一、IOU:


注意:求交区域的时候,一定要和0比较大小,如果是负数就说明压根不相交
import numpy as np
def ComputeIOU(boxA, boxB):
## 计算相交框的坐标
x1 = np.max([boxA[0], boxB[0]])
x2 = np.min([boxA[2], boxB[2]])
y1 = np.max([boxA[1], boxB[1]])
y2 = np.min([boxA[3], boxB[3]])
## 计算交区域,并区域,及IOU
interArea = np.max([x2-x1+1, 0])*np.max([y2-y1+1,0]) ##一定要和0比较大小,如果是负数就说明压根不相交
unionArea = (boxA[2]-boxA[0]+1)*(boxA[3]-boxA[1]+1) + (boxB[2]-boxB[0]+1)*(boxB[3]-boxB[1]+1)-interArea
iou = interArea/unionArea
return iou
boxA = [1,1,3,3]
boxB = [2,2,4,4]
IOU = ComputeIOU(boxA, boxB)
二、NMS:
1. 对整个bboxes排序的写法
import numpy as np
def nms(dets, iou_thred, cfd_thred):
if len(dets)==0: return []
bboxes = np.array(dets)
## 对整个bboxes排序
bboxes = bboxes[np.argsort(bboxes[:,4])]
pick_bboxes = []
# print(bboxes)
while bboxes.shape[0] and bboxes[-1,-1] >= cfd_thred:
bbox = bboxes[-1]
x1 = np.maximum(bbox[0], bboxes[:-1,0])
y1 = np.maximum(bbox[1], bboxes[:-1,1])
x2 = np.minimum(bbox[2], bboxes[:-1,2])
y2 = np.minimum(bbox[3], bboxes[:-1,3])
inters = np.maximum(x2-x1+1, 0) * np.maximum(y2-y1+1, 0)
unions = (bbox[2]-bbox[0]+1)*(bbox[3]-bbox[1]+1) + (bboxes[:-1,2]-bboxes[:-1,0]+1)*(bboxes[:-1,3]-bboxes[:-1,1]+1) - inters
ious = inters/unions
keep_indices = np.where(ious<iou_thred)
bboxes = bboxes[keep_indices] ## indices一定不包括自己
pick_bboxes.append(bbox)
return np.asarray(pick_bboxes)
dets = [[187, 82, 337, 317, 0.9], [150, 67, 305, 282, 0.75], [246, 121, 368, 304, 0.8]]
dets_nms = nms(dets, 0.5, 0.3)
print(dets_nms)
2. 不改变bboxes,维护orders的写法:
始终维护orders,代表到原bboxes的映射(map)
优化1:仅维护orders,不改变原bboxes
优化2:提前计算好bboxes的面积,以免在循环中多次重复计算
import numpy as np
def nms(dets, iou_thred, cfd_thred):
if len(dets)==0: return []
bboxes = np.array(dets)
## 维护orders
orders = np.argsort(bboxes[:,4])
pick_bboxes = []
x1 = bboxes[:,0]
y1 = bboxes[:,1]
x2 = bboxes[:,2]
y2 = bboxes[:,3]
areas = (x2-x1+1)*(y2-y1+1) ## 提前计算好bboxes面积,防止在循环中重复计算
while orders.shape[0] and bboxes[orders[-1],-1] >= cfd_thred:
bbox = bboxes[orders[-1]]
xx1 = np.maximum(bbox[0], x1[orders[:-1]])
yy1 = np.maximum(bbox[1], y1[orders[:-1]])
xx2 = np.minimum(bbox[2], x2[orders[:-1]])
yy2 = np.minimum(bbox[3], y2[orders[:-1]])
inters = np.maximum(xx2-xx1+1, 0) * np.maximum(yy2-yy1+1, 0)
unions = areas[orders[-1]] + areas[orders[:-1]] - inters
ious = inters/unions
keep_indices = np.where(ious<iou_thred)
pick_bboxes.append(bbox)
orders = orders[keep_indices]
return np.asarray(pick_bboxes)
dets = [[187, 82, 337, 317, 0.9], [150, 67, 305, 282, 0.75], [246, 121, 368, 304, 0.8]]
dets_nms = nms(dets, 0.5, 0.3)
print(dets_nms)
三、正向卷积:
torch官方的Conv2d需要传入的参数
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)
输入和输出的特征图尺寸大小关系:
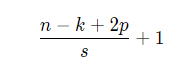
1.对于padding的处理是重开一个输出特征图尺寸的矩阵,然后给非padding区域赋值。或者直接用np.pad函数
2.卷积通过逐元素相乘并求和实现。使用numpy的np.multiply和np.sum函数。在inputs上逐行和逐列操作并赋值到outputs中。np.multiply可以广播,所以可以同时对多个卷积核操作,例如卷积核251633与特征图区域1633经过multiply和sum后得到251,就是输出特征图该像素点上的多通道特征。这样可以省去对各卷积核的一层循环。
3.直接利用range中的间隔模拟stride,由于总共有n-k+2p-1个有效位置,因此range的边界是n-k+2p-1。
import numpy as np
def conv2d(inputs, kernels, padding, bias, stride):
c, w, h = inputs.shape
# inputs_pad = np.zeros((c,w+2*padding,h+2*padding))
# inputs_pad[:, padding:w+padding, padding:h+padding] = inputs
# print(inputs_pad.shape, '\n', inputs_pad)
# inputs = inputs_pad
inputs = np.pad(inputs, ((0,0),(1,1),(1,1))) ## 可以直接用np.pad函数实现pad
kernels_num, kernel_size = kernels.shape[0], kernels.shape[2]
outputs = np.ones((kernels_num, (w-kernel_size+2*padding)//stride+1, (h-kernel_size+2*padding)//stride+1))
for i in range(0, w-kernel_size+2*padding+1, stride):
for j in range(0, h-kernel_size+2*padding+1, stride):
outputs[:, i//stride, j//stride] = np.sum(np.multiply(kernels, inputs[:, i:i+kernel_size, j:j+kernel_size]), axis=(1,2,3))+bias
return outputs
inputs = np.ones((16,9,9))
kernels = np.ones((25,16,3,3))
bias = np.arange(1,kernels.shape[0]+1)
stride = 2
padding = 1
outputs = conv2d(inputs, kernels, padding, bias, stride)
print("input{}".format(inputs.shape))
print("kenerls{}, stride{}".format(kernels.shape, stride))
print("output{}".format(outputs.shape))
print(outputs)
四、池化:
torch官方的Pool2d需要传入的参数
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=(2, 1), padding=(0, 1))
没写padding了,stride在w和h方向也没区分。。。
## 池化操作
def pooling(inputs, pool_size, stride, mode='max'):
c, w, h = inputs.shape
k = pool_size
outputs = np.zeros((c,(w-k)//stride+1, (h-k)//stride+1))
if mode == 'max':
for i in range(0, w-k+1, stride):
for j in range(0, h-k+1, stride):
outputs[:, i//stride, j//stride] = np.max(inputs[:,i:i+k,j:j+k], axis=(1,2))
return outputs
elif mode == 'avg':
for i in range(0, w-k+1, stride):
for j in range(0, h-k+1, stride):
outputs[:, i//stride, j//stride] = np.mean(inputs[:,i:i+k,j:j+k], axis=(1,2))
return outputs
else:
raise ValueError('not support this mode, choose "max" or "avg" ')
pool_size = 2
stride = 2
mode = 'max'
inputs = np.arange(1,76).reshape((3,5,5))
print("inputs:{}".format(inputs.shape), '\n',inputs)
outputs = pooling(inputs, pool_size, stride, mode)
print("outputs:{}".format(outputs.shape), '\n',outputs)