1.激活函数
1.1 Sigmoid函数
Sigmoid 是常用的非线性的激活函数,表达式如下:
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
?
x
f(x) = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-x}}
f(x)=1+e?x1?
- 特性:它能够把输入的连续实值变换为 0 0 0和 1 1 1之间的输出,特别的,如果是非常大的负数,那么输出就是 0 0 0;如果是非常大的正数,输出就是 1 1 1.
- 缺点:在深度神经网络中梯度反向传递时导致梯度爆炸和梯度消失,其中梯度爆炸发生的概率非常小,而梯度消失发生的概率比较大。
1.2 tanh函数
tanh函数也是非线性函数,其函数解析式为:
t
a
n
h
(
x
)
=
e
x
?
e
?
x
e
x
+
e
?
x
tanh(x) = \frac{e^x - e^{-x}}{e^x + e^{-x}}
tanh(x)=ex+e?xex?e?x?
tanh读作Hyperbolic Tangent,它解决了Sigmoid函数的不是zero-centered输出问题,然而,梯度消失(gradient vanishing)的问题和幂运算的问题仍然存在。
1.3 Relu函数
Relu函数实际上就是个取最大值函数,其函数解析式如下所示:
f
(
x
)
=
max
?
(
0
,
x
)
f(x) = \max{(0, x)}
f(x)=max(0,x)
Relu是目前最常用的激活函数,一般搭建人工神经网络时推荐优先尝试Relu并非全区间可导,但我们可以取sub-gradient-
- 解决了
gradient vanishing问题 (在正区间) - 计算速度非常快,只需要判断输入是否大于 0 0 0
- 收敛速度远快于
Sigmoid和tanh
- 解决了
-
ReLU的输出不是zero-centeredDead ReLU Problem,指的是某些神经元可能永远不会被激活,导致相应的参数永远不能被更新。有两个主要原因可能导致这种情况产生: (1) 非常不幸的参数初始化,这种情况比较少见 (2)learning rate太高导致在训练过程中参数更新太大,不幸使网络进入这种状态。解决方法是可以采用Xavier初始化方法,以及避免将learning rate设置太大或使用adagrad等自动调节learning rate的算法。
1.4 Leaky ReLU函数(PReLU)
函数表达式:
f
(
x
)
=
max
?
(
α
x
,
x
)
f(x) = \max(\alpha x, x)
f(x)=max(αx,x)
人们为了解决Dead ReLU Problem,提出了将ReLU的前半段设为
α
x
\alpha x
αx而非
0
0
0,通常
α
=
0.01
\alpha=0.01
α=0.01。另外一种直观的想法是基于参数的方法,即
P
a
r
a
m
e
t
r
i
c
R
e
L
U
:
f
(
x
)
=
max
?
(
α
x
,
x
)
Parametric ReLU:f(x) = \max(\alpha x, x)
ParametricReLU:f(x)=max(αx,x),其中
α
\alpha
α
可由方向传播算法学出来。理论上来讲,Leaky ReLU有ReLU的所有优点,外加不会有Dead ReLU问题,但是在实际操作当中,并没有完全证明Leaky ReLU总是好于ReLU。
1.5 ELU(Exponential Linear Units) 函数
函数表达式:
f
(
x
)
=
{
x
,
i
f
?
x
>
0
α
(
e
x
?
1
)
,
o
t
h
e
r
w
i
s
e
f(x) = \left\{\begin{matrix} x ,&if\ x > 0\\ \alpha(e^x - 1), &otherwise \end{matrix}\right.
f(x)={x,α(ex?1),?if?x>0otherwise?
ELU不会有Dead ReLU问题 输出的均值接近
0
0
0,zero-centered。但计算量偏大,在目前的实际应用中并未被证明总是好于ReLU。
1.6 UnitStep 阶跃函数
函数表达式:
f
(
x
)
=
{
1
,
i
f
?
x
>
0
0
,
o
t
h
e
r
w
i
s
e
f(x) = \left\{\begin{matrix} 1 ,&if\ x > 0\\ 0, &otherwise \end{matrix}\right.
f(x)={1,0,?if?x>0otherwise?
一般用于感知机的激活函数。但感知机用梯度下降法求解更优。
2.感知机模型(神经元模型)
设输入空间(特征空间)为 X ? R n X\subseteq\R^n X?Rn,输出空间为 Y = { 0 , 1 } Y = \{0, 1\} Y={0,1}
输入 x ∈ X x \in X x∈X为实例的特征向量,输出 y ∈ Y y \in Y y∈Y为实例的类别
由输入空间到输出空间的如下函数称为感知机:
f
(
x
)
=
s
i
g
n
(
w
x
+
b
)
f(x) = sign(wx + b)
f(x)=sign(wx+b)
其中
w
w
w和
b
b
b为模型参数,
w
∈
R
n
w \in \R^n
w∈Rn称为权值,
b
∈
R
b \in \R
b∈R称为偏置。
s
i
g
n
sign
sign是符号函数。
假设我们目前的任务是通过感知机对具有 n n n维特征的向量进行分类。我们可以将该感知机的模型视作一个神经元模型。 n n n维向量( ( x 1 , x 2 , … , x n ) (x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n) (x1?,x2?,…,xn?))对应的是神经元的 n n n个输入。
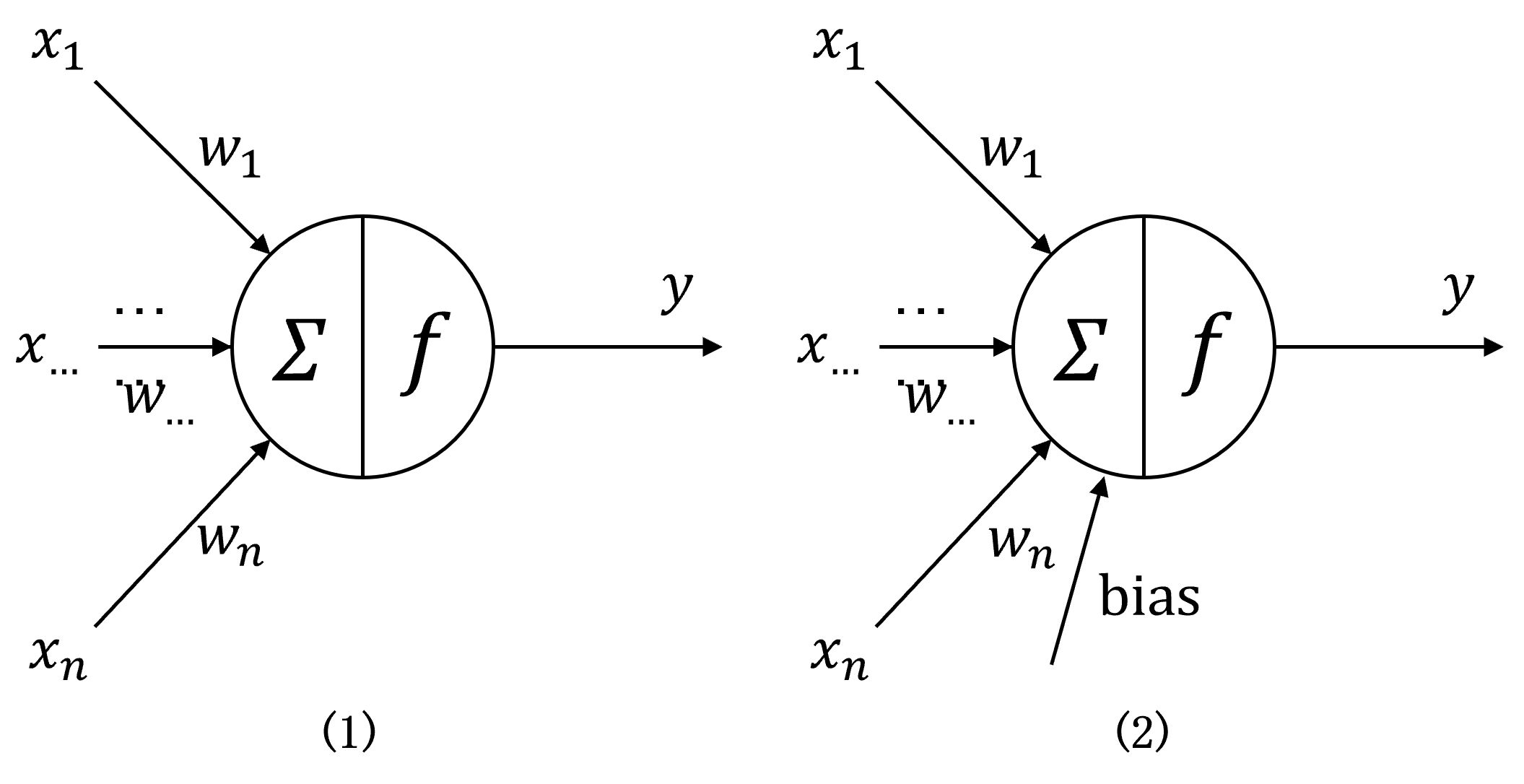
我们对这 n n n个输入分别乘其对应的权值后求和,经过激活函数后得到分类结果。
但是我们注意到,当神经网络的输入向量为 0 0 0时,会产生激活失败误分类的情况,为了避免这种情况,我们对其加偏置项后再进入激活函数,也就是感知机模型中的 b b b。
我们首先对输入向量乘对应的权值加偏置项后得到
∑
k
=
1
k
≤
n
w
x
i
+
b
\sum_{k = 1}^{k \leq n} wx_i + b
∑k=1k≤n?wxi?+b,将其经过激活函数后与标签进行比对,并根据是否与标签相等来更新参数的值:
w
=
w
+
α
×
(
y
?
y
^
)
×
x
b
=
b
+
α
×
(
y
?
y
^
)
w = w + \alpha \times(y - \hat{y})\times x \\ b = b + \alpha \times (y - \hat{y})
w=w+α×(y?y^?)×xb=b+α×(y?y^?)
其中
α
\alpha
α为步长,又称学习率。以上过程对所有训练数据执行一次后,可以得到一轮训练后的
w
w
w和
b
b
b。
显然,由于权值参数对应于 n n n维特征向量,因此 w w w的维度一定与输入向量的特征维数有关。
此处给出基于Python实现的感知机模型。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class ActivateFunction(object):
@staticmethod
def Sigmoid(x):
return (1 / (1 + np.exp(-x)))
@staticmethod
def ReLu(x):
if x <= 0: return 0
else: return x
#return np.max(0, x)
@staticmethod
def Softmax(x):
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
@staticmethod
def UnitStep(x):
return 1 if x > 0 else 0
class Perceptron(object):
#初始化一个具有n维特征的感知机
def __init__(self, input_num, activator):
self.activator = activator
self.size = input_num
self.weights = [0.0 for i in range(input_num)]
self.bias = 0.0
#预测值
def Predict(self, input_vec):
return self.activator(np.dot(input_vec, self.weights) + self.bias)
#单轮训练
def SingleIteration(self, input_vecs, labels, rate):
samples = zip(input_vecs, labels)
for (input_vec, label) in samples:
output = self.Predict(input_vec)
delta = label - output
input_vec = np.array(input_vec)
self.weights += rate * delta * input_vec
self.bias += rate * delta
#多轮训练入口
def fit(self, input_vecs, labels, iteration, rate):
input_vecs, labels = np.array(input_vecs), np.array(labels)
for i in range(iteration):
self.SingleIteration(input_vecs, labels, rate)
#获取训练后的得到参数
def GetParameters(self):
return self.weights, self.bias
if __name__ == "__main__":
data, label = [], []
file = open(r'.\Python\x.txt')
for line in file.readlines():
line_data = line.strip().split(',')
data.append([float(line_data[0]), float(line_data[1])])
file.close()
file = open(r'.\Python\y.txt')
for line in file.readlines():
line_data = line.strip().split(',')
label = list(map(int, line_data))
file.close
p = Perceptron(2, ActivateFunction.UnitStep)
p.fit(data, label, 1000, 0.1)
w, b = p.GetParameters()
x1 = np.arange(-5, 10, 0.1)
x2 = (w[0] * x1 + b) / (-w[1])
data = np.array(data)
label = np.array(label)
idx_p = np.where(label == 1)
idx_n = np.where(label != 1)
data_p = data[idx_p]
data_n = data[idx_n]
plt.scatter(data_p[:, 0], data_p[:, 1], color='red')
plt.scatter(data_n[:, 0], data_n[:, 1], color='blue')
plt.plot(x1, x2)
plt.show()
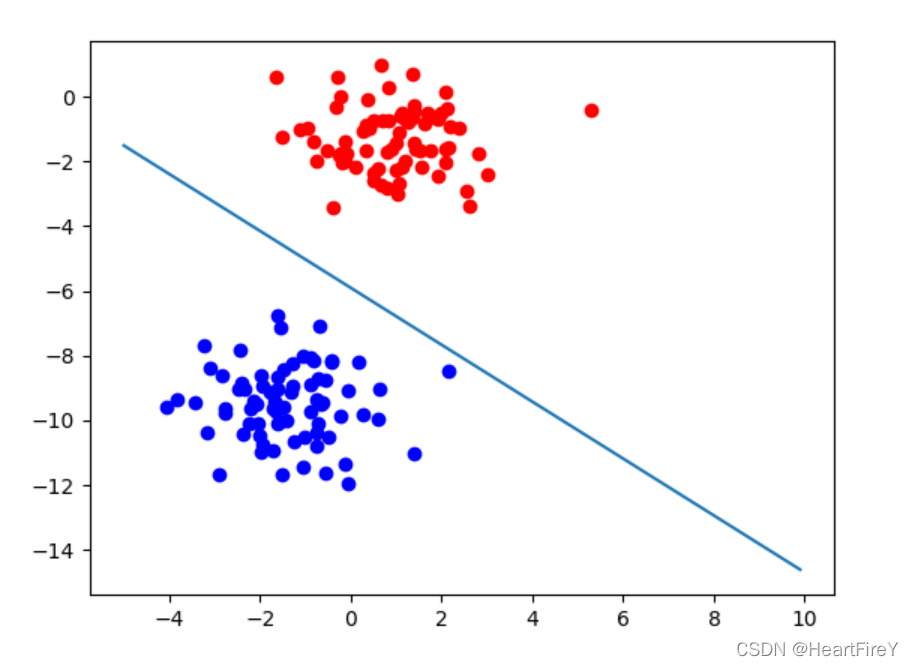
分类效果示例如上所示。