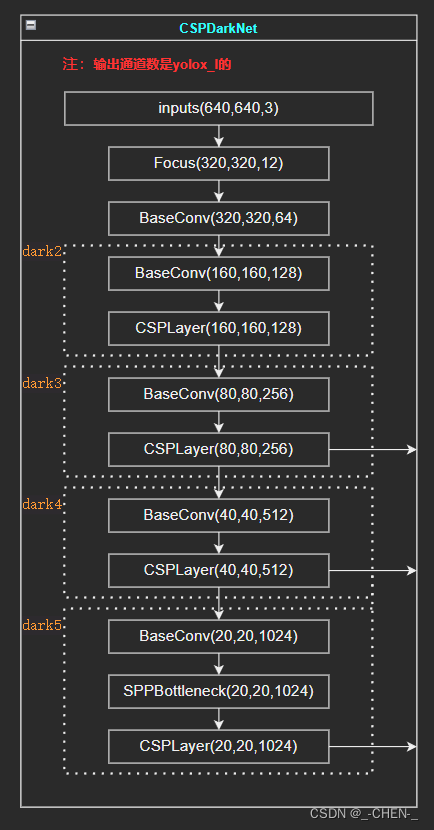
CSPDarkNet主干网络主要由Focus、CSPLayer、BaseConv、DWConv、Bottleneck、SPPBottleneck组成,其网络结构如下图所示:
基础模块
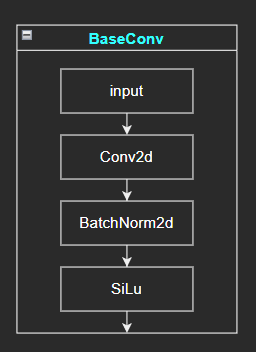
BaseConv
BaseConvert由一个卷积层,一个BN层和一个激活层组成
class BaseConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
ksize,
stride,
groups=1,
bias=False,
act="silu"):
super(BaseConv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=ksize,
stride=stride,
groups=groups,
padding=(ksize - 1) // 2,
bias=bias)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels, eps=0.001, momentum=0.03)
self.act = get_activation(act, inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def get_activation(name="silu", inplace=True):
if name == "silu":
module = SiLU()
elif name == "relu":
module = nn.ReLU(inplace=inplace)
elif name == "lrelu":
module = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=inplace)
else:
raise AttributeError("Unsupported act type: {}".format(name))
return module
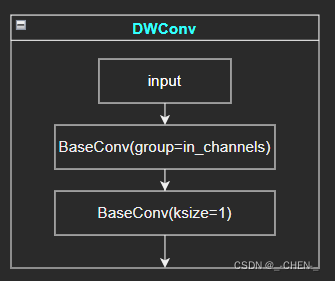
DWConv
深度可分离卷积,由一个逐通道卷积和一个逐点卷积构成,具体介绍
class DWConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
ksize,
stride=1,
act="silu"):
super(DWConv, self).__init__()
self.dconv = BaseConv(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=in_channels,
ksize=ksize,
stride=stride,
groups=in_channels,
act=act)
self.pconv = BaseConv(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
ksize=1,
stride=1,
groups=1,
act=act)
def forward(self, x):
return self.pconv(self.dconv(x))
Focus网络实现
Focus网络将输入图片分别从第一行第一列、第一行第二列、第二行第一列、第二行第二例开始,每隔一个像素取出一个像素组成一个新的图片,就会得到四个长宽缩小一半的图像,再将其堆叠在一起,使得通道数变为原来的4倍,即12
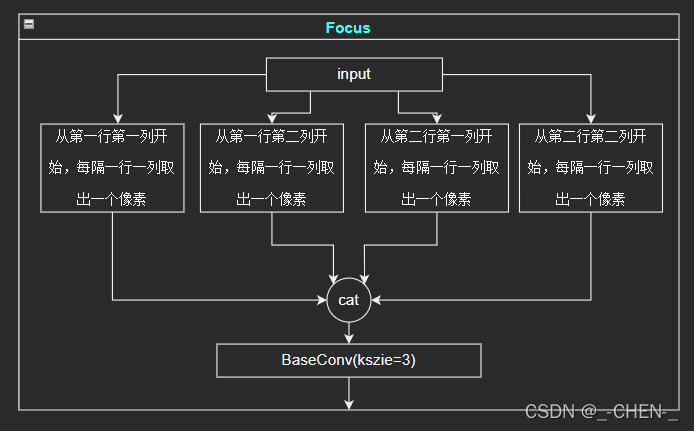
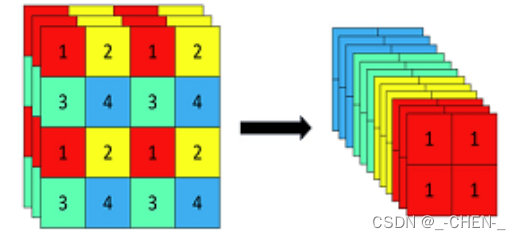
使用python的切片可以很方便的截取出四个独立的特征层,再使用torch.cat将其堆叠
class Focus(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
ksize=1,
stride=1,
act="silu"):
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = BaseConv(in_channels=in_channels * 4,
out_channels=out_channels,
ksize=ksize,
stride=stride,
act=act)
def forward(self, x):
patch_top_left = x[..., ::2, ::2]
patch_bot_left = x[..., 1::2, ::2]
patch_top_right = x[..., ::2, 1::2]
patch_bot_right = x[..., 1::2, 1::2]
x = torch.cat((patch_top_left, patch_bot_left, patch_top_right, patch_bot_right,), dim=1)
return self.conv(x)
CSPLayer网络实现
CSPLayer网络由残差网络Bottleneck堆叠而成,Bottleneck主干部分由一个1X1的卷积和一个3X3的卷积组成,残差边部分不做任何处理,最后将两者相加
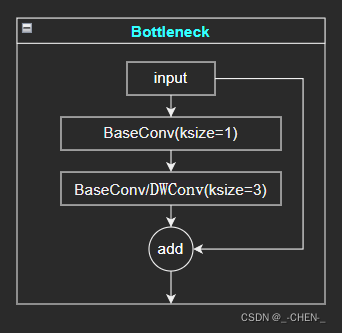
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
shortcut=True,
expansion=0.5,
depthwise=False,
act="silu"):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
hidden_channels = int(out_channels * expansion)
Conv = DWConv if depthwise else BaseConv
self.conv1 = BaseConv(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=hidden_channels,
ksize=1,
stride=1,
act=act)
self.conv2 = Conv(in_channels=hidden_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
ksize=3,
stride=1,
act=act)
self.use_add = shortcut and in_channels == out_channels
def forward(self, x):
y = self.conv2(self.conv1(x))
if self.use_add:
y = y + x
return y
CSPLayer主干部分继续进行原来的残差块的堆叠;另一部分则像一个残差边一样,经过少量处理直接连接到最后。因此可以认为CSP中存在一个大的残差边。
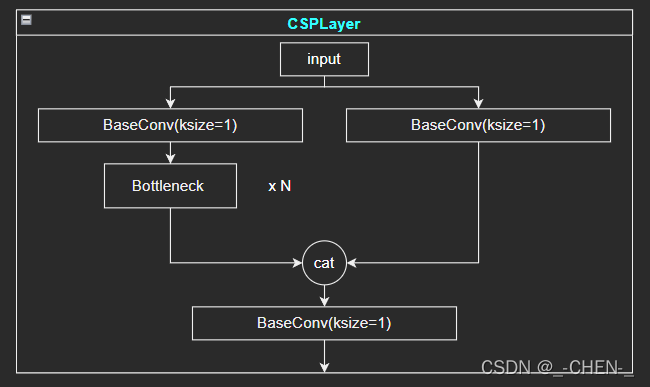
class CSPLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
n=1,
shortcut=True,
expansion=0.5,
depthwise=False,
act="silu"):
super(CSPLayer, self).__init__()
hidden_channels = int(out_channels * expansion)
self.conv1 = BaseConv(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=hidden_channels,
ksize=1,
stride=1,
act=act)
self.conv2 = BaseConv(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=hidden_channels,
ksize=1,
stride=1,
act=act)
self.conv3 = BaseConv(in_channels=hidden_channels * 2,
out_channels=out_channels,
ksize=1,
stride=1,
act=act)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*[Bottleneck(in_channels=hidden_channels,
out_channels=hidden_channels,
shortcut=shortcut,
expansion=1,
depthwise=depthwise,
act=act) for _ in range(n)])
def forward(self, x):
x_1 = self.conv1(x)
x_2 = self.conv2(x)
x_1 = self.m(x_1)
x = torch.cat((x_1, x_2), dim=1)
return self.conv3(x)
SPPBottleneck网络实现
SPPBottleneck网络通过不同池化核大小的最大池化进行特征提取,提高网络的感受野
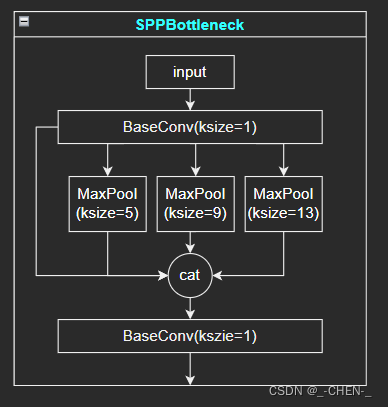
class SPPBottleneck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
ksizes=(5, 9, 13),
act="silu"):
super(SPPBottleneck, self).__init__()
hidden_channels = in_channels // 2
self.conv1 = BaseConv(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=hidden_channels,
ksize=1,
stride=1,
act=act)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=ksize, stride=1, padding=ksize // 2) for ksize in ksizes])
conv2_channels = hidden_channels * (len(ksizes) + 1)
self.conv2 = BaseConv(in_channels=conv2_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
ksize=1,
stride=1,
act=act)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], dim=1)
x = self.conv2(x)
return x
CSPDarkNet网络实现
根据下图使用前面实现的一些基础模块网络搭建YOLOX的主干网络CSPDarkNet
class CSPDarknet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dep_mul,
wid_mul,
out_features=("dark3", "dark4", "dark5"),
depthwise=False,
act="silu"):
super(CSPDarknet, self).__init__()
self.out_features = out_features
Conv = DWConv if depthwise else BaseConv
base_channels = int(wid_mul * 64)
base_depth = max(round(dep_mul * 3), 1)
self.stem = Focus(in_channels=3,
out_channels=base_channels,
ksize=3,
act=act)
self.dark2 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(in_channels=base_channels,
out_channels=base_channels * 2,
ksize=3,
stride=2,
act=act),
CSPLayer(in_channels=base_channels * 2,
out_channels=base_channels * 2,
n=base_depth,
depthwise=depthwise,
act=act)
)
self.dark3 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(in_channels=base_channels * 2,
out_channels=base_channels * 4,
ksize=3,
stride=2,
act=act),
CSPLayer(in_channels=base_channels * 4,
out_channels=base_channels * 4,
n=base_depth * 3,
depthwise=depthwise,
act=act)
)
self.dark4 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(in_channels=base_channels * 4,
out_channels=base_channels * 8,
ksize=3,
stride=2,
act=act),
CSPLayer(in_channels=base_channels * 8,
out_channels=base_channels * 8,
n=base_depth * 3,
depthwise=depthwise,
act=act)
)
self.dark5 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(in_channels=base_channels * 8,
out_channels=base_channels * 16,
ksize=3,
stride=2,
act=act),
SPPBottleneck(in_channels=base_channels * 16,
out_channels=base_channels * 16,
act=act),
CSPLayer(in_channels=base_channels * 16,
out_channels=base_channels * 16,
n=base_depth,
shortcut=False,
depthwise=depthwise,
act=act)
)
def forward(self, x):
outputs = {}
x = self.stem(x)
outputs["stem"] = x
x = self.dark2(x)
outputs["dark2"] = x
x = self.dark3(x)
outputs["dark3"] = x
x = self.dark4(x)
outputs["dark4"] = x
x = self.dark5(x)
outputs["dark5"] = x
return {k: v for k, v in outputs.items() if k in self.out_features}