本文档隶属于工程机械臂末端柔顺控制(Ros+Gazebo仿真实现)
0 为什么要写这玩意儿?
要实现末端柔顺控制至少得先具备检测末端力数据以及发送控制指令给机器人的功能,力传感器和机器人位置控制器我们已经在如何给Gazebo中的仿真机械臂添加一个力传感器?中实现了,接下来就要写一个上位机程序来采集力传感器数据以及给机械臂发送控制指令。
1 工程目录
工程目录如下:
RosCommunication
include(存放头文件)
RosCommunication.h
lib(存放生成的库文件)
src(存放源文件)
RosCommunication.cpp
test_RosCommunication.cpp
bin(存放可执行文件)
build(存放编译过程中的中间文件:不用管)
CMakeLists.txt本文虽使用了ROS的部分官方头文件,但并未按照ROS模式的工程目录进行编写。
2 头文件RosCommunication.h
代码如下:
#pragma once
/* This file name is RosCommunication.h */
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "sensor_msgs/JointState.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/WrenchStamped.h"
#include "std_msgs/Float64MultiArray.h"
#include <string>
/* This is a dedicated ROS communication class. There are three methods in this class */
class RosCommunication
{
public:
RosCommunication(std::string JointCommandTopic, std::string JointStateTopic, std::string FtSensorTopic, ros::NodeHandle &nh);
RosCommunication() = delete;
RosCommunication(const RosCommunication &) = delete;
RosCommunication &operator=(const RosCommunication &) = delete;
public:
//Send joint control commands(JointArray) to the JointCommandTopic
void SetJointPosition(const std_msgs::Float64MultiArray &JointArray);
//Get a joint state message from the JointStateTopic
sensor_msgs::JointState::ConstPtr GetJointState();
//Get a force message from the FtSensorTopic
geometry_msgs::WrenchStamped::ConstPtr GetForce();
private:
std::string JointCommandTopic;
std::string JointStateTopic;
std::string FtSensorTopic;
ros::Publisher pub;
ros::NodeHandle nh;
};
2.1 引用的四个头文件
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "sensor_msgs/JointState.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/WrenchStamped.h"
#include "std_msgs/Float64MultiArray.h"第一个文件懂的都懂,不懂就去看看ROS/C++入门,后面三个依次为ROS官方定义的机械臂关节状态、力传感器数据以及机器人控制指令的三个消息类型。
2.2 构造函数
RosCommunication(std::string JointCommandTopic, std::string JointStateTopic, std::string FtSensorTopic, ros::NodeHandle &nh);
RosCommunication() = delete;
RosCommunication(const RosCommunication &) = delete;
RosCommunication &operator=(const RosCommunication &) = delete;这一段好理解,首先来说后三个就是禁用默认构造、拷贝构造和等号运算操作,其实不禁用也行,就怕出现某些误操作。
第一个构造函数为有参构造,要求以此传入控制指令话题,关节状态话题,传感器数据话题以及引用形式传入的节点句柄。
2.3成员函数
//Send joint control commands(JointArray) to the JointCommandTopic
void SetJointPosition(const std_msgs::Float64MultiArray &JointArray);
//Get a joint state message from the JointStateTopic
sensor_msgs::JointState::ConstPtr GetJointState();
//Get a force message from the FtSensorTopic
geometry_msgs::WrenchStamped::ConstPtr GetForce();这个简单,看注释就行。
2.4成员变量
std::string JointCommandTopic;
std::string JointStateTopic;
std::string FtSensorTopic;
ros::Publisher pub;
ros::NodeHandle nh;也简单,成员变量分别对应有参构造参数,以及多了一个Publisher类,后面会用到。
3 源文件RosCommunication.cpp
#include "RosCommunication.h"
RosCommunication::RosCommunication(std::string JointCommandTopic, std::string JointStateTopic, std::string FtSensorTopic, ros::NodeHandle &nh)
{
this->JointCommandTopic = JointCommandTopic;
this->JointStateTopic = JointStateTopic;
this->FtSensorTopic = FtSensorTopic;
this->nh = nh;
this->pub = this->nh.advertise<std_msgs::Float64MultiArray>(this->JointCommandTopic, 10);
}
void RosCommunication::SetJointPosition(const std_msgs::Float64MultiArray &JointArray)
{
while (this->pub.getNumSubscribers() < 1);
this->pub.publish(JointArray);
}
sensor_msgs::JointState::ConstPtr RosCommunication::GetJointState()
{
return ros::topic::waitForMessage<sensor_msgs::JointState>(this->JointStateTopic);
}
geometry_msgs::WrenchStamped::ConstPtr RosCommunication::GetForce()
{
return ros::topic::waitForMessage<geometry_msgs::WrenchStamped>(this->FtSensorTopic);
}有参构造函数就是给每一个成员变量赋值,同时利用传入的节点句柄初始化pub。
最后两个成员函数很简单,直接从相应话题上获取一个消息就行。
SetJointPosition成员函数:给机械臂发送控制指令,实现也很简单,传入一条控制指令,写一个while循环判断当前是否有接受者,没有就陷入死循环,然后发送数据就行。
4 测试文件test_RosCommunication.cpp
#include "RosCommunication.h"
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "RosCommunication");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
std::string JointStateTopic = "/joint_states";
std::string JointCommandTopic = "/robot_controller/command";
std::string FtSensorTopic = "/ft_sensor_topic";
RosCommunication RC(JointCommandTopic, JointStateTopic, FtSensorTopic, nh);
sensor_msgs::JointState::ConstPtr state;
geometry_msgs::WrenchStamped::ConstPtr force;
std_msgs::Float64MultiArray JointArray;
JointArray.data.push_back(0.1);
JointArray.data.push_back(0.0);
JointArray.data.push_back(0.0);
JointArray.data.push_back(0.0);
JointArray.data.push_back(0.0);
JointArray.data.push_back(0.0);
std::cout << "command:";
int command;
while (std::cin >> command)
{
if(command == 1)
{
RC.SetJointPosition(JointArray);
JointArray.data[0] += 0.1;
state = RC.GetJointState();
force = RC.GetForce();
std::cout << "joint state:"
<< "\n";
for (double joint : state->position)
{
std::cout << joint << ", ";
}
std::cout << "\n";
std::cout << "force:"
<< "\n";
std::cout << " x: " << force->wrench.force.x << "\n";
std::cout << " y: " << force->wrench.force.y << "\n";
std::cout << " z: " << force->wrench.force.z << "\n";
}
if(command == 2)
{
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
首先创建了相应的话题以及节点句柄,并初始化了一个RosCommunication类,这里的测试逻辑是,你在终端输入1并回车,就会分别调用三个方法,实现每输入一次1,机械臂的第一个关节角就是旋转0.1弧度,同时显示目前机械臂的关节状态和传感器力数据。输入2的时候程序退出。
5 CMakeList.txt文件
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5.0)
project(RosCommunicationLib)
set(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib)
set(CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin)
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
roscpp
)
file(GLOB ${PROJECT_NAME}_SOURCES "./src/*.cpp")
file(GLOB ${PROJECT_NAME}_HEADERS "./include/*.h")
include_directories(include ${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_libraries(${catkin_LIBRARIES})
add_library(${PROJECT_NAME} SHARED ${${PROJECT_NAME}_SOURCES})
add_executable(test_RosCommunication ${${PROJECT_NAME}_SOURCES})set(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib)
set(CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin)这两句是设置生成的可执行文件放入文件夹bin中,生成的库文件放入文件夹lib中。
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
roscpp
)
这一句,查找roscpp,这一条语句会自动把我们使用的ros头文件和相应实现的库文件分别传入catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS和catkin_LIBRARIES这两个变量当中。
file(GLOB ${PROJECT_NAME}_SOURCES "./src/*.cpp")
file(GLOB ${PROJECT_NAME}_HEADERS "./include/*.h")这个是我们自己设置了两个变量,一个是将src目录下的所有cpp文件设置为${PROJECT_NAME}_SOURCES变量,另一个是将include目录下所有的h文件设置为${PROJECT_NAME}_HEADERS变量。
include_directories(include ${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_libraries(${catkin_LIBRARIES})
add_library(${PROJECT_NAME} SHARED ${${PROJECT_NAME}_SOURCES})
add_executable(test_RosCommunication ${${PROJECT_NAME}_SOURCES})第一条:设置头文件搜索路径,包括我们自己的include目录和ros的头文件路径catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS
第二条:需要链接的库文件,即ros库文件catkin_LIBRARIES
第三条:生成动态库,将${PROJECT_NAME}_SOURCES中的所有文件打包为名为${PROJECT_NAME}的库文件
第四条:生成可执行文件,将${PROJECT_NAME}_SOURCES中的所有文件生成名为test_RosCommunication的可执行文件,并且自动通过第二条语句链接好ROS库。
6 执行
进入build目录,使用cmake..命令,然后使用make命令。然后你就能看到bin目录下多出一个可执行文件,lib目录下多出一个.so库文件。
随后新建窗口,启动ur机械臂仿真界面,参考如何给Gazebo中的仿真机械臂添加一个力传感器?
进入bin目录,运行可执行文件,在终端输入1你就会看到以下内容:
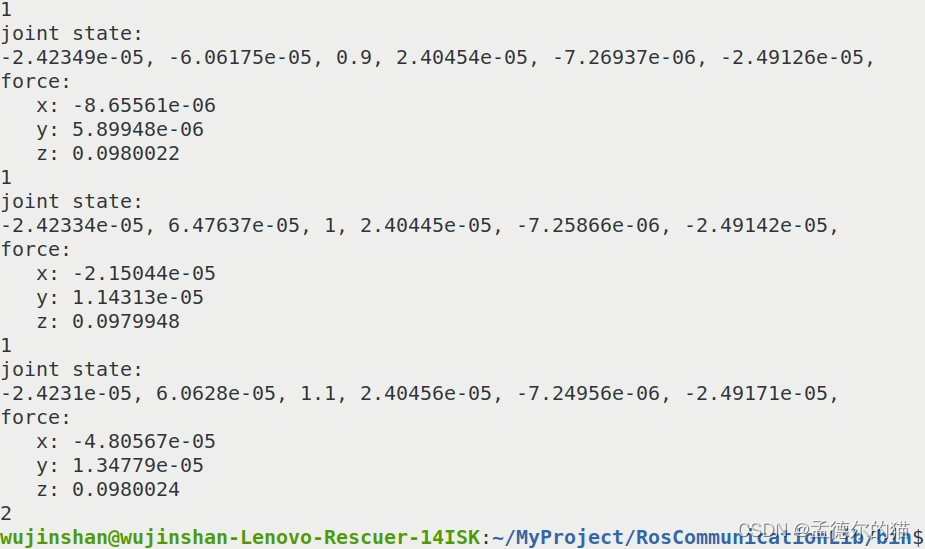
注意,关节状态信息里面,gazebo发布的关节状态是交换了第一个关节和第三个关节的数据,咱也不知道为什么会这样,就是发出了的消息里面的joint_name刚好交换了第一个关节和第三个关节,所以第一个关节每次旋转0.1弧度的数字就会显示在第三个。