【读论文】AUTOMATED TRAINING SAMPLE LABELING USING LABORATORY SPECTRA(1996)
P Hsieh,DA Landgrebe
DOI:10.1109/IGARSS.1996.516819
摘要
This paper presents a method for automatically labeling training samples in mineral identification problems.A previous work showed that an experienced human operator can successfully identify training samples by visually comparing the strong absorption features of the laboratory spectra to those of the adjusted remotely sensed spectra.
However, it is obviously a time-consuming process. The purpose of this research is to automate the labeling process.Thc method proposed in this paper consists of a data preprocessor and correlation detection. This data preprocessor is used for shape adjustment and scale unification.
It includes three parts:
(1) the log residue method;
(2) reference levelsetting;
(3) signal normalization.
The desired number of training samples can be specified to guarantee that enough training samples are drawn from the data set. After training samples are labeled, a series of statistical pattern recognition analysis methods are applied to the original remotely sensed data set to do classification.
The data set used in the paper is Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS)data taken over the Cuprite mining District, Nevada in 1992.The result is compared to a previous work that requires a human operator to visually label training samples and a rough gcologic ground truth map.
It shows that this automated labeling method not only saves human laboring but also achieves a fair performance of classification.
本文提出了一种在矿物识别问题中自动标注训练样本的方法。先前的工作表明,有经验的操作员可以通过将实验室光谱的强吸收特征与调整后的遥感光谱的强吸收特征进行视觉比较,成功地识别训练样本。
然而,这显然是一个耗时的过程。这项研究的目的是使标签过程自动化。该方法由数据预处理器和相关检测两部分组成。该数据预处理器用于形状调整和尺度统一。
它包括三个部分:
1)对数残差法;
2)参考电平设置;
3)信号归一化。
可以指定所需数量的训练样本,以保证从数据集中提取足够的训练样本。在对训练样本进行标记之后,将一系列统计模式识别分析方法应用于原始遥感数据集进行分类。
论文中使用的数据集是1992年在内华达州赤铜矿矿区上空拍摄的机载可见光 /红外成像光谱仪(AVIRIS)数据。将该结果与先前的工作进行比较,该先前的工作需要人类操作员在视觉上标记训练样本和粗略的地质地面真实图。
结果表明,这种自动标注方法不仅节省了人力,而且获得了良好的分类性能。
结论
The thematic maps in Fig. 2 show that the result (min size=220) is similar to the previous work[l]. From the viewpoint of pattern recognition, using laboratory spectra to label training samples is a way in which the means of classes in the suhspacc (31 features) are utilized to identify training samples.
Without the second order statistics information, the noise in the hypotheses is assumed a white noise. That is, all classcs are assumed to have the same covariance matrices in the 3 1 -dimensional subspace. After training samples are collected, a classifier is designed from data in the whole space.
When a ground truth map is not available, it is necessary to use other knowledge to train a classifier. In mineral identification, the strong absorption features of laboratory reflectance spectra are generally considered helpful in classificalion. For other ground types, photo interpretation or clustcring techniques may he useful for labeling training samplcs.
图2中的专题地图显示,结果(最小尺寸=220)与之前的工作[l]类似。从模式识别的角度来看,使用实验室光谱标记训练样本是一种利用suhspacc(31个特征)中的类来识别训练样本的方法。
在没有二阶统计信息的情况下,假设假设中的噪声为白噪声。也就是说,假设所有类在31维子空间中具有相同的协方差矩阵。在收集训练样本后,根据整个空间的数据设计分类器。
当地面真值图不可用时,有必要使用其他知识来训练分类器。在矿物鉴定中,实验室反射光谱的强吸收特征通常被认为有助于分类。对于其他地面类型,照片判读或聚类技术可能有助于标记训练样本。
1.该论文研究了什么?
一种在矿物识别问题中自动标注训练样本的方法。许多矿物在其反射光谱中具有独特的和诊断性的吸收特征。在没有地面真值图的情况下对遥感数据进行分类,可以使用实验室反射光谱作为标准,使用对数残差法调整为类似反射光谱后再由人工将其与实验室反射光谱进行比较,如果足够相似则将其标注为训练样本。现采用信号检测技术代替目视比较。
2.创新点在哪?
任何自动比较方法都难以在没有任何数量信息的情况下比较信号。提出了一种归一化方法,在不损失光谱吸收特征的情况下,建立一个共同的比较背景。实验室反射光谱和AJI调整信号被归一化为零平均响应和单位能量。
3.研究方法是什么?
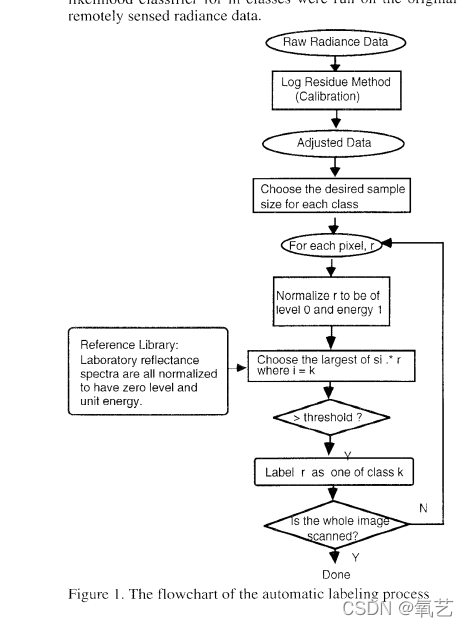
4.得到的结论是什么?
当地面真实图不可用时,需要使用其他知识来训练分类器。在矿物识别中,实验室反射光谱的强吸收特征通
常被认为有助于分类。对于其他地面类型,照片解释或聚类技术对于标记训练样本可能是有用的。
[1] Hsieh P , Landgrebe D A . Automated training sample labeling using laboratory spectra[C]// International Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE, 1996.