
上面是传统的CRF模型,状态发射概率加上状态转移概率。CRF++就是用模版来设置两个概率特征函数。在BiLSTM+CRF中发射概率是由BiLSTM(或者其他的什么模型)给出的,所以CRF就是一个状态转移矩阵,给标签之间加上了约束。
下面就是CRF层,就是一个参数矩阵,里面存储着状态之间的转移概率,在训练中这个矩阵也得到优化。
self.transitions = nn.Parameter( #概率转移矩阵
torch.randn(self.tagset_size, self.tagset_size))? ? ? ? 跟CRF相关的代码主要是 计算损失(前向计算)和维特比解码两部分。
-
?计算损失:
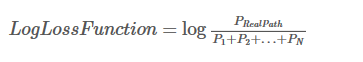
? ? ? ? CRF的损失是正确的(真实)路径概率与全部路径概率比值。
? ? ? ? 形式可以变为:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 其中:Si = EmissionScore + TransitionScore

1.全部路径分数
????????首先是全部路径的分数(概率)和。并不需要把全部的路径真的都求出来,因为它的损失函数的形式可以迭代地去求,根据前一步的情况就可以求出本步的全部路径分数。


? ? ? ? 从步骤三可以看出,前一步的log_sum_exp结果可以直接用在本步上,加上发射和转移概率之后在进行log_sum_exp计算就是该步的全部路径分数。
# loss的前半部分log_sum_exp的结果,计算所有可能路径的得分
# 基于动态规划的思想,可以先计算到w_i的log_sum_exp,然后计算到w_i+1的log_sum_exp
def _forward_alg(self, feats):
# Do the forward algorithm to compute the partition function
# init_alphas: (1, tagset_size)
init_alphas = torch.full((1, self.tagset_size), -10000.)
# START_TAG has all of the score.
init_alphas[0][self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]] = 0.
# Wrap in a variable so that we will get automatic backprop
# forward_var: (1, tagset_size)
# 上一步的分数信息
forward_var = init_alphas
# Iterate through the sentence
# feats: (seq_length, tagset_size)
# feat: (tagset_size)
for feat in feats:
# The forward tensors at this timestep
# 本步路径分数信息
alphas_t = []
for next_tag in range(self.tagset_size):
# broadcast the emission score: it is the same regardless of the previous tag
# emit_score: (1, tagset_size)
emit_score = feat[next_tag].view(1, -1).expand(1, self.tagset_size)
# the ith entry of trans_score is the score of transitioning to next_tag from i
# trans_score: (1, tagset_size)
trans_score = self.transitions[next_tag].view(1, -1)
# The ith entry of next_tag_var is the value for the edge (i -> next_tag) before we do log-sum-exp
# next_tag_var: (1, tagset_size)
# 这里forward_var是已经用log_sum_exp计算完之后的数值了
# 但是加上本节点的两个概率之后再计算log_sum_exp不影响结果
next_tag_var = forward_var + trans_score + emit_score
# The forward variable for this tag is log-sum-exp of all the scores
alphas_t.append(log_sum_exp(next_tag_var).view(1))
# forward_var: (1, tagset_size)
forward_var = torch.cat(alphas_t).view(1, -1)
# terminal_var: (1, tagset_size)
terminal_var = forward_var + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]]
# alpha: (1)
alpha = log_sum_exp(terminal_var)
return alpha2.最佳路径分数
# loss的后半部分S(X,y)的结果,计算序列y的得分
def _score_sentence(self, feats, tags):
# Gives the score of a provided tag sequence
score = torch.zeros(1)
# tags: (seq + 1)
tags = torch.cat([torch.tensor([self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]], dtype=torch.long), tags])
# feats: (seq_length, tagset_size)
# feat: (tagset_size)
for i, feat in enumerate(feats):
# feat[tags[i+1]]为tags[i+1]的发射概率
# self.transitions[tags[i + 1], tags[i]]为从tags[i]转移到tags[i + 1]的概率值
score = score + self.transitions[tags[i + 1], tags[i]] + feat[tags[i + 1]]
score = score + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG], tags[-1]]
return score-
?维特比解码:

def _viterbi_decode(self, feats):
#利用发射矩阵和状态转移矩阵使用维特比算法,解码出概率最大的BIO状态路径,并给出分数
backpointers = []
# Initialize the viterbi variables in log space
# 初始化的时候,让START概率=1,由于是对数空间,log(1)=0,其他为0,log(0)以-10000代替
init_vvars = torch.full((1, self.tagset_size), -10000.)
init_vvars[0][self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]] = 0
# forward_var at step i holds the viterbi variables for step i-1
forward_var = init_vvars
for feat in feats: #遍历每一个单词,feat是发射到该单词的概率向量
# 下面两个变量都是在每一步保存变量的,每一步都是tag_size个节点
# 当前步最佳路径(保存的前一步的最佳转移节点)
bptrs_t = [] # holds the backpointers for this step
# 当前步的路径最佳分数
viterbivars_t = [] # holds the viterbi variables for this step
#计算某一单词的所有可能的状态转移到next_tag状态的概率
for next_tag in range(self.tagset_size):
# next_tag_var[i] holds the viterbi variable for tag i at the
# previous step, plus the score of transitioning
# from tag i to next_tag.
# We don't include the emission scores here because the max
# does not depend on them (we add them in below)
# 求转移到next_tag概率,其实就是乘以转移矩阵中相应的值,因为是log空间,*改+
next_tag_var = forward_var + self.transitions[next_tag]
best_tag_id = argmax(next_tag_var) # 选出转移到next_tag状态概率最大的路径
bptrs_t.append(best_tag_id) #记录从哪里转移过来的,以后回溯要用
viterbivars_t.append(next_tag_var[0][best_tag_id].view(1)) #记录转移到next_tag的概率
# Now add in the emission scores, and assign forward_var to the set
# of viterbi variables we just computed
# 计算完前一个单词的所有状态到该单词的所有状态的概率后,再乘以发射概率
forward_var = (torch.cat(viterbivars_t) + feat).view(1, -1)
backpointers.append(bptrs_t) #保存最优路径,用于回溯
# Transition to STOP_TAG 最后计算转移到STOP标签的概率
terminal_var = forward_var + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]]
best_tag_id = argmax(terminal_var)
path_score = terminal_var[0][best_tag_id]
# Follow the back pointers to decode the best path. 回溯找到最优路径
best_path = [best_tag_id]
for bptrs_t in reversed(backpointers):
best_tag_id = bptrs_t[best_tag_id]
best_path.append(best_tag_id)
# Pop off the start tag (we dont want to return that to the caller)
start = best_path.pop()
assert start == self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG] # Sanity check
best_path.reverse() # 将最优路径转为从左到右
return path_score, best_path #返回最优路径的分数和最优路径