SOM是神经网络的一种,它可以将相互关系复杂且非线性的高维数据,映射到具有简单几何结构及相互关系的低维空间中进行展示。(低维映射能够反映高维特征之间的拓扑结构)
可以实现数据的可视化;聚类;分类;特征抽取等任务。(主要做数据可视化)
网络结构
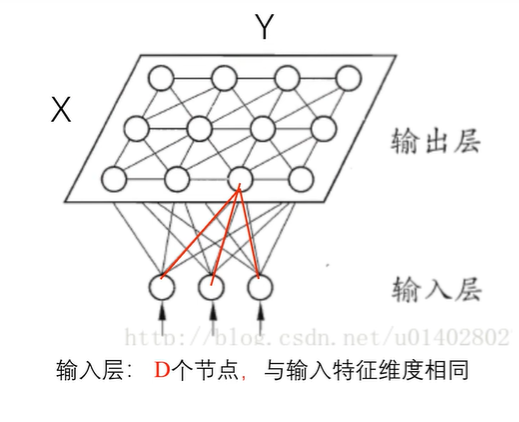
相关解释
?
模型训练过程
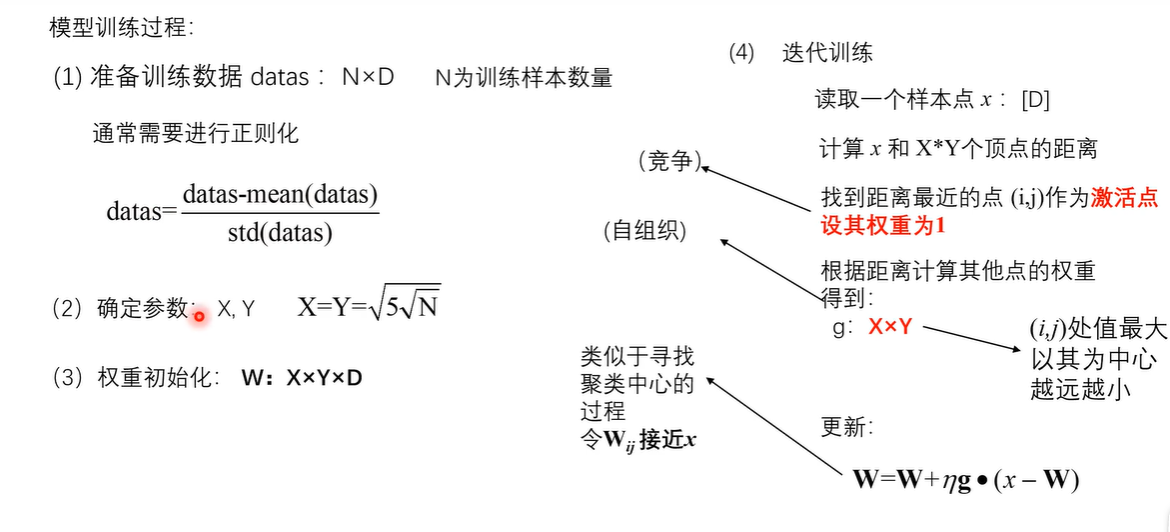
具体细节
代码实现
seeds_dataset数据集
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1QYU70IGu8XEtHGDmm29KlA?pwd=yame 提取码: yame 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便哦
训练模型
import numpy as np
import random
import tqdm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
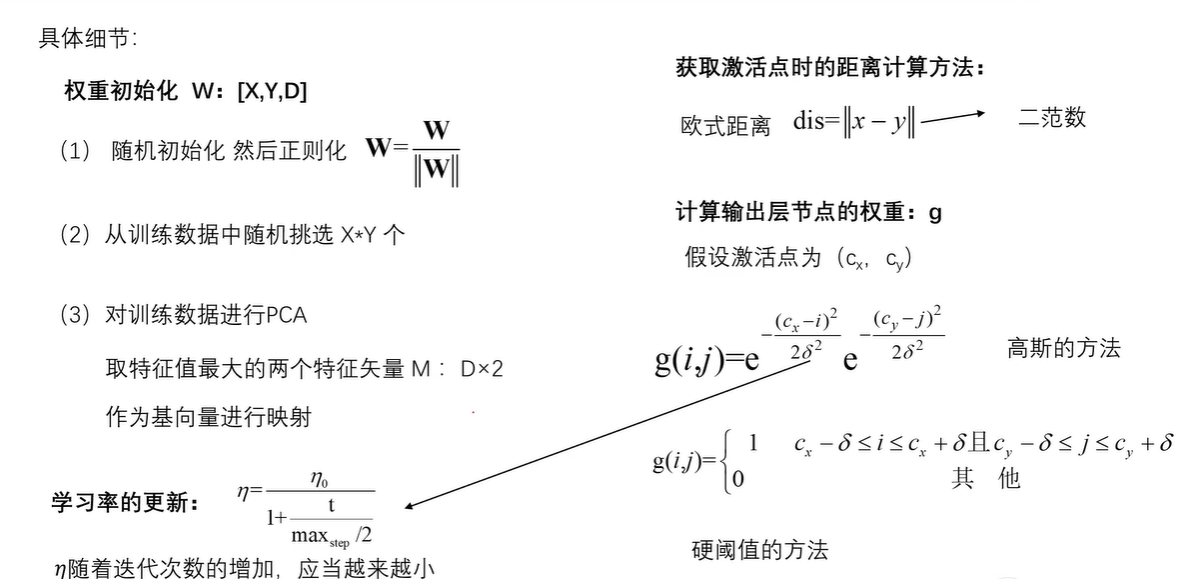
# 利用高斯距离法计算临近点的权重
# X,Y 模板大小,c 中心点的位置, sigma 影响半径
def gaussion_neighborhood(X, Y, c, sigma):
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(X), np.arange(Y))
d = 2 * sigma * sigma
ax = np.exp(-np.power(xx - xx.T[c], 2) / d)
ay = np.exp(-np.power(yy - yy.T[c], 2) / d)
return (ax * ay).T
# 利用bubble距离法计算临近点的权重
# X,Y 模板大小,c 中心点的位置, sigma 影响半径
def bubble_neighborhood(X, Y, c, sigma):
neigx = np.arange(X)
neigY = np.arange(Y)
ax = np.logical_and(neigx > c[0] - sigma,
neigx < c[0] + sigma)
ay = np.logical_and(neigy > c[1] - sigma,
neigy < c[1] + sigma)
return np.outer(ax, ay) * 1.
# 计算学习率
def get_learning_rate(lr, t, max_steps):
return lr / (1 + t / (max_steps / 2))
# 计算欧式距离
def euclidean_distance(x, w):
dis = np.expand_dims(x, axis=(0, 1)) - w
return np.linalg.norm(dis, axis=-1)
# 特征标准化 (x-mu)/std
def feature_normalization(data):
mu = np.mean(data, axis=0, keepdims=True)
sigma = np.std(data, axis=0, keepdims=True)
return (data - mu) / sigma
# 获取激活节点的位置
def get_winner_index(x, w, dis_fun=euclidean_distance):
# 计算输入样本和各个节点的距离
dis = dis_fun(x, w)
# 找到距离最小的位置
index = np.where(dis == np.min(dis))
return (index[0][0], index[1][0])
def weights_PCA(X, Y, data):
N, D = np.shape(data)
weights = np.zeros([X, Y, D])
pc_length, pc = np.linalg.eig(np.cov(np.transpose(data)))
pc_order = np.argsort(-pc_length)
for i, c1 in enumerate(np.linspace(-1, 1, X)):
for j, c2 in enumerate(np.linspace(-1, 1, Y)):
weights[i, j] = c1 * pc[pc_order[0]] + c2 * pc[pc_order[1]]
return weights
# 计算量化误差
def get_quantization_error(datas, weights):
w_x, w_y = zip(*[get_winner_index(d, weights) for d in datas])
error = datas - weights[w_x, w_y]
error = np.linalg.norm(error, axis=-1)
return np.mean(error)
def train_SOM(X,
Y,
N_epoch,
datas,
init_lr=0.5,
sigma=0.5,
dis_fun=euclidean_distance,
neighborhood_fun=gaussion_neighborhood,
init_weight_fun=None,
seed=20):
# 获取输入特征的维度
N, D = np.shape(datas)
# 训练的步数
N_steps = N_epoch * N
# 对权重进行初始化
rng = np.random.RandomState(seed)
if init_weight_fun is None:
weights = rng.rand(X, Y, D) * 2 - 1
weights /= np.linalg.norm(weights, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
else:
weights = init_weight_fun(X, Y, datas)
for n_epoch in range(N_epoch):
print("Epoch %d" % (n_epoch + 1))
# 打乱次序
index = rng.permutation(np.arange(N))
for n_step, _id in enumerate(index):
# 取一个样本
x = datas[_id]
# 计算learning rate(eta)
t = N * n_epoch + n_step
eta = get_learning_rate(init_lr, t, N_steps)
# 计算样本距离每个顶点的距离,并获得激活点的位置
winner = get_winner_index(x, weights, dis_fun)
# 根据激活点的位置计算临近点的权重
new_sigma = get_learning_rate(sigma, t, N_steps)
g = neighborhood_fun(X, Y, winner, new_sigma)
g = g * eta
# 进行权重的更新
weights = weights + np.expand_dims(g, -1) * (x - weights)
# 打印量化误差
print("quantization_error= %.4f" % (get_quantization_error(datas, weights)))
return weights
def get_U_Matrix(weights):
X, Y, D = np.shape(weights)
um = np.nan * np.zeros((X, Y, 8)) # 8邻域
ii = [0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1]
jj = [-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1]
for x in range(X):
for y in range(Y):
w_2 = weights[x, y]
for k, (i, j) in enumerate(zip(ii, jj)):
if (x + i >= 0 and x + i < X and y + j >= 0 and y + j < Y):
w_1 = weights[x + i, y + j]
um[x, y, k] = np.linalg.norm(w_1 - w_2)
um = np.nansum(um, axis=2)
return um / um.max()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# seed 数据展示
columns = ['area', 'perimeter', 'compactness', 'length_kernel', 'width_kernel',
'asymmetry_coefficient', 'length_kernel_groove', 'target']
data = pd.read_csv('seeds_dataset.txt',
names=columns,
sep='\t+', engine='python')
labs = data['target'].values
label_names = {1: 'Kama', 2: 'Rosa', 3: 'Canadian'}
datas = data[data.columns[:-1]].values
N, D = np.shape(datas)
print(N, D)
# 对训练数据进行正则化处理
datas = feature_normalization(datas)
# SOM的训练
weights = train_SOM(X=9, Y=9, N_epoch=4, datas=datas, sigma=1.5, init_weight_fun=weights_PCA)
# 获取UMAP
UM = get_U_Matrix(weights)
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 9))
plt.pcolor(UM.T, cmap='bone_r') # plotting the distance map as background
plt.colorbar()
markers = ['o', 's', 'D']
colors = ['C0', 'C1', 'C2']
for i in range(N):
x = datas[i]
w = get_winner_index(x, weights)
i_lab = labs[i] - 1
plt.plot(w[0] + .5, w[1] + .5, markers[i_lab], markerfacecolor='None',
markeredgecolor=colors[i_lab], markersize=12, markeredgewidth=2)
plt.show()
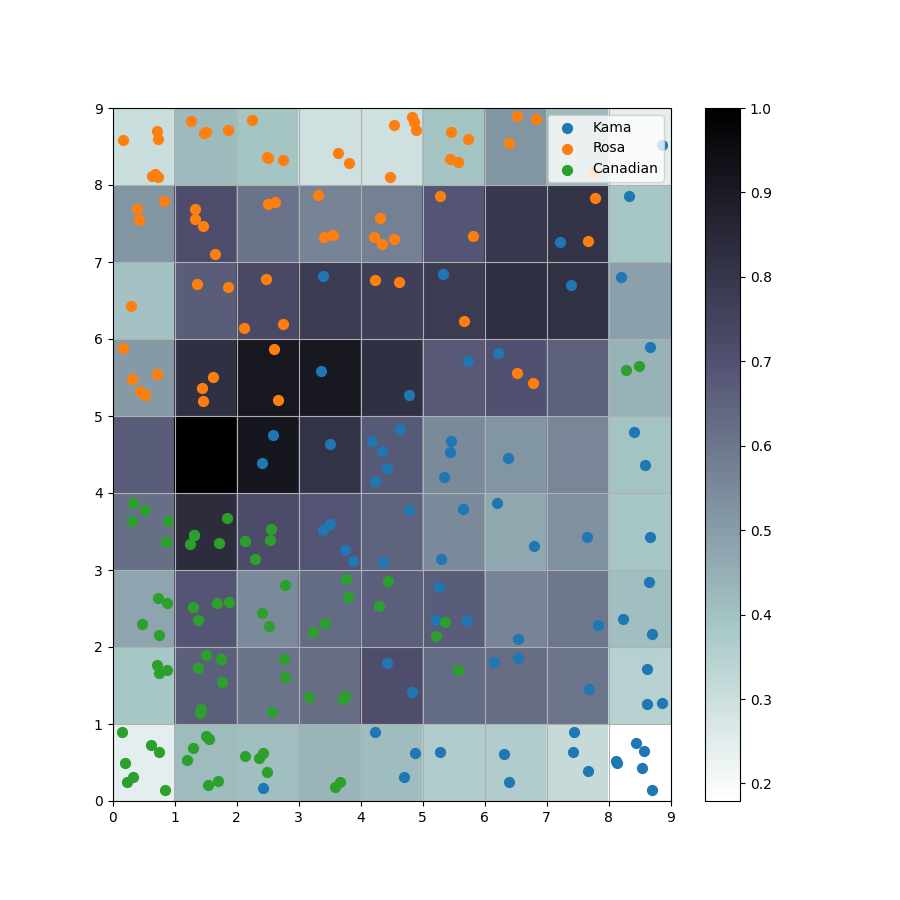
结果图
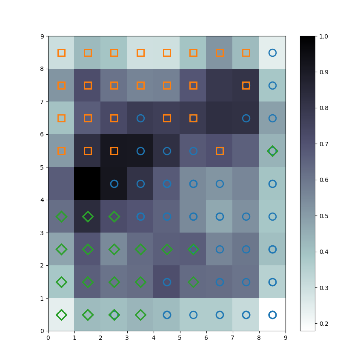
SOM数据展示
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from SOM import train_SOM, feature_normalization, get_U_Matrix, get_winner_index, weights_PCA
from collections import defaultdict, Counter
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
if __name__ == "__main__":
# seed 数据展示
columns = ['area', 'perimeter', 'compactness', 'length_kernel', 'width_kernel',
'asymmetry_coefficient', 'length_kernel_groove', 'target']
data = pd.read_csv('seeds_dataset.txt',
names=columns,
sep='\t+', engine='python')
labs = data['target'].values
label_names = {1: 'Kama', 2: 'Rosa', 3: 'Canadian'}
datas = data[data.columns[:-1]].values
N, D = np.shape(datas)
print(N, D)
# 对训练数据进行正则化处理
datas = feature_normalization(datas)
# SOM的训练
X = 9
Y = 9
weights = train_SOM(X=X, Y=Y, N_epoch=4, datas=datas, sigma=1.5, init_weight_fun=weights_PCA)
# 获取UMAP
UM = get_U_Matrix(weights)
print(UM)
# '''画散点图'''
# 显示UMAP
plt.figure(1, figsize=(9, 9))
plt.pcolor(UM.T, cmap='bone_r') # plotting the distance map as background
plt.colorbar()
markers = ['o', 's', 'D']
colors = ['C0', 'C1', 'C2']
# 计算每个样本点投射后的坐标
w_x, w_y = zip(*[get_winner_index(d, weights) for d in datas])
w_x = np.array(w_x)
w_y = np.array(w_y)
# 分别把每一类的散点在响应的方格内进行打印(+随机位置偏移)
for c in np.unique(labs):
idx_target = (labs == c)
plt.scatter(w_x[idx_target] + .5 + (np.random.rand(np.sum(idx_target)) - .5) * .8,
w_y[idx_target] + .5 + (np.random.rand(np.sum(idx_target)) - .5) * .8,
s=50, c=colors[c - 1], label=label_names[c])
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.grid()
# plt.show()
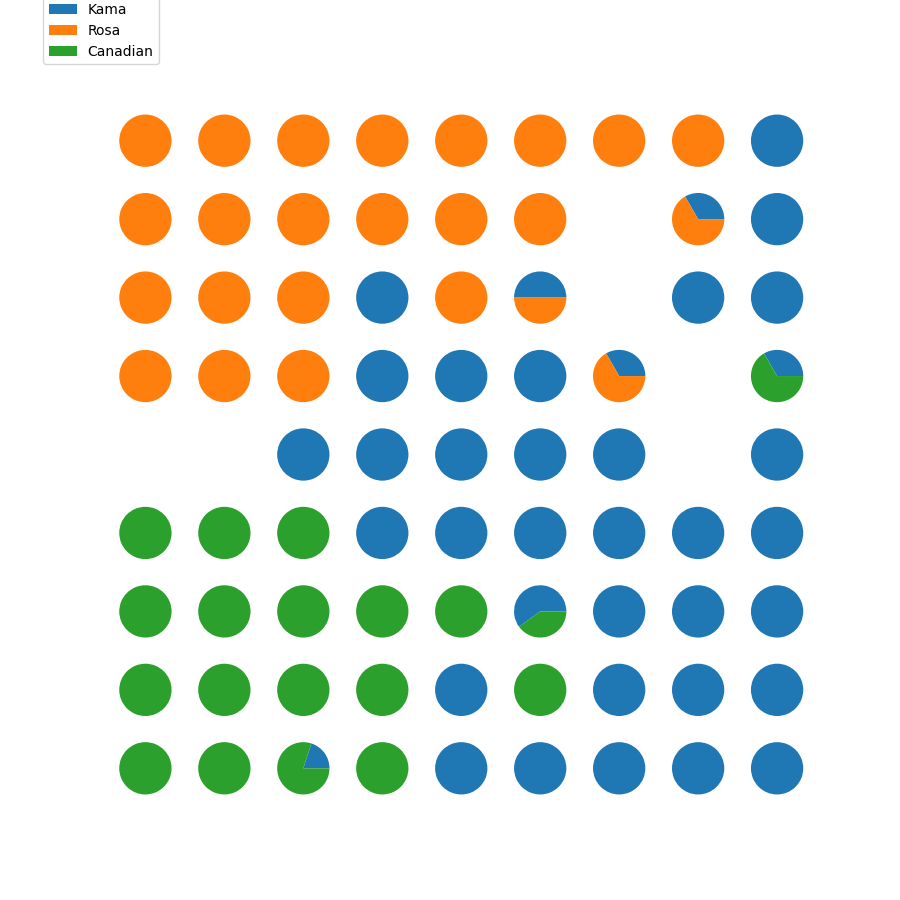
''' 画饼图'''
# 计算输出层的每个节点上映射了哪些数据
win_map = defaultdict(list)
for x, lab in zip(datas, labs):
win_map[get_winner_index(x, weights)].append(lab)
# 统计每个输出节点上,映射了各类数据、各多少个
for pos in win_map:
win_map[pos] = Counter(win_map[pos])
fig = plt.figure(2, figsize=(9, 9))
# 按照 X,Y对画面进行分格
the_grid = gridspec.GridSpec(Y, X, fig)
print(the_grid)
# 在每个格子里面画饼图
for pos in win_map.keys():
label_fracs = [win_map[pos][l] for l in label_names.keys()]
plt.subplot(the_grid[Y - 1 - pos[1],
pos[0]], aspect=1)
patches, texts = plt.pie(label_fracs)
plt.legend(labels=label_names.values(), loc='upper left', bbox_to_anchor=(-6, 10))
# plt.savefig('resulting_images/som_seed_pies.png')
plt.show()
?结果图