大家好,今天和大家分享一下如何使用 TensorFlow 自定义 指数学习率下降、阶梯学习率下降、余弦学习率下降 方法,并使用 Mnist数据集验证自定义的学习率下降策略。
创建的自定义学习率类方法,需要继承 tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule
1. 指数学习率下降
指数学习率下降公式为:?
其中??代表初始的学习率,
?代表学习率衰减系数,
?代表epoch,即每次迭代学习率衰减一次
以初始学习率??,学习率衰减系数?
?,
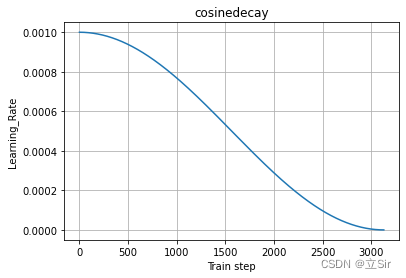
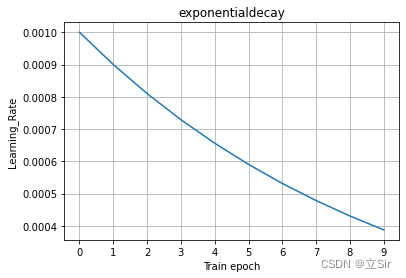
?为例指数学习率下降曲线如下图所示。
如果以step作为指数调整的标准,那么指数 n 等于当前的 step 除以 一个 epoch 包含的总 step。
我这里以 epoch 作为指数调整的标准。
首先创建一个学习率自定义类,继承 keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule 自定义学习率调度器。
先对所有的属性完成初始化,其中 self.current 返回训练时每一个 step 的学习率,self.epoch 代表指数学习率计算公式中的指数项 n,self.learning_rate_list 用于记录训练时每个 epoch 的学习率。
在__call__方法中,step % self.print_step,其中 step 代表训练时传入的当前的 step,而 print_step 是外部指定的每经过多少个step调整一次学习率,并记录下当前 epoch 的学习率,返回调整后的学习率。如果不满足 if 条件,那么这些 step 的学习率就是上一次调整后的学习率。
以 epoch 作为指数调整标准的代码如下:
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# 当前学习率 = 初始学习率 * 衰减系数 ^{迭代了多少次}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# eager模式防止graph报错
tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(True)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# 继承学习率的类
class ExponentialDecay(keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule):
'''
initial_lr: 初始的学习率
decay_rate: 学习率衰减系数
min_lr: 学习率下降的最小
print_step: 训练时多少个batch打印一次学习率
'''
# 初始化
def __init__(self, initial_lr, decay_rate, min_lr, print_step):
# 继承父类的初始化方法
super(ExponentialDecay, self).__init__()
# 属性分配
self.initial_lr = tf.cast(initial_lr, tf.float32)
self.decay_rate = tf.cast(decay_rate, tf.float32)
self.min_lr = tf.cast(min_lr, tf.float32)
self.print_step = print_step
# 记录记录每个epoch的学习率
self.learning_rate_list = []
# 最开始时,学习率为初始学习率
self.current = self.initial_lr
# 初始的迭代次数为0
self.epoch = 0
# 前向传播
def __call__(self, step):
# 每多少个batch调整一次学习率, 一个batch处理32张图
if step % self.print_step == 0:
# 学习率指数下降,设置为每个epoch调整一次
learning_rate = self.initial_lr * pow(self.decay_rate, self.epoch)
# 调整当前学习率, 每一轮的学习率不能低于最小学习率
self.current = tf.where(learning_rate>self.min_lr, learning_rate, self.min_lr)
# 迭代次数加一
self.epoch = self.epoch + 1
# 将当前学习率保存下来
self.learning_rate_list.append(learning_rate.numpy().item())
# 打印学习率变化
print('learning_rate:', learning_rate.numpy().item())
# 返回调整后的学习率
return self.current
# 否则就返回上一次调整的学习率
else:
return self.current2. 阶梯学习率下降
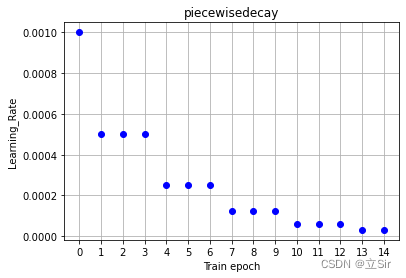
思路:每经过多少个 step 之后,学习率下降为上一次的 decay_rate 倍。例如初始学习率为0.001,每经过三个 epoch,学习率就下降为原来的 0.5 倍,实现分段下降,示意图如下:
首先创建一个学习率自定义类,继承 keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule 自定义学习率调度器。
先对所有的属性完成初始化,其中 self.change_step 在外部定义,代表每经过多少个 step 调整一次学习率。调整方式是当前学习率 self.current 乘以调整倍数?self.decay_rate,得到调整后的学习率并返回结果。如果不满足 if 条件,即当前 step 不需要调整,就返回上一次调整后的学习率。self.learning_rate_list 列表中记录训练过程中的每个 epoch 的学习率,训练完成后之后可以读取查看。
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# 自定义的分段常数下降方法
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# eager模式防止graph报错
tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(True)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# 继承学习率的类
class PiecewiseConstantDecay(keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule):
'''
initial_lr: 初始的学习率
decay_rate: 学习率衰减系数
min_lr: 学习率下降的最小
change_step: 多少个epoch下降一次
print_step: 训练时多少个step打印一次学习率
'''
# 初始化
def __init__(self, initial_lr, decay_rate, min_lr, change_step, print_step):
# 继承父类的初始化方法
super(PiecewiseConstantDecay, self).__init__()
# 属性分配
self.initial_lr = tf.cast(initial_lr, tf.float32)
self.decay_rate = tf.cast(decay_rate, tf.float32)
self.min_lr = tf.cast(min_lr, tf.float32)
self.change_step = change_step
self.print_step = print_step
# 记录记录每个epoch的学习率
self.learning_rate_list = []
# 最开始时,学习率为初始学习率
self.current = self.initial_lr
# 前向传播
def __call__(self, step): # 这个step不是epoch
# 多少个step记录一次学习率,外部指定为一个epoch记录一次
if step % self.print_step == 0:
# 训练过程中打印每一个epoch的学习率
print('current learning_rate is ', self.current.numpy().item())
# 记录下当前epoch的学习率
self.learning_rate_list.append(self.current.numpy().item())
# 多少个step调整一次学习率
if step % self.change_step == 0:
# 计算调整后的学习率
learning_rate = self.current * self.decay_rate
# 更新当前学习率指标, 学习率不能小于指定的最小值
self.current = tf.where(learning_rate>self.min_lr, learning_rate, self.min_lr)
# 返回调整后的学习率
return self.current
# 如果为满足调整要求,就返回上一次调整的学习率
else:
return self.current3. 余弦学习率下降
余弦学习率下降公式为:
其中,?代表初始学习率,
?是指当前是第几个 step,
?是指多少个 step 之后学习率衰减为0
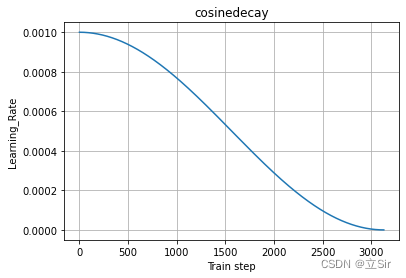
以初始学习率为 0.001,所有 epoch 结束后学习率降为 0 为例,学习率余弦下降曲线如下:
首先创建一个学习率自定义类,继承 keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule 自定义学习率调度器。
先对所有的属性完成初始化,其中?self.current 用来记录当前 step 的学习率,self.learning_rate_list 用来记录训练时所有 step 的学习率,训练结束后可调用查看。
训练时模型会传入当前的 step,调整每一个 step 的学习率 learning_rate,并且要求调整后的学习率不能低于最小学习率?self.min_lr,使用 tf.where() 函数对比调整后的学习率和最小学习率,选出最大的作为返回结果的学习率。
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# 余弦学习率下降
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# eager模式防止graph报错
tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(True)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# 继承学习率的类
class CosineDecay(keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule):
'''
initial_lr: 初始的学习率
decay_rate: 学习率衰减到最低点的步长
min_lr: 学习率下降的最小
print_step: 训练时多少个step打印一次学习率
'''
# 初始化
def __init__(self, initial_lr, decay_step, min_lr, print_step):
# 继承父类初始化方法
super(CosineDecay, self).__init__()
# 属性分配
self.initial_lr = tf.cast(initial_lr, dtype=tf.float32)
self.decay_step = tf.cast(decay_step, dtype=tf.float32)
self.min_lr = tf.cast(min_lr, dtype=tf.float32)
self.print_step = print_step
# 最开始的当前学习率等于初始学习率
self.current = self.initial_lr
# 记录每个epoch的学习率值
self.learning_rate_list = []
# 前向传播
def __call__(self, step):
# 余弦衰减计算公式
learning_rate = 0.5 * self.initial_lr * (1 + tf.math.cos(step*math.pi / self.decay_step))
# 更新当前学习率指标, 学习率不能小于指定的最小值
self.current = tf.where(learning_rate>self.min_lr, learning_rate, self.min_lr)
# 记录每个step的学习率
self.learning_rate_list.append(self.current.numpy().item())
# 多少个step打印一次学习率,外部设置每个epoch打印一次学习率
if step % self.print_step == 0:
# 在训练时打印当前学习率
print('learning_rate has changed to: ', self.current.numpy().item())
return self.current4. 实验验证
这里以学习率余弦衰减策略为例,来验证上面定义的学习率方法能不能用。
数据预处理和模型构建部分就不讲了,这部分都很基础。直接看到第(6)部分模型训练。
首先需要对我们定义的学习率下降的类 CosineDecay 进行实例化,传入计算公式中所需的初始学习率 initial_lr,余弦值下降到0所需的步长 decay_step,用变量 cosinedecay 来接收。
将自定义的学习率衰减方法传入至Adam优化器,这样在训练时就能接收到模型传入的每个step,用于计算衰减。
自定义方法也可以参照官方文档:自定义的学习速率调度
以Mnist手写数据集图像10分类问题为例,完整代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
# 调用GPU加速
gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices(device_type='GPU')
for gpu in gpus:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu, True)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# (1)读取手写数字数据集
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
print('x_train.shape:', x_train.shape, 'y_train.shape:', y_train.shape) # (60000, 28, 28) , (60000,)
print('x_test.shape:', x_test.shape) # (10000, 28, 28)
# 记录一共训练多少张图
total_train_num = x_train.shape[0]
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# (2)余弦学习率下降
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# eager模式防止graph报错
tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(True)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# 继承学习率的类
class CosineDecay(keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule):
'''
initial_lr: 初始的学习率
decay_rate: 学习率衰减到最低点的步长
min_lr: 学习率下降的最小
print_step: 训练时多少个step打印一次学习率
'''
# 初始化
def __init__(self, initial_lr, decay_step, min_lr, print_step):
# 继承父类初始化方法
super(CosineDecay, self).__init__()
# 属性分配
self.initial_lr = tf.cast(initial_lr, dtype=tf.float32)
self.decay_step = tf.cast(decay_step, dtype=tf.float32)
self.min_lr = tf.cast(min_lr, dtype=tf.float32)
self.print_step = print_step
# 最开始的当前学习率等于初始学习率
self.current = self.initial_lr
# 记录每个epoch的学习率值
self.learning_rate_list = []
# 前向传播
def __call__(self, step):
# 余弦衰减计算公式
learning_rate = 0.5 * self.initial_lr * (1 + tf.math.cos(step*math.pi / self.decay_step))
# 更新当前学习率指标, 学习率不能小于指定的最小值
self.current = tf.where(learning_rate>self.min_lr, learning_rate, self.min_lr)
# 记录每个step的学习率
self.learning_rate_list.append(self.current.numpy().item())
# 多少个step打印一次学习率,外部设置每个epoch打印一次学习率
if step % self.print_step == 0:
# 在训练时打印当前学习率
print('learning_rate has changed to: ', self.current.numpy().item())
return self.current
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# (3)参数设置
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# 每个step处理32张图
batch_size = 32
# 迭代次数
num_epochs = 10
# 初始学习率
initial_lr = 0.001
# 学习率衰减系数
decay_rate = 0.9
# 学习率下降的最小值
min_lr = 0
# 每个epoch打印一次学习率, 1个batch处理32张图
# 共60000张图,需要60000/32个batch,即1875个step
print_step = total_train_num / batch_size
# 余弦下降到0所需的步长
decay_step = total_train_num / batch_size * num_epochs
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# (4)构造数据集
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
def processing(x,y): # 预处理函数
x = 2 * tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32)/255.0 - 1 # 归一化
x = tf.expand_dims(x, axis=-1) # 增加通道维度
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x,y
# 构造训练集
train_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
train_ds = train_ds.map(processing).batch(batch_size).shuffle(10000)
# 构造测试集
test_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test))
test_ds = test_ds.map(processing).batch(batch_size)
# 迭代器查看数据是否正确
sample = next(iter(train_ds))
print('x_batch:', sample[0].shape, 'y_batch:', sample[1].shape) # (32, 28, 28, 1), (32,)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# (5)构造模型
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
inputs = keras.Input(sample[0].shape[1:]) # 构造输入层
# [28,28,1]==>[28,28,32]
x = layers.Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu')(inputs)
# [28,28,32]==>[14,14,32]
x = layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=2, padding='same')(x)
# [14,14,32]==>[14,14,64]
x = layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x)
# [14,14,64]==>[7,7,64]
x = layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=2, padding='same')(x)
# [7,7,64]==>[None,7*7*64]
x = layers.Flatten()(x)
# [None,7*7*64]==>[None,128]
x = layers.Dense(128)(x)
# [None,128]==>[None,10]
outputs = layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(x)
# 构建模型
model = keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
# 查看模型结构
model.summary()
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# (6)模型训练
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# 接收学习率调整方法
cosinedecay = CosineDecay(initial_lr=initial_lr, # 初始学习率
decay_step=decay_step, # 学习率衰减系数
min_lr=min_lr, # 最小学习率值
print_step=print_step) # 每个epoch打印一次学习率值
# 设置adam优化器,指定学习率
opt = keras.optimizers.Adam(cosinedecay)
# 网络编译
model.compile(optimizer=opt, # 学习率
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', # 损失
metrics=['accuracy']) # 监控指标
# 网络训练
model.fit(train_ds, epochs=num_epochs, validation_data=test_ds)
# 绘制学习率变化曲线
plt.plot(range(decay_step), cosinedecay.learning_rate_list)
plt.xlabel("Train step")
plt.ylabel("Learning_Rate")
plt.title('cosinedecay')
plt.grid()
plt.show()打印训练过程,可以看到每个epoch都打印了当前的学习率
Epoch 1/10
learning_rate has changed to: 0.0010000000474974513
313/313 [==============================] - 6s 19ms/step - loss: 0.6491 - accuracy: 0.7977 - val_loss: 0.0725 - val_accuracy: 0.9783
Epoch 2/10
learning_rate has changed to: 0.0009755282662808895
313/313 [==============================] - 6s 18ms/step - loss: 0.0673 - accuracy: 0.9793 - val_loss: 0.0278 - val_accuracy: 0.9911
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Epoch 9/10
learning_rate has changed to: 9.54914721660316e-05
313/313 [==============================] - 6s 18ms/step - loss: 8.1648e-04 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 7.3570e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000
Epoch 10/10
learning_rate has changed to: 2.4471701181028038e-05
313/313 [==============================] - 6s 19ms/step - loss: 8.0403e-04 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 7.2831e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000绘制学习率曲线,每个epoch的学习率保存在了 self.learning_rate_list 列表中,通过 cosinedecay.learning_rate_list 调用该列表