目录
subpixel ineterpolation亚像素插值(二次曲线拟合视差值)
完整测试代码:
SGBM的算法流程(对比SGM)
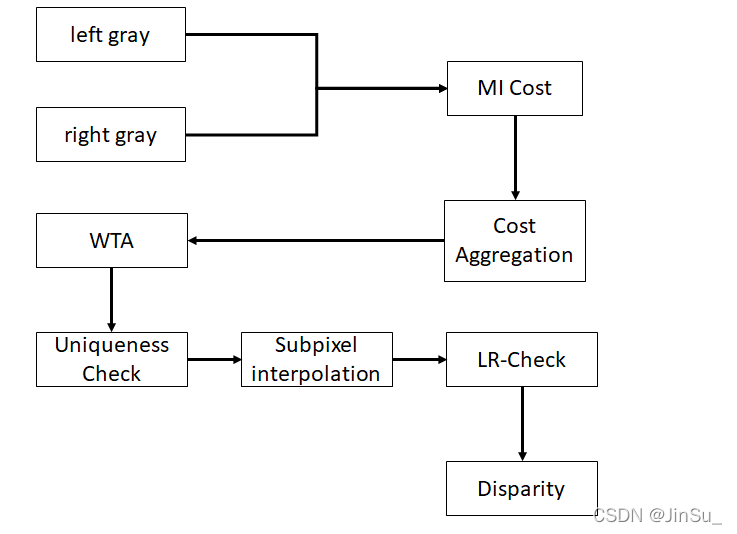
原始的SGM算法流程如下:
SGBM的算法流程如下:
?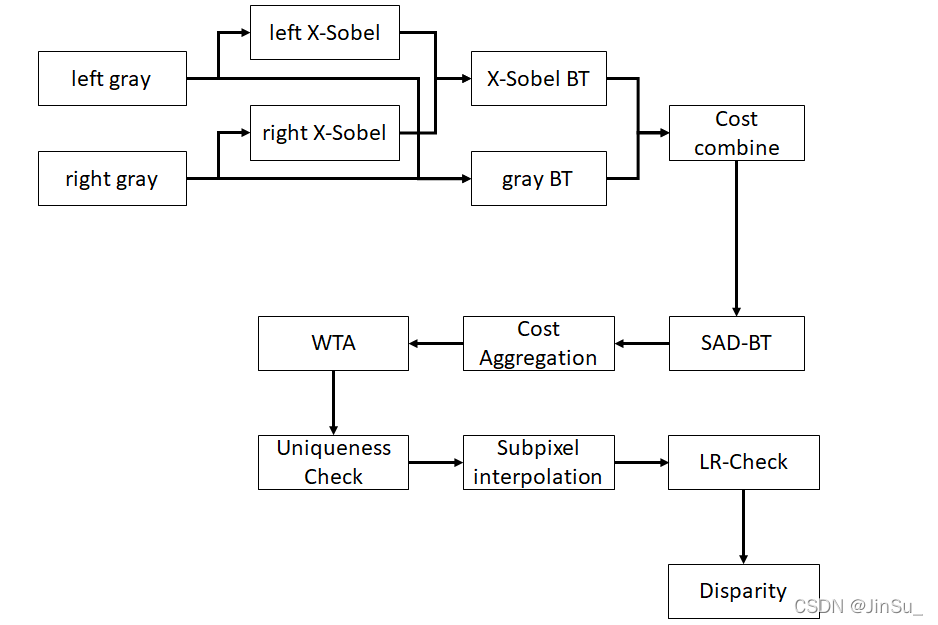
对比之后可以发现,SGBM和SGM区别的地方在于匹配代价的计算:SGBM采用的是SAD-BT,而SGM采用的是MI。
MI是指互信息(MI,Mutual Information),一种全局的代价计算方法,耗时较多。
而OpenCV在实现SGBM的时候采用了BT代价,这是一种一维匹配代价,所以在应用中不仅是用x-sobel和原图gray生成加权融合的BT代价,而且采用SAD的思路,采用邻域求和的方法,计算SAD-BT,这样计算出来的代价就是局部块代价,每个像素点的匹配代价会包含周围局部区域的信息。
对比之后可以发现,其他步骤都是一致的,比如代价聚合cost aggregation,赢者通吃wta,亚像素插值subpixel interpolation等等。
这些步骤的具体原理可以参考:
下面我们开始探索最本质的区别:BT代价
BT代价(xsobel和原始灰度gray)
BT代价的原理
BT代价是一维匹配代价。
对比AD,AD也是一维匹配代价:像素灰度差值的绝对值。
对比census,census是二维匹配代价(比如,census核函数尺寸为5\times5,会包含到局部5\times5的区域信息)
参考:
Birchfield S , Tomasi C . Depth Discontinuities by Pixel-to-Pixel Stereo[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1999, 35(3):269-293.
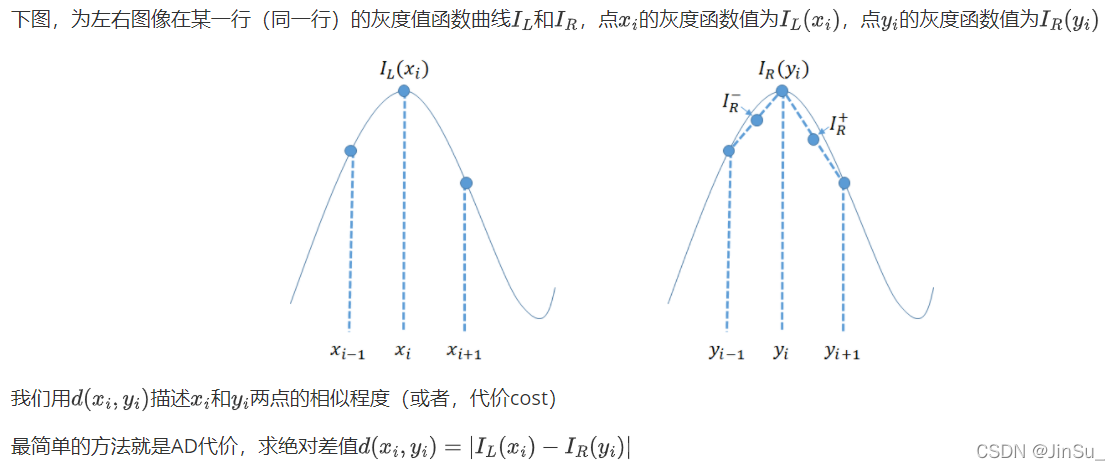

 ?
?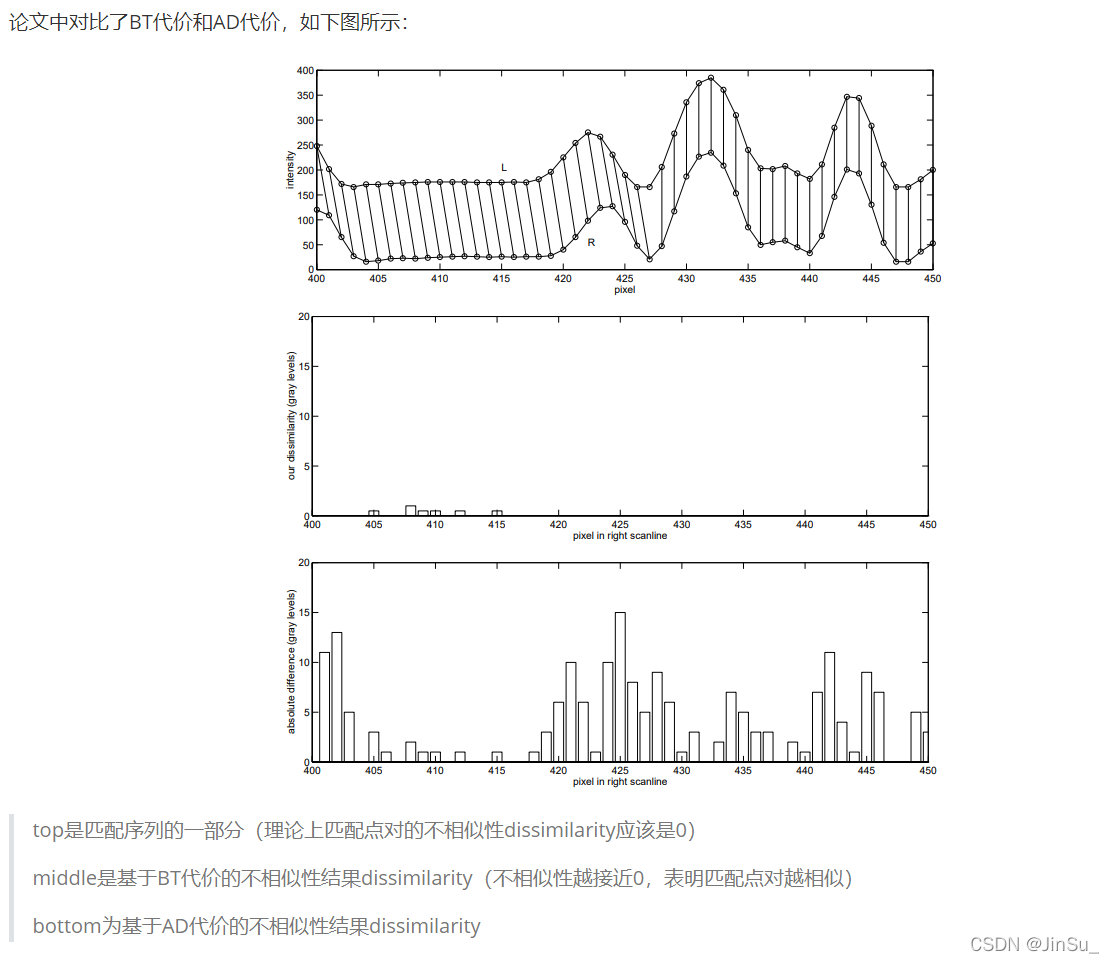
可以看出,
在序列比较平稳时,即相邻像素点的灰度值很接近时,两种方法的结果是相近的,
而当匹配序列起浮变化的时候(类似图像中的不连续区域),基于BT代价的不相似性依旧是接近于0,而AD则出现很大的波动。
由此可见,对于图片的不连续区域,利用BT代价计算法可以有效的进行准确匹配而不会产生过多的误差,证明该方法是可行且具有显著效果的。
X-Sobel的滤波计算过程

X-Sobel BT和gray BT加权融合

SAD-BT代价(邻域求和运算)
因为BT代价是一维匹配,所以通常要结合SAD的思路,采用邻域求和的方法,计算SAD-BT,这样计算出来的代价就是局部块代价,每个像素点的匹配代价会包含周围局部区域的信息。
SAD(sum of absolute differences),参考:
关于双目立体视觉的三大基本算法SAD、SSD、SGBM及发展现状的总结_何呵呵0706的博客-CSDN博客_sad和ssd算法

subpixel ineterpolation亚像素插值(二次曲线拟合视差值)
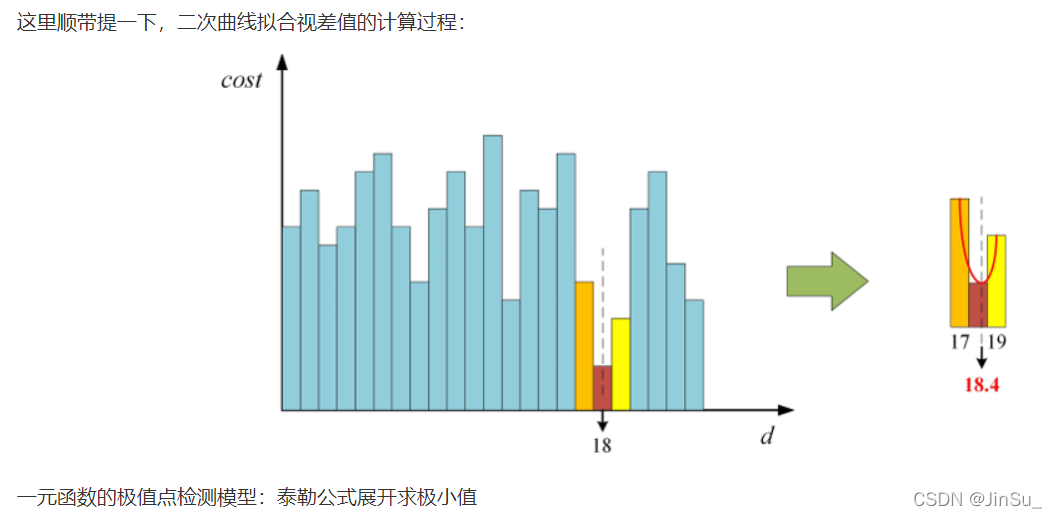
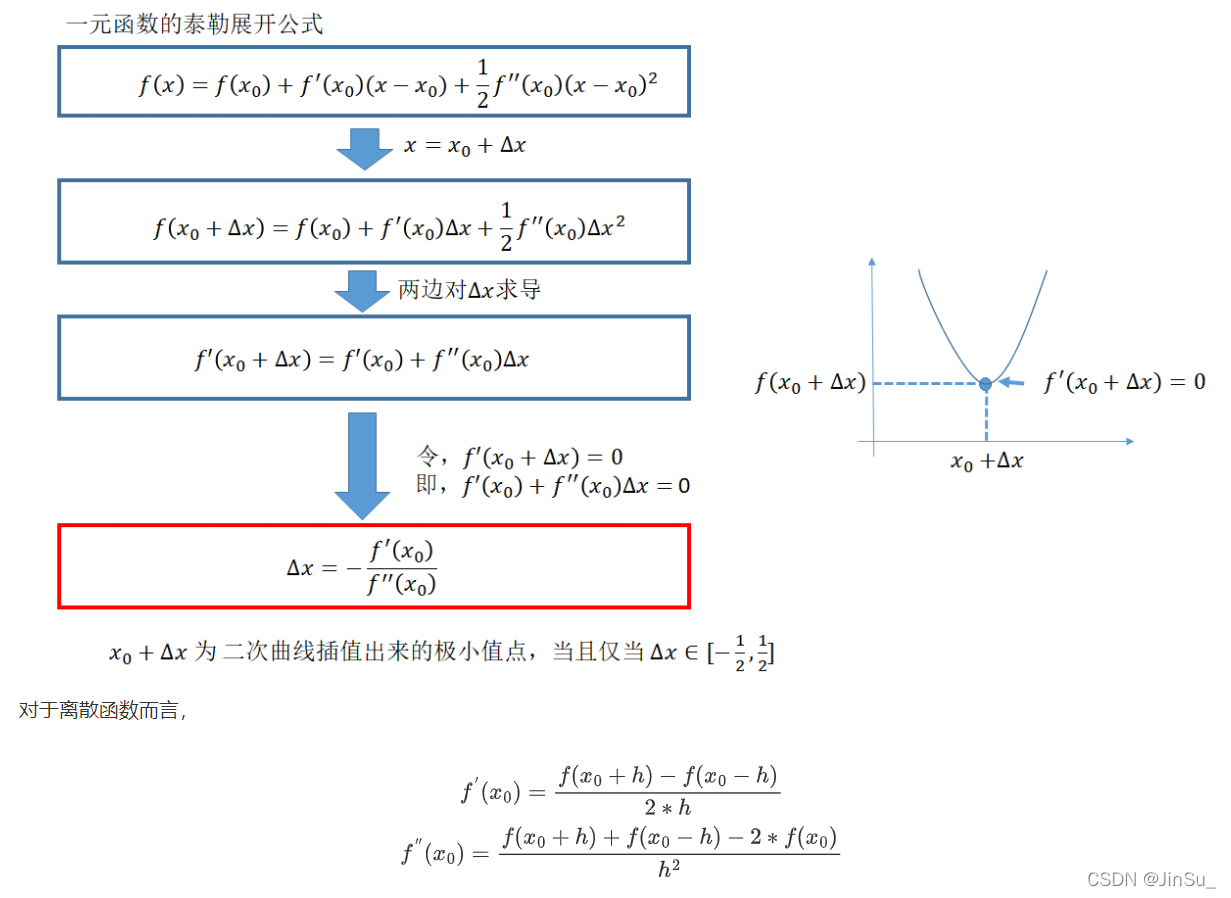
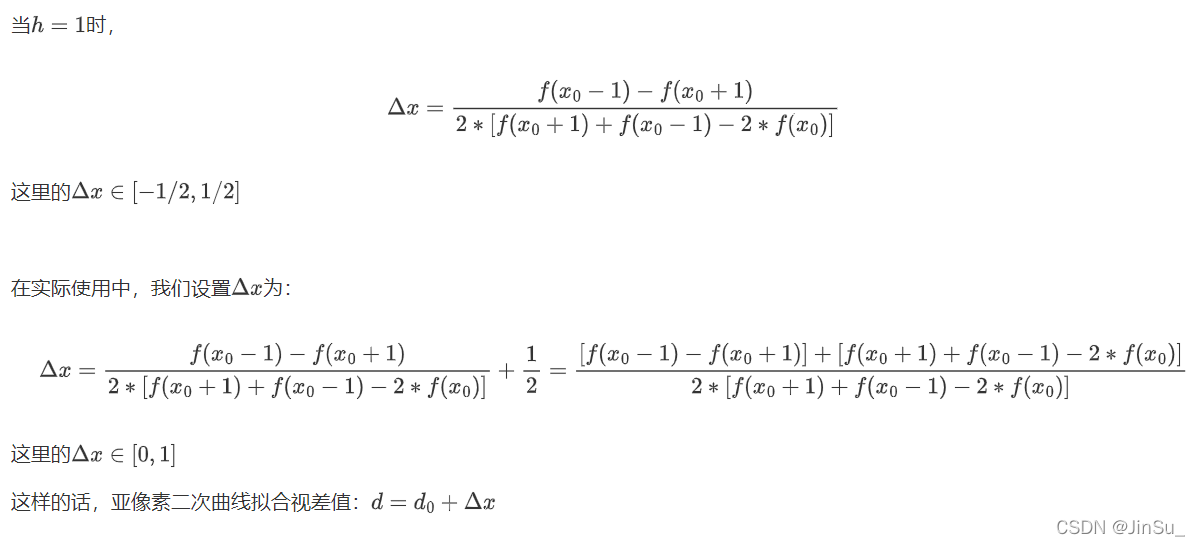
OpenCV的具体代码-实现详解
????
OpenCV-SGBM源码中的关键数据变量
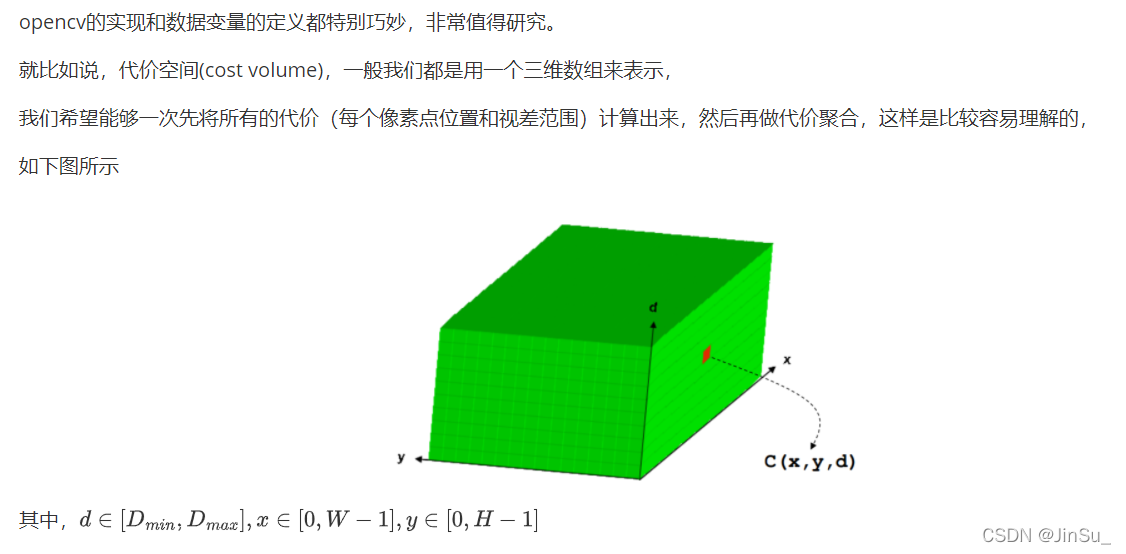
int width1 = width + std::min(minD, 0) - std::max(maxD, 0);//行代价空间的宽度
int D = params.numDisparities;//视差范围,行代价空间的高度
int Da = (int)cv::alignSize(D, cv::v_int16::nlanes);//内存对齐,如果D为64,则不变,Da==D
int Dlra = Da + cv::v_int16::nlanes;//Additional memory is necessary to store disparity values(MAX_COST) for d=-1 and d=D
int DISP_SHIFT = cv::StereoMatcher::DISP_SHIFT;//视差偏移量
int DISP_SCALE = (1 << DISP_SHIFT);//视差偏移映射的系数scale,若DISP_SHIFT,则DISP_SCALE为16。
//即在存放视差的时候都要乘以DISP_SCALE,这样的话,视差1会被映射为16,视差1.25会被映射为20,视差2会被映射为32,
//后续取出视差进行实际计算的时候要手动偏移或者除以16,才能得到真实视差值;这样的好处就是用short变量存放float值,可以存放二次曲线插值出来的浮点型视差
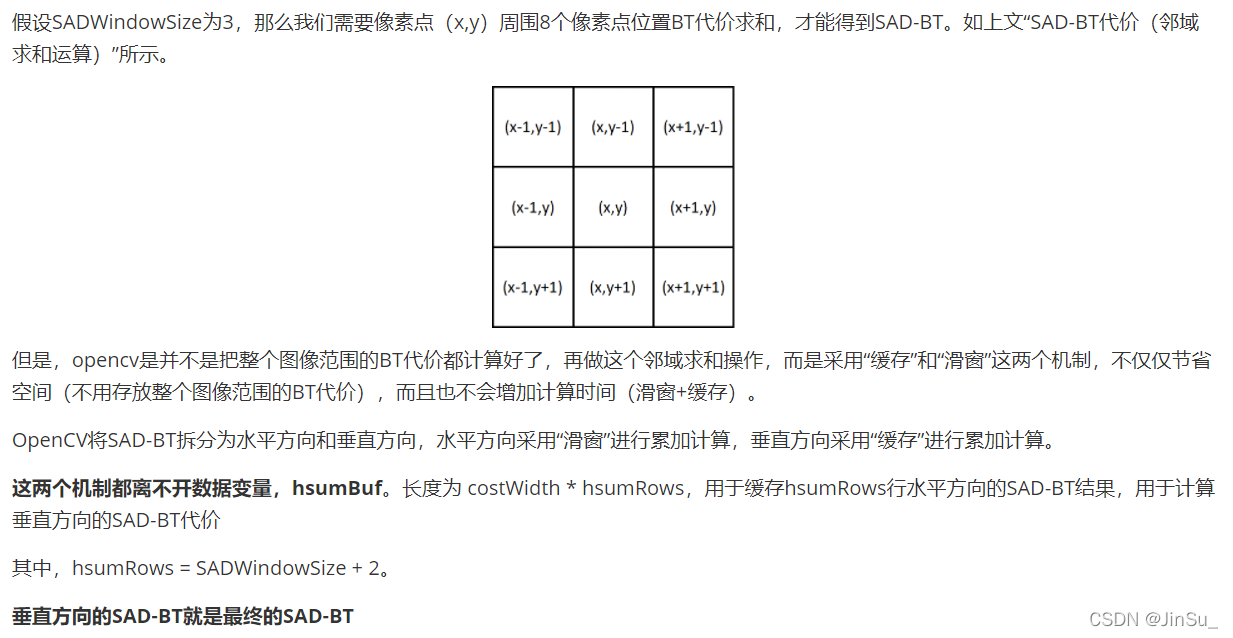
int SADWindowSize = 3;//SAD-BT代价邻域的尺寸,奇数,可以为3、5、7等
int P1 = 8 * 1 * SADWindowSize * SADWindowSize;//设置惩罚P1
int P2 = 32 * 1 * SADWindowSize * SADWindowSize;//设置惩罚P2,opencv-sgbm的P2是固定的,不同于sgm的P2是根据灰度值自适应调整
int SW2 = SADWindowSize / 2;//半个SAD窗口的长度
int SH2 = SADWindowSize / 2;
int costWidth = width1 * Da;//所谓的二维数组实际上是可以存放为一维数组,二维的数据width1 * Da可以存放为长度为costWidth的一维数组
int costHeight = 1;//若是5个路径则为1,若是8个路径则为图像实际高度,这里默认为1;
typedef short CostType;//代价数值类型为short,16bit
typedef uchar PixType;//图像像素的像素值类型为unsigned char,8bit
typedef short DispType;//视差数据类型为short,16bit
BufferSGBM;//opencv 4开始用一个统一的数据结构管理所有内存变量,比如代价空间Cbuf(存放SAD-BT代价),聚合代价Sbuf,单像素BT代价pixDiff等等。
//BufferSGBM中管理的比较重要的数据变量,如下:
CostType *Cbuf;//长度为 costWidth * costHeight,用于存放SAD-BT代价
CostType *Sbuf;//长度为 costWidth * costHeight,用于存放聚合代价
int hsumRows = SADWindowSize + 2;//缓存行数
CostType *pixDiff;//长度为 costWidth,某行的像素点对之间的BT代价(水平扫描线上点和点之间的BT代价)
CostType *hsumBuf;//长度为 costWidth * hsumRows,用于缓存hsumRows行水平方向的SAD-BT结果,用于计算垂直方向的SAD-BT代价
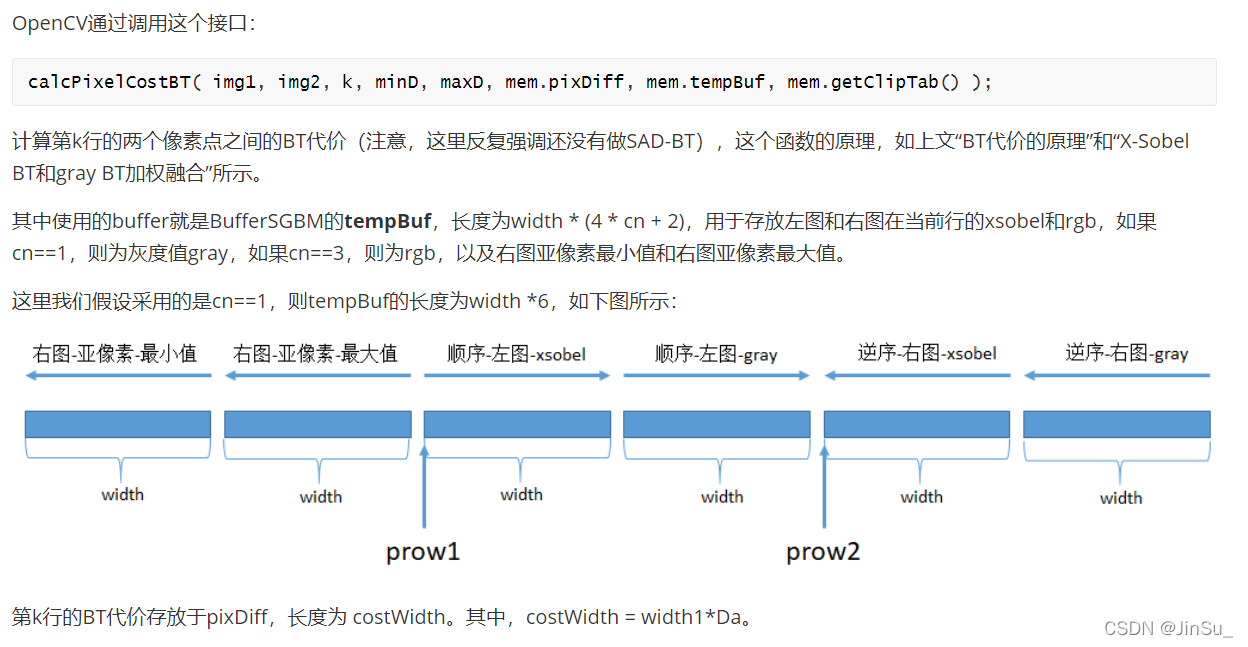
PixType *tempBuf;//长度为 width * (4 * cn + 2),用于存放左图和右图在当前行的xsobel和rgb(如果cn==1,则为灰度值gray,如果cn==3,则为rgb),以及右图亚像素最小值和右图亚像素最大值
uchar dirs = 16;
uchar dirs2 = 8;
std::vector<CostType *> Lr;//尺寸为 [2] * [(width1 * dirs2 + 2 * dirs)*Dlra]
std::vector<CostType *> minLr;//尺寸为 [2] * [width1 * dirs2 + 2 * dirs]
PixType *clipTab;//长度为256 + 1024 * 2,xsobel映射表,映射关系如上文“X-Sobel的滤波计算过程”所示X-Sobel BT和gray BT的实现
X-Sobel BT和gray BT的计算过程在calcPixelCostBT函数中实现,
/*
For each pixel row1[x], max(maxD, 0) <= minX <= x < maxX <= width - max(0, -minD),
and for each disparity minD<=d<maxD the function
computes the cost (cost[(x-minX)*(maxD - minD) + (d - minD)]), depending on the difference between
row1[x] and row2[x-d]. The subpixel algorithm from
"Depth Discontinuities by Pixel-to-Pixel Stereo" by Stan Birchfield and C. Tomasi
is used, hence the suffix BT.
the temporary buffer should contain width2*2 elements
*/
static void calcPixelCostBT( const Mat& img1, const Mat& img2, int y,
int minD, int maxD, CostType* cost,
PixType* buffer, const PixType* tab,
int xrange_min = 0, int xrange_max = DEFAULT_RIGHT_BORDER )
{
int x, c, width = img1.cols, cn = img1.channels();
int minX1 = std::max(maxD, 0), maxX1 = width + std::min(minD, 0);
int D = (int)cv::alignSize(maxD - minD, cv::v_int16::nlanes), width1 = maxX1 - minX1;
// This minX1 & maxX2 correction is defining which part of calculatable line must be calculated
// That is needs of parallel algorithm
xrange_min = (xrange_min < 0) ? 0 : xrange_min;
xrange_max = (xrange_max == DEFAULT_RIGHT_BORDER) || (xrange_max > width1) ? width1 : xrange_max;
maxX1 = minX1 + xrange_max;
minX1 += xrange_min;
width1 = maxX1 - minX1;
int minX2 = std::max(minX1 - maxD, 0), maxX2 = std::min(maxX1 - minD, width);
int width2 = maxX2 - minX2;
const PixType *row1 = img1.ptr<PixType>(y), *row2 = img2.ptr<PixType>(y);
PixType *prow1 = buffer + width2 * 2, *prow2 = prow1 + width * cn * 2;
for (c = 0; c < cn * 2; c++)
{
prow1[width * c] = prow1[width * c + width - 1] =
prow2[width * c] = prow2[width * c + width - 1] = tab[0];
}
int n1 = y > 0 ? -(int)img1.step : 0, s1 = y < img1.rows - 1 ? (int)img1.step : 0;
int n2 = y > 0 ? -(int)img2.step : 0, s2 = y < img2.rows - 1 ? (int)img2.step : 0;
int minX_cmn = std::min(minX1, minX2) - 1;
int maxX_cmn = std::max(maxX1, maxX2) + 1;
minX_cmn = std::max(minX_cmn, 1);
maxX_cmn = std::min(maxX_cmn, width - 1);
if (cn == 1){
for (x = minX_cmn; x < maxX_cmn; x++){
prow1[x] = tab[(row1[x + 1] - row1[x - 1]) * 2 + row1[x + n1 + 1] - row1[x + n1 - 1] + row1[x + s1 + 1] - row1[x + s1 - 1]];//顺序存放左图xsobel
prow2[width - 1 - x] = tab[(row2[x + 1] - row2[x - 1]) * 2 + row2[x + n2 + 1] - row2[x + n2 - 1] + row2[x + s2 + 1] - row2[x + s2 - 1]];//逆序存放右图xsobel
prow1[x + width] = row1[x];//顺序存放左图原始灰度值
prow2[width - 1 - x + width] = row2[x];//逆序存放右图原始灰度值
}
}
else
{
for (x = minX_cmn; x < maxX_cmn; x++)
{
prow1[x] = tab[(row1[x * 3 + 3] - row1[x * 3 - 3]) * 2 + row1[x * 3 + n1 + 3] - row1[x * 3 + n1 - 3] + row1[x * 3 + s1 + 3] - row1[x * 3 + s1 - 3]];
prow1[x + width] = tab[(row1[x * 3 + 4] - row1[x * 3 - 2]) * 2 + row1[x * 3 + n1 + 4] - row1[x * 3 + n1 - 2] + row1[x * 3 + s1 + 4] - row1[x * 3 + s1 - 2]];
prow1[x + width * 2] = tab[(row1[x * 3 + 5] - row1[x * 3 - 1]) * 2 + row1[x * 3 + n1 + 5] - row1[x * 3 + n1 - 1] + row1[x * 3 + s1 + 5] - row1[x * 3 + s1 - 1]];
prow2[width - 1 - x] = tab[(row2[x * 3 + 3] - row2[x * 3 - 3]) * 2 + row2[x * 3 + n2 + 3] - row2[x * 3 + n2 - 3] + row2[x * 3 + s2 + 3] - row2[x * 3 + s2 - 3]];
prow2[width - 1 - x + width] = tab[(row2[x * 3 + 4] - row2[x * 3 - 2]) * 2 + row2[x * 3 + n2 + 4] - row2[x * 3 + n2 - 2] + row2[x * 3 + s2 + 4] - row2[x * 3 + s2 - 2]];
prow2[width - 1 - x + width * 2] = tab[(row2[x * 3 + 5] - row2[x * 3 - 1]) * 2 + row2[x * 3 + n2 + 5] - row2[x * 3 + n2 - 1] + row2[x * 3 + s2 + 5] - row2[x * 3 + s2 - 1]];
prow1[x + width * 3] = row1[x * 3];
prow1[x + width * 4] = row1[x * 3 + 1];
prow1[x + width * 5] = row1[x * 3 + 2];
prow2[width - 1 - x + width * 3] = row2[x * 3];
prow2[width - 1 - x + width * 4] = row2[x * 3 + 1];
prow2[width - 1 - x + width * 5] = row2[x * 3 + 2];
}
}
memset(cost + xrange_min * D, 0, width1 * D * sizeof(cost[0]));//代价数组初始化为0
buffer -= width - maxX2;
cost -= (minX1 - xrange_min) * D + minD; // simplify the cost indices inside the loop
//这里开始计算BT代价,opencv计算的BT代价分为两个部分:xsobel和原始图灰度值
//BT代价的计算原理参考博文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41541249/article/details/106546206
for (c = 0; c < cn * 2; c++, prow1 += width, prow2 += width)//这个循环先计算xsobel的BT代价,再计算原始灰度值的BT代价
{
// std::cout<<"c:"<<c<<std::endl;
int diff_scale = c < cn ? 0 : 2;
// precompute
// v0 = min(row2[x-1/2], row2[x], row2[x+1/2]) and
// v1 = max(row2[x-1/2], row2[x], row2[x+1/2]) and
// to process values from [minX2, maxX2) we should check memory location (width - 1 - maxX2, width - 1 - minX2]
// so iterate through [width - maxX2, width - minX2)
for (x = width - maxX2; x < width - minX2; x++)
{
int v = prow2[x];
int vl = x > 0 ? (v + prow2[x - 1]) / 2 : v;
int vr = x < width - 1 ? (v + prow2[x + 1]) / 2 : v;
int v0 = std::min(vl, vr);
v0 = std::min(v0, v);
int v1 = std::max(vl, vr);
v1 = std::max(v1, v);
buffer[x] = (PixType)v0;//右图-亚像素-最小值,就是右图的I_min,如上文“BT代价的原理”所示
buffer[x + width2] = (PixType)v1;//右图-亚像素-最大值,就是右图的I_max
}
for (x = minX1; x < maxX1; x++)
{
int u = prow1[x];//左图 (i,j)
int ul = x > 0 ? (u + prow1[x - 1]) / 2 : u;
int ur = x < width - 1 ? (u + prow1[x + 1]) / 2 : u;
int u0 = std::min(ul, ur);
u0 = std::min(u0, u);//左图-亚像素-最小值,就是左图的I_min
int u1 = std::max(ul, ur);
u1 = std::max(u1, u);//左图-亚像素-最大值,就是左图的I_max
int d = minD;
#if CV_SIMD
//这里采用simd128处理uchar数据(8 bit),一次可以处理16个uchar数据
//如果是short类型的数据(16 bit),simd128一次只能处理8个short数据
cv::v_uint8 _u = cv::vx_setall_u8((uchar)u), _u0 = cv::vx_setall_u8((uchar)u0);
cv::v_uint8 _u1 = cv::vx_setall_u8((uchar)u1);
for (; d <= maxD - 2 * cv::v_int16::nlanes; d += 2 * cv::v_int16::nlanes)
{
cv::v_uint8 _v = cv::vx_load(prow2 + width - x - 1 + d);
cv::v_uint8 _v0 = cv::vx_load(buffer + width - x - 1 + d);
cv::v_uint8 _v1 = cv::vx_load(buffer + width - x - 1 + d + width2);
cv::v_uint8 c0 = cv::v_max(_u - _v1, _v0 - _u);
cv::v_uint8 c1 = cv::v_max(_v - _u1, _u0 - _v);
cv::v_uint8 diff = cv::v_min(c0, c1);
cv::v_int16 _c0 = cv::vx_load_aligned(cost + x * D + d);
cv::v_int16 _c1 = cv::vx_load_aligned(cost + x * D + d + cv::v_int16::nlanes);
cv::v_uint16 diff1, diff2;
cv::v_expand(diff, diff1, diff2);//Expand uint8 values to the uint16 type. uint8x16 ==> int16x8 int16x8
cv::v_store_aligned(cost + x * D + d, _c0 + cv::v_reinterpret_as_s16(diff1 >> diff_scale));
cv::v_store_aligned(cost + x * D + d + cv::v_int16::nlanes, _c1 + cv::v_reinterpret_as_s16(diff2 >> diff_scale));
}
#endif
for (; d < maxD; d++)
{
//u = 左图 (i,j)
//u0 = 左图-亚像素-最小值
//u1 = 左图-亚像素-最大值
int v = prow2[width - x - 1 + d];//右图(i-d,j)
int v0 = buffer[width - x - 1 + d];//右图-亚像素-最小值
int v1 = buffer[width - x - 1 + d + width2];//右图-亚像素-最大值
int c0 = std::max(0, u - v1);
c0 = std::max(c0, v0 - u);//计算d(x,y)
int c1 = std::max(0, v - u1);
c1 = std::max(c1, u0 - v);//计算d(y,x)
//X-Sobel BT和gray BT加权融合
//这里分为两个循环分别计算X-Sobel BT和gray BT
//先计算X-Sobel BT,加权,权重为1,存放于cost[x * D + d]
//再计算gray BT。加权,权重为1/4,取出cost[x * D + d],加权累加
cost[x * D + d] = (CostType)(cost[x * D + d] + (std::min(c0, c1)>> diff_scale));//xsobel代价的权重 是 原图代价的权重的4倍(diff_scale=2)
//X-Sobel BT的权重比gray BT的权重更高,这样的话,算法会更偏向与纹理特征
}
}
}
}SAD-BT的实现
SAD-BT的计算过程在computeDisparitySGBM函数中实现,
/*
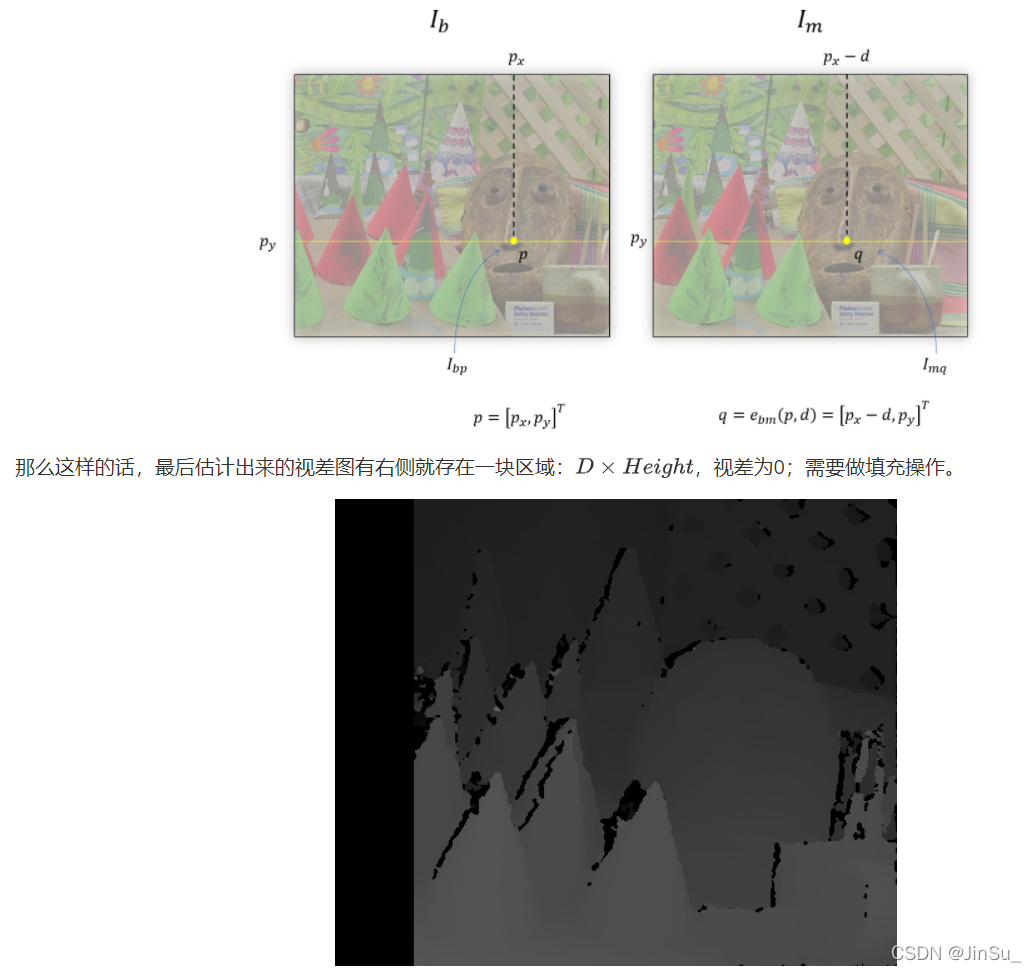
computes disparity for "roi" in img1 w.r.t. img2 and write it to disp1buf.
that is, disp1buf(x, y)=d means that img1(x+roi.x, y+roi.y) ~ img2(x+roi.x-d, y+roi.y).
minD <= d < maxD.
disp2full is the reverse disparity map, that is:
disp2full(x+roi.x,y+roi.y)=d means that img2(x+roi.x, y+roi.y) ~ img1(x+roi.x+d, y+roi.y)
note that disp1buf will have the same size as the roi and
disp2full will have the same size as img1 (or img2).
On exit disp2buf is not the final disparity, it is an intermediate result that becomes
final after all the tiles are processed.
the disparity in disp1buf is written with sub-pixel accuracy
(4 fractional bits, see StereoSGBM::DISP_SCALE),
using quadratic interpolation, while the disparity in disp2buf
is written as is, without interpolation.
disp2cost also has the same size as img1 (or img2).
It contains the minimum current cost, used to find the best disparity, corresponding to the minimal cost.
*/
static void computeDisparitySGBM( const Mat& img1, const Mat& img2,
Mat& disp1, const StereoSGBMParams& params )因为这个函数里面不只是包含SAD-BT的计算,还包括了代价聚合,所以就不完整展开,这里只解释其中的一部分。
开始之前,要强调:
当y == 0 时,设置 k = 0,1,会计算第0行和第1行的BT代价,hsumAdd是当前行的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
当y != 0时,设置k = y + SH2,默认 k = y + 1,会计算下一行的BT代价,hsumAdd是下一行的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
if (pass == 1) // compute C on the first pass, and reuse it on the second pass, if any.
{
int dy1 = y == 0 ? 0 : y + SH2, dy2 = y == 0 ? SH2 : dy1;
//当y == 0 时,设置 k = 0,1
//当y!=0时,设置k = y + SH2,默认 k = y + 1
for (k = dy1; k <= dy2; k++)
{
CostType *hsumAdd = mem.getHSumBuf(std::min(k, height - 1));//缓存第k行水平方向的SAD-BT代价
if (k < height)
{
//计算像素点之间的BT代价,(i,j) <---> (i-d,j);这里的pixDiff用于存放第k行像素点之间的BT代价
calcPixelCostBT(img1, img2, k, minD, maxD, mem.pixDiff, mem.tempBuf, mem.getClipTab());
//接下来计算block-cost,也就是SAD窗口中所有像素点BT代价相加
memset(hsumAdd, 0, Da * sizeof(CostType));
#if CV_SIMD
cv::v_int16 h_scale = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)SW2 + 1);
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
{
cv::v_int16 v_hsumAdd = cv::vx_load_aligned(mem.pixDiff + d) * h_scale;
for (x = Da; x <= SW2 * Da; x += Da)
v_hsumAdd += cv::vx_load_aligned(mem.pixDiff + x + d);
cv::v_store_aligned(hsumAdd + d, v_hsumAdd);
}
#else
for (d = 0; d < D; d++)
{
//第一个SAD窗口的block-cost为第一列的BT代价*(SW2 + 1)+第二列的BT代价;简单理解就是边缘填充pading;这里还没有完成第一个SAD窗口
//同时,也是opencv求block-cost的巧妙方法的初始值,初始化hsumAdd
hsumAdd[d] = (CostType)(mem.pixDiff[d] * (SW2 + 1));
for (x = Da; x <= SW2 * Da; x += Da)
hsumAdd[d] = (CostType)(hsumAdd[d] + mem.pixDiff[x + d]);
}
#endif
if (y > 0)
{
const CostType *hsumSub = mem.getHSumBuf(std::max(y - SH2 - 1, 0));//上SH2+1行的水平方向的SAD-BT
const CostType *Cprev = mem.getCBuf(y - 1);//上一行的垂直方向的SAD-BT
#if CV_SIMD
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
cv::v_store_aligned(C + d, cv::vx_load_aligned(Cprev + d) + cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + d) - cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumSub + d));
#else
for (d = 0; d < D; d++){
C[d] = (CostType)(Cprev[d] + hsumAdd[d] - hsumSub[d]);//在垂直方向累加
}
#endif
for (x = Da; x < width1 * Da; x += Da)
{
const CostType *pixAdd = mem.pixDiff + std::min(x + SW2 * Da, (width1 - 1) * Da);
const CostType *pixSub = mem.pixDiff + std::max(x - (SW2 + 1) * Da, 0);
#if CV_SIMD
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
{
cv::v_int16 hv = cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + x - Da + d) - cv::vx_load_aligned(pixSub + d) + cv::vx_load_aligned(pixAdd + d);//下一行的水平方向的SAD-BT
cv::v_store_aligned(hsumAdd + x + d, hv);
cv::v_store_aligned(C + x + d, cv::vx_load_aligned(Cprev + x + d) - cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumSub + x + d) + hv);//在垂直方向累加
}
#else
for (d = 0; d < D; d++)
{
int hv = hsumAdd[x + d] = (CostType)(hsumAdd[x - Da + d] + pixAdd[d] - pixSub[d]);//下一行的水平方向的SAD-BT
C[x + d] = (CostType)(Cprev[x + d] + hv - hsumSub[x + d]);//在垂直方向累加
}
#endif
}
}
else//y==0
{
#if CV_SIMD
cv::v_int16 v_scale = cv::vx_setall_s16(k == 0 ? (short)SH2 + 1 : 1);
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
cv::v_store_aligned(C + d, cv::vx_load_aligned(C + d) + cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + d) * v_scale);
#else
int scale = k == 0 ? SH2 + 1 : 1;
for (d = 0; d < D; d++)
C[d] = (CostType)(C[d] + hsumAdd[d] * scale);//第一个SAD窗口的block-cost为第一行的BT代价*(SH2 + 1)+第二行的BT代价;简单理解就是边缘填充pading
#endif
for (x = Da; x < width1 * Da; x += Da)
{
const CostType *pixAdd = mem.pixDiff + std::min(x + SW2 * Da, (width1 - 1) * Da);
const CostType *pixSub = mem.pixDiff + std::max(x - (SW2 + 1) * Da, 0);
#if CV_SIMD
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
{
cv::v_int16 hv = cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + x - Da + d) + cv::vx_load_aligned(pixAdd + d) - cv::vx_load_aligned(pixSub + d);//当前行(第k行)的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
cv::v_store_aligned(hsumAdd + x + d, hv);
cv::v_store_aligned(C + x + d, cv::vx_load_aligned(C + x + d) + hv * v_scale);
}
#else
for (d = 0; d < D; d++)
{
CostType hv = (CostType)(hsumAdd[x - Da + d] + pixAdd[d] - pixSub[d]);//下一个SAD窗口在水平方向累加
hsumAdd[x + d] = hv;//当前行(第k行)的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
C[x + d] = (CostType)(C[x + d] + hv * scale);//第一个SAD窗口的block-cost为第一行的BT代价*(SH2 + 1)+第二行的BT代价 | k=0时scale=SH2 + 1,k=1时scale=1
}
#endif
}
}
}
else
{
if (y > 0)
{
const CostType *hsumSub = mem.getHSumBuf(std::max(y - SH2 - 1, 0));
const CostType *Cprev = mem.getCBuf(y - 1);
#if CV_SIMD
for (x = 0; x < width1 * Da; x += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
cv::v_store_aligned(C + x, cv::vx_load_aligned(Cprev + x) - cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumSub + x) + cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + x));
#else
for (x = 0; x < width1 * Da; x++)
C[x] = (CostType)(Cprev[x] + hsumAdd[x] - hsumSub[x]);
#endif
}
else
{
#if CV_SIMD
for (x = 0; x < width1 * Da; x += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
cv::v_store_aligned(C + x, cv::vx_load_aligned(C + x) + cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + x));
#else
for (x = 0; x < width1 * Da; x++)
C[x] = (CostType)(C[x] + hsumAdd[x]);
#endif
}
}
}
// also, clear the S buffer
mem.clearSBuf(y);
}水平方向的SAD-BT的实现
CostType *hsumAdd = mem.getHSumBuf(std::min(k, height - 1));hsumAdd是缓存在hsumBuf的第k行水平方向的SAD-BT代价,
当y == 0 时,设置 k = 0,1,会计算第0行和第1行的BT代价,hsumAdd是当前行的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
当y != 0时,设置k = y + SH2,默认 k = y + 1,会计算下一行的BT代价,hsumAdd是下一行的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
这里我们举个例子说明,水平方向的SAD-BT的实现:
y == 0,k == 0时,
这里涉及到四个变量hsumAdd、pixdiff、pixAdd和pixSub
hsumAdd表示要存放第0行的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
pixdiff表示为第0行的BT代价。
pixAdd表示当前位置x的水平方向前 SW2 的pixdiff,单位是Da
pixSub表示当前位置x的水平方向后 (SW2 + 1)的pixdiff,单位是Da
当x=0时,也就是:
memset(hsumAdd, 0, Da * sizeof(CostType));
#if CV_SIMD
cv::v_int16 h_scale = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)SW2 + 1);
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
{
cv::v_int16 v_hsumAdd = cv::vx_load_aligned(mem.pixDiff + d) * h_scale;
for (x = Da; x <= SW2 * Da; x += Da)
v_hsumAdd += cv::vx_load_aligned(mem.pixDiff + x + d);
cv::v_store_aligned(hsumAdd + d, v_hsumAdd);
}
#else
for (d = 0; d < D; d++)
{
//第一个SAD窗口的block-cost为第一列的BT代价*(SW2 + 1)+第二列的BT代价;简单理解就是边缘填充pading;这里还没有完成第一个SAD窗口
//同时,也是opencv求block-cost的巧妙方法的初始值,初始化hsumAdd
hsumAdd[d] = (CostType)(mem.pixDiff[d] * (SW2 + 1));
for (x = Da; x <= SW2 * Da; x += Da)
hsumAdd[d] = (CostType)(hsumAdd[d] + mem.pixDiff[x + d]);
}
#endif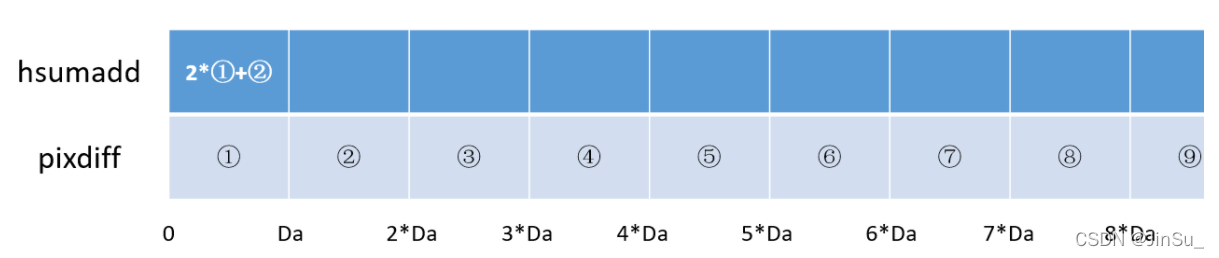
当x由Da开始递增时, ?
#if CV_SIMD
cv::v_int16 v_scale = cv::vx_setall_s16(k == 0 ? (short)SH2 + 1 : 1);
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
cv::v_store_aligned(C + d, cv::vx_load_aligned(C + d) + cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + d) * v_scale);
#else
int scale = k == 0 ? SH2 + 1 : 1;
for (d = 0; d < D; d++)
C[d] = (CostType)(C[d] + hsumAdd[d] * scale);//第一个SAD窗口的block-cost为第一行的BT代价*(SH2 + 1)+第二行的BT代价;简单理解就是边缘填充pading
#endif
for (x = Da; x < width1 * Da; x += Da)
{
const CostType *pixAdd = mem.pixDiff + std::min(x + SW2 * Da, (width1 - 1) * Da);
const CostType *pixSub = mem.pixDiff + std::max(x - (SW2 + 1) * Da, 0);
#if CV_SIMD
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
{
cv::v_int16 hv = cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + x - Da + d) + cv::vx_load_aligned(pixAdd + d) - cv::vx_load_aligned(pixSub + d);//当前行(第k行)的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
cv::v_store_aligned(hsumAdd + x + d, hv);
cv::v_store_aligned(C + x + d, cv::vx_load_aligned(C + x + d) + hv * v_scale);
}
#else
for (d = 0; d < D; d++)
{
CostType hv = (CostType)(hsumAdd[x - Da + d] + pixAdd[d] - pixSub[d]);//下一个SAD窗口在水平方向累加
hsumAdd[x + d] = hv;//当前行(第k行)的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
C[x + d] = (CostType)(C[x + d] + hv * scale);//第一个SAD窗口的block-cost为第一行的BT代价*(SH2 + 1)+第二行的BT代价 | k=0时scale=SH2 + 1,k=1时scale=1
}
#endif
}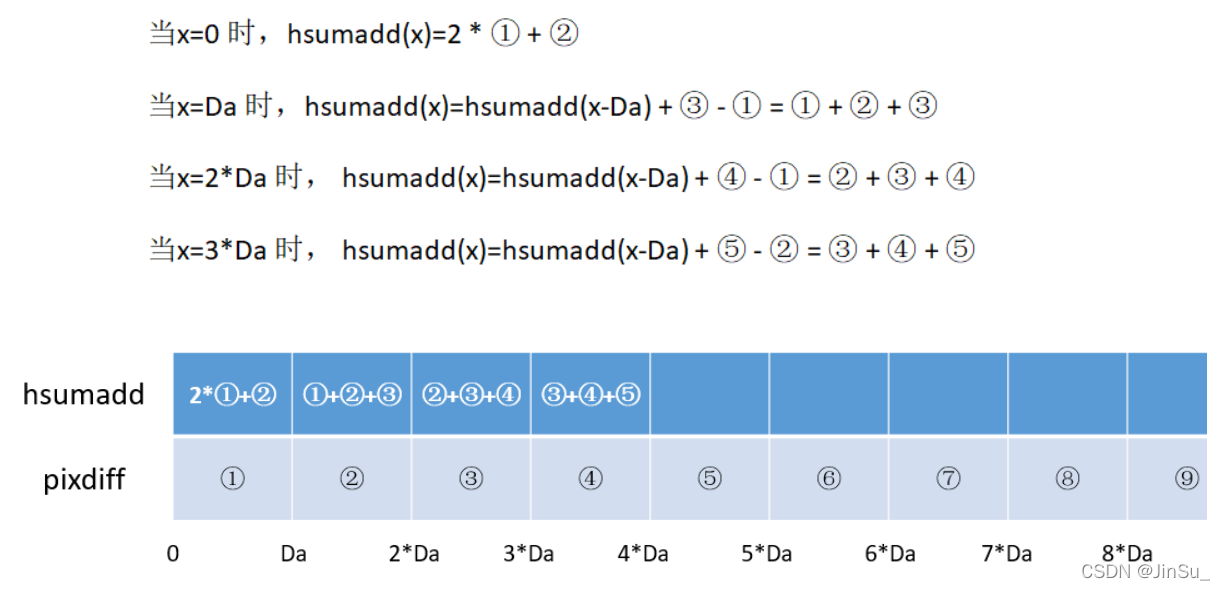
因此,hsumAdd是第k行的水平方向的SAD-BT代价。
当y == 0 时,设置 k = 0,1,会计算第0行和第1行的BT代价,hsumAdd是当前行的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
当y != 0时,设置k = y + SH2,默认 k = y + 1,会计算下一行的BT代价,hsumAdd是下一行的水平方向的SAD-BT代价
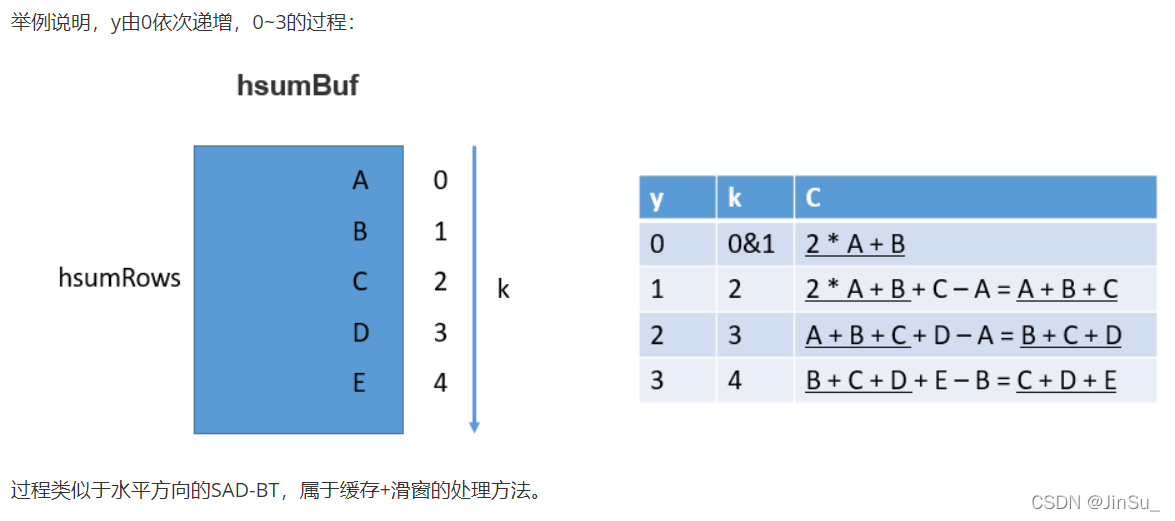
垂直方向的SAD-BT的实现
const CostType *hsumSub = mem.getHSumBuf(std::max(y - SH2 - 1, 0));//上SH2+1行的水平方向的SAD-BT
const CostType *Cprev = mem.getCBuf(y - 1);//上一行的垂直方向的SAD-BT
#if CV_SIMD
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
cv::v_store_aligned(C + d, cv::vx_load_aligned(Cprev + d) + cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + d) - cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumSub + d));
#else
for (d = 0; d < D; d++){
C[d] = (CostType)(Cprev[d] + hsumAdd[d] - hsumSub[d]);//在垂直方向累加
}
#endif
for (x = Da; x < width1 * Da; x += Da)
{
const CostType *pixAdd = mem.pixDiff + std::min(x + SW2 * Da, (width1 - 1) * Da);
const CostType *pixSub = mem.pixDiff + std::max(x - (SW2 + 1) * Da, 0);
#if CV_SIMD
for (d = 0; d < Da; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)
{
cv::v_int16 hv = cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumAdd + x - Da + d) - cv::vx_load_aligned(pixSub + d) + cv::vx_load_aligned(pixAdd + d);//下一行的水平方向的SAD-BT
cv::v_store_aligned(hsumAdd + x + d, hv);
cv::v_store_aligned(C + x + d, cv::vx_load_aligned(Cprev + x + d) - cv::vx_load_aligned(hsumSub + x + d) + hv);//在垂直方向累加
}
#else
for (d = 0; d < D; d++)
{
int hv = hsumAdd[x + d] = (CostType)(hsumAdd[x - Da + d] + pixAdd[d] - pixSub[d]);//下一行的水平方向的SAD-BT
C[x + d] = (CostType)(Cprev[x + d] + hv - hsumSub[x + d]);//在垂直方向累加
}
#endif
}
代价聚合的实现
/*
[formula 13 in the paper]
compute L_r(p, d) = C(p, d) +
min(L_r(p-r, d),
L_r(p-r, d-1) + P1,
L_r(p-r, d+1) + P1,
min_k L_r(p-r, k) + P2) - min_k L_r(p-r, k)
where p = (x,y), r is one of the directions.
we process all the directions at once:
0: r=(-dx, 0)
1: r=(-1, -dy)
2: r=(0, -dy)
3: r=(1, -dy) !!!Note that only directions 0 to 3 are processed
4: r=(-2, -dy)
5: r=(-1, -dy*2)
6: r=(1, -dy*2)
7: r=(2, -dy)
*/
//代价聚合-正向*4
for (x = x1; x != x2; x += dx)
{
int delta0 = P2 + *mem.getMinLr(lrID, x - dx);
int delta1 = P2 + *mem.getMinLr(1 - lrID, x - 1, 1);
int delta2 = P2 + *mem.getMinLr(1 - lrID, x, 2);
int delta3 = P2 + *mem.getMinLr(1 - lrID, x + 1, 3);
CostType *Lr_p0 = mem.getLr(lrID, x - dx);
CostType *Lr_p1 = mem.getLr(1 - lrID, x - 1, 1);
CostType *Lr_p2 = mem.getLr(1 - lrID, x, 2);
CostType *Lr_p3 = mem.getLr(1 - lrID, x + 1, 3);
Lr_p0[-1] = Lr_p0[D] = MAX_COST;
Lr_p1[-1] = Lr_p1[D] = MAX_COST;
Lr_p2[-1] = Lr_p2[D] = MAX_COST;
Lr_p3[-1] = Lr_p3[D] = MAX_COST;
CostType *Lr_p = mem.getLr(lrID, x);
const CostType *Cp = C + x * Da;
CostType *Sp = S + x * Da;
CostType *minL = mem.getMinLr(lrID, x);
d = 0;
#if CV_SIMD
cv::v_int16 _P1 = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)P1);
cv::v_int16 _delta0 = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)delta0);
cv::v_int16 _delta1 = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)delta1);
cv::v_int16 _delta2 = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)delta2);
cv::v_int16 _delta3 = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)delta3);
cv::v_int16 _minL0 = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)MAX_COST);
cv::v_int16 _minL1 = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)MAX_COST);
cv::v_int16 _minL2 = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)MAX_COST);
cv::v_int16 _minL3 = cv::vx_setall_s16((short)MAX_COST);
for (; d <= D - cv::v_int16::nlanes; d += cv::v_int16::nlanes)//循环中,d最大为D - cv::v_int16::nlanes
{
cv::v_int16 Cpd = cv::vx_load_aligned(Cp + d);
cv::v_int16 Spd = cv::vx_load_aligned(Sp + d);
cv::v_int16 L;
L = cv::v_min(cv::v_min(cv::v_min(cv::vx_load_aligned(Lr_p0 + d), cv::vx_load(Lr_p0 + d - 1) + _P1), cv::vx_load(Lr_p0 + d + 1) + _P1), _delta0) - _delta0 + Cpd;
cv::v_store_aligned(Lr_p + d, L);
_minL0 = cv::v_min(_minL0, L);
Spd += L;
L = cv::v_min(cv::v_min(cv::v_min(cv::vx_load_aligned(Lr_p1 + d), cv::vx_load(Lr_p1 + d - 1) + _P1), cv::vx_load(Lr_p1 + d + 1) + _P1), _delta1) - _delta1 + Cpd;
cv::v_store_aligned(Lr_p + d + Dlra, L);
_minL1 = cv::v_min(_minL1, L);
Spd += L;
L = cv::v_min(cv::v_min(cv::v_min(cv::vx_load_aligned(Lr_p2 + d), cv::vx_load(Lr_p2 + d - 1) + _P1), cv::vx_load(Lr_p2 + d + 1) + _P1), _delta2) - _delta2 + Cpd;
cv::v_store_aligned(Lr_p + d + Dlra * 2, L);
_minL2 = cv::v_min(_minL2, L);
Spd += L;
L = cv::v_min(cv::v_min(cv::v_min(cv::vx_load_aligned(Lr_p3 + d), cv::vx_load(Lr_p3 + d - 1) + _P1), cv::vx_load(Lr_p3 + d + 1) + _P1), _delta3) - _delta3 + Cpd;
cv::v_store_aligned(Lr_p + d + Dlra * 3, L);
_minL3 = cv::v_min(_minL3, L);
Spd += L;
cv::v_store_aligned(Sp + d, Spd);
}
#if CV_SIMD_WIDTH > 32
minL[0] = v_reduce_min(_minL0);
minL[1] = v_reduce_min(_minL1);
minL[2] = v_reduce_min(_minL2);
minL[3] = v_reduce_min(_minL3);
#else
// Get minimum for L0-L3
cv::v_int16 t0, t1, t2, t3;
cv::v_zip(_minL0, _minL2, t0, t2);
cv::v_zip(_minL1, _minL3, t1, t3);
cv::v_zip(cv::v_min(t0, t2), cv::v_min(t1, t3), t0, t1);
t0 = cv::v_min(t0, t1);
t0 = cv::v_min(t0, cv::v_rotate_right<4>(t0));
#if CV_SIMD_WIDTH == 32
CostType buf[v_int16::nlanes];
v_store_low(buf, v_min(t0, v_rotate_right<8>(t0)));
minL[0] = buf[0];
minL[1] = buf[1];
minL[2] = buf[2];
minL[3] = buf[3];
#else
cv::v_store_low(minL, t0);
#endif
#endif
#else
minL[0] = MAX_COST;
minL[1] = MAX_COST;
minL[2] = MAX_COST;
minL[3] = MAX_COST;
#endif
for (; d < D; d++)
{
int Cpd = Cp[d], L;
int Spd = Sp[d];
L = Cpd + std::min((int)Lr_p0[d], std::min(Lr_p0[d - 1] + P1, std::min(Lr_p0[d + 1] + P1, delta0))) - delta0;//
Lr_p[d] = (CostType)L;
minL[0] = std::min(minL[0], (CostType)L);
Spd += L;
L = Cpd + std::min((int)Lr_p1[d], std::min(Lr_p1[d - 1] + P1, std::min(Lr_p1[d + 1] + P1, delta1))) - delta1;
Lr_p[d + Dlra] = (CostType)L;
minL[1] = std::min(minL[1], (CostType)L);
Spd += L;
L = Cpd + std::min((int)Lr_p2[d], std::min(Lr_p2[d - 1] + P1, std::min(Lr_p2[d + 1] + P1, delta2))) - delta2;
Lr_p[d + Dlra * 2] = (CostType)L;
minL[2] = std::min(minL[2], (CostType)L);
Spd += L;
L = Cpd + std::min((int)Lr_p3[d], std::min(Lr_p3[d - 1] + P1, std::min(Lr_p3[d + 1] + P1, delta3))) - delta3;
Lr_p[d + Dlra * 3] = (CostType)L;
minL[3] = std::min(minL[3], (CostType)L);
Spd += L;
Sp[d] = cv::saturate_cast<CostType>(Spd);
}
}
在这个地方我之前一直以为4个路径的值是由前面的代码进行过整理,但其实不是,并没有提前进行整理。前面所有的计算都只是在计算BT以及SAD-BT。
但是所谓的代价路径必须是遍历整个图像,比如:
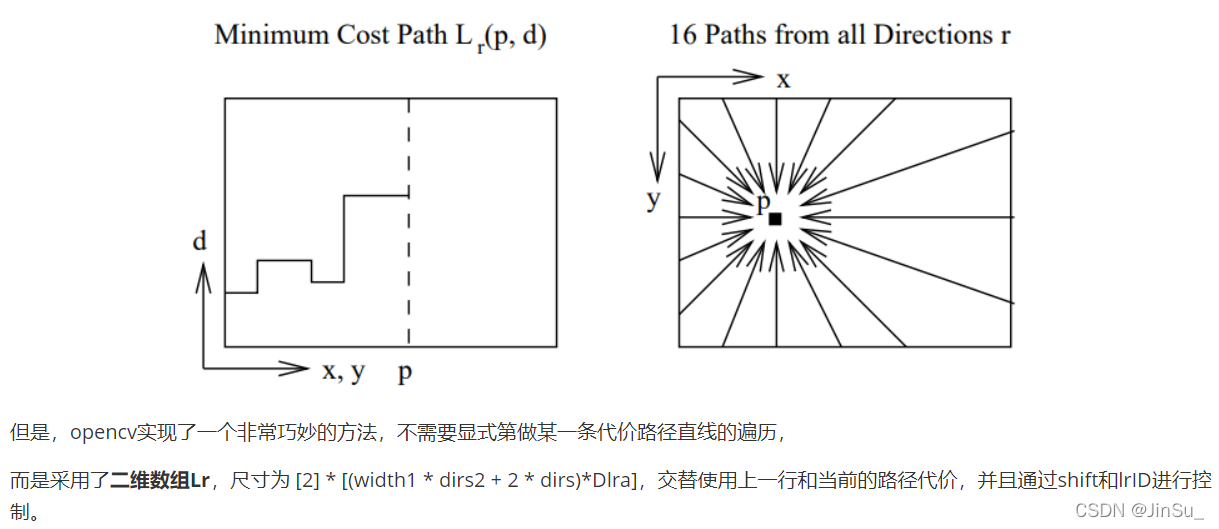

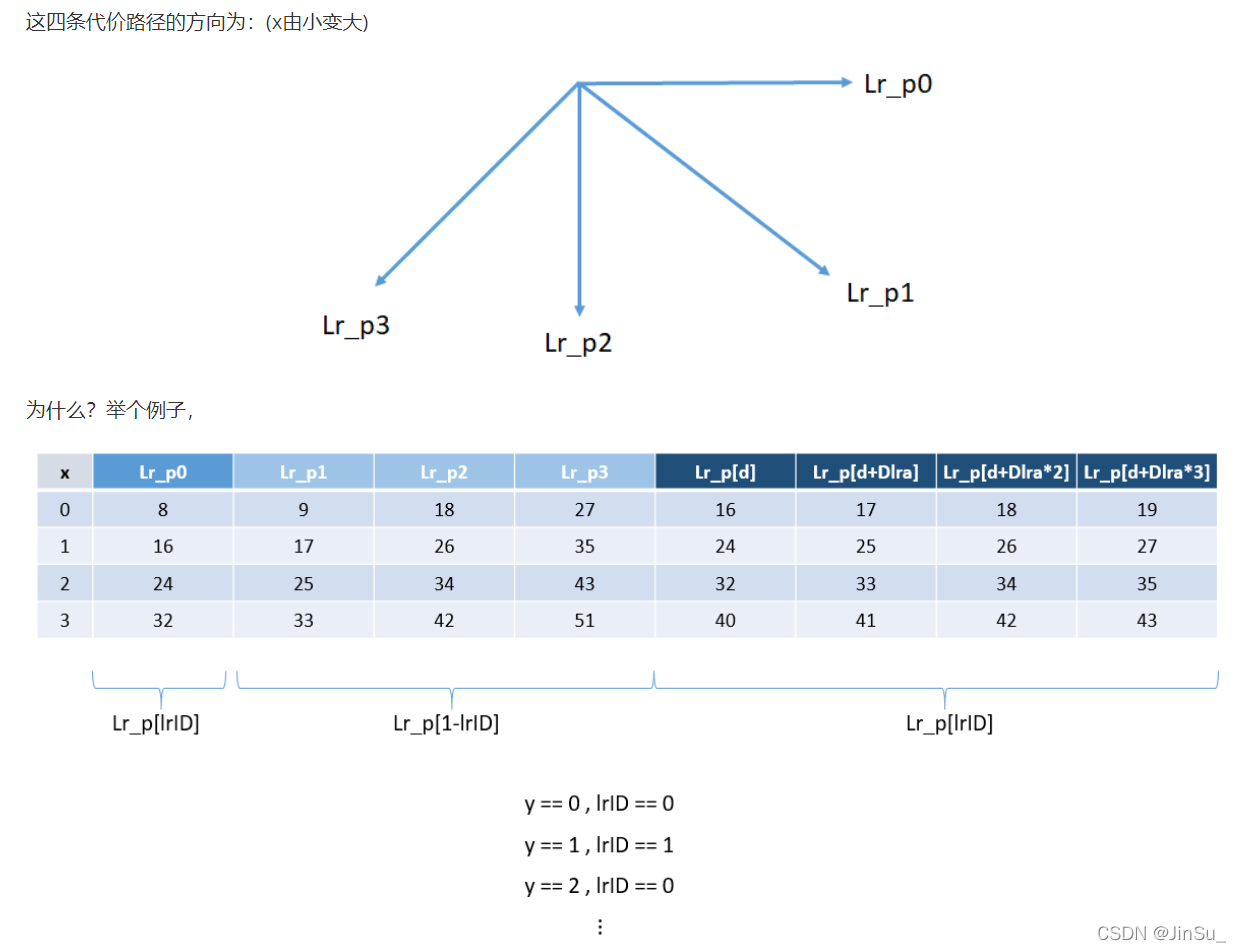
仔细观察一下这张表,你会发现,Lr_p0取出上一个路径点和存放当前路径点的代价,都是在Lr[lrID]上,而且刚好是x方向的偏移。
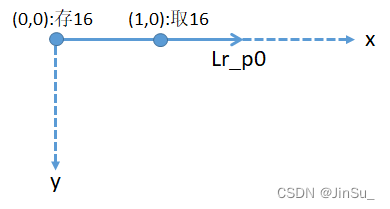
再观察Lr_p2,同一行,y=0存放的位置和y=1取出的位置相等,而y由0变1的过程,lrID也由0变1。因此,Lr_p2取出上一个路径点是y的负方向,所以Lr_p2的方向是y轴的正方向。
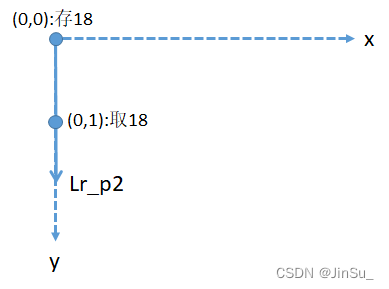
再观察Lr_p1,
再观察Lr_p3,
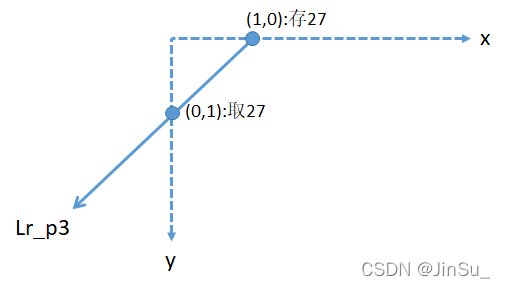
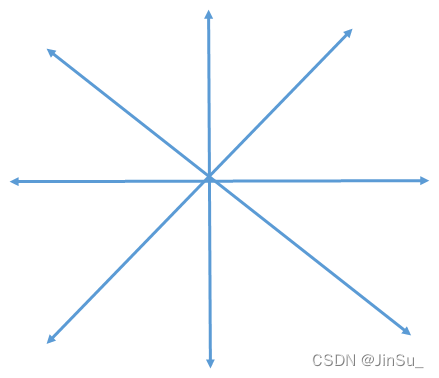
opencv默认是5条代价路径和8条代价路径。如果是5条代价路径,则就是
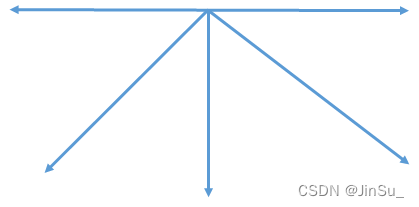
?如果是8条路径,也就是full_dp,则为: