本文以SOLO网络为例演示网络的训练与部署,其他paddle深度学习框架支持的算法同理可行
训练:
1.环境搭建:
paddle深度学习框架可从官网获取:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/
默认CUDA、cuDNN库已安装完成,已可以使用GPU算力。
目前paddle深度学习框架支持Windows、macOS、Linux以及部分国产芯片对应的操作系统,本文使用Ubuntu18.04;选择你所熟悉的安装方式及对应的CUDA库版本,本文选用pip安装方式、CUDA库为11.0版本。
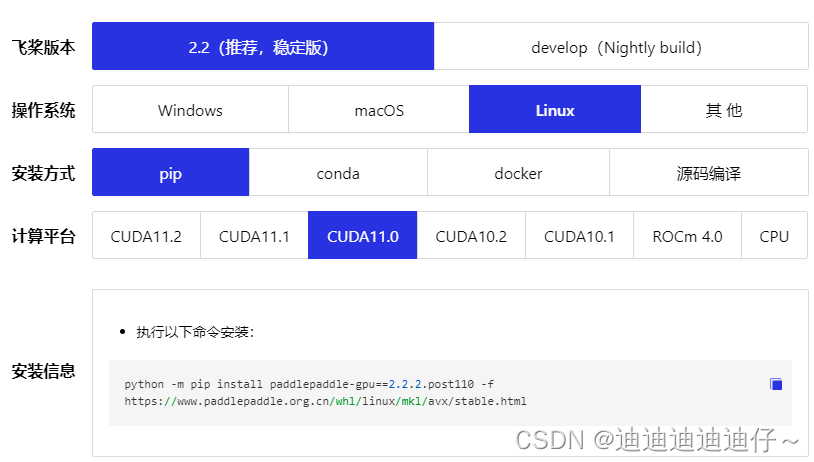
打开终端,输入安装信息中的安装命令
python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.2.post110 -f https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/whl/linux/mkl/avx/stable.html
安装过后验证安装成功
python
# 在您的Python解释器中确认PaddlePaddle安装成功
>>> import paddle
>>> paddle.utils.run_check()
选择你喜欢的路径打开终端,输入如下命令获取PaddleDetection源码
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection.git
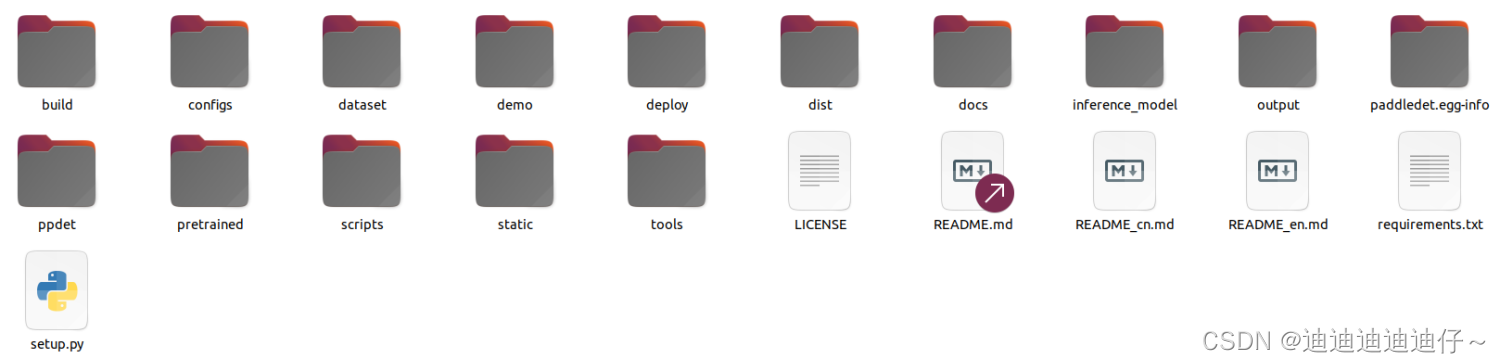
在当前路径下会出现名为PaddleDetection-release-2.x的文件夹,文件夹中内容如下:
# 安装其他依赖
cd PaddleDetection
pip install -r requirements.txt
# 编译安装paddledet
python setup.py install
安装后确认测试通过:
python ppdet/modeling/tests/test_architectures.py
测试通过后会提示如下信息:
.......
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 7 tests in 12.816s
OK
2.准备数据集:
使用录像设备从不同角度、光线条件下拍摄所需识别目标物,获得视频
使用下文的代码从视频中提取帧,得到原始数据集
# coding=utf-8
import cv2
import os
import threading
from threading import Lock, Thread
video_path = "/home/zyy/桌面/paddle/video/" # 视频所在文件夹路径
pic_path = "/home/zyy/桌面/paddle/video/pic2" # 输出图像路径
filelist = os.listdir(video_path) # 返回指定的文件夹下包含的文件或文件夹名字的列表,这个列表按字母顺序排序。
def video2pic(filename):
# print(filename)
cnt = 0
dnt = 0
if os.path.exists(pic_path + str(filename)):
pass
else:
os.mkdir(pic_path + str(filename))
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path + str(filename)) # 读入视频
while True:
# get a frame
ret, image = cap.read()
if image is None:
break
# show a frame
w = image.shape[1]
h = image.shape[0]
if (cnt % 10) == 0:
cv2.imencode('.jpg', image)[1].tofile(pic_path + str(filename) + '/' + str(dnt) + '.jpg')
# cv2.imwrite('C:/Users/JiangHuiQi/Desktop/pic/' + str(filename) + '/' + str(dnt) + '.jpg', image) #含中文路径,不可行
print(pic_path + str(filename) + '/' + str(dnt) + '.jpg')
dnt = dnt + 1
# cv2.namedWindow('sliding_slice',0)
# cv2.imshow('image', image)
# cv2.waitKey(1000)
cnt = cnt + 1
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
for filename in filelist:
threading.Thread(target=video2pic, args=(filename,)).start()
安装PaddleSeg,使用其标注我们的数据集
通过git将PaddleSeg克隆到本地:
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg.git
安装所需环境(若需要使用到GDAL和SimpleITK请参考垂类分割进行安装):
pip install -r requirements.txt
安装好所需环境后,进入EISeg,可通过直接运行eiseg打开EISeg:
cd PaddleSeg\EISeg
python -m eiseg
或使用PIP安装
pip install eiseg
安装完成后输入如下命令即可运行软件。
eiseg
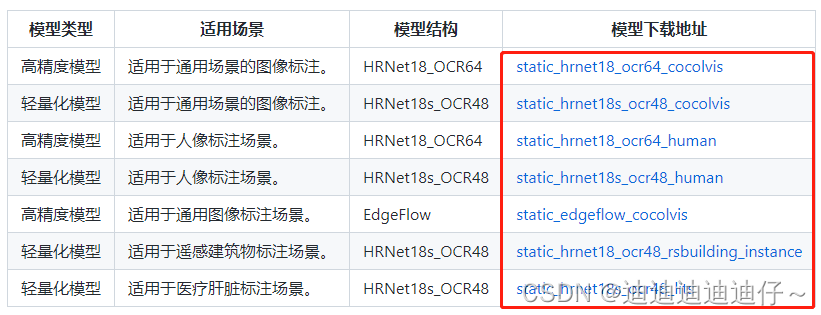
在https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/tree/release/2.4/EISeg页面内选择对应你任务及要求的的预训练模型下载
在软件中点击加载权重文件按钮,将下载的预训练模型加载,
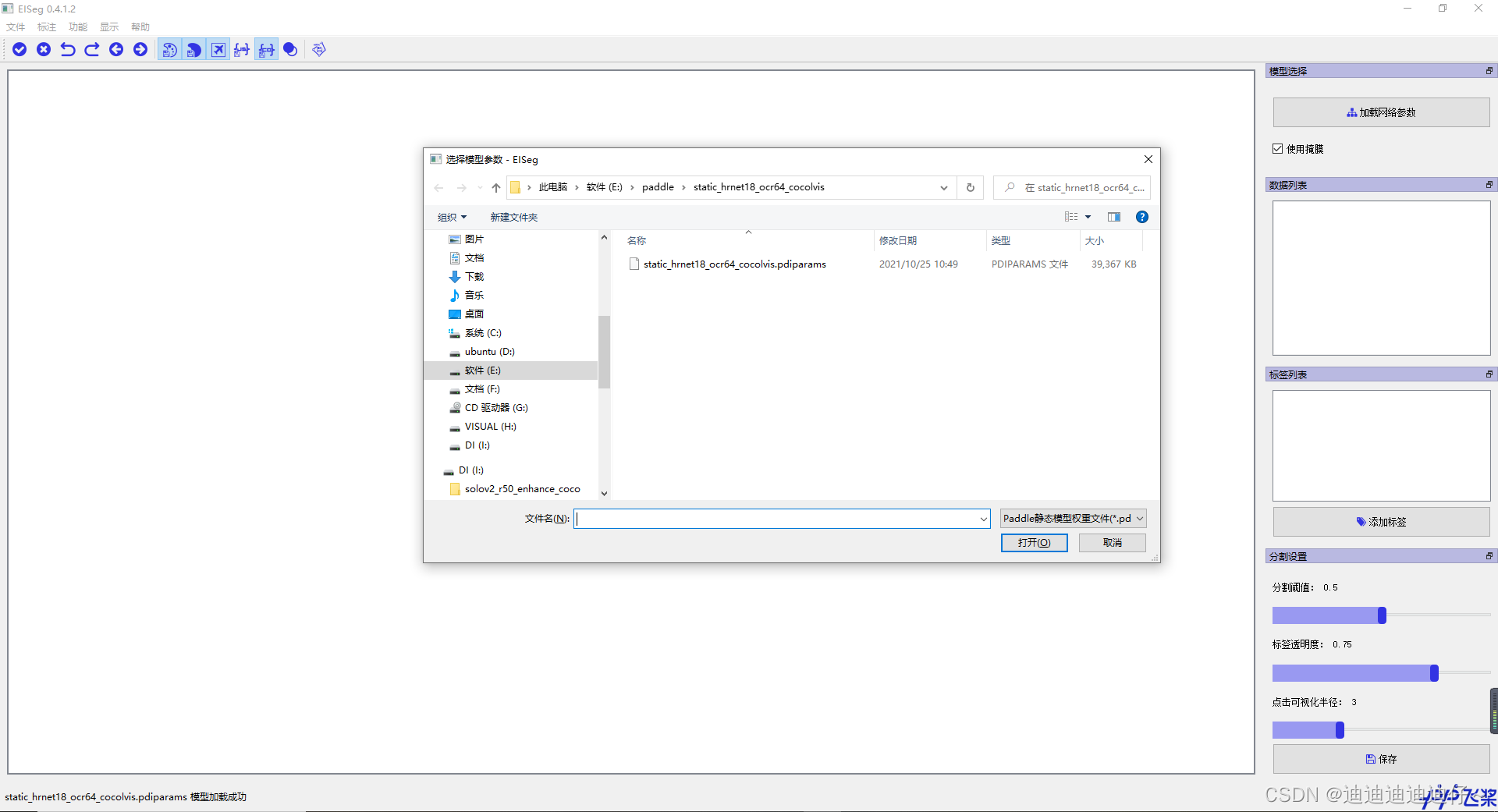
选择文件菜单、打开文件夹选项将原始数据集导入标注软件

标注数据集

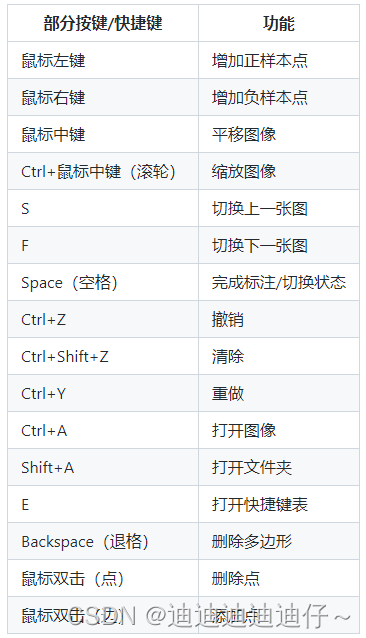
下图为软件使用方法(按键/快捷键)
数据集标注完成后,在PaddleDetection/dataset路径下创建你自己的数据集文件夹
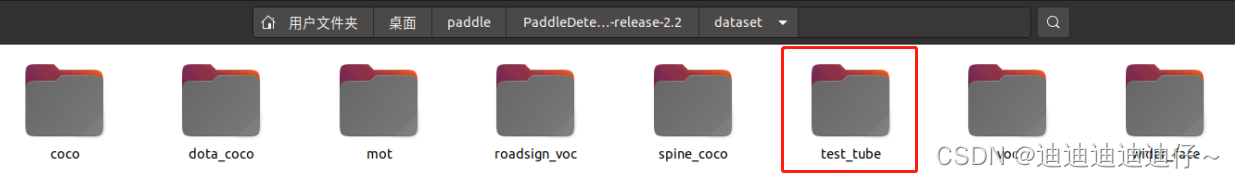
文件夹中创建如下两个子文件夹

annotations文件夹中放置标注结果,images文件夹中放置原始图像数据集
至此,数据集准备工作完成
3.修改配置文件开始训练自己的网络
在PaddleDetection/configs/datasets路径下创建你自己的数据集描述文件test_tube.yml
metric: COCO
num_classes: 2
TrainDataset:
!COCODataSet
image_dir: iamges
anno_path: annotations/train.json
dataset_dir: dataset/test_tube
data_fields: ['image', 'gt_bbox', 'gt_class', 'gt_poly', 'is_crowd']
EvalDataset:
!COCODataSet
image_dir: iamges
anno_path: annotations/val.json
dataset_dir: dataset/test_tube
TestDataset:
!ImageFolder
anno_path: annotations/test.json
在PaddleDetection/configs/solov2路径下修改网络描述文件solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco.yml
_BASE_: [
'../datasets/test_tube.yml',
'../runtime.yml',
'_base_/solov2_r50_fpn.yml',
'_base_/optimizer_1x.yml',
'_base_/solov2_reader.yml',
]
pretrain_weights: pretrained/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco.pdparams
weights: output/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco/model_final
进入https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/tree/release/2.4/configs/solov2链接下载solov2预训练模型
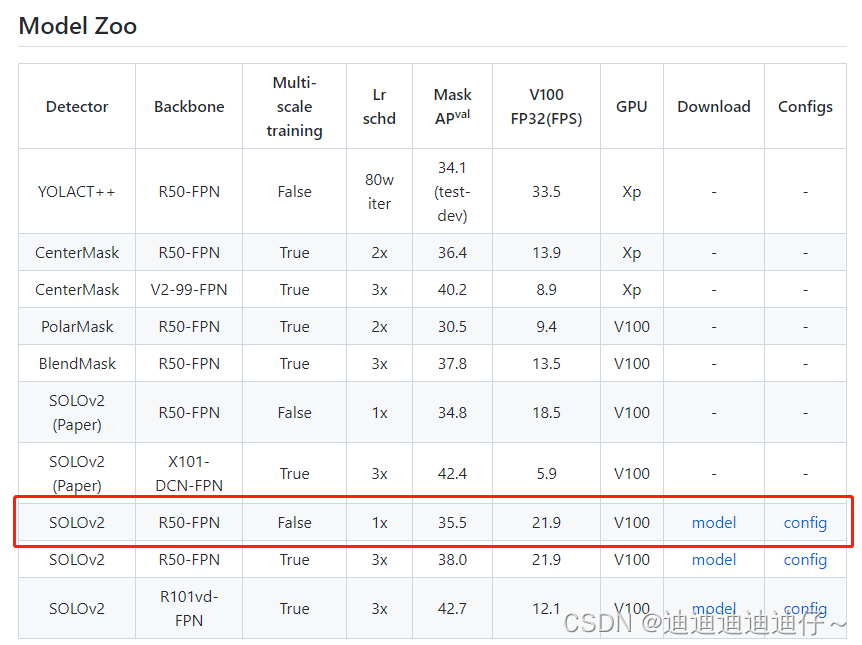
将下载下来的预训练模型保存在PaddleDetection/pretrained/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco路径下
使用如下命令开启网络训练
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 #windows和Mac下不需要执行该命令
python tools/train.py -c configs/solov2/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco.yml
网络训练完成即可以在PaddleDetection/output/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco文件夹中找到model_final.pdparams模型权重文件
至此,基于Paddle深度学习框架的神经网络训练过程完成
预测
使用如下命令运行网络预测图像
python tools/infer.py -c configs/solov2/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco.yml --infer_img=dataset/test_tube/images/1737.jpg -o weights=output/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco/model_final.pdparams

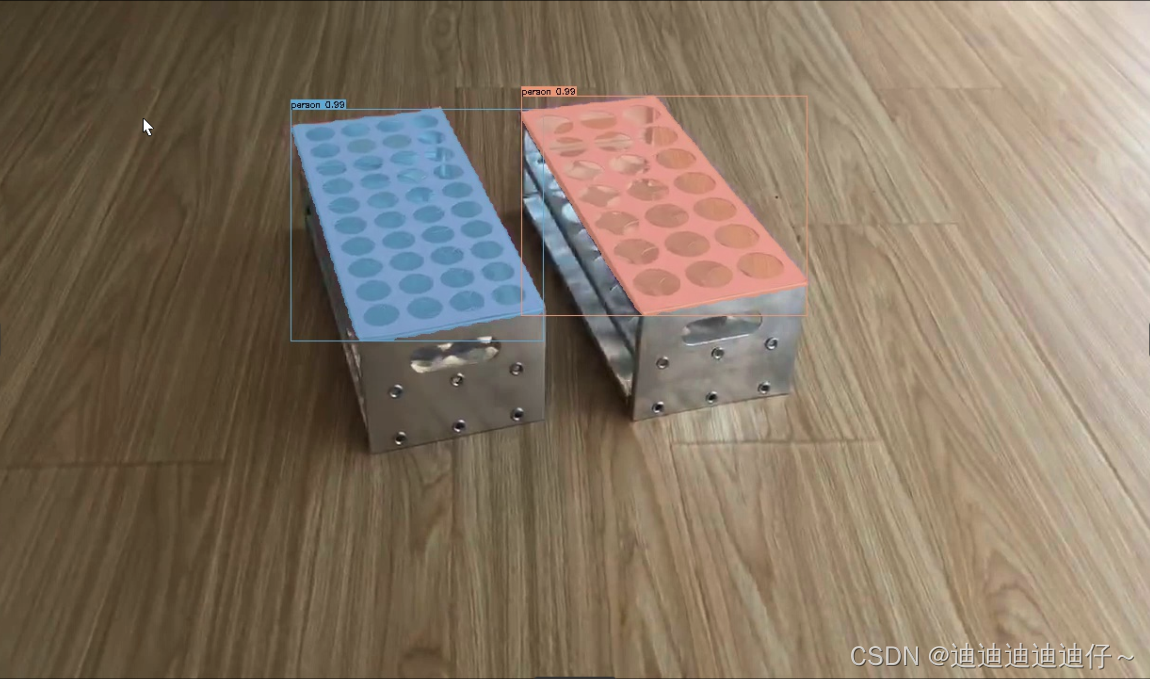
模型导出
在模型训练过程中保存的模型文件是包含前向预测和反向传播的过程,在实际的工业部署则不需要反向传播,因此需要将模型进行导成部署需要的模型格式。 在PaddleDetection中提供了 tools/export_model.py脚本来导出模型
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/solov2/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco.yml --output_dir=./inference_model \
-o weights=output/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco/model_final.pdparams
预测模型会导出到inference_model/solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco目录下,分别为infer_cfg.yml, model.pdiparams, model.pdiparams.info,model.pdmodel
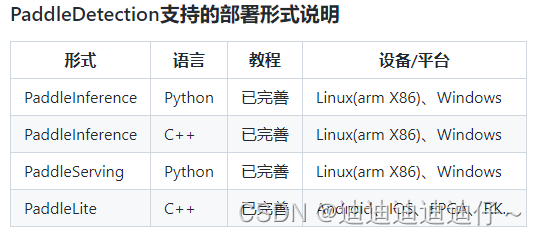
预测部署
PaddleDetection提供了PaddleInference、PaddleServing、PaddleLite多种部署形式,支持服务端、移动端、嵌入式等多种平台,提供了完善的Python和C++部署方案。
在这里,我们以Python为例,说明如何使用PaddleInference进行模型部署
python deploy/python/infer.py --model_dir=./inference_model /solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco --image_file=dataset/test_tube/images/1737.jpg --device=GPU
同时infer.py提供了丰富的接口,用户进行接入视频文件、摄像头进行预测,更多内容请参考https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/inference/demo_tutorial/x86_linux_demo.html
本文使用Nvidia Jetson AGX Xavier开发套件,以NV Jetson上预测部署示例进行演示
首先,进入链接https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/inference/user_guides/download_lib.html下载安装Linux预测库,我们选用python预测库中的Jetpack版本
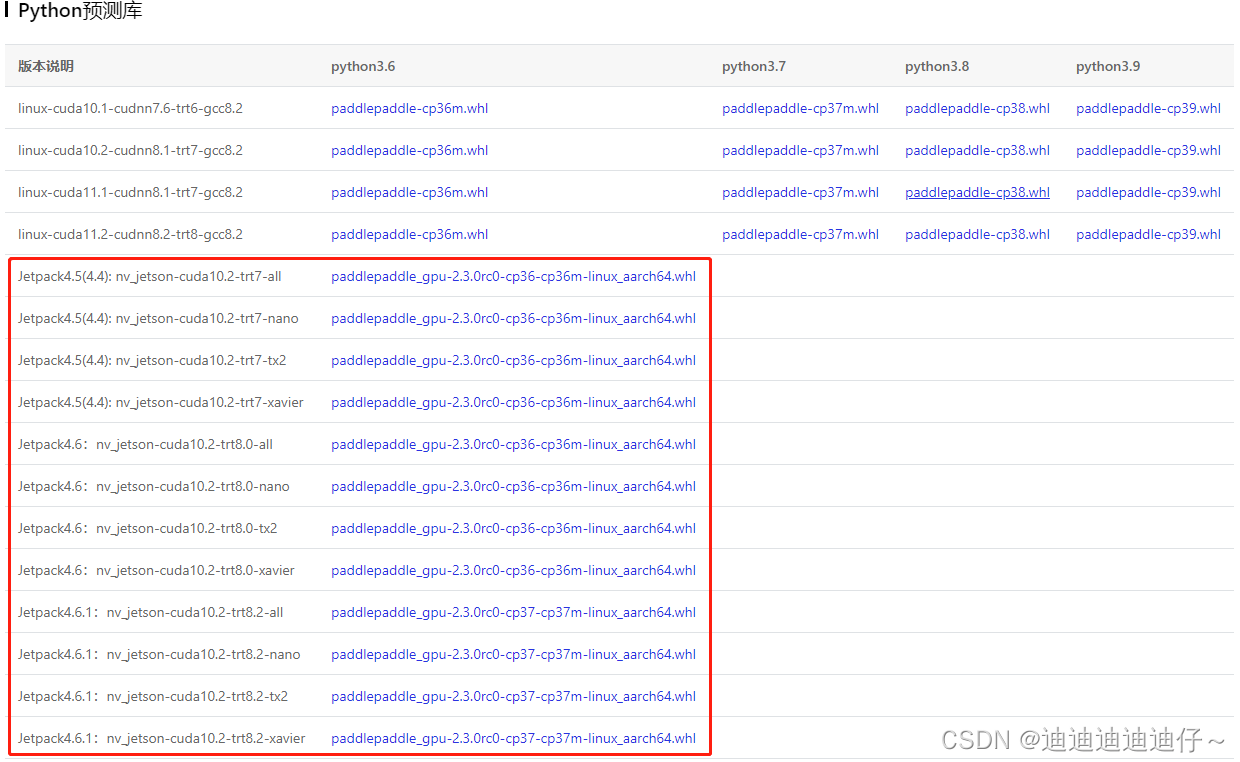
注意:选择与你硬件、软件环境相同的库下载
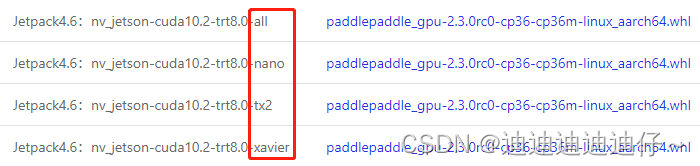
下载完成后在文件路径下运行即可完成预测库安装
pip install paddlepaddle_gpu-2.3.0rc0-cp36-cp36m-linux_aarch64.whl
安装完成后在终端内测试安装成功,引用不报错则安装成功
python
>> import paddle.inference as paddle_infer
>>
进入链接https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Inference-Demo下载所有代码
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Inference-Demo.git
在Paddle-Inference-Demo/Python路径下存有部分demo示例
本文提供solov2网络推理的代码示例如下
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import argparse
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import time
from paddle.inference import Config
from paddle.inference import create_predictor
from utils import preprocess, draw_bbox
def init_predictor(args):
if args.model_dir != "":
config = Config(args.model_dir)
else:
config = Config(args.model_file, args.params_file)
config.enable_memory_optim()
if args.use_gpu:
config.enable_use_gpu(1000, 0)
else:
# If not specific mkldnn, you can set the blas thread.
# The thread num should not be greater than the number of cores in the CPU.
config.set_cpu_math_library_num_threads(4)
config.enable_mkldnn()
predictor = create_predictor(config)
return predictor
def run(predictor, img):
# copy img data to input tensor
input_names = predictor.get_input_names()
for i, name in enumerate(input_names):
input_tensor = predictor.get_input_handle(name)
input_tensor.reshape(img[i].shape)
input_tensor.copy_from_cpu(img[i].copy())
# do the inference
predictor.run()
results = []
# get out data from output tensor
output_names = predictor.get_output_names()
for i, name in enumerate(output_names):
output_tensor = predictor.get_output_handle(name)
output_data = output_tensor.copy_to_cpu()
results.append(output_data)
return results
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--model_file",
type=str,
default="",
help="Model filename, Specify this when your model is a combined model."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--params_file",
type=str,
default="",
help=
"Parameter filename, Specify this when your model is a combined model."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--model_dir",
type=str,
default="",
help=
"Model dir, If you load a non-combined model, specify the directory of the model."
)
parser.add_argument("--use_gpu",
type=int,
default=0,
help="Whether use gpu.")
return parser.parse_args()
def get_mask_center(maskimage):
cnts = cv2.findContours(maskimage, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0]
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnts[0])
cX = x + w//2
cY = y + h//2
center = (cX, cY)
return center
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = parse_args()
img_name = '1677.jpg'
save_img_name = 'res_1677.jpg'
im_size = 608
pred = init_predictor(args)
img = cv2.imread(img_name)
data = preprocess(img, im_size)
scale_factor = np.array([im_size * 1. / img.shape[0], im_size * 1. / img.shape[1]]).reshape((1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
print(scale_factor.shape)
im_shape = np.array([im_size, im_size]).reshape((1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
result = run(pred, [im_shape, data, scale_factor])
"""
result[0][0]: 检出实例总个数
result[1][i]: 每个实例的类别 # 猜测,需要验证
result[2][i]: 对应每个检出实例的置信度score
result[3][i]: 对应每个检出实例的归一化掩模图mask
"""
masks = result[3].shape
for i in range(masks[0]):
if result[2][i] < 0.9:
continue
else:
maskimage = 255*result[3][i]
maskimage = cv2.resize(maskimage, (1280,720))
cv2.imshow('mask', np.array(maskimage))
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("center:", get_mask_center(maskimage))
代码会将检测到的实例对应的mask掩模依次显示在屏幕上,最后输出每个实例的中心像素坐标(u,v)。
本文还提供一种tensorRT加速的solov2网络推理代码
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import argparse
import cv2
from paddle.inference import Config
from paddle.inference import create_predictor
from paddle.inference import PrecisionType
from utils import preprocess
import time
shape_file = "shape_range_info.pbtxt"
def init_predictor(args):
if args.model_dir is not "":
config = Config(args.model_dir)
else:
config = Config(args.model_file, args.params_file)
config.enable_memory_optim()
if args.tune:
config.collect_shape_range_info(shape_file)
if args.use_gpu:
config.enable_use_gpu(1000, 0)
if args.use_trt:
# using dynamic shpae mode, the max_batch_size will be ignored.
config.enable_tensorrt_engine(
workspace_size=1 << 30,
max_batch_size=1,
min_subgraph_size=5,
precision_mode=PrecisionType.Half,
use_static=False,
use_calib_mode=False)
if args.tuned_dynamic_shape:
config.enable_tuned_tensorrt_dynamic_shape(shape_file, True)
else:
# If not specific mkldnn, you can set the blas thread.
# The thread num should not be greater than the number of cores in the CPU.
config.set_cpu_math_library_num_threads(4)
config.enable_mkldnn()
print("Enable TensorRT is: {}".format(config.tensorrt_engine_enabled()))
predictor = create_predictor(config)
return predictor
def run(predictor, img):
# copy img data to input tensor
input_names = predictor.get_input_names()
for i, name in enumerate(input_names):
input_tensor = predictor.get_input_handle(name)
input_tensor.reshape(img[i].shape)
input_tensor.copy_from_cpu(img[i].copy())
# do the inference
predictor.run()
results = []
# get out data from output tensor
output_names = predictor.get_output_names()
for i, name in enumerate(output_names):
output_tensor = predictor.get_output_handle(name)
output_data = output_tensor.copy_to_cpu()
results.append(output_data)
return results
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--model_file",
type=str,
default="",
help="Model filename, Specify this when your model is a combined model."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--params_file",
type=str,
default="",
help="Parameter filename, Specify this when your model is a combined model."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--model_dir",
type=str,
default="",
help="Model dir, If you load a non-combined model, specify the directory of the model."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--use_gpu", type=int, default=0, help="Whether use gpu.")
parser.add_argument(
"--use_trt", type=int, default=0, help="Whether use trt.")
parser.add_argument(
"--tune",
type=int,
default=0,
help="Whether use tune to get shape range.")
parser.add_argument(
"--tuned_dynamic_shape",
type=int,
default=0,
help="Whether use tuned dynamic shape.")
return parser.parse_args()
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = parse_args()
img_name = 'kite.jpg'
save_img_name = 'res.jpg'
im_size = 608
pred = init_predictor(args)
img = cv2.imread(img_name)
data = preprocess(img, im_size)
scale_factor = np.array([im_size * 1. / img.shape[0], im_size * 1. / img.shape[1]]).reshape((1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
im_shape = np.array([im_size, im_size]).reshape((1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
for i in range(0,20):
time_start = time.time()
result = run(pred, [im_shape, data, scale_factor])
"""
result[0][0]: 检出实例总个数
result[1][i]: 每个实例的类别 # 猜测,需要验证
result[2][i]: 对应每个检出实例的置信度score
result[3][i]: 对应每个检出实例的归一化掩模图mask
"""
time_end = time.time()
print(i,'Time cost = %fs' % (time_end - time_start))
print("class index: ", np.argmax(result[0][0]))
注:上述tensorRT加速推理代码在使用之前需要配套的shape_range_info.pbtxt文件,shape_range_info.pbtxt文件通过Paddle-Inference-Demo/python/paddle_trt/tuned_dynamic_shape/路径下的infer_tune.py文件获得
进入https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/models/tree/develop/PaddleCV/image_classification链接选择对应特征提取网络的模型并下载,由于我们之前使用的预训练模型为solov2_r50_fpn_1x_coco.pdparams,我们此处下载ResNet50模型即可
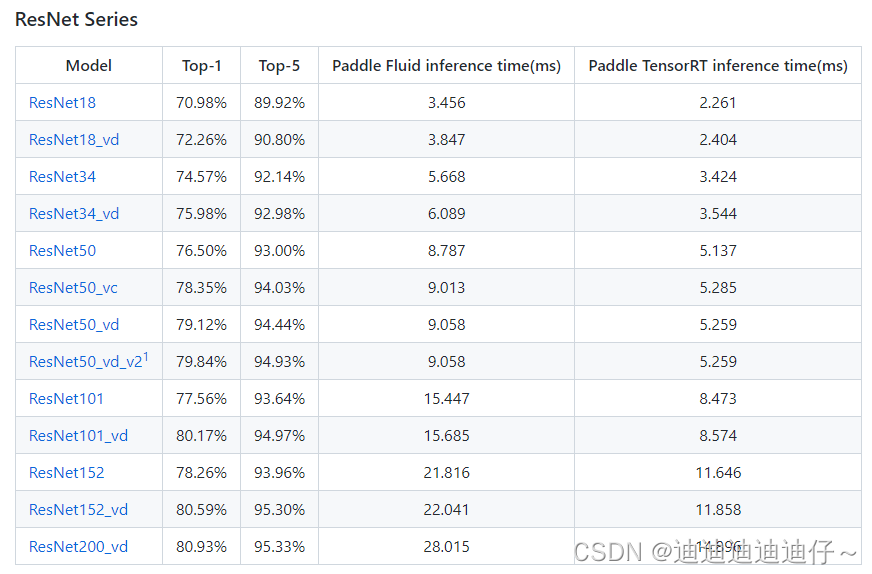
使用如下命令得到对应的shape_range_info.pbtxt文件
python infer_tune.py --model_file ./resnet50/inference.pdmodel --params_file ./resnet50/inference.pdiparams --tune 1
至此,完成基于Paddle深度学习框架的神经网络部署
详情请参考:
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/release/2.4/docs/tutorials/PrepareDataSet.md
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/release/2.4/docs/tutorials/INSTALL_cn.md
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/release/2.4/docs/tutorials/PrepareDataSet.md
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/tree/release/2.4/EISeg
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/release/2.4/docs/tutorials/GETTING_STARTED_cn.md
