5.2.1 用jieba库实现中文分词
- 要从中文文本中提取高频词汇,需要使用中文分词(Chinese Word Segmentation)技术。分词是指将一个文本序列切分成一个个单独的词。我们知道,在英文的行文中,单词之间以空格作为分隔符,而中文的词语之间没有一个形式上的分解符,因此,中文分词比英文分词要复杂一些。在Python中,可以利用jieba库来快速完成中文分词。
1.jieba 库的安装与基本用法
import jieba
word = jieba.cut('我爱北京天安门')
for i in word:
print(i)
注意:用cut()函数分词得到的word不是一个列表,而是一个迭代器。所谓迭代器其实和列表很相似,可以把它理解成一个“隐身的列表”。但是迭代器里的元素要通过for循环语句来访问,所以第3行代码和第4行代码不能改写成print(word)。
2.读取文本内容并进行分词
- 下面先来讲解如何从文本文件中读取内容并进行分词,代码如下:
import jieba
report = open('信托行业报告.txt','r').read()
words = jieba.cut(report)
for word in words:
print(word)
3.按指定长度提取分词后的词
- 这里以提取长度大于等于4个字的词为例进行讲解,代码如下:
import jieba
report = open('信托行业报告.txt','r').read()
words = jieba.cut(report)
report_words = []
for word in words: #将长度大于等于4个字的词放入列表
if len(word) >= 4:
report_words.append(word)
print(report_words)
4.统计高频词汇
- 统计高频词汇并不复杂,用collections库中的Counter()函数就可以完成,代码如下:
import jieba
report = open('信托行业报告.txt','r').read()
words = jieba.cut(report)
report_words = []
for word in words: #将长度大于等于4个字的词放入列表
if len(word) >= 4:
report_words.append(word)
from collections import Counter
result = Counter(report_words)
print(result)
- 这样便可以打印输出每个词的出现次数。如果只想看出现次数排名前50位的词,可以用most_common()函数来完成,将上述第10行代码改写成如下代码:
import jieba
report = open('信托行业报告.txt','r').read()
words = jieba.cut(report)
report_words = []
for word in words: #将长度大于等于4个字的词放入列表
if len(word) >= 4:
report_words.append(word)
from collections import Counter
result = Counter(report_words).most_common(50) #取最多的50组
print(result)
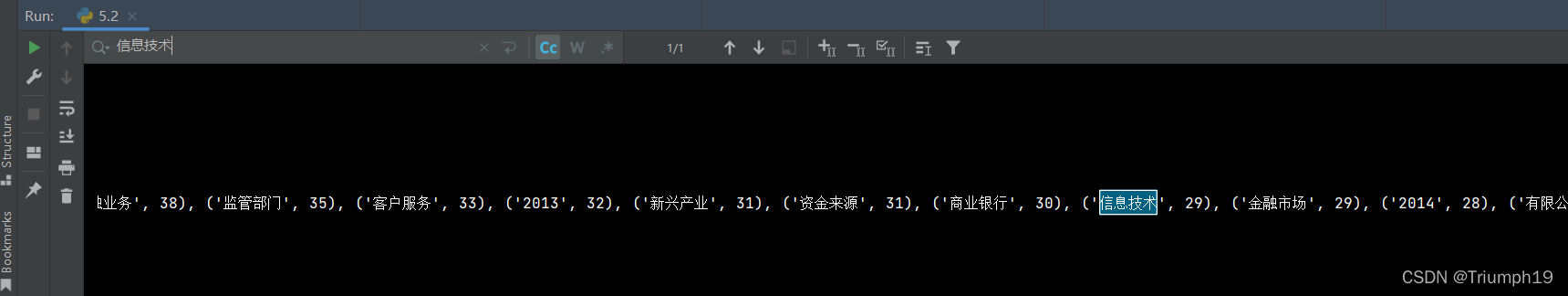
- 将result打印输出,结果如下图所示。可以看到,里面的一些高频词还是能体现整个行业的某些情况的。例如,最近几年行业年度报告里频繁提到“信息技术”与“人工智能”这类词,那么它们也的确体现了行业的未来发展趋势。
5.2.2 用wordcloud库绘制词云图
1.wordcloud库的基本用法
- 以前面做了长度筛选的分词结果report_words为例讲解wordcloud库的基本用法,代码如下:
- 如果wordcloud安装失败,可参考python中安装wordcloud的方法
# 1.读取文本内容,并用jieba库中的cut()函数进行分词
import jieba
report = open('信托行业报告.txt','r').read()
words = jieba.cut(report)
# 2.通过for循环语句提取列表words中长度大于等于4个字的词
report_words = []
for word in words: #将长度大于等于4个字的词放入列表
if len(word) >= 4:
report_words.append(word)
#print(report_words)
# 3.获得打印输出高频词的出现次数
from collections import Counter
result = Counter(report_words).most_common(50) #取最多的50组
#print(result)
# 4.绘制词云图
from wordcloud import WordCloud #导入相关库
content = ' '.join(report_words) #把列表转换为字符串
wc = WordCloud(font_path='simhei.ttf',#字体文件路径(这里为黑体)
background_color='white',#背景颜色(这里为白色)
width=1000,#宽度
height=600,#高度
).generate(content) #绘制词云图
wc.to_file('词云图.png') #导出成PNG格式图片(使用相对路径)

2.绘制特定形状的词云图
- 我们还可以将词云图绘制成特定的形状。首先导入相关库,代码如下:
from PIL import Image
from numpy as np
from wordcloud import WordCloud #导入相关库
- 第一行代码导入用于处理图片的PIL库。第二行导入用于处理数据的NumPy库,在本书作者编写的《Python金融大数据挖掘与分析全流程详解》的第6章就有该库的详细了解。
- 导入相关库后,就可以绘制指定形状的词云图了,代码如下:
# 1.读取文本内容,并用jieba库中的cut()函数进行分词
import jieba
report = open('信托行业报告.txt','r').read()
words = jieba.cut(report)
# 2.通过for循环语句提取列表words中长度大于等于4个字的词
report_words = []
for word in words: #将长度大于等于4个字的词放入列表
if len(word) >= 4:
report_words.append(word)
#print(report_words)
# 3.获得打印输出高频词的出现次数
from collections import Counter
result = Counter(report_words).most_common(50) #取最多的50组
#print(result)
# 4.绘制特定形状的词云图
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from wordcloud import WordCloud #导入相关库
background_pic = '微博.jpg' #形状蒙版图片转换为数值数组
images = Image.open(background_pic) #打开形状蒙版图片
maskImages = np.array(images) #将形状蒙版图片转换为数值数组
content = ' '.join(report_words) #把列表转换为字符串
wc = WordCloud(font_path='simhei.ttf',#字体文件路径(这里为黑体)
background_color='white',#背景颜色(这里为白色)
width=1000,#宽度
height=600,#高度
mask = maskImages #应用形状蒙版
).generate(content) #绘制词云图
wc.to_file('词云图+自定义形状.png') #导出成PNG格式图片(使用相对路径)
- 如何省略了第30行代码,那么得到的图形就和第一个词云图是一样的。

- 最终生成的词云图的颜色还是默认颜色(具体的颜色效果请读者自行运行代码后查看)。
3.绘制特定颜色的词云图
- 接下来讲解如何在特定形状的基础上,按特定颜色绘制词云图。首先导入相关库,代码如下:
from wordcloud import WordCloud,ImageColorGenerator
from imageio import imread
- 第一行代码除了从wordcloud库中导入WordCloud模块,还导入了ImageColorGenerator模块,用于获取颜色;第2行代码导入imageio库中的imread模块,用于读取图像。
- 然后在绘制特定词云图的代码后面加上如下代码:
# 1.读取文本内容,并用jieba库中的cut()函数进行分词
import jieba
report = open('信托行业报告.txt','r').read()
words = jieba.cut(report)
# 2.通过for循环语句提取列表words中长度大于等于4个字的词
report_words = []
for word in words: #将长度大于等于4个字的词放入列表
if len(word) >= 4:
report_words.append(word)
#print(report_words)
# 3.获得打印输出高频词的出现次数
from collections import Counter
result = Counter(report_words).most_common(50) #取最多的50组
#print(result)
# 4.绘制特定形状的词云图
# 获取词云图形状参数mask
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from wordcloud import WordCloud #导入相关库
background_pic = '微博.jpg' #形状蒙版图片转换为数值数组
images = Image.open(background_pic) #打开形状蒙版图片
maskImages = np.array(images) #将形状蒙版图片转换为数值数组
content = ' '.join(report_words) #把列表转换为字符串
wc = WordCloud(font_path='simhei.ttf',#字体文件路径(这里为黑体)
background_color='white',#背景颜色(这里为白色)
width=1000,#宽度
height=600,#高度
mask = maskImages #应用形状蒙版
).generate(content) #绘制词云图
# 修改词云图的底层颜色,这个blackgroud_pic就是之前的背景图片
from wordcloud import WordCloud,ImageColorGenerator
from imageio import imread
back_color = imread(background_pic) #读取图片
image_colors = ImageColorGenerator(back_color) #获取图片的颜色
wc.recolor(color_func=image_colors) #为词云图上色
wc.to_file('词云图+自定义形状+颜色.png') #导出成PNG格式图片(使用相对路径)

- 最终生成的词云图,可以看到除了形状是新浪微博徽标的轮廓,词的颜色也是新浪微博徽标的特定颜色(具体的颜色效果读者自行运行代码后查看)。
5.2.3案例实战:新浪微博词云图绘制
- 下面基于3.6节从新浪微博爬取的内容,结合本节学习的知识绘制词云图。
requests获取网页源代码失败
import requests
headers = {'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/100.0.4896.60 Safari/537.36'}
# 1.获取网页源代码
url = 'https://s.weibo.com/weibo?q=阿里巴巴'
res = requests.get(url, headers=headers).text
print(res)
用Selenium获取真实的网页源代码
爬取并汇总每条微博的内容
# 再去掉空格和中文括号里的内容(46和47行代码)
# 1.获取真实的网页源代码
import time
from selenium import webdriver
def get_browser():
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_experimental_option('excludeSwitches', ['enable-automation'])
options.add_argument("--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)
driver.execute_cdp_cmd("Page.addScriptToEvaluateOnNewDocument", {
"source": """
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'webdriver', {
get: () => undefined
})
"""
})
return driver
#if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'https://s.weibo.com/weibo?q=阿里巴巴'
browser = get_browser()
browser.get(url)
time.sleep(6)
data = browser.page_source
#print(data)
# 2.使用正则表达式提取数据
import re
p_source = '<p node-type="feed_list_content" nick-name="(.*?)"'
source = re.findall(p_source,data)
p_title = '<p node-type="feed_list_content" nick-name=.*? class="txt">(.*?)</p>'
title = re.findall(p_title,data,re.S)
# print(title)
# print(source)
# 3.数据清洗、打印输出、汇总
title_all = '' #创建一个空字符串,用于汇总数据
for i in range(len(title)):
title[i] = title[i].strip()
title[i] = re.sub('<.*?>','',title[i])
title[i] = re.sub('[\u200b]','',title[i])
title[i] = re.sub('(.*?)','',title[i])
title[i] = re.sub(' ','',title[i])
title_all = title_all + title[i] #通过字符串拼接汇总数据
print(str(i + 1) + '.' + title[i] + '-' + source[i])
接着进行过分词
# 4. 用jieba库中的cut()函数进行分词
words = jieba.cut(title_all) #传入的就是上面汇总的title_all
# 5.通过for循环语句提取长度大于等于两个字的词
report_words = []
for word in words:
if len(word) == 2:
report_words.append(word)
#print(report_words)
# 6.获取词频最高的50个词
result = Counter(report_words).most_common(50)
#print(result)
绘制词云图
# 再去掉空格和中文括号里的内容(46和47行代码)
# 1.获取真实的网页源代码
import time
from selenium import webdriver
def get_browser():
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_experimental_option('excludeSwitches', ['enable-automation'])
options.add_argument("--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)
driver.execute_cdp_cmd("Page.addScriptToEvaluateOnNewDocument", {
"source": """
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'webdriver', {
get: () => undefined
})
"""
})
return driver
#if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'https://s.weibo.com/weibo?q=阿里巴巴'
browser = get_browser()
browser.get(url)
time.sleep(6)
data = browser.page_source
#print(data)
# 2.使用正则表达式提取数据
import re
p_source = '<p node-type="feed_list_content" nick-name="(.*?)"'
source = re.findall(p_source,data)
p_title = '<p node-type="feed_list_content" nick-name=.*? class="txt">(.*?)</p>'
title = re.findall(p_title,data,re.S)
# print(title)
# print(source)
# 3.数据清洗、打印输出、汇总
title_all = '' #创建一个空字符串,用于汇总数据
for i in range(len(title)):
title[i] = title[i].strip()
title[i] = re.sub('<.*?>','',title[i])
title[i] = re.sub('[\u200b]','',title[i])
title[i] = re.sub('(.*?)','',title[i])
title[i] = re.sub(' ','',title[i])
title_all = title_all + title[i] #通过字符串拼接汇总数据
print(str(i + 1) + '.' + title[i] + '-' + source[i])
# 4. 用jieba库中的cut()函数进行分词
import jieba
words = jieba.cut(title_all) #传入的就是上面汇总的title_all
# 5.通过for循环语句提取长度大于等于两个字的词
report_words = []
for word in words:
if len(word) == 2:
report_words.append(word)
#print(report_words)
# 6.获取词频最高的50个词
from collections import Counter
result = Counter(report_words).most_common(50)
#print(result)
# 7.按特定形状和特定颜色绘制词云图
# (1)获取词云图形状参数mask
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from wordcloud import WordCloud #导入相关库
background_pic = '微博.jpg' #形状蒙版图片转换为数值数组
images = Image.open(background_pic) #打开形状蒙版图片
maskImages = np.array(images) #将形状蒙版图片转换为数值数组
# (2)按照形状蒙版绘制词云图
content = ' '.join(report_words) #把列表转换为字符串
wc = WordCloud(font_path='simhei.ttf',#字体文件路径(这里为黑体)
background_color='white',#背景颜色(这里为白色)
width=1000,#宽度
height=600,#高度
mask = maskImages #应用形状蒙版
).generate(content) #绘制词云图
# (3)修改词云图的底层颜色,这个blackgroud_pic就是之前的背景图片
from wordcloud import WordCloud,ImageColorGenerator
from imageio import imread
back_color = imread(background_pic) #读取图片
image_colors = ImageColorGenerator(back_color) #获取图片的颜色
wc.recolor(color_func=image_colors) #为词云图上色
wc.to_file('微博内容词云图.png') #导出成PNG格式图片(使用相对路径)
