Convolutional Complex Knowledge Graph Embeddings
1 介绍
1.1 思想
该论文的核心就是结合ComplEx和维度卷积的形式,进行知识图谱补全。
1.2 知识图谱中存在的关系
- symmetric(对称)
if ( h , r , t ) ? ? ( t , r , h ) (h, r, t) ?? (t, r, h) (h,r,t)??(t,r,h) for all pairs of entities h , t ∈ E h, t \in \mathbf {E} h,t∈E - anti-symmetric(反对称)
if ( h , r , t ) ∈ G ? ( t , r , h ) ? G (h, r, t) ∈ G ? (t, r, h) \notin \mathbb G (h,r,t)∈G?(t,r,h)∈/?G for all h ≠ t h \neq t h?=t - transitive/composite(传递关系)
if ( h , r , t ) ∈ G ∧ ( t , r , y ) ∈ G ? ( h , r , y ) ∈ G (h, r, t) ∈ G ∧ (t, r, y) ∈ G ? (h, r, y) ∈ G (h,r,t)∈G∧(t,r,y)∈G?(h,r,y)∈G for all h , t , y ∈ E h, t, y \in \mathbf {E} h,t,y∈E - inverse(逆关系)
h and t是实体, , ( h , r , t ) ∈ G ? ? ( t , r ? 1 , h ) ∈ G , (h, r, t) \in \mathbb G ?? (t, r^{-1}, h) \in \mathbb G ,(h,r,t)∈G??(t,r?1,h)∈G
1.3 ComplEx特点
将数据的维度引入复平面,可以执行以上四种类型的数据,但是在传递关系效果不好。
2 模型
2.1 公式
给一组三元组
(
h
,
r
,
t
)
(\mathrm{h}, \mathrm{r}, \mathrm{t})
(h,r,t), ConEx,:
C
3
d
?
R
\mathbb{C}^{3 d} \mapsto \mathbb{R}
C3d?R 计算CONEx评分 :
C
3
d
?
R
\mathbb{C}^{3 d} \mapsto \mathbb{R}
C3d?R 公式为:
ConEx
?
(
h
,
r
,
t
)
=
Re
?
(
?
conv
?
(
e
h
,
e
r
)
,
e
h
,
e
r
,
e
t
 ̄
?
)
\operatorname{ConEx}(\mathrm{h}, \mathrm{r}, \mathrm{t})=\operatorname{Re}\left(\left\langle\operatorname{conv}\left(\mathbf{e}_{h}, \mathbf{e}_{r}\right), \mathbf{e}_{h}, \mathbf{e}_{r}, \overline{\mathbf{e}_{t}}\right\rangle\right)
ConEx(h,r,t)=Re(?conv(eh?,er?),eh?,er?,et???)
其中
conv
?
(
?
,
?
)
:
C
2
d
?
C
d
\operatorname{conv}(\cdot, \cdot): \mathbb{C}^{2 d} \mapsto \mathbb{C}^{d}
conv(?,?):C2d?Cd 定义为:
conv
?
(
e
h
,
e
r
)
=
f
(
vec
?
(
f
(
[
e
h
,
e
r
]
?
ω
)
)
?
W
+
b
)
\operatorname{conv}\left(\mathbf{e}_{h}, \mathbf{e}_{r}\right)=f\left(\operatorname{vec}\left(f\left(\left[\mathbf{e}_{h}, \mathbf{e}_{r}\right] * \omega\right)\right) \cdot \mathbf{W}+\mathbf{b}\right)
conv(eh?,er?)=f(vec(f([eh?,er?]?ω))?W+b)
将公式展开为ComplEx的形式为:
ConEx
?
(
h
,
r
,
t
)
=
Re
?
(
∑
k
=
1
d
(
γ
)
k
(
e
h
)
k
(
e
r
)
k
(
e
t
 ̄
)
k
)
=
?
Re
?
(
γ
)
,
Re
?
(
e
h
)
,
Re
?
(
e
r
)
,
Re
?
(
e
t
)
?
+
?
Re
?
(
γ
)
,
Re
?
(
e
h
)
,
Im
?
(
e
r
)
,
Im
?
(
e
t
)
?
+
?
Im
?
(
γ
)
,
Im
?
(
e
h
)
,
Re
?
(
e
r
)
,
Im
?
(
e
t
)
?
?
?
Im
?
(
γ
)
,
Im
?
(
e
h
)
,
Im
?
(
e
r
)
,
Re
?
(
e
t
)
?
\begin{aligned} \operatorname{ConEx}(h, r, t)=& \operatorname{Re}\left(\sum_{k=1}^{d}(\gamma)_{k}\left(\mathbf{e}_{h}\right)_{k}\left(\mathbf{e}_{r}\right)_{k}\left(\overline{\mathbf{e}_{t}}\right)_{k}\right) \\ =&\left\langle\operatorname{Re}(\gamma), \operatorname{Re}\left(\mathbf{e}_{h}\right), \operatorname{Re}\left(\mathbf{e}_{r}\right), \operatorname{Re}\left(\mathbf{e}_{t}\right)\right\rangle \\ &+\left\langle\operatorname{Re}(\gamma), \operatorname{Re}\left(\mathbf{e}_{h}\right), \operatorname{Im}\left(\mathbf{e}_{r}\right), \operatorname{Im}\left(\mathbf{e}_{t}\right)\right\rangle \\ &+\left\langle\operatorname{Im}(\gamma), \operatorname{Im}\left(\mathbf{e}_{h}\right), \operatorname{Re}\left(\mathbf{e}_{r}\right), \operatorname{Im}\left(\mathbf{e}_{t}\right)\right\rangle \\ &-\left\langle\operatorname{Im}(\gamma), \operatorname{Im}\left(\mathbf{e}_{h}\right), \operatorname{Im}\left(\mathbf{e}_{r}\right), \operatorname{Re}\left(\mathbf{e}_{t}\right)\right\rangle \end{aligned}
ConEx(h,r,t)==?Re(k=1∑d?(γ)k?(eh?)k?(er?)k?(et??)k?)?Re(γ),Re(eh?),Re(er?),Re(et?)?+?Re(γ),Re(eh?),Im(er?),Im(et?)?+?Im(γ),Im(eh?),Re(er?),Im(et?)???Im(γ),Im(eh?),Im(er?),Re(et?)??
其中
e
t
 ̄
\overline{\mathbf{e}_{t}}
et??是
e
t
\mathbf{e}_{t}
et?的共轭,而
γ
\gamma
γ 是
conv
?
(
e
h
,
e
r
)
\operatorname{conv}\left(\mathbf{e}_{h}, \mathbf{e}_{r}\right)
conv(eh?,er?) 卷积后的结果. 乘法包括
conv
?
(
?
,
?
)
\operatorname{conv}(\cdot, \cdot)
conv(?,?) ,并且卷积之后产生两个结果,
Re
?
(
γ
)
\operatorname{Re}(\gamma)
Re(γ) and
Im
?
(
γ
)
\operatorname{Im}(\gamma)
Im(γ) 。
2.2 损失函数
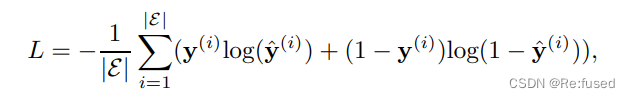
其中
y
^
∈
R
∣
ε
∣
\widehat{y}\in \mathbb R^{\left\vert \varepsilon \right\vert }
y
?∈R∣ε∣为预测概率的向量,
y
∈
[
0
,
1
]
∣
ε
∣
y\in [0, 1]^{\left\vert \varepsilon \right\vert }
y∈[0,1]∣ε∣
3 代码
class ConEx(torch.nn.Module):
""" Convolutional Complex Knowledge Graph Embeddings"""
def __init__(self, params=None):
super(ConEx, self).__init__()
self.name = 'ConEx'
self.loss = torch.nn.BCELoss()
self.param = params
self.embedding_dim = self.param['embedding_dim']
self.num_entities = self.param['num_entities']
self.num_relations = self.param['num_relations']
self.kernel_size = self.param['kernel_size']
self.num_of_output_channels = self.param['num_of_output_channels']
# Embeddings.
self.emb_ent_real = nn.Embedding(self.param['num_entities'], self.embedding_dim) # real
self.emb_ent_i = nn.Embedding(self.param['num_entities'], self.embedding_dim) # imaginary i
self.emb_rel_real = nn.Embedding(self.param['num_relations'], self.embedding_dim) # real
self.emb_rel_i = nn.Embedding(self.param['num_relations'], self.embedding_dim) # imaginary i
# Dropouts
self.input_dp_ent_real = torch.nn.Dropout(self.param['input_dropout'])
self.input_dp_ent_i = torch.nn.Dropout(self.param['input_dropout'])
self.input_dp_rel_real = torch.nn.Dropout(self.param['input_dropout'])
self.input_dp_rel_i = torch.nn.Dropout(self.param['input_dropout'])
# Batch Normalization
self.bn_ent_real = torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(self.embedding_dim)
self.bn_ent_i = torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(self.embedding_dim)
self.bn_rel_real = torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(self.embedding_dim)
self.bn_rel_i = torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(self.embedding_dim)
# Convolution
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(in_channels=1, out_channels=self.num_of_output_channels,
kernel_size=(self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size), stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)
self.fc_num_input = self.embedding_dim * 4 * self.num_of_output_channels # 4 because of 4 real values in 2 complex numbers
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(self.fc_num_input, self.embedding_dim * 2)
self.bn_conv1 = torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(self.num_of_output_channels)
self.bn_conv2 = torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(self.embedding_dim * 2)
self.feature_map_dropout = torch.nn.Dropout2d(self.param['feature_map_dropout'])
def residual_convolution(self, C_1, C_2):
emb_ent_real, emb_ent_imag_i = C_1
emb_rel_real, emb_rel_imag_i = C_2
# Think of x a n image of two complex numbers.
x = torch.cat([emb_ent_real.view(-1, 1, 1, self.embedding_dim),
emb_ent_imag_i.view(-1, 1, 1, self.embedding_dim),
emb_rel_real.view(-1, 1, 1, self.embedding_dim),
emb_rel_imag_i.view(-1, 1, 1, self.embedding_dim)], 2)
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(self.bn_conv1(x))
x = self.feature_map_dropout(x)
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1) # reshape for NN.
x = F.relu(self.bn_conv2(self.fc(x)))
return torch.chunk(x, 2, dim=1)
def forward_head_batch(self, *, e1_idx, rel_idx):
"""
Given a head entity and a relation (h,r), we compute scores for all entities.
[score(h,r,x)|x \in Entities] => [0.0,0.1,...,0.8], shape=> (1, |Entities|)
Given a batch of head entities and relations => shape (size of batch,| Entities|)
"""
# (1)
# (1.1) Complex embeddings of head entities and apply batch norm.
emb_head_real = self.bn_ent_real(self.emb_ent_real(e1_idx))
emb_head_i = self.bn_ent_i(self.emb_ent_i(e1_idx))
# (1.2) Complex embeddings of relations and apply batch norm.
emb_rel_real = self.bn_rel_real(self.emb_rel_real(rel_idx))
emb_rel_i = self.bn_rel_i(self.emb_rel_i(rel_idx))
# (2) Apply convolution operation on (1).
C_3 = self.residual_convolution(C_1=(emb_head_real, emb_head_i),
C_2=(emb_rel_real, emb_rel_i))
a, b = C_3
# (3) Apply dropout out on (1).
emb_head_real = self.input_dp_ent_real(emb_head_real)
emb_head_i = self.input_dp_ent_i(emb_head_i)
emb_rel_real = self.input_dp_rel_real(emb_rel_real)
emb_rel_i = self.input_dp_rel_i(emb_rel_i)
"""
# Remove convolution from the score calculation.
real_real_real = torch.mm(emb_head_real * emb_rel_real, self.emb_ent_real.weight.transpose(1, 0))
real_imag_imag = torch.mm(emb_head_real * emb_rel_i, self.emb_ent_i.weight.transpose(1, 0))
imag_real_imag = torch.mm(emb_head_i * emb_rel_real, self.emb_ent_i.weight.transpose(1, 0))
imag_imag_real = torch.mm(emb_head_i * emb_rel_i, self.emb_ent_real.weight.transpose(1, 0))
score = real_real_real + real_imag_imag + imag_real_imag - imag_imag_real
"""
# (4)
# (4.1) Hadamard product of (2) and (1).
# (4.2) Hermitian product of (4.1) and all entities.
real_real_real = torch.mm(a * emb_head_real * emb_rel_real, self.emb_ent_real.weight.transpose(1, 0))
real_imag_imag = torch.mm(a * emb_head_real * emb_rel_i, self.emb_ent_i.weight.transpose(1, 0))
imag_real_imag = torch.mm(b * emb_head_i * emb_rel_real, self.emb_ent_i.weight.transpose(1, 0))
imag_imag_real = torch.mm(b * emb_head_i * emb_rel_i, self.emb_ent_real.weight.transpose(1, 0))
score = real_real_real + real_imag_imag + imag_real_imag - imag_imag_real
return torch.sigmoid(score)
def forward_head_and_loss(self, e1_idx, rel_idx, targets):
return self.loss(self.forward_head_batch(e1_idx=e1_idx, rel_idx=rel_idx), targets)
def init(self):
xavier_normal_(self.emb_ent_real.weight.data)
xavier_normal_(self.emb_ent_i.weight.data)
xavier_normal_(self.emb_rel_real.weight.data)
xavier_normal_(self.emb_rel_i.weight.data)
def get_embeddings(self):
entity_emb = torch.cat((self.emb_ent_real.weight.data, self.emb_ent_i.weight.data), 1)
rel_emb = torch.cat((self.emb_rel_real.weight.data, self.emb_rel_i.weight.data), 1)
return entity_emb, rel_emb
def forward_triples(self, *, e1_idx, rel_idx, e2_idx):
# (1)
# (1.1) Complex embeddings of head entities and apply batch norm.
emb_head_real = self.emb_ent_real(e1_idx)
emb_head_i = self.emb_ent_i(e1_idx)
# (1.2) Complex embeddings of relations.
emb_tail_real = self.emb_ent_real(e2_idx)
emb_tail_i = self.emb_ent_i(e2_idx)
# (1.2) Complex embeddings of tail entities.
emb_rel_real = self.emb_rel_real(rel_idx)
emb_rel_i = self.emb_rel_i(rel_idx)
# (2) Apply convolution operation on (1).
C_3 = self.residual_convolution(C_1=(emb_head_real, emb_head_i),
C_2=(emb_rel_real, emb_rel_i))
a, b = C_3
# (3) Apply dropout out on (1).
emb_head_real = self.input_dp_ent_real(emb_head_real)
emb_head_i = self.input_dp_ent_i(emb_head_i)
emb_rel_real = self.input_dp_rel_real(emb_rel_real)
emb_rel_i = self.input_dp_rel_i(emb_rel_i)
# (4)
# (4.1) Hadamard product of (2) and (1).
# (4.2) Hermitian product of (4.1) and tail entities
# Compute multi-linear product embeddings
real_real_real = (a * emb_head_real * emb_rel_real * emb_tail_real).sum(dim=1)
real_imag_imag = (a * emb_head_real * emb_rel_i * emb_tail_i).sum(dim=1)
imag_real_imag = (b * emb_head_i * emb_rel_real * emb_tail_i).sum(dim=1)
imag_imag_real = (b * emb_head_i * emb_rel_i * emb_tail_real).sum(dim=1)
score = real_real_real + real_imag_imag + imag_real_imag - imag_imag_real
return torch.sigmoid(score)
def forward_triples_and_loss(self, e1_idx, rel_idx, e2_idx, targets):
scores = self.forward_triples(e1_idx=e1_idx, rel_idx=rel_idx, e2_idx=e2_idx)
return self.loss(scores, targets)
