1、使用stackplot()绘制堆积面积图
(1)
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=np.arange(6)
y1=np.array([1,4,3,5,6,7])
y2=np.array([1,3,4,2,7,6])
y3=np.array([3,4,3,6,5,5])
plt.stackplot(x,y1,y2,y3)
plt.show()

2、使用hist()绘制直方图
(1)
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
scores=np.random.randint(0,100,50)
plt.hist(scores,bins=8,histtype='stepfilled')
plt.show()

(2)灰度直方图
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
random_state=np.random.RandomState(19680801)
random_x=random_state.randn(10000)
plt.hist(random_x,bins=25)
plt.show()

3、使用pie()绘制饼图或圆环图
(1)
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data=np.array([20,50,10,15,13,55])
pie_labels=np.array(['a','b','c','d','e','f'])
plt.pie(data,radius=1.5,labels=pie_labels,autopct='%3.2f%%')
plt.show()
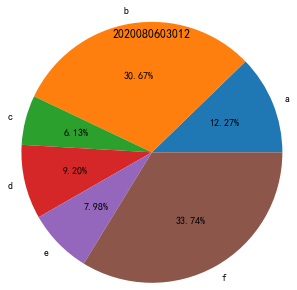
(2)
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data=np.array([20,50,10,15,13,55])
pie_labels=np.array(['a','b','c','d','e','f'])
plt.pie(data,radius=1.5,wedgeprops={'width':0.9},labels=pie_labels,autopct='%3.2f%%',pctdistance=0.75)
plt.show()
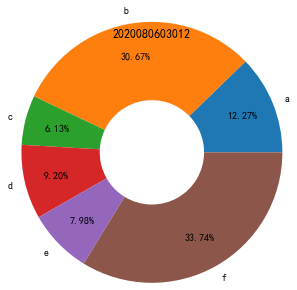
(3)实例
plt.title(2020080603012)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
kinds = ['购物', '人情往来', '餐饮美食', '通信物流', '生活日用','交通出行', '休闲娱乐', '其他']
money_scale = [800 / 3000, 100 / 3000, 1000 / 3000, 200 / 3000,300 / 3000, 200 / 3000, 200 / 3000, 200 / 3000]
dev_position = [0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1]
plt.pie(money_scale, labels=kinds, autopct='%3.1f%%', shadow=True,explode=dev_position, startangle=90)
plt.show()

4、使用scatter()绘制散点图和气泡图
(1)
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
num = 50
x = np.random.rand(num)
y = np.random.rand(num)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()

(2)
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
num = 50
x = np.random.rand(num)
y = np.random.rand(num)
area = (30 * np.random.rand(num)) **2
plt.scatter(x, y, s=area)
plt.show()

(3)实例
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei'
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
x_speed = np.arange(10, 210, 10)
y_distance = np.array([0.5, 2.0, 4.4, 7.9, 12.3,17.7, 24.1, 31.5, 39.9, 49.2,59.5, 70.8, 83.1, 96.4, 110.7,126.0, 142.2, 159.4, 177.6, 196.8])
plt.scatter(x_speed, y_distance, s=50, alpha=0.9)
plt.show()

5、使用boxplot绘制箱型图
(1)
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = np.random.randn(100)
plt.boxplot(data, meanline=True, widths=0.3, patch_artist=True,showfliers=False)
plt.show()

(2)实例:2017年和2018年发电量统计
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
data_2018 = np.array([5200, 5254.5, 5283.4, 5107.8, 5443.3, 5550.6,6400.2, 6404.9, 5483.1, 5330.2, 5543, 6199.9])
data_2017 = np.array([4605.2, 4710.3, 5168.9, 4767.2, 4947, 5203, 6047.4, 5945.5, 5219.6, 5038.1, 5196.3, 5698.6])
plt.boxplot([data_2018, data_2017], labels=('2018年', '2017年'),
meanline=True, widths=0.5, vert=False, patch_artist=True)
plt.show()

6、使用polar()绘制雷达图
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
dim_num = 6
data = np.array([[0.40, 0.32, 0.35, 0.30, 0.30, 0.88],
[0.85, 0.35, 0.30, 0.40, 0.40, 0.30],
[0.43, 0.89, 0.30, 0.28, 0.22, 0.30],
[0.30, 0.25, 0.48, 0.85, 0.45, 0.40],
[0.20, 0.38, 0.87, 0.45, 0.32, 0.28],
[0.34, 0.31, 0.38, 0.40, 0.92, 0.28]])
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, dim_num, endpoint=False)
angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]]))
data = np.concatenate((data, [data[0]]))
radar_labels = ['研究型(I)', '艺术型(A)', '社会型(S)',
'企业型(E)', '传统型(C)', '现实型(R)']
radar_labels = np.concatenate((radar_labels, [radar_labels[0]]))
plt.polar(angles, data)
plt.thetagrids(angles * 180/np.pi, labels=radar_labels)
plt.fill(angles, data, alpha=0.25)
plt.show()

7、使用errorbar()绘制误差棒图
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(5)
y = (25, 32, 34, 20, 25)
y_offset = (3, 5, 2, 3, 3)
plt.errorbar(x, y, yerr=y_offset, capsize=3, capthick=2)
plt.show()

(2)实例:4个树种不同季节的细跟生物量
plt.title(2020080603012)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
x = np.arange(3)
y1 = np.array([2.04, 1.57, 1.63])
y2 = np.array([1.69, 1.61, 1.64])
y3 = np.array([4.65, 4.99, 4.94])
y4 = np.array([3.39, 2.33, 4.10])
error1 = [0.16, 0.08, 0.10]
error2 = [0.27, 0.14, 0.14]
error3 = [0.34, 0.32, 0.29]
error4 = [0.23, 0.23, 0.39]
bar_width = 0.2
plt.bar(x, y1, bar_width)
plt.bar(x + bar_width, y2, bar_width, align="center",
tick_label=["春季", "夏季", "秋季"])
plt.bar(x + 2*bar_width, y3, bar_width)
plt.bar(x + 3*bar_width, y4, bar_width)
plt.errorbar(x, y1, yerr=error1, capsize=3, elinewidth=2, fmt=' k,')
plt.errorbar(x + bar_width, y2, yerr=error2, capsize=3, elinewidth=2, fmt='k,')
plt.errorbar(x + 2*bar_width, y3, yerr=error3, capsize=3, elinewidth=2, fmt='k,')
plt.errorbar(x + 3*bar_width, y4, yerr=error4, capsize=3, elinewidth=2, fmt='k,')
plt.show()
