论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805.pdf
官方代码:GitHub - google-research/bert: TensorFlow code and pre-trained models for BERT
bert后处理模型
在run_classifier.py中的create_model函数中,“bert后处理模型”代码为:
output_layer = model.get_pooled_output()
hidden_size = output_layer.shape[-1].value
output_weights = tf.get_variable(
"output_weights", [num_labels, hidden_size],
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.02))
output_bias = tf.get_variable(
"output_bias", [num_labels], initializer=tf.zeros_initializer())
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
if is_training:
# I.e., 0.1 dropout
output_layer = tf.nn.dropout(output_layer, keep_prob=0.9)
logits = tf.matmul(output_layer, output_weights, transpose_b=True)
logits = tf.nn.bias_add(logits, output_bias)
probabilities = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=-1)
log_probs = tf.nn.log_softmax(logits, axis=-1)bert后处理模型的本意是根据不同的任务将结果输出为想要的结果。
本篇博客是针对两句话语义是否相同来做的判断,属于分类任务,接下来就可以往分类任务的角度来构建输出结果。
output_layer = model.get_pooled_output()其实对应的就是
with tf.variable_scope("pooler"):
# We "pool" the model by simply taking the hidden state corresponding
# to the first token. We assume that this has been pre-trained
first_token_tensor = tf.squeeze(self.sequence_output[:, 0:1, :], axis=1)
self.pooled_output = tf.layers.dense(
first_token_tensor,
config.hidden_size,
activation=tf.tanh,
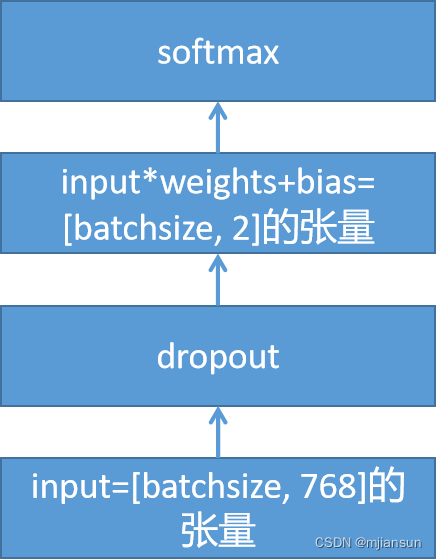
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(config.initializer_range))取出了bert基础模型的输出,将其[CLS]这个标签位的内容取出来,然后全连接输出[batchsize, 768]形状的张量。
hidden_size = output_layer.shape[-1].value
output_weights = tf.get_variable(
"output_weights", [num_labels, hidden_size],
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.02))
output_bias = tf.get_variable(
"output_bias", [num_labels], initializer=tf.zeros_initializer())
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
if is_training:
# I.e., 0.1 dropout
output_layer = tf.nn.dropout(output_layer, keep_prob=0.9)
logits = tf.matmul(output_layer, output_weights, transpose_b=True)
logits = tf.nn.bias_add(logits, output_bias)上述代码其实就是在完成如下操作?
?
损失函数
probabilities = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=-1)
log_probs = tf.nn.log_softmax(logits, axis=-1)
one_hot_labels = tf.one_hot(labels, depth=num_labels, dtype=tf.float32)
per_example_loss = -tf.reduce_sum(one_hot_labels * log_probs, axis=-1)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(per_example_loss)损失其实就没什么好讲的,就是简单的交叉熵损失函数,具体使用的公式如下:
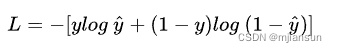
训练与测试
本任务的训练与测试的总体环节相同,仅仅是训练多了损失需要更新参数,测试不需要损失,直接输出概率最大的那个类即可。