前言
针对数字图像处理一书的近期学习做个总结
会用代码对图像进行一系列求梯度,下采样,上采样操作
一、图像的基本操作
1用Image.open()读入图像
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
image = Image.open("F:/test_image/rose2.jfif")
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
2 如何用plt.imshow()输出灰度图
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=1),
transforms.Resize((2000,2500))
]
)
image = data_transform(image)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
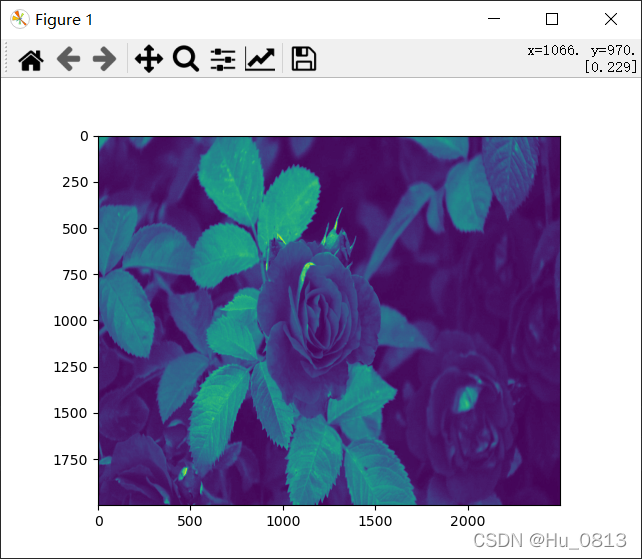
3两张图片结合输出
类似于加水印的方法,在经过数据处理之后的值为[0 - 255] ,我们可以将下列图片与上面的 rose 做成一种水印的方法,首先先将该图亮度值转换
注意 若转化为tensor类型,则此时的灰度值从[0 - 255] 变为[0.0 - 1.0]
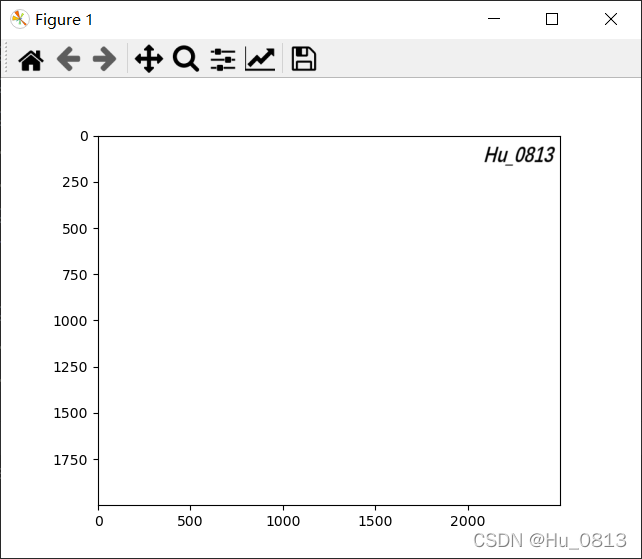
image2 = Image.open('F:/test_image/Hu.png')
image2 = data_transform(image2)
image2 = np.array(image2)
image2 = np.where(image2 > 50, 0, 255)
plt.imshow(image2)
plt.show()
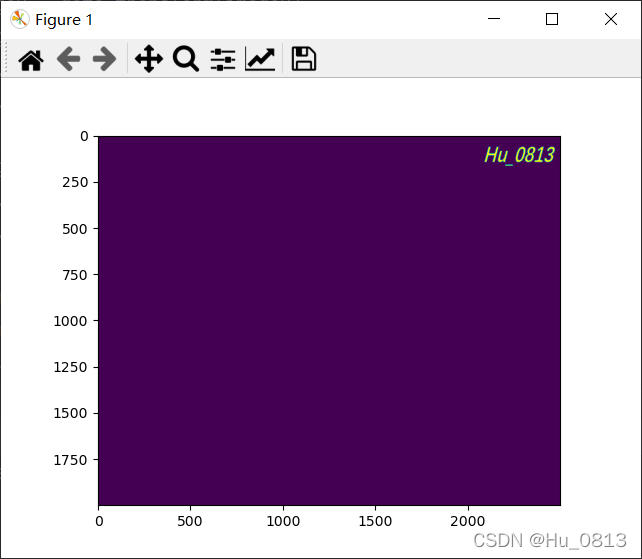
因为图像可以用矩阵表示,所以我们可以将花和名字相加输出
image += image2
plt.imshow(image,cmap='gray')
plt.show()
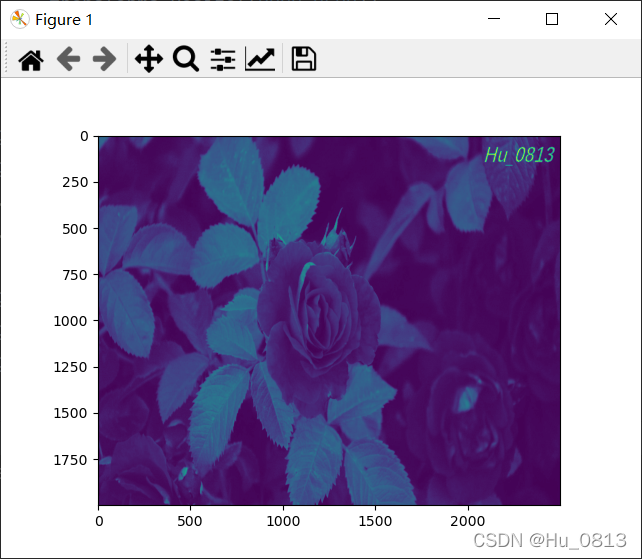
视觉上感觉变暗了,可以通过对比像素值验证
二、噪声
1.人为给图像加入噪声
我们试着将上述图像添加10%的噪声(白点)类似于老式电视机的雪花点
当然也可以用-255和0选择黑色噪声
w, h = image.size # PIL中的size为 w, h
noise_salt = np.random.randint(0, 256, size=(h, w))
ratio = 0.1
noise_salt = np.where(noise_salt < ratio*255, 255, 0) #加10%的噪声
image = image + noise_salt
#但是存在一个饱和相加减的问题。也就是说,如果图像与噪声之和>255,或者<0,比如266,那么最终的像素值为16,反而变暗
image = np.where(image > 255, 255, image) #这样就可以解决
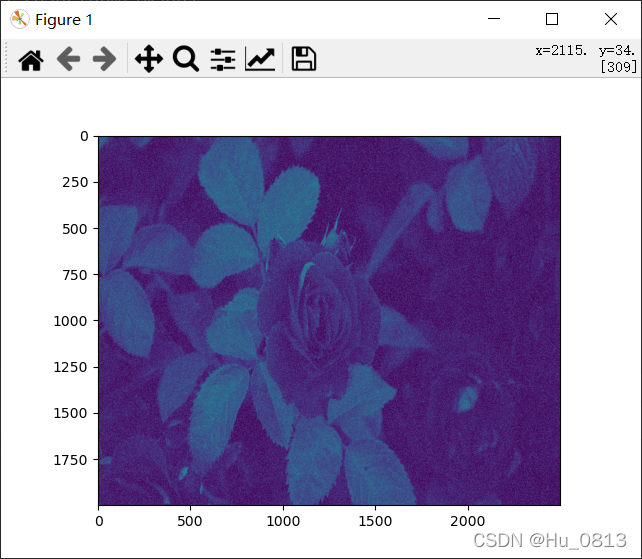
2.还有一种常见的高斯噪声:每个像素点周围都有噪声,可以自行对比
w, h = image.size
noise_Gauss = np.random.normal(0, 100, size=(h, w))
image = image + noise_Gauss
image = np.where(image>255,255,np.where(image<0,0,image))
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
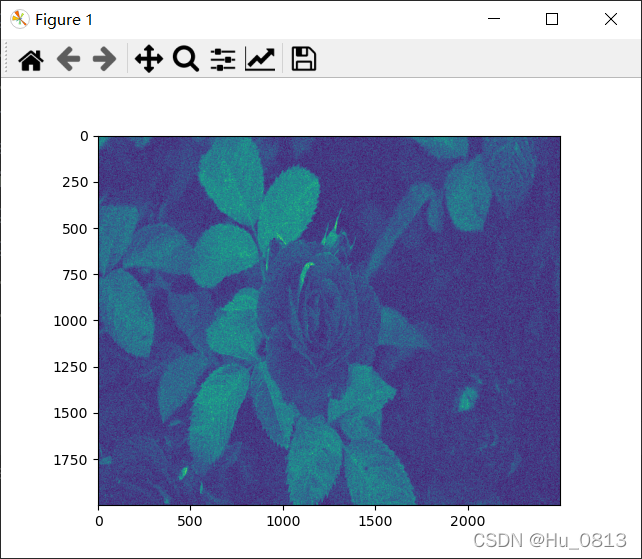
2.平均像素值降噪
此时的 image = image + noise_salt
因为图像中每个像素点的值与其旁边的像素点的值比较接近,所以我们可以采用平均像素值的方法降低噪声
下图是5%的噪声
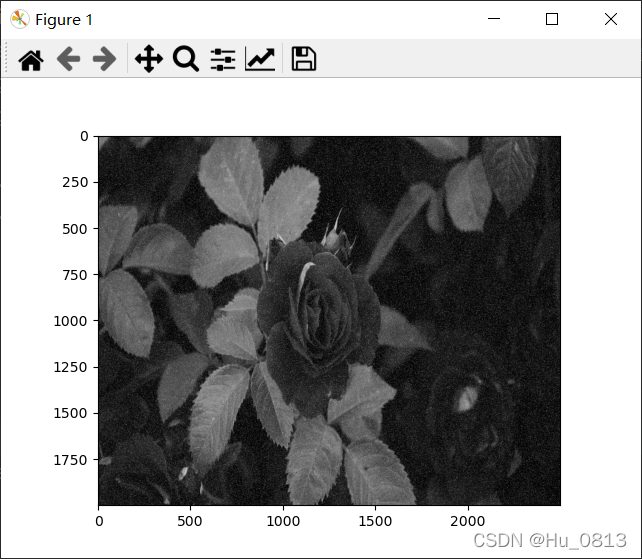
for x in range(1,h-1):
for y in range(1,w-1):
imge_avg = 0
for i in [-1,0,1]:
for j in [-1,0,1]:
imge_avg +=image[x+i][y+j]
image[x][y] = imge_avg // 9
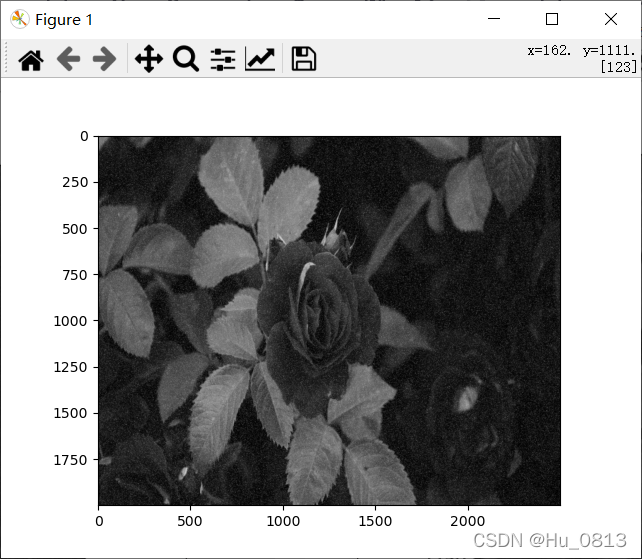
三 求图像边缘
两个具有不同灰度的均匀图像区域的边界称为边缘。沿边缘方向的灰度变化比较平缓,而边缘法线方向的灰度变化比较剧烈
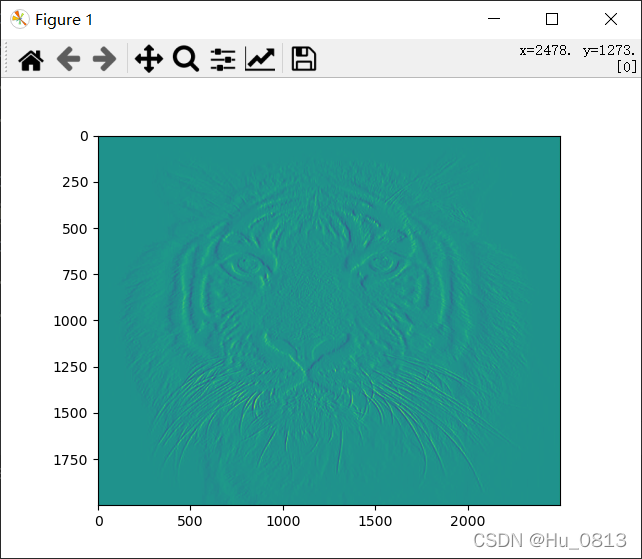
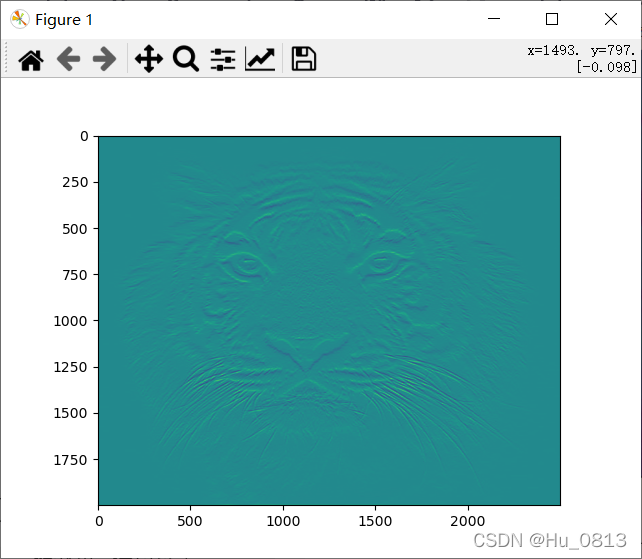
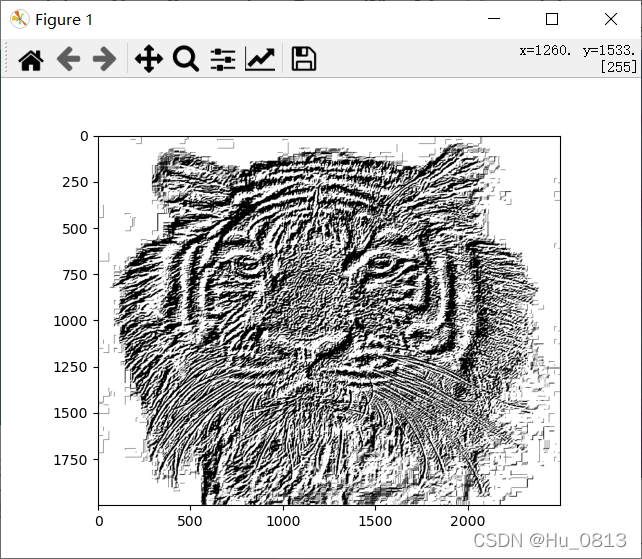
而表示两个数的剧烈程度 我们可以用一阶导数来计算,单位像素的一阶导数就是相邻两个像素值的差值,但是对于相邻位置的权重分配不用,以下采用sobel边缘检测,第三张图放大梯度之后产生噪声,可用均值处理降噪
完整代码如下
import torch
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=1),
transforms.Resize((2000,2500)),
transforms.ToTensor()
]
)
image = Image.open("F:/test_image/tiger.jfif")
image = data_transform(image)
image = torch.unsqueeze(image, 0)
class Sobel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Sobel, self).__init__()
self.edge_conv = nn.Conv2d(1, 2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
edge_kx = np.array([[1, 0, -1], [2, 0, -2], [1, 0, -1]])
edge_ky = np.array([[1, 2, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -2, -1]])
edge_k = np.stack((edge_kx, edge_ky))
edge_k = torch.from_numpy(edge_k).float().view(2, 1, 3, 3)
self.edge_conv.weight = nn.Parameter(edge_k)
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
def forward(self, x):
out = self.edge_conv(x)
out = out.contiguous().view(-1, 2, x.size(2), x.size(3))
return out
sober = Sobel()
grad = sober(image)
grad_x = grad[:,0,:,:]
grad_x = torch.squeeze(grad_x,0)
grad_x = torch.squeeze(grad_x,0)
grad_x = np.array(grad_x)
plt.imshow(grad_x)
plt.show()
grad_y = grad[:,1,:,:]
grad_y = torch.squeeze(grad_y,0)
grad_y = torch.squeeze(grad_y,0)
grad_y = np.array(grad_y)
plt.imshow(grad_y)
plt.show()
grad = grad_x + grad_y
#print(grad)
grad = np.where(grad>0, 255,np.where(grad<0,0,grad))
plt.imshow(grad,cmap='gray')
plt.show()