(1)Consider using this encoder-decoder model for machine translation.

This model is a “conditional language model” in the sense that the encoder portion (shown in green) is modeling the probability of the input sentence x.
[A]True
[B]False
答案:B
解析:输入的是句子x的特征,不是概率。
(2)In beam search, if you increase the beam width B, which of the following would you expect to be true? Check all that apply.
[A]Beam search will run more slowly.
[B]Beam search will use up more memory.
[C]Beam search will generally find better solutions (i.e. do a better job maximizing P(y|x) )
[D]Beam search will converge after fewer steps.
答案:A,B,C
解析:beam search 是每一步选择B个概率最大的,B越大,则选择的句子越多,运行的也越慢,内存消耗也越多,但是得到的结果会更好。
(3)In machine translation, if we carry out beam search without using sentence normalization, the algorithm will tend to output overly short translations.
[A]True
[B]False
答案:A
解析:beam search需要最大化
∏
t
=
1
T
y
P
(
y
<
t
>
∣
x
,
y
<
1
>
,
.
.
.
,
y
<
t
?
1
>
)
\prod_{t=1}^{T_y}{P\left( y^{<t>}|x,y^{<1>},...,y^{<t-1>} \right)}
t=1∏Ty??P(y<t>∣x,y<1>,...,y<t?1>)
其中每一项都是小于1的,所以越乘概率会越小,在没有归一化的情况下,通常短句子的概率更大些。
(4)Suppose you are building a speech recognition system, which uses an RNN model to map from audio clip
x
x
x to a text transcript
y
y
y. Your algorithm uses beam search to try to find the value of
y
y
y that maximizes
P
(
y
∣
x
)
P(y|x)
P(y∣x).
On a dev set example, given an input audio clip, your algorithm outputs the transcript
y
^
=
"
I
′
m
?
b
u
i
l
d
i
n
g
?
a
n
?
A
?
E
y
e
?
s
y
s
t
e
m
?
i
n
?
S
i
l
l
y
?
c
o
n
?
V
a
l
l
e
y
.
"
\hat{y}="I'm\ building\ an\ A\ Eye\ system\ in\ Silly\ con\ Valley."
y^?="I′m?building?an?A?Eye?system?in?Silly?con?Valley.", whereas a human gives a much superior transcript
y
?
=
"
I
′
m
?
b
u
i
l
d
i
n
g
?
a
n
?
A
I
?
s
y
s
t
e
m
?
i
n
?
S
i
l
i
c
o
n
?
V
a
l
l
e
y
.
"
y^{*}="I'm\ building\ an\ AI\ system\ in\ Silicon\ Valley."
y?="I′m?building?an?AI?system?in?Silicon?Valley."
According to your model,
P
(
y
^
∣
x
)
=
1.09
?
1
0
?
7
P(\hat{y}|x)=1.09*10^{-7}
P(y^?∣x)=1.09?10?7
P
(
y
?
∣
x
)
=
7.21
?
1
0
?
8
P(y^{*}|x)=7.21*10^{-8}
P(y?∣x)=7.21?10?8
Would you expect increasing the beam width B to help correct this example?
[A]No, because
P
(
y
?
∣
x
)
≤
P
(
y
^
∣
x
)
P(y^{*}|x) \leq P(\hat{y}|x)
P(y?∣x)≤P(y^?∣x) indicates the error should be attributed to the RNN rather than to the search algorithm.
[B]No, because
P
(
y
?
∣
x
)
≤
P
(
y
^
∣
x
)
P(y^{*}|x) \leq P(\hat{y}|x)
P(y?∣x)≤P(y^?∣x) indicates the error should be attributed to the search algorithm rather than to the RNN.
[C]Yes, because
P
(
y
?
∣
x
)
≤
P
(
y
^
∣
x
)
P(y^{*}|x) \leq P(\hat{y}|x)
P(y?∣x)≤P(y^?∣x) indicates the error should be attributed to the RNN rather than to the search algorithm.
[D]Yes, because
P
(
y
?
∣
x
)
≤
P
(
y
^
∣
x
)
P(y^{*}|x) \leq P(\hat{y}|x)
P(y?∣x)≤P(y^?∣x) indicates the error should be attributed to the search algorithm rather than to the RNN.
答案:A
解析:见3.5 Error analysis in beam search
(5)Continuing the example from Q4, suppose you work on your algorithm for a few more weeks, and now find that for the vast majority of examples on which your algorithm makes a mistake,
P
(
y
?
∣
x
)
>
P
(
y
^
∣
x
)
P(y^{*}|x) > P(\hat{y}|x)
P(y?∣x)>P(y^?∣x). This suggest you should focus your attention on improving the search algorithm.
[A]True
[B]False
答案:A
(6)Consider the attention model for machine translation.
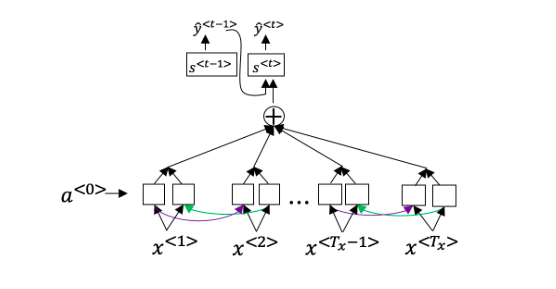
Further, here is the formula for
α
<
t
,
t
′
>
\alpha ^{<t,t'>}
α<t,t′>
α
<
t
,
t
′
>
=
exp
?
(
e
<
t
,
t
′
>
)
∑
t
′
=
1
T
x
exp
?
(
e
<
t
,
t
′
>
)
\alpha ^{<t,t'>}=\frac{\exp \left( e^{<t,t'>} \right)}{\sum_{t'=1}^{Tx}{\exp \left( e^{<t,t'>} \right)}}
α<t,t′>=∑t′=1Tx?exp(e<t,t′>)exp(e<t,t′>)?
Which of the following statements about
α
<
t
,
t
′
>
\alpha ^{<t,t'>}
α<t,t′> are true? Check all that apply.
[A]We expect
α
<
t
,
t
′
>
\alpha ^{<t,t'>}
α<t,t′> to be generally larger for value of
a
<
t
′
>
a^{<t'>}
a<t′> that are highly relevant to the value the network should output for
y
<
t
>
y^{<t>}
y<t>. (Note the indices in the superscripts.)
[B]We expect
α
<
t
,
t
′
>
\alpha ^{<t,t'>}
α<t,t′> to be generally larger for value of
a
<
t
>
a^{<t>}
a<t> that are highly relevant to the value the network should output for
y
<
t
′
>
y^{<t'>}
y<t′>. (Note the indices in the superscripts.)
[C]
∑
t
a
<
t
,
t
′
>
=
1
\sum_t{a^{<t,t'>}}=1
∑t?a<t,t′>=1 (Note the summation is over t)
[D]
∑
t
′
a
<
t
,
t
′
>
=
1
\sum_{t'}{a^{<t,t'>}}=1
∑t′?a<t,t′>=1 (Note the summation is over t’)
答案:A,D
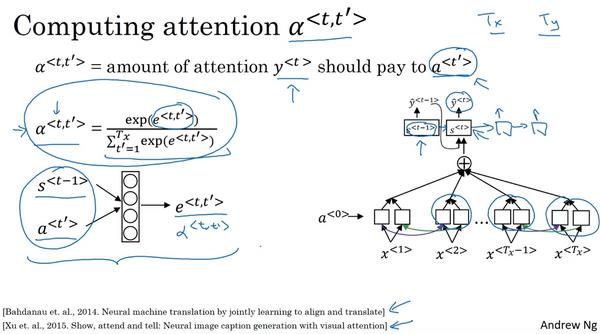
(7)The network learns where to “pay attention” by learning the values
e
<
t
,
t
′
>
e^{<t,t'>}
e<t,t′>, which are computed using a small neural network:
We can’t replace
s
<
t
?
1
>
s^{<t-1>}
s<t?1> with
s
<
t
>
s^{<t>}
s<t> as an input to this neural network. This is because
s
<
t
>
s^{<t>}
s<t> depends on
α
<
t
,
t
′
>
\alpha ^{<t,t'>}
α<t,t′> which in turn depends on
e
<
t
,
t
′
>
e^{<t,t'>}
e<t,t′>; so at the time we need to evaluate this network, we haven’t computed
s
<
t
>
s^{<t>}
s<t> yet.
[A]True
[B]False
答案:A
(8)Compared to the encoder-decoder model shown in Question 1 of this quiz (which does not use an attention mechanism), we expect the attention model to have the greatest advantage when:
[A]The input sequence length
T
x
Tx
Tx is large.
[B]The input sequence length
T
x
Tx
Tx is small.
答案:A
解析:

绿色是加入注意力机制以后的Bleu 评分,可以看到对于长句子,加入注意力机制能有效的提升翻译的准确性。
(9)Under the CTC model, identical repeated characters not separated by the “blank” character(_) are collapsed. Under the CTC model, what dpes the following string collapse to?
__coo_o_kk___b_ooooo__oo_kkk
[A]cokbok
[B]cookbook
[C]cook book
[D]coookkboooooookkk
答案:B
解析:CTC 损失函数的一个基本规则是将空白符之间的重复的字符折叠起来。
(10)in trigger word detection,
x
<
t
>
x^{<t>}
x<t> is:
[A]Features of the audio (such as spectrogram features) at time t.
[B]The t-th input word, represented as either a one-hot vector or a word embedding.
[C]Whether the trigger word is being said at time t.
[D]Whether someone has just finished saying the trigger word at time t.
答案:A
解析:见3.10 Trigger Word Detection
