前言
??卷积神经网络取得了突破性进展,效果也非常理想,但是卷积神经网络的学习过程难以从理论上难以解释,因此被不少人诟病。因此可视化其的学习过程十分重要,DeepDream 模型的目的也正是如此。DeepDearm 模型在2015年由谷歌提出,理论基础是2013年所提出的《Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks》,该文章提出了使用梯度上升的方法可视化网络每一层的特征,即用一张噪声图像输入网络,反向更新的时候不更新网络权重,而是更新初始图像的像素值,以这种训练图像的方式可视化网络。深度学习领域奠基性的经典教材《深度学习》的封面就是使用 DeepDream 模型生成的。

1 DeepDream原理
??DeepDream 为了说明CNN学习到的各特征的意义,将采用放大处理的方式。具体来说就是使用梯度上升的方法可视化网络每一层的特征,即用一张噪声图像输入网络,但反向更新的时候不更新网络权重,而是更新初始图像的像素值,以这种“训练图像”的方式可视化网络。此外输入图像也可以是一些正常的图片,这样的话就是生成背景图像之类的。
??DeepDream 如何放大图像特征?比如:有 一个网络学习了分类猫和狗的任务,给这个网络一张云的图像,这朵云可能比较像狗,那么机器提取的特征可能也会像狗。假设对应一个特征最后输入概率为[0.6,0.4],0.6表示为狗的概率,0.4则表示为猫的概率,那么采用
L
2
L_2
L2?范数可以很好达到放大特征的效果。对于这样一个特征,
L
2
=
x
1
2
+
x
2
2
L_2 = x_1^{2} + x_2^{2}
L2?=x12?+x22?,若
x
1
x_1
x1? 越大,
x
2
x_2
x2?越小,则
L
2
L_2
L2?越大,所以只需要最大化
L
2
L_2
L2?就能保证当
x
1
x_1
x1? >
x
1
x_1
x1?的时候, 迭代的轮数越多
x
1
x_1
x1?越大,
x
2
x_2
x2?越小,所以图像就会越来越像狗。每次迭代相当 于计算
L
2
L_2
L2?范数,然后用梯度上升的方法调整图像。优化的就不再是优化权重参数,而是特征值或像素点,因此,构建损失函数时,不使用通常的交叉熵,而是最大化特征值的L2范数。使图像经过网络之后提取的特征更像网络隐含的特征。具体实现的时候还要通过多尺度、随机 移动等方法获取比较好的结果。
2 DeepDream算法流程
??使用基本图像,它输入到预训练的CNN。并正向传播到特定层。
??为了更好地理解该层学到了什么,我们需要最大化通过该层激活值。这里要解释一下什么是激活值,激活值表示属于某类的概率大小,比如说二分类问题中,用[0,1]表示两类的标签,我们规定当神经网络的输出大于0就被分类到1(100% 被激活),小于0就分到0(没有被激活),所以在此情况下激活值只有100%或者0%,但是我们在平常的多分类任务中希望它可以是0%~100%的任意值。激活值越大,激活程度越高,对于分类,也就意味着它属于这一类的概率越大。DeepDream 以该层输出为梯度,然后在输入图像上完成渐变上升,以最大化该层的激活值。不过,光这样做并不能产生好的图像。为了提高训练质量,需要使用一些技术使得到的图像更好。通常可以进行高斯模糊以使图像更平滑,使用多尺度(又称为八度)的图像进行计算。先连续缩小输入图像,然后,再逐步放大,并将结果合并为一个图像输出。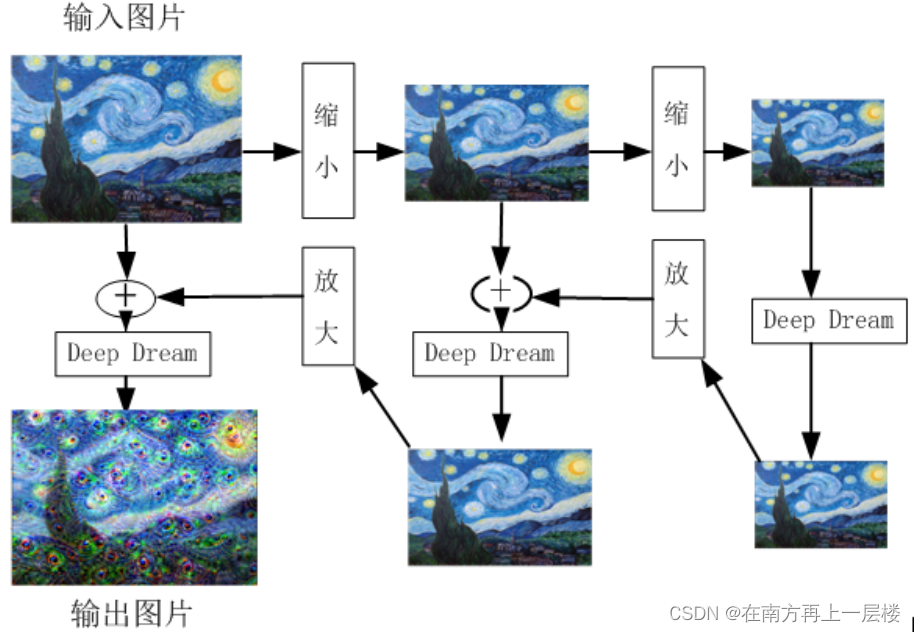
??先对图像连续做二次等比例缩小,该比例是1.5,之所以要缩小,图像缩小是为了让图像的像素点调整后所得结果图案能显示的更加平滑,过程主要是抑制了图像的高频成分,放大了低频成分。缩小二次后,把图像每个像素点当作参数,对它们求偏导,这样就可以知道如何调整图像像素点能够对给定网络层的输出产生最大化的刺激。
3 PyTorch实现DeepDream
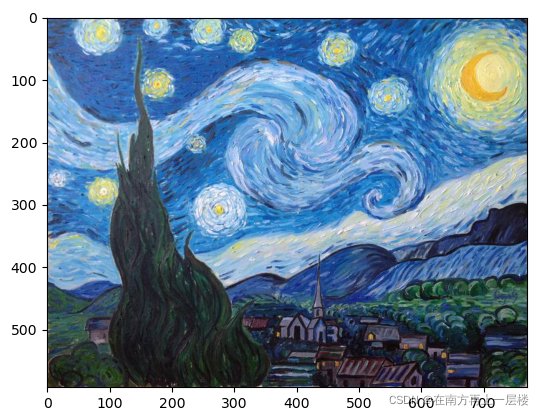
??本次实现是取 VGG19 模型为预训练模型,将获取的特征最大化之后展示在一张普通的图像上,本次使用的是梵高的星空图。为了训练更加有效,还使用对图像进行不同大小的缩放处理。
1) 下载预训练模型。VGG19 模型包括了三种不同的模块,第一个是特征提取模块 (features) ,一共有36层,第二个是池化层 (avgpool) ,只有一层,第三个是分类层 (classifier) ,一共有6层。
vgg = models.vgg19(pretrained = True).to(device)
modulelist = list(vgg.features.modules())
2) 函数 prod 主要功能是传入输入图像,正 向传播到 VGG19 的指定层(如第8层或第32层等),然后,用梯度上升更新输入图像的特征值。
def prod(image, feature_layers, iterations, lr, transform, device, vgg, modulelist) :
input = transform(image).unsqueeze(0)
input = input.to(device).requires_grad_(True)
vgg.zero_grad()
for i in range(iterations) :
out = input
for j in range(feature_layers) :
out = modulelist[j + 1](out)
loss = out.norm()
loss.backward()
with torch.no_grad() :
input += lr * input.grad
input = input.squeeze()
# input = input.transpose(0, 1)
# input = input.transpose(1, 2)
input = input.permute(1, 2, 0)
input = np.clip(deprocess(input, device).detach().cpu().numpy(), 0, 1)
image = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(input * 255))
return image
3) 函数 deep_dream_vgg 是一个递归函数,多次缩小图像,然后调用函数 prod 。接着再放大结果,并与按一定比例图像混合在一起,最终得到与输入图像相同大小的输出图像。
def deep_dream_vgg(image, feature_layers, iterations, lr, transform, device, vgg, modulelist, octave_scale = 2, num_octaves = 100) :
if num_octaves > 0 :
image1 = image.filter(ImageFilter.GaussianBlur(2))
if (image1.size[0] / octave_scale < 1 or image1.size[1] / octave_scale < 1) :
size = image1.size
else :
size = (int(image1.size[0] / octave_scale), int(image1.size[1] / octave_scale))
image1 = image1.resize(size, Image.ANTIALIAS)
image1 = deep_dream_vgg(image1, feature_layers, iterations, lr, transform, device, vgg, modulelist, octave_scale, num_octaves - 1)
size = (image.size[0], image.size[1])
image1 = image1.resize(size, Image.ANTIALIAS)
image = ImageChops.blend(image, image1, 0.6)
# PIL.ImageChops.blend(image1, image2, alpha)
# out = image1 * (1.0 - alpha) + image2 * alpha
img_result = prod(image, feature_layers, iterations, lr, transform, device, vgg, modulelist)
img_result = img_result.resize(image.size)
return img_result
4 全部代码(详细注释)
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter, ImageChops
from torchvision import models
from torchvision import transforms
#下载图片
def load_image(path) :
img = Image.open(path)
return img
#因为在图像处理过程中有归一化的操作,所以要"反归一化"
def deprocess(image, device):
image = image * torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225], device = device) + torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], device = device)
return image
#传入输入图像,正 向传播到VGG19的指定层,然后,用梯度上升更新 输入图像的特征值。
def prod(image, feature_layers, iterations, lr, transform, device, vgg, modulelist) :
input = transform(image).unsqueeze(0) #对图像进行resize,转成tensor和归一化操作,要增加一个维度,表示一个样本,[1, C, H, W]
input = input.to(device).requires_grad_(True) #对图片进行追踪计算梯度
vgg.zero_grad() #梯度清零
for i in range(iterations) :
out = input
for j in range(feature_layers) : #遍历features模块的各层
out = modulelist[j + 1](out) #以上一层的输出特征作为下一层的输入特征
loss = out.norm() #计算特征的二范数
loss.backward() #反向传播计算梯度,其中图像的每个像素点都是参数
with torch.no_grad() :
input += lr * input.grad #更新原始图像的像素值
input = input.squeeze() #训练完成后将表示样本数的维度去除
# 交互维度
# input = input.transpose(0, 1)
# input = input.transpose(1, 2)
input = input.permute(1, 2, 0) #维度转换,因为tensor的维度是(C, H, W),而array是(H, W, C)
input = np.clip(deprocess(input, device).detach().cpu().numpy(), 0, 1)#将像素值限制在(0, 1)之间
image = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(input * 255))#将array类型的图像转成PIL类型图像,要乘以255是因为转成tensor时函数自动除以了255
return image
#多次缩小图像,然后调用函数 prod。接着在放大结果,并与按一定比例图像混合在一起,最终得到与输入 图像相同大小的输出图像。
#octave_scale参数决定了有多少个尺度的图像, num_octaves参数决定一共有多少张图像
#octave_scale和num_octaves两个参数的选定对生成图像的影响很大。
def deep_dream_vgg(image, feature_layers, iterations, lr, transform, device, vgg, modulelist, octave_scale = 2, num_octaves = 100) :
if num_octaves > 0 :
image1 = image.filter(ImageFilter.GaussianBlur(2))#高斯模糊
if (image1.size[0] / octave_scale < 1 or image1.size[1] / octave_scale < 1) :#当图像的大小小于octave_scale时图像尺度不再变化
size = image1.size
else :
size = (int(image1.size[0] / octave_scale), int(image1.size[1] / octave_scale))
image1 = image1.resize(size, Image.ANTIALIAS)#缩小图片
image1 = deep_dream_vgg(image1, feature_layers, iterations, lr, transform, device, vgg, modulelist, octave_scale, num_octaves - 1)#递归
size = (image.size[0], image.size[1])
image1 = image1.resize(size, Image.ANTIALIAS)#放大图像
image = ImageChops.blend(image, image1, 0.6) #按一定比例将图像混合在一起
# PIL.ImageChops.blend(image1, image2, alpha)
# out = image1 * (1.0 - alpha) + image2 * alpha
img_result = prod(image, feature_layers, iterations, lr, transform, device, vgg, modulelist)
img_result = img_result.resize(image.size)
return img_result
if __name__ == '__main__':
#对图像进行预处理
tranform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(), #将PIL类型转成tensor类型,注意再次过程中像素值已经转到了[0, 1]之间,方式是除以255
transforms.Normalize(mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406], #归一化
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
vgg = models.vgg19(pretrained = True).to(device)
modulelist = list(vgg.features.modules())#要注意网络层转成列表元素之后,第一个元素是全部的网络层,下标从1开始迭代网络层,这也是后面是modulelist[j + 1]的原因
night_sky = load_image('starry_night.jpg')
night_sky_30 = deep_dream_vgg(night_sky, 36, 6, 0.2, tranform, device, vgg, modulelist)
plt.imshow(night_sky_30)
plt.show()
运行结果:
输入图像:

VGG19 的第10层学习的特征:
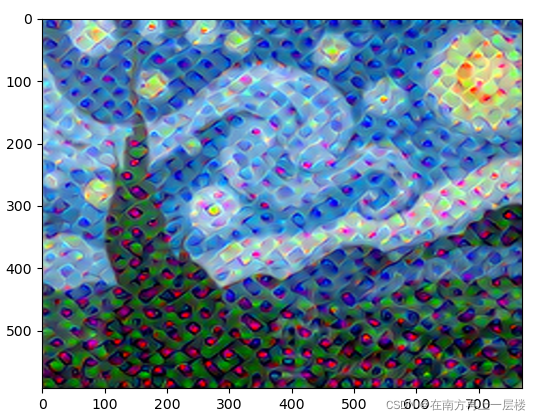
VGG19 的第20层学习的特征: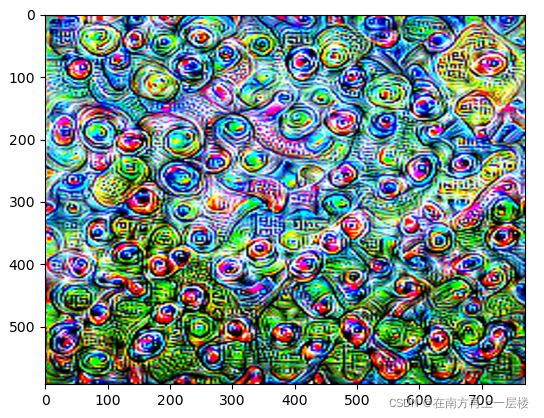
VGG19 的第30层学习的特征:
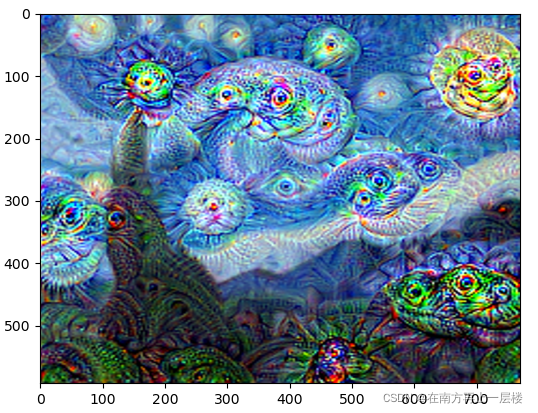

??VGG19 预训练模型是基于ImageNet大数据集训练的模型,该数据集共有1000个类别。从上面的结果可以看出,越靠近顶部的层,其激活值表现就越全面或抽象,如像某些类别(比如狗)的图案。