目录
二、跟踪系统的辅助输入和全局参数-PedestrianTrackingFromMovingCameraExample
三、为跟踪系统初始化创建系统对象-setupSystemObjects
五、检测人员-detectPeoplepeopleDetectorACF
六、预测现有轨道的新位置-predictNewLocationsOfTracks
七、将检测分配给轨道-detectionToTrackAssignment
八、更新分配的曲目-updateAssignedTracks
九、更新未分配的曲目-updateUnassignedTracks
十二、显示跟踪结果-displayTrackingResults
一、算法目的
此示例演示如何从移动摄像机对视频中的人员执行自动检测和跟踪。
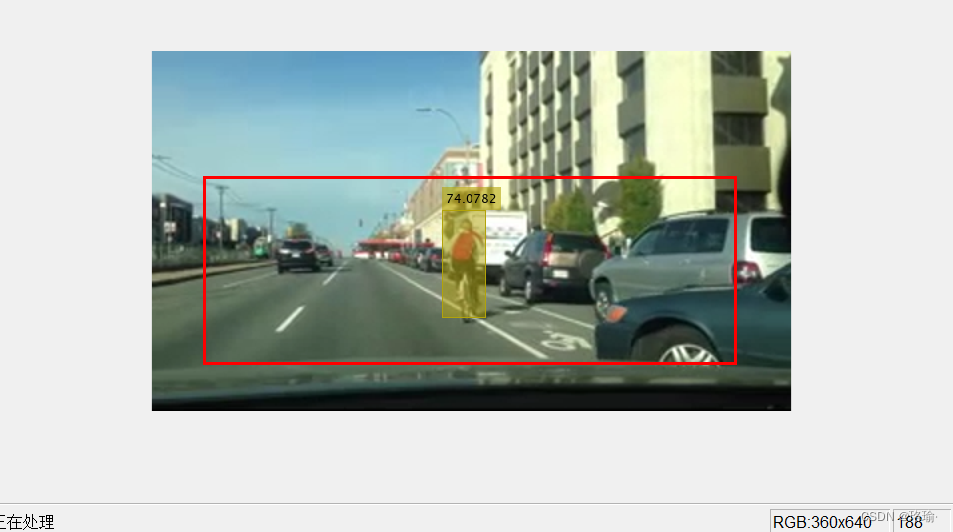
算法结果如下图所示:
算法程序采用嵌套程序,后面分别为每个嵌套程序的大致用途。全部程序如下所示:(该程序在2021版本下,可以正常运行,其他版本不清楚能否运行)
function PedestrianTrackingFromMovingCameraExample()
% 此示例演示如何使用安装在行驶中的摄像机跟踪行人
% Create system objects used for reading video, loading prerequisite data file, detecting pedestrians, and displaying the results.
videoFile = 'vippedtracking.mp4';
scaleDataFile = 'pedScaleTable.mat'; % An auxiliary file that helps to determine the size of a pedestrian at different pixel locations.
obj = setupSystemObjects(videoFile, scaleDataFile);
detector = peopleDetectorACF('caltech');
% Create an empty array of tracks.
tracks = initializeTracks();
% ID of the next track.
nextId = 1;
% Set the global parameters.
option.ROI = [40 95 400 140]; % A rectangle [x, y, w, h] that limits the processing area to ground locations.
option.scThresh = 0.3; % A threshold to control the tolerance of error in estimating the scale of a detected pedestrian.
option.gatingThresh = 0.9; % A threshold to reject a candidate match between a detection and a track.
option.gatingCost = 100; % A large value for the assignment cost matrix that enforces the rejection of a candidate match.
option.costOfNonAssignment = 10; % A tuning parameter to control the likelihood of creation of a new track.
option.timeWindowSize = 16; % A tuning parameter to specify the number of frames required to stabilize the confidence score of a track.
option.confidenceThresh = 2; % A threshold to determine if a track is true positive or false alarm.
option.ageThresh = 8; % A threshold to determine the minimum length required for a track being true positive.
option.visThresh = 0.6; % A threshold to determine the minimum visibility value for a track being true positive.
% Detect people and track them across video frames.
stopFrame = 1629; % stop on an interesting frame with several pedestrians
for fNum = 1:stopFrame
frame = readFrame(obj.reader);
[centroids, bboxes, scores] = detectPeople();
predictNewLocationsOfTracks();
[assignments, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = ...
detectionToTrackAssignment();
updateAssignedTracks();
updateUnassignedTracks();
deleteLostTracks();
createNewTracks();
displayTrackingResults();
% Exit the loop if the video player figure is closed.
if ~isOpen(obj.videoPlayer)
break;
end
end
%% 为跟踪系统初始化创建系统对象
function obj = setupSystemObjects(videoFile,scaleDataFile)
% Initialize Video I/O
% Create objects for reading a video from a file, drawing the
% detected and tracked people in each frame, and playing the video.
% Create a video file reader.
obj.reader = VideoReader(videoFile);
% Create a video player.
obj.videoPlayer = vision.VideoPlayer('Position', [29, 597, 643, 386]);
% Load the scale data file
ld = load(scaleDataFile, 'pedScaleTable');
obj.pedScaleTable = ld.pedScaleTable;
end
%% 初始化轨道
function tracks = initializeTracks()
% Create an empty array of tracks
tracks = struct(...
'id', {}, ...
'color', {}, ...
'bboxes', {}, ...
'scores', {}, ...
'kalmanFilter', {}, ...
'age', {}, ...
'totalVisibleCount', {}, ...
'confidence', {}, ...
'predPosition', {});
end
%% 检测人员
function [centroids, bboxes, scores] = detectPeople()
% Resize the image to increase the resolution of the pedestrian.
% This helps detect people further away from the camera.
resizeRatio = 1.5;
frame = imresize(frame, resizeRatio, 'Antialiasing',false);
% Run ACF people detector within a region of interest to produce
% detection candidates.
[bboxes, scores] = detect(detector, frame, option.ROI, ...
'WindowStride', 2,...
'NumScaleLevels', 4, ...
'SelectStrongest', false);
% Look up the estimated height of a pedestrian based on location of their feet.
height = bboxes(:, 4) / resizeRatio;
y = (bboxes(:,2)-1) / resizeRatio + 1;
yfoot = min(length(obj.pedScaleTable), round(y + height));
estHeight = obj.pedScaleTable(yfoot);
% Remove detections whose size deviates from the expected size,
% provided by the calibrated scale estimation.
invalid = abs(estHeight-height)>estHeight*option.scThresh;
bboxes(invalid, :) = [];
scores(invalid, :) = [];
% Apply non-maximum suppression to select the strongest bounding boxes.
[bboxes, scores] = selectStrongestBbox(bboxes, scores, ...
'RatioType', 'Min', 'OverlapThreshold', 0.6);
% Compute the centroids
if isempty(bboxes)
centroids = [];
else
centroids = [(bboxes(:, 1) + bboxes(:, 3) / 2), ...
(bboxes(:, 2) + bboxes(:, 4) / 2)];
end
end
%% 预测现有轨道的新位置
function predictNewLocationsOfTracks()
for i = 1:length(tracks)
% Get the last bounding box on this track.
bbox = tracks(i).bboxes(end, :);
% Predict the current location of the track.
predictedCentroid = predict(tracks(i).kalmanFilter);
% Shift the bounding box so that its center is at the predicted location.
tracks(i).predPosition = [predictedCentroid - bbox(3:4)/2, bbox(3:4)];
end
end
%% 将检测分配给轨道
function [assignments, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = ...
detectionToTrackAssignment()
% Compute the overlap ratio between the predicted boxes and the
% detected boxes, and compute the cost of assigning each detection
% to each track. The cost is minimum when the predicted bbox is
% perfectly aligned with the detected bbox (overlap ratio is one)
predBboxes = reshape([tracks(:).predPosition], 4, [])';
cost = 1 - bboxOverlapRatio(predBboxes, bboxes);
% Force the optimization step to ignore some matches by
% setting the associated cost to be a large number. Note that this
% number is different from the 'costOfNonAssignment' below.
% This is useful when gating (removing unrealistic matches)
% technique is applied.
cost(cost > option.gatingThresh) = 1 + option.gatingCost;
% Solve the assignment problem.
[assignments, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = ...
assignDetectionsToTracks(cost, option.costOfNonAssignment);
end
%% 更新分配的曲目
function updateAssignedTracks()
numAssignedTracks = size(assignments, 1);
for i = 1:numAssignedTracks
trackIdx = assignments(i, 1);
detectionIdx = assignments(i, 2);
centroid = centroids(detectionIdx, :);
bbox = bboxes(detectionIdx, :);
% Correct the estimate of the object's location
% using the new detection.
correct(tracks(trackIdx).kalmanFilter, centroid);
% Stabilize the bounding box by taking the average of the size
% of recent (up to) 4 boxes on the track.
T = min(size(tracks(trackIdx).bboxes,1), 4);
w = mean([tracks(trackIdx).bboxes(end-T+1:end, 3); bbox(3)]);
h = mean([tracks(trackIdx).bboxes(end-T+1:end, 4); bbox(4)]);
tracks(trackIdx).bboxes(end+1, :) = [centroid - [w, h]/2, w, h];
% Update track's age.
tracks(trackIdx).age = tracks(trackIdx).age + 1;
% Update track's score history
tracks(trackIdx).scores = [tracks(trackIdx).scores; scores(detectionIdx)];
% Update visibility.
tracks(trackIdx).totalVisibleCount = ...
tracks(trackIdx).totalVisibleCount + 1;
% Adjust track confidence score based on the maximum detection
% score in the past 'timeWindowSize' frames.
T = min(option.timeWindowSize, length(tracks(trackIdx).scores));
score = tracks(trackIdx).scores(end-T+1:end);
tracks(trackIdx).confidence = [max(score), mean(score)];
end
end
%% 更新未分配的曲目
function updateUnassignedTracks()
for i = 1:length(unassignedTracks)
idx = unassignedTracks(i);
tracks(idx).age = tracks(idx).age + 1;
tracks(idx).bboxes = [tracks(idx).bboxes; tracks(idx).predPosition];
tracks(idx).scores = [tracks(idx).scores; 0];
% Adjust track confidence score based on the maximum detection
% score in the past 'timeWindowSize' frames
T = min(option.timeWindowSize, length(tracks(idx).scores));
score = tracks(idx).scores(end-T+1:end);
tracks(idx).confidence = [max(score), mean(score)];
end
end
%% 删除丢失的曲目
function deleteLostTracks()
if isempty(tracks)
return;
end
% Compute the fraction of the track's age for which it was visible.
ages = [tracks(:).age]';
totalVisibleCounts = [tracks(:).totalVisibleCount]';
visibility = totalVisibleCounts ./ ages;
% Check the maximum detection confidence score.
confidence = reshape([tracks(:).confidence], 2, [])';
maxConfidence = confidence(:, 1);
% Find the indices of 'lost' tracks.
lostInds = (ages <= option.ageThresh & visibility <= option.visThresh) | ...
(maxConfidence <= option.confidenceThresh);
% Delete lost tracks.
tracks = tracks(~lostInds);
end
%% 创建新轨道
function createNewTracks()
unassignedCentroids = centroids(unassignedDetections, :);
unassignedBboxes = bboxes(unassignedDetections, :);
unassignedScores = scores(unassignedDetections);
for i = 1:size(unassignedBboxes, 1)
centroid = unassignedCentroids(i,:);
bbox = unassignedBboxes(i, :);
score = unassignedScores(i);
% Create a Kalman filter object.
kalmanFilter = configureKalmanFilter('ConstantVelocity', ...
centroid, [2, 1], [5, 5], 100);
% Create a new track.
newTrack = struct(...
'id', nextId, ...
'color', 255*rand(1,3), ...
'bboxes', bbox, ...
'scores', score, ...
'kalmanFilter', kalmanFilter, ...
'age', 1, ...
'totalVisibleCount', 1, ...
'confidence', [score, score], ...
'predPosition', bbox);
% Add it to the array of tracks.
tracks(end + 1) = newTrack; %#ok<AGROW>
% Increment the next id.
nextId = nextId + 1;
end
end
%% 显示跟踪结果
function displayTrackingResults()
displayRatio = 4/3;
frame = imresize(frame, displayRatio);
if ~isempty(tracks)
ages = [tracks(:).age]';
confidence = reshape([tracks(:).confidence], 2, [])';
maxConfidence = confidence(:, 1);
avgConfidence = confidence(:, 2);
opacity = min(0.5,max(0.1,avgConfidence/3));
noDispInds = (ages < option.ageThresh & maxConfidence < option.confidenceThresh) | ...
(ages < option.ageThresh / 2);
for i = 1:length(tracks)
if ~noDispInds(i)
% scale bounding boxes for display
bb = tracks(i).bboxes(end, :);
bb(:,1:2) = (bb(:,1:2)-1)*displayRatio + 1;
bb(:,3:4) = bb(:,3:4) * displayRatio;
frame = insertShape(frame, ...
'FilledRectangle', bb, ...
'Color', tracks(i).color, ...
'Opacity', opacity(i));
frame = insertObjectAnnotation(frame, ...
'rectangle', bb, ...
num2str(avgConfidence(i)), ...
'Color', tracks(i).color);
end
end
end
frame = insertShape(frame, 'Rectangle', option.ROI * displayRatio, ...
'Color', [255, 0, 0], 'LineWidth', 3);
step(obj.videoPlayer, frame);
end
end二、跟踪系统的辅助输入和全局参数-PedestrianTrackingFromMovingCameraExample
此跟踪系统需要一个数据文件,其中包含将图像中的像素位置与标记行人位置的边界框的大小相关联的信息。这种先验知识存储在向量中。中的第 n 个条目表示成人的估计身高(以像素为单位)。该指数参考了行人脚的近似 Y 坐标。pedScaleTablepedScaleTablen
为了获得这样的矢量,从与测试环境相同的视点和相似的场景中拍摄了一组训练图像。训练图像包含与摄像机不同距离的行人图像。使用图像标注器应用程序,手动注释图像中行人的边界框。边界框的高度以及图像中行人的位置用于通过回归生成比例数据文件。下面是一个帮助器函数,用于显示拟合线性回归模型的算法步骤:helperTableOfScales.m
还有一组全局参数可以进行调整以优化跟踪性能。您可以使用以下说明来了解这些参数如何影响跟踪性能。
-
ROI:以 [x, y, w, h] 的形式表示感兴趣区域。它将处理区域限制为地面位置。 -
scThresh:用于比例估计的容差阈值。当检测到的刻度和预期刻度之间的差异超过容差时,候选检测将被视为不切实际,并从输出中删除。 -
gatingThresh:距离测量的门控参数。当匹配检测到的边界框和预测的边界框的成本超过阈值时,系统将从跟踪考虑中删除两个边界框的关联。 -
gatingCost:分配成本矩阵的值,用于阻止对检测分配的可能跟踪。 -
costOfNonAssignment:用于不分配检测或跟踪的分配成本矩阵的值。将其设置得太低会增加创建新轨道的可能性,并可能导致轨道碎片。将其设置得太高可能会导致单个轨道对应于一系列单独的移动对象。 -
timeWindowSize:估计轨道置信度所需的帧数。 -
confidenceThresh:置信度阈值,用于确定轨道是否为真阳性。 -
ageThresh:轨道的最小长度为真阳性。 -
visThresh:用于确定轨迹是否为真阳性的最小可见性阈值。
三、为跟踪系统初始化创建系统对象-setupSystemObjects
该函数创建用于读取和显示视频帧的系统对象,并加载缩放数据文件。
矢量存储在比例数据文件中,用于编码我们对目标和场景的先验知识。从样本中训练回归量后,可以计算图像中每个可能的 Y 位置的预期高度。这些值存储在向量中。中的第 n 个条目表示我们估计的成人身高(以像素为单位)。该指数参考了行人脚的近似 Y 坐标。
四、初始化轨道-initializeTracks
该函数创建一个轨道数组,其中每个轨道都是一个表示视频中移动对象的结构。该结构的目的是维护被跟踪对象的状态。状态由用于检测到跟踪分配、跟踪终止和显示的信息组成。
该结构包含以下字段:
-
id:轨道的整数 ID。 -
color:用于显示目的的轨道的颜色。 -
bboxes:一个 N x 4 矩阵,用于表示对象的边界框,当前框位于最后一行。每行都有一种形式 [x, y, width, height]。 -
scores:一个 N x 1 向量,用于记录来自人员检测器的分类分数,当前检测分数位于最后一行。 -
kalmanFilter:用于基于运动的跟踪的卡尔曼滤镜对象。我们跟踪图像中物体的中心点; -
age:自轨道初始化以来的帧数。 -
totalVisibleCount:检测到对象的总帧数(可见)。 -
confidence:一对两个数字,表示我们对赛道的信任程度。它将过去的最大和平均检测分数存储在预定义的时间范围内。 -
predPosition:下一帧中的预测边界框。
五、检测人员-detectPeoplepeopleDetectorACF
该函数返回检测到的人员的质心、边界框和分类分数。它对 返回 的检测器的原始输出执行滤波和非最大抑制。
-
centroids:每行采用 [x,y] 形式的 N x 2 矩阵。 -
bboxes:一个 N x 4 矩阵,每行采用 [x、 y、 宽度、高度] 的形式。 -
scores:每个元素的 N x 1 向量是相应帧处的分类分数。
六、预测现有轨道的新位置-predictNewLocationsOfTracks
使用 Kalman 过滤器预测当前帧中每个轨迹的质心,并相应地更新其边界框。我们将前一帧中边界框的宽度和高度作为当前对大小的预测。
七、将检测分配给轨道-detectionToTrackAssignment
将当前帧中的对象检测分配给现有轨道是通过最大限度地降低成本来完成的。成本是使用函数计算的,是预测边界框和检测到的边界框之间的重叠比率。在这个例子中,我们假设由于视频的高帧率和人的低运动速度,这个人将在连续的帧中逐渐移动。bboxOverlapRatio
该算法包括两个步骤:
步骤 1:使用度量值计算将每个检测分配给每个轨道的成本。当人们走向或远离相机时,他们的运动将不能仅通过质心点准确描述。成本考虑了图像平面上的距离以及边界框的比例。这样可以防止将远离摄像机的检测分配给离摄像机更近的轨迹,即使它们的质心重合也是如此。选择此成本函数将简化计算,而无需诉诸更复杂的动态模型。结果存储在 MxN 矩阵中,其中 M 是磁道数,N 是检测数。bboxOverlapRatio
步骤 2:使用函数解决成本矩阵所表示的分配问题。该函数采用成本矩阵和不向跟踪分配任何检测的开销。assignDetectionsToTracks
未将检测分配给跟踪的成本值取决于 cost 函数返回的值范围。必须通过实验调整此值。将其设置得太低会增加创建新轨道的可能性,并可能导致轨道碎片。将其设置得太高可能会导致单个轨道对应于一系列单独的移动对象。
该函数使用匈牙利算法的 Munkres 版本来计算赋值,从而最大限度地降低总成本。它返回一个 M x 2 矩阵,其中包含其两列中已分配轨迹和检测的相应索引。它还返回未分配的跟踪和检测的索引。
八、更新分配的曲目-updateAssignedTracks
该函数使用相应的检测来更新每个分配的轨道。它调用 来校正位置估计的方法。接下来,它通过取最近(最多)4 个框的大小的平均值来存储新的边界框,并将轨道的年龄和总可见计数增加 1。最后,该函数根据之前的检测分数调整轨道的置信度分数。
九、更新未分配的曲目-updateUnassignedTracks
该函数将每个未分配的轨迹标记为不可见,将其期限增加 1,并将预测的边界框追加到轨迹。置信度设置为零,因为我们不确定为什么没有将其分配给轨道。
十、删除丢失的曲目-deleteLostTracks
该函数删除连续帧数过多而不可见的轨道。它还会删除最近创建的轨道,这些轨道在许多帧中总体上是不可见的。deleteLostTracks
噪声检测往往会导致产生错误的轨迹。对于此示例,我们在以下情况下删除曲目:
-
该对象被跟踪了很短的时间。当错误检测显示几个帧并为其启动跟踪时,通常会发生这种情况。
-
对于大多数帧,轨道被标记为不可见。
-
它在过去几帧内未能收到强检测,这表示为最大检测置信度分数。
十一、创建新轨道-createNewTracks
从未分配的检测创建新轨道。假定任何未分配的检测都是新轨道的开始。在实践中,可以使用其他提示来消除噪声检测,例如大小、位置或外观。
十二、显示跟踪结果-displayTrackingResults
该函数为视频帧上的每个轨道绘制一个彩色边界框。框的透明度级别以及显示的分数表示检测和跟踪的置信度。
