clear all; close all;
I=fitsread('solarspectra.fts');
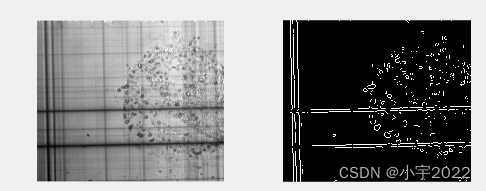
J=mat2gray(I);
BW=edge(J);
figure;
subplot(121);
imshow(J);
subplot(122);
imshow(BW);
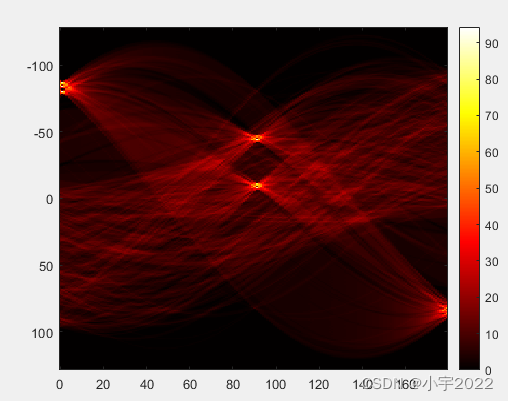
theta=0:179;
[R, xp]=radon(BW, theta);
figure;
imagesc(theta, xp, R);
colormap(hot);
colorbar;
Rmax=max(max(R))
[row, column]=find(R>=Rmax)
x=xp(row)
angel=theta(column)
close all; clear all; clc; %关闭所有图形窗口,清除工作空间所有变量,清空命令行
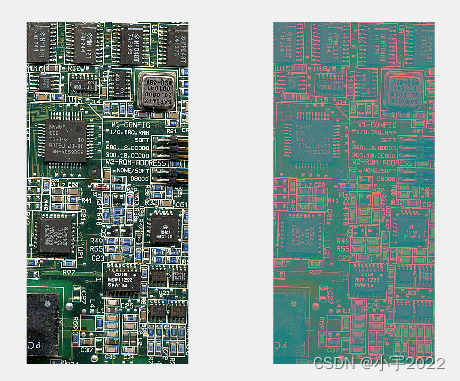
RGB = imread('board.tif'); %读入RGB图像
YCBCR = rgb2ycbcr(RGB); %将RGB图像转换为YCBCR图像
figure;
subplot(121), imshow(RGB) %显示RGB图像
subplot(122), imshow(YCBCR) %显示YCBCR图像
with(mydata,smoothScatter(x,y,main="Scatterplot Colored by Smoothed Densities"))
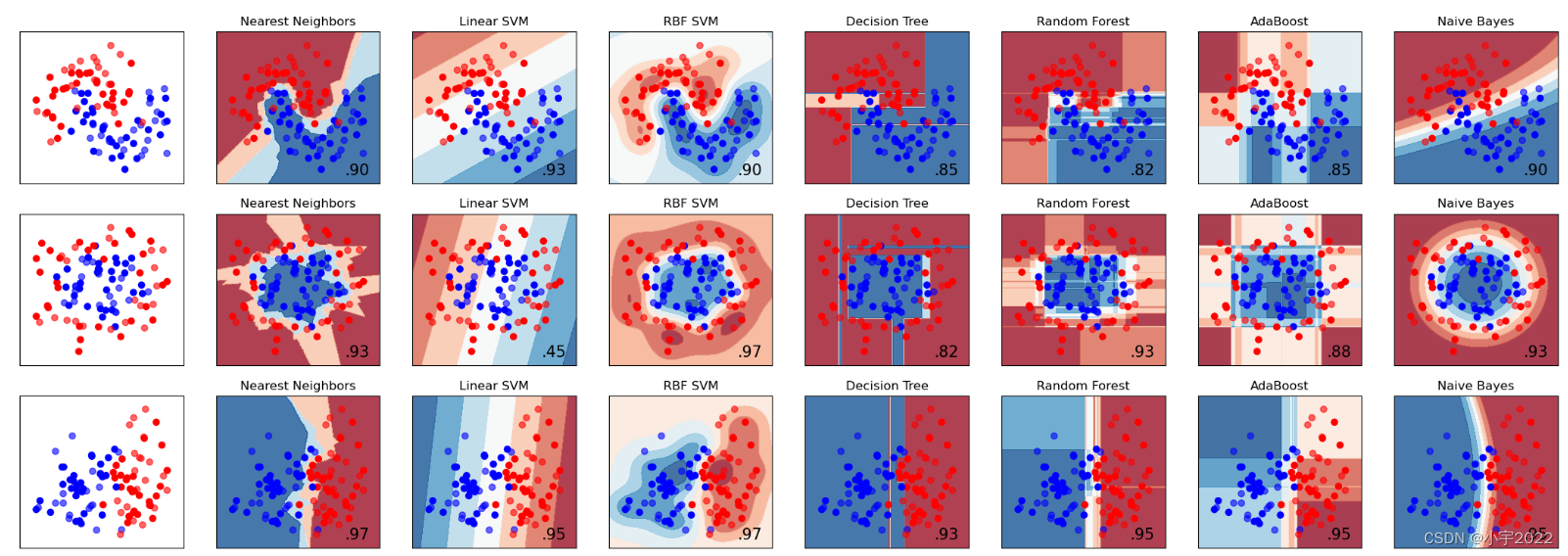
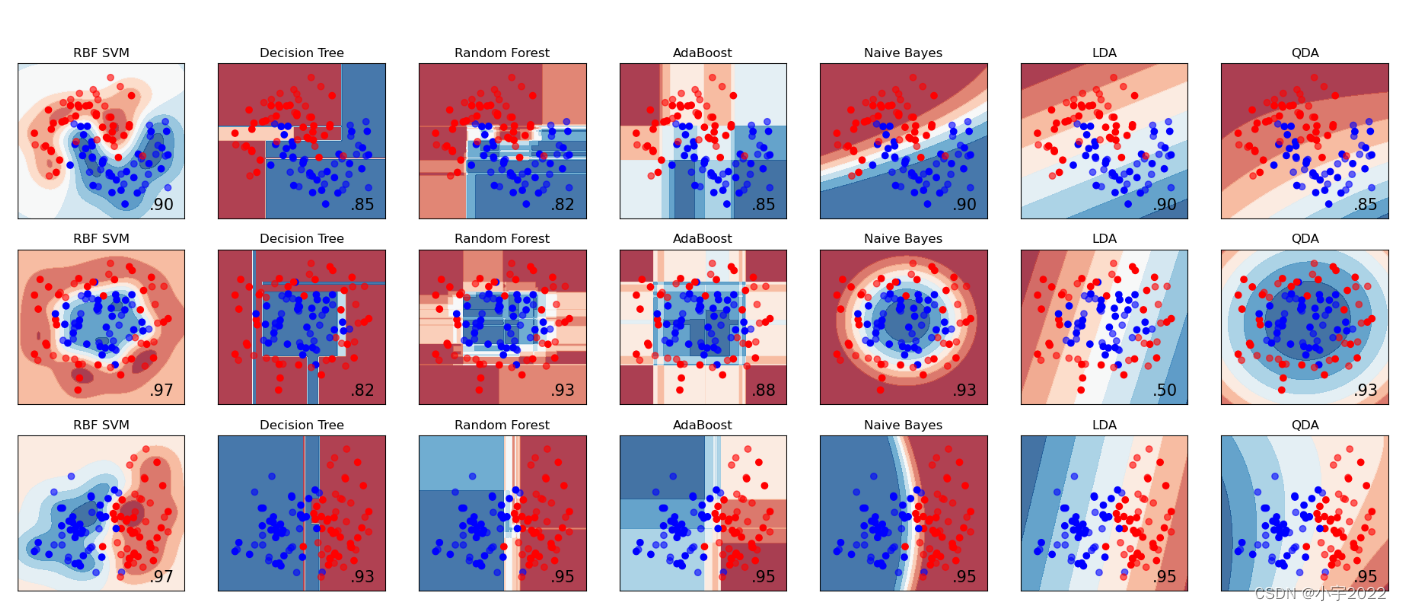
5.4 Random Forest 与其他机器学习分类算法对比
这里随机生成了三个样本集,分割面近似为月形、圆形和线形的。我们可以重点对比一下决策树和随机森林对样本空间的分割:
1)从准确率上可以看出,随机森林在这三个测试集上都要优于单棵决策树,90%>88%,90%=90%,88%=88%;
2)从特征空间上直观地可以看出,随机森林比决策树拥有更强的分割能力(非线性拟合能力)。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons, make_circles, make_classification
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis as LDA
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis as QDA
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
names = ["Nearest Neighbors", "Linear SVM", "RBF SVM", "Decision Tree",
"Random Forest", "AdaBoost", "Naive Bayes", "LDA", "QDA"]
classifiers = [
KNeighborsClassifier(3),
SVC(kernel="linear", C=0.025),
SVC(gamma=2, C=1),
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5),
RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5, n_estimators=10, max_features=1),
AdaBoostClassifier(),
GaussianNB(),
LDA(),
QDA()]
X, y = make_classification(n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2,
random_state=1, n_clusters_per_class=1)
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
X += 2 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
linearly_separable = (X, y)
datasets = [make_moons(noise=0.3, random_state=0),
make_circles(noise=0.2, factor=0.5, random_state=1),
linearly_separable
]
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(27, 9))
i = 1
# iterate over datasets
for ds in datasets:
# preprocess dataset, split into training and test part
X, y = ds
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=.4)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# just plot the dataset first
cm = plt.cm.RdBu
cm_bright = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#0000FF'])
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
# Plot the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
i += 1
# iterate over classifiers
for name, clf in zip(names, classifiers):
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = clf.score(X_test, y_test)
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
if hasattr(clf, "decision_function"):
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
else:
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1]
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cm, alpha=.8)
# Plot also the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright,
alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
ax.set_title(name)
ax.text(xx.max() - .3, yy.min() + .3, ('%.2f' % score).lstrip('0'),
size=15, horizontalalignment='right')
i += 1
figure.subplots_adjust(left=.02, right=.98)
plt.show()```
