文章目录
HRNet CVPR2019
HRNet,是高分辨率网络 (High-Resolution Net) 的缩写。
1. 简介
中科大和微软亚洲研究院,发布了新的人体姿态估计模型,刷新了三项COCO纪录,还中选了CVPR 2019。
这个名叫HRNet的神经网络,拥有与众不同的并联结构,可以随时保持高分辨率表征,不只靠从低分辨率表征里,恢复高分辨率表征。如此一来,姿势识别的效果明显提升:
在COCO数据集的关键点检测、姿态估计、多人姿态估计这三项任务里,HRNet都超越了所有前辈。
改变输入头,就可以做目标分割,分类等任务
2. 网络架构
2.1 总揽图

第一步stem net
从 IMG 到 1/4 大小的 feature map,得到此尺寸的特征图后,之后的 HRNet 始终保持此尺寸的图片
第二步HRNet 4 stages:如下图所示的 4 阶段 由 HighResolutionModule 组成的模型
- 每个stage产生的multi-scale特征图
- stage 的连接处有 transition 结构,用于在不同 stage 之间连接,完成 channels 及 feature map 大小对应。
第三步segment head
将stage4输出的4种scale特征concat到一起,加上num_channels->num_classes层,得到分割结果
2.2 3*3卷积块
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
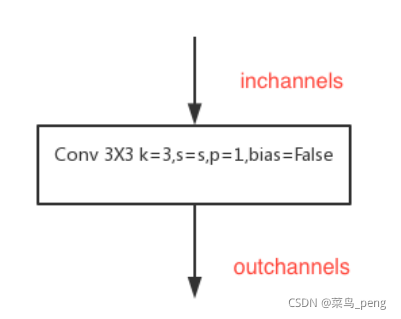
2.3 BasicBlock
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
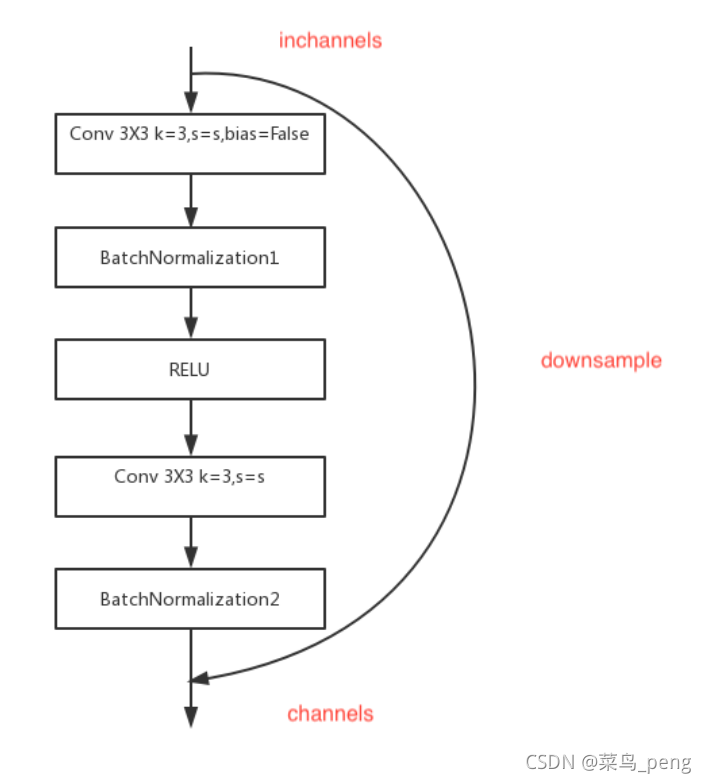
2.4 三层残差块
expansion的参数,这个参数用来控制卷积的输入输出通道数。
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1,
bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion,
momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
2.5 HighResolutionNet
- 原图先降成1/4大小
- 执行1个stage1(4个block)
- 通过卷积生成1/2分辨率的流(现在有两条流)
- 执行1个stage2(两个流的4个block以及两个流之间交融)
- 通过卷积生成1/4分辨率的流(现在有三条流)
- 执行4个stage3(三个流的4个block以及三个流之间交融)
- 通过卷积生成1/8分辨率的流(现在有四条流)
- 执行3个stage4(四个流的4个block以及四个流之间交融)
- 上采样下面三条流,使之大小变回原大小,在concat拼接channel用于后续分割任务
结构初始化 __init__()
HRNet 类定义,通过 config 指定的模型结构,实例化特定结构的模型,构建过程如下
def __init__(self, config, **kwargs):
"""
# stem net
# 两层 3x3 conv,stride=2,得到 1/4 大小的 feature map
# 开始 HRModule 阶段
# 每个 stage 不仅保留之前所有 size 的特征,还增加一个新的下采样 size 特征
# stage1: [1/4]
# stage2: [1/4, 1/8]
# stage3: [1/4, 1/8, 1/16]
# stage4: [1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32]
# last_layers,即 segment head
# 从 num_channels 到 num_classes,完成语义分割
"""
构建 stage 间转换层 _make_transition_layer()
transition layer 完成 stage 之间连接需要的 两种转换
- input channels 转换
- feature size downsample
def _make_transition_layer(self, num_channels_pre_layer, num_channels_cur_layer):
"""
:param num_channels_pre_layer: pre_stage output channels list
:param num_channels_cur_layer: cur_stage output channels list
cur 总比 pre 多一个 output_channel 对应增加的 1/2 下采样
stage2 stage3 stage4
pre: [256] [48,96] [48,96,192]
cur: [48,96] [48,96,192] [48,96,192,384]
每个 stage channels 数量也对应了 stage2/3/4 使用 BASIC block; expansion=1
:return:
transition_layers:
1.完成 pre_layer 到 cur_layer input channels 数量对应
2.完成 feature map 尺寸对应
"""
以下为 hrnet_w48 的 transition 具体结构
# stage 1-2
(transition1): ModuleList(
# input channels,从 1/4 到 1/4,完成通道数量转换
(0): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(256, 48, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(48, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU()
)
# input channels + downsample,从 1/4 到 1/8,不仅通道数量,而且使用 stride=2 进行下采样
(1): Sequential(
(0): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(256, 96, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU()
)
)
)
# stage 2-3
(transition2): ModuleList(
(0): None # 因为 同层对应的连接处的 feature map channels 和 size 一致,所以不需要转换
(1): None
# downsample,stage2 末尾,从 1/8 到 1/16,需要使用 stride=2 下采样
(2): Sequential(
(0): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(96, 192, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU()
)
)
)
# stage 3-4
(transition3): ModuleList(
(0): None
(1): None
(2): None
# downsample,同 stage2 用法一样,因为前3个branch对应的 feature map 可以直接连接,所以只要对末尾完成 1/16 到 1/32 下采样
(3): Sequential(
(0): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(384, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU()
)
)
)
构建 stage1 的 layer _make_layer()
stage1 产生 1/4 feature map,没有 branch 分支结构,采用与 resnet 完成一样的 _make_layer() 函数构建层
def _make_layer(self, block, inplanes, planes, blocks, stride=1):
"""
:param block: BasicBlock / Bottleneck
:param inplanes: 输入通道数
:param planes: 中间通道数
:param blocks: layer 内 block 重复次数
:param stride: 步长 >1 说明 layer 连接处有下采样,需要 downsample
:return:
"""
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
# stride=1 and inplanes == planes * block.expansion; 为 layer 内部 block
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
构建 stage 2/3/4 的 layer _make_stage
stage 2/3/4 为 HRNet 核心结构,用到了 HighResolutionModule,内含 branch 构建和 特征 fuse 模块
def _make_stage(self, layer_config, num_inchannels, multi_scale_output=True):
"""
创建 num_modules 个 HighResolutionModule 结构,每个 module 末尾完成 hrnet 特有的特征融合模块
:param layer_config: 从 yaml config 文件读取到的 stage 配置
:param num_inchannels: 由 NUM_CHANNELS 和 block.expansion 相乘得到
:param multi_scale_output: 都是 True
:return:
num_modules 个 HighResolutionModule 串联结构
其中每个 HighResolutionModule 先有 branch 分支并行,末尾处再将不同 scale 的特征交叉 sum 融合
"""
# eg. stage2
num_modules = layer_config['NUM_MODULES'] # 1, HighResolutionModule 重复次数
num_branches = layer_config['NUM_BRANCHES'] # 2, 并行分支数,高度
num_blocks = layer_config['NUM_BLOCKS'] # [4,4],每个分支 block 重复次数
num_channels = layer_config['NUM_CHANNELS'] # [48,96],每个分支 channels
block = blocks_dict[layer_config['BLOCK']] # BASIC
fuse_method = layer_config['FUSE_METHOD'] # SUM,multi scale 特征融合方式
modules = []
for i in range(num_modules): # HighResolutionModule 重复次数
if not multi_scale_output and i == num_modules - 1:
reset_multi_scale_output = False
else:
reset_multi_scale_output = True
modules.append(
HighResolutionModule(num_branches, # 高度
block, # BASIC/BOTTLENECK
num_blocks, # 宽度
num_inchannels, # block feature 宽度
num_channels,
fuse_method,
reset_multi_scale_output)
)
num_inchannels = modules[-1].get_num_inchannels() # cls method
return nn.Sequential(*modules), num_inchannels
2.6 高分辨率模块HighResolutionModule
实现下图红框中的,branch 并行 多 scale 特征提取 和 末端将 多 scale 特征通过 upsample/downsample 方式融合

class HighResolutionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_inchannels,
num_channels, fuse_method, multi_scale_output=True):
super(HighResolutionModule, self).__init__()
self._check_branches(
num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_inchannels, num_channels)
self.num_inchannels = num_inchannels
self.fuse_method = fuse_method
self.num_branches = num_branches
self.multi_scale_output = multi_scale_output
self.branches = self._make_branches(
num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_channels)
self.fuse_layers = self._make_fuse_layers()
self.relu = nn.ReLU(False)
check_branches()
这个函数的作用是检查,在高分辨率模块中num_branches(int类型),和len(num_inchannels(里面的元素是int)),和len(num_channels(里面的元素是int))它们三个的值是否相等。
def _check_branches(self, num_branches, blocks, num_blocks,
num_inchannels, num_channels):
if num_branches != len(num_blocks):
error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_BLOCKS({})'.format(
num_branches, len(num_blocks))
logger.error(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
if num_branches != len(num_channels):
error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_CHANNELS({})'.format(
num_branches, len(num_channels))
logger.error(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
if num_branches != len(num_inchannels):
error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_INCHANNELS({})'.format(
num_branches, len(num_inchannels))
logger.error(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
构建一个横向分支make_one_branch
它的作用就是创建一个新的分支,如图
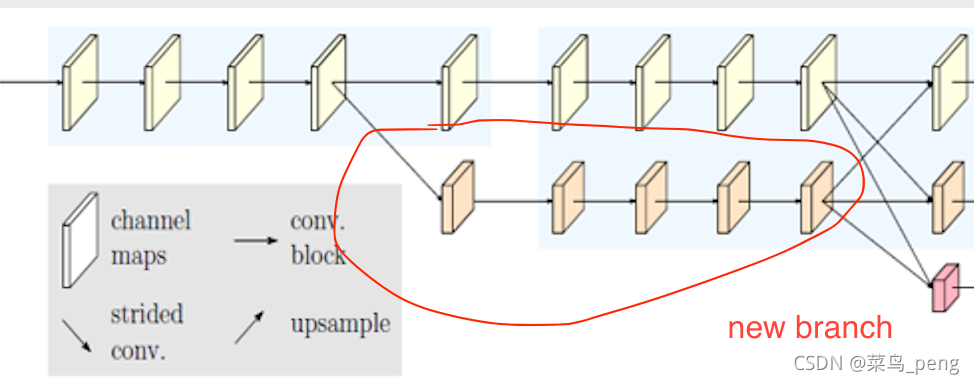
def _make_one_branch(self, branch_index, block, num_blocks, num_channels,
stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or \
self.num_inchannels[branch_index] != num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.num_inchannels[branch_index],
num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion,
momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.num_inchannels[branch_index],
num_channels[branch_index], stride, downsample))
self.num_inchannels[branch_index] = \
num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion
for i in range(1, num_blocks[branch_index]):
layers.append(block(self.num_inchannels[branch_index],
num_channels[branch_index]))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
make_branches函数是看看每个stage里面有多少branch,然后有几个就调用几次_make_one_branch函数。
根据 stage cfg 中指定的 branch 数量,构建多个并行的 branch,调用之前的 _make_one_branch(),如 stage 2/3/4 各有 2/3/4 个 branches
def _make_branches(self, num_branches, block, num_blocks, num_channels):
"""
并行分支的 ModuleList 结构
:param num_branches: 分支数
:param block: BASIC/BOTTLENECK
:param num_blocks: 每个分支 block 重复次数
:param num_channels: 每个分支 channel
:return:
"""
branches = []
for i in range(num_branches):
branches.append( # add one branch, 内部 features, stride=1
self._make_one_branch(i, block, num_blocks, num_channels, stride=1))
return nn.ModuleList(branches) # 使用 ModuleList 得到并行分支结果
forward
def forward(self, x):
if self.num_branches == 1:
return [self.branches[0](x[0])]
for i in range(self.num_branches):
x[i] = self.branches[i](x[i])
x_fuse = []
for i in range(len(self.fuse_layers)):
y = x[0] if i == 0 else self.fuse_layers[i][0](x[0])
for j in range(1, self.num_branches):
if i == j:
y = y + x[j]
else:
y = y + self.fuse_layers[i][j](x[j])
x_fuse.append(self.relu(y))
return x_fuse
构建 multi-scale 特征融合层:fuse_layer函数
HighResolutionModule 末尾的特征融合层
以下图红框即 stage3 中 蓝色 branch 输出结果为例,其输出结果要转换成 4 种尺度的特征,用于每个 branch 末尾的特征融合
- 1/8 ↗ 1/4,不同层,channel 不同,size 不同 👉 通道转换 + 上采样 (在 forward 函数中由双线性插值完成)
- 1/8 → 1/8,相同层,channel 一致,size 一致 👉 None,直接使用 feature
- 1/8 ↘ 1/16,不同层,channel 不同,size 不同 👉 通道转换 + 下采样 (通过串联的 stride=2 的 3x3 conv 完成)
- 1/8 ↘ 1/32,同上

def _make_fuse_layers(self):
"""
混合 branch 输出结果,得到 fusion 特征
:return:
fuse ModuleList(): 每个 branch 都会输出一组 生成不同大小 output 的 Sequential
[
branch1 ModuleList(), 1/4 -> [1/4, 1/8, 1/16]
branch2 ModuleList(), 1/8 -> [1/4, 1/8, 1/16]
branch3 ModuleList(), 1/16 -> [1/4, 1/8, 1/16]
]
"""
if self.num_branches == 1:
return None
num_branches = self.num_branches
num_inchannels = self.num_inchannels
fuse_layers = []
for i in range(num_branches if self.multi_scale_output else 1):
fuse_layer = []
for j in range(num_branches):
if j > i: # ↗, 深 -> 浅, 通道转换,上采样 (forward 完成)
fuse_layer.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_inchannels[j], num_inchannels[i], # 通道转换
1, 1, 0, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(num_inchannels[i], momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)))
elif j == i: # → 同层
fuse_layer.append(None)
else: # ↘, 浅 -> 深, 下采样
conv3x3s = []
for k in range(i - j):
if k == i - j - 1: # 下采样次数
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_inchannels[j], num_inchannels[i],
3, 2, 1, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(num_inchannels[i], momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)))
else:
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_inchannels[j], num_inchannels[j],
3, 2, 1, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(num_inchannels[j], momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False)))
fuse_layer.append(nn.Sequential(*conv3x3s))
fuse_layers.append(nn.ModuleList(fuse_layer))
return nn.ModuleList(fuse_layers)
transition_layers函数(上图中画叉的那一个分支)
transition layer 完成 stage 之间连接需要的 两种转换
(1)input channels 转换
(2)feature size downsample
def _make_transition_layer(
self, num_channels_pre_layer, num_channels_cur_layer):
num_branches_cur = len(num_channels_cur_layer)
num_branches_pre = len(num_channels_pre_layer)
transition_layers = []
for i in range(num_branches_cur):
if i < num_branches_pre:
if num_channels_cur_layer[i] != num_channels_pre_layer[i]:
transition_layers.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_channels_pre_layer[i],
num_channels_cur_layer[i],
3,
1,
1,
bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(
num_channels_cur_layer[i], momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)))
else:
transition_layers.append(None)
else:
conv3x3s = []
for j in range(i+1-num_branches_pre):
inchannels = num_channels_pre_layer[-1]
outchannels = num_channels_cur_layer[i] \
if j == i-num_branches_pre else inchannels
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
inchannels, outchannels, 3, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannels, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)))
transition_layers.append(nn.Sequential(*conv3x3s))
return nn.ModuleList(transition_layers)
3. 训练
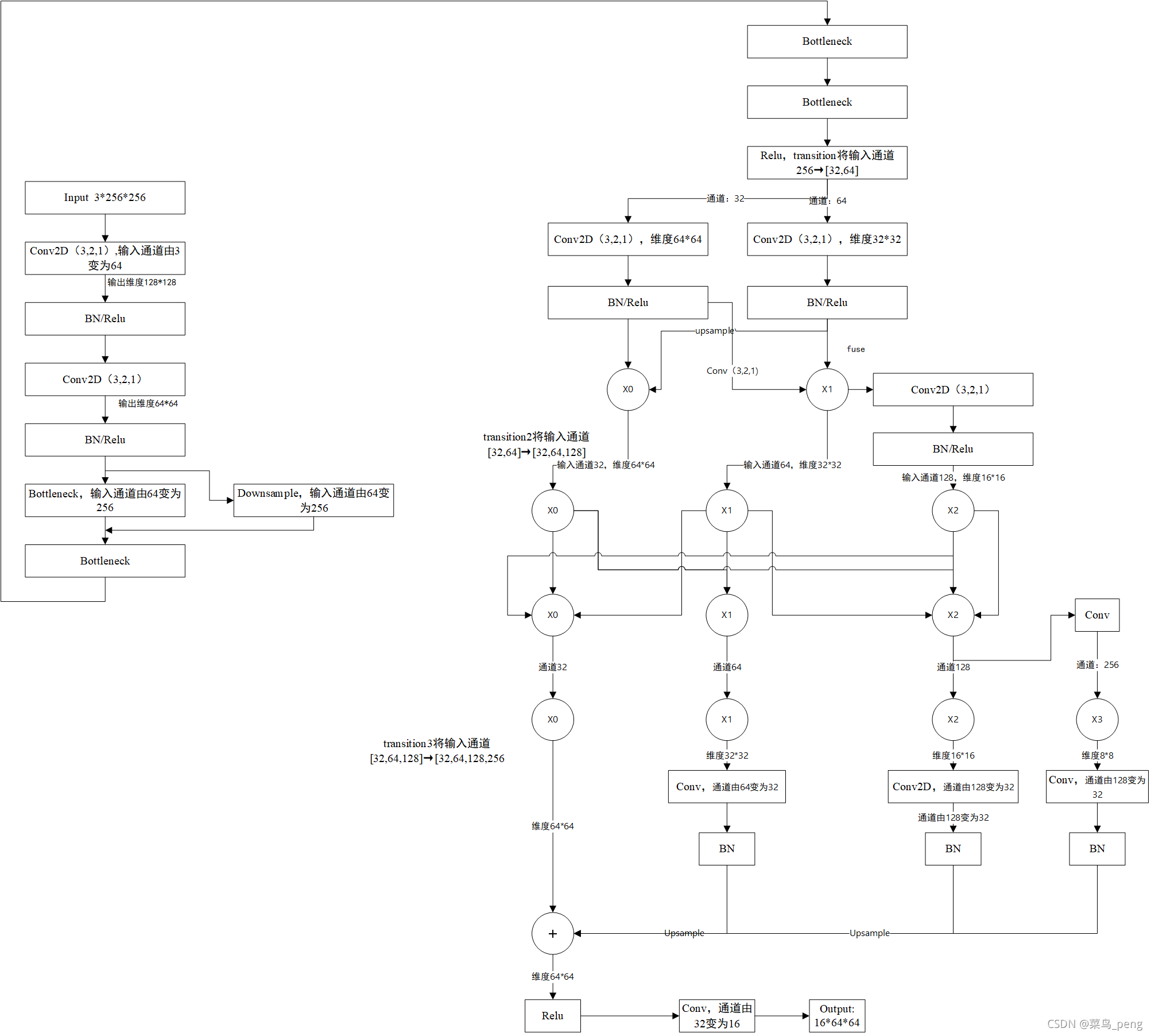
- 构建 stage1 的 layer _make_layer()
stage1 产生 1/4 feature map,没有 branch 分支结构,采用与 resnet 完成一样的 _make_layer() 函数构建层 - 构建 stage 2/3/4 的 layer _make_stage
stage 2/3/4 为 HRNet 核心结构,用到了核心类 HighResolutionModule,内含 make_branches 构建和特征 _make_fuse_layers 模块
4. 代码
4.1 简易版
import torch
from torch import nn
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, bn_momentum=0.1):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=bn_momentum)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=bn_momentum)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion, momentum=bn_momentum)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, bn_momentum=0.1):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=bn_momentum)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=bn_momentum)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class StageModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, stage, output_branches, c, bn_momentum):
super(StageModule, self).__init__()
self.stage = stage
self.output_branches = output_branches
self.branches = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(self.stage):
w = c * (2 ** i)
branch = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(w, w, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
BasicBlock(w, w, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
BasicBlock(w, w, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
BasicBlock(w, w, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
)
self.branches.append(branch)
self.fuse_layers = nn.ModuleList()
# for each output_branches (i.e. each branch in all cases but the very last one)
for i in range(self.output_branches):
self.fuse_layers.append(nn.ModuleList())
for j in range(self.stage): # for each branch
if i == j:
self.fuse_layers[-1].append(nn.Sequential()) # Used in place of "None" because it is callable
elif i < j:
self.fuse_layers[-1].append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(c * (2 ** j), c * (2 ** i), kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c * (2 ** i), eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=(2.0 ** (j - i)), mode='nearest'),
))
elif i > j:
ops = []
for k in range(i - j - 1):
ops.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(c * (2 ** j), c * (2 ** j), kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1),
bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c * (2 ** j), eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True,
track_running_stats=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
))
ops.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(c * (2 ** j), c * (2 ** i), kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1),
bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c * (2 ** i), eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True),
))
self.fuse_layers[-1].append(nn.Sequential(*ops))
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
assert len(self.branches) == len(x)
x = [branch(b) for branch, b in zip(self.branches, x)]
x_fused = []
for i in range(len(self.fuse_layers)):
for j in range(0, len(self.branches)):
if j == 0:
x_fused.append(self.fuse_layers[i][0](x[0]))
else:
x_fused[i] = x_fused[i] + self.fuse_layers[i][j](x[j])
for i in range(len(x_fused)):
x_fused[i] = self.relu(x_fused[i])
return x_fused
class HRNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c=48, nof_joints=17, bn_momentum=0.1):
super(HRNet, self).__init__()
# Input (stem net)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=bn_momentum, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=bn_momentum, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
# Stage 1 (layer1) - First group of bottleneck (resnet) modules
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=bn_momentum, affine=True, track_running_stats=True),
)
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
Bottleneck(64, 64, downsample=downsample),
Bottleneck(256, 64),
Bottleneck(256, 64),
Bottleneck(256, 64),
)
# Fusion layer 1 (transition1) - Creation of the first two branches (one full and one half resolution)
self.transition1 = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, c, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c, eps=1e-05, momentum=bn_momentum, affine=True, track_running_stats=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
),
nn.Sequential(nn.Sequential( # Double Sequential to fit with official pretrained weights
nn.Conv2d(256, c * (2 ** 1), kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c * (2 ** 1), eps=1e-05, momentum=bn_momentum, affine=True, track_running_stats=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)),
])
# Stage 2 (stage2) - Second module with 1 group of bottleneck (resnet) modules. This has 2 branches
self.stage2 = nn.Sequential(
StageModule(stage=2, output_branches=2, c=c, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
)
# Fusion layer 2 (transition2) - Creation of the third branch (1/4 resolution)
self.transition2 = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Sequential(), # None, - Used in place of "None" because it is callable
nn.Sequential(), # None, - Used in place of "None" because it is callable
nn.Sequential(nn.Sequential( # Double Sequential to fit with official pretrained weights
nn.Conv2d(c * (2 ** 1), c * (2 ** 2), kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c * (2 ** 2), eps=1e-05, momentum=bn_momentum, affine=True, track_running_stats=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)), # ToDo Why the new branch derives from the "upper" branch only?
])
# Stage 3 (stage3) - Third module with 4 groups of bottleneck (resnet) modules. This has 3 branches
self.stage3 = nn.Sequential(
StageModule(stage=3, output_branches=3, c=c, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
StageModule(stage=3, output_branches=3, c=c, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
StageModule(stage=3, output_branches=3, c=c, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
StageModule(stage=3, output_branches=3, c=c, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
)
# Fusion layer 3 (transition3) - Creation of the fourth branch (1/8 resolution)
self.transition3 = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Sequential(), # None, - Used in place of "None" because it is callable
nn.Sequential(), # None, - Used in place of "None" because it is callable
nn.Sequential(), # None, - Used in place of "None" because it is callable
nn.Sequential(nn.Sequential( # Double Sequential to fit with official pretrained weights
nn.Conv2d(c * (2 ** 2), c * (2 ** 3), kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c * (2 ** 3), eps=1e-05, momentum=bn_momentum, affine=True, track_running_stats=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)), # ToDo Why the new branch derives from the "upper" branch only?
])
# Stage 4 (stage4) - Fourth module with 3 groups of bottleneck (resnet) modules. This has 4 branches
self.stage4 = nn.Sequential(
StageModule(stage=4, output_branches=4, c=c, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
StageModule(stage=4, output_branches=4, c=c, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
StageModule(stage=4, output_branches=1, c=c, bn_momentum=bn_momentum),
)
# Final layer (final_layer)
self.final_layer = nn.Conv2d(c, nof_joints, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = [trans(x) for trans in self.transition1] # Since now, x is a list (# == nof branches)
x = self.stage2(x)
# x = [trans(x[-1]) for trans in self.transition2] # New branch derives from the "upper" branch only
x = [
self.transition2[0](x[0]),
self.transition2[1](x[1]),
self.transition2[2](x[-1])
] # New branch derives from the "upper" branch only
x = self.stage3(x)
# x = [trans(x) for trans in self.transition3] # New branch derives from the "upper" branch only
x = [
self.transition3[0](x[0]),
self.transition3[1](x[1]),
self.transition3[2](x[2]),
self.transition3[3](x[-1])
] # New branch derives from the "upper" branch only
x = self.stage4(x)
x = self.final_layer(x[0])
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 抄袭代码来源https://github.com/stefanopini/simple-HRNet/blob/master/models/hrnet.py
# model = HRNet(48, 17, 0.1)
model = HRNet(32, 17, 0.1)
device = torch.device('cpu')
model = model.to(device)
y = model(torch.ones(2, 3, 512, 512).to(device))
print(y.shape)
print(torch.min(y).item(), torch.mean(y).item(), torch.max(y).item())
4.2 原版
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Copyright (c) Microsoft
# Licensed under the MIT License.
# Written by RainbowSecret (yhyuan@pku.edu.cn)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
__all__ = ['hrnet18', 'hrnet32', 'hrnet48']
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, groups=1, dilation=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False, dilation=dilation)
def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
if groups != 1 or base_width != 64:
raise ValueError('BasicBlock only supports groups=1 and base_width=64')
if dilation > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("Dilation > 1 not supported in BasicBlock")
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
width = int(planes * (base_width / 64.)) * groups
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, width)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(width, width, stride, groups, dilation)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(width, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = norm_layer(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class HighResolutionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_inchannels,
num_channels, fuse_method, multi_scale_output=True, norm_layer=None):
super(HighResolutionModule, self).__init__()
self._check_branches(
num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_inchannels, num_channels)
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
self.norm_layer = norm_layer
self.num_inchannels = num_inchannels
self.fuse_method = fuse_method
self.num_branches = num_branches
self.multi_scale_output = multi_scale_output
self.branches = self._make_branches(
num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_channels)
self.fuse_layers = self._make_fuse_layers()
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def _check_branches(self, num_branches, blocks, num_blocks,
num_inchannels, num_channels):
if num_branches != len(num_blocks):
error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_BLOCKS({})'.format(
num_branches, len(num_blocks))
print(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
if num_branches != len(num_channels):
error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_CHANNELS({})'.format(
num_branches, len(num_channels))
print(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
if num_branches != len(num_inchannels):
error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_INCHANNELS({})'.format(
num_branches, len(num_inchannels))
print(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
def _make_one_branch(self, branch_index, block, num_blocks, num_channels,
stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or \
self.num_inchannels[branch_index] != num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.num_inchannels[branch_index],
num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
self.norm_layer(num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.num_inchannels[branch_index],
num_channels[branch_index], stride, downsample, norm_layer=self.norm_layer))
self.num_inchannels[branch_index] = \
num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion
for i in range(1, num_blocks[branch_index]):
layers.append(block(self.num_inchannels[branch_index],
num_channels[branch_index], norm_layer=self.norm_layer))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _make_branches(self, num_branches, block, num_blocks, num_channels):
branches = []
for i in range(num_branches):
branches.append(
self._make_one_branch(i, block, num_blocks, num_channels))
return nn.ModuleList(branches)
def _make_fuse_layers(self):
if self.num_branches == 1:
return None
num_branches = self.num_branches
num_inchannels = self.num_inchannels
fuse_layers = []
for i in range(num_branches if self.multi_scale_output else 1):
fuse_layer = []
for j in range(num_branches):
if j > i:
fuse_layer.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_inchannels[j],
num_inchannels[i],
1,
1,
0,
bias=False),
self.norm_layer(num_inchannels[i])))
elif j == i:
fuse_layer.append(None)
else:
conv3x3s = []
for k in range(i - j):
if k == i - j - 1:
num_outchannels_conv3x3 = num_inchannels[i]
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_inchannels[j],
num_outchannels_conv3x3,
3, 2, 1, bias=False),
self.norm_layer(num_outchannels_conv3x3)))
else:
num_outchannels_conv3x3 = num_inchannels[j]
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_inchannels[j],
num_outchannels_conv3x3,
3, 2, 1, bias=False),
self.norm_layer(num_outchannels_conv3x3),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)))
fuse_layer.append(nn.Sequential(*conv3x3s))
fuse_layers.append(nn.ModuleList(fuse_layer))
return nn.ModuleList(fuse_layers)
def get_num_inchannels(self):
return self.num_inchannels
def forward(self, x):
if self.num_branches == 1:
return [self.branches[0](x[0])]
for i in range(self.num_branches):
x[i] = self.branches[i](x[i])
x_fuse = []
for i in range(len(self.fuse_layers)):
y = x[0] if i == 0 else self.fuse_layers[i][0](x[0])
for j in range(1, self.num_branches):
if i == j:
y = y + x[j]
elif j > i:
width_output = x[i].shape[-1]
height_output = x[i].shape[-2]
y = y + F.interpolate(
self.fuse_layers[i][j](x[j]),
size=[height_output, width_output],
mode='bilinear',
align_corners=True
)
else:
y = y + self.fuse_layers[i][j](x[j])
x_fuse.append(self.relu(y))
return x_fuse
blocks_dict = {
'BASIC': BasicBlock,
'BOTTLENECK': Bottleneck
}
class HighResolutionNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
cfg,
norm_layer=None):
super(HighResolutionNet, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
self.norm_layer = norm_layer
# stem network
# stem net
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = self.norm_layer(64)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1,
bias=False)
self.bn2 = self.norm_layer(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
# stage 1
self.stage1_cfg = cfg['STAGE1']
num_channels = self.stage1_cfg['NUM_CHANNELS'][0]
block = blocks_dict[self.stage1_cfg['BLOCK']]
num_blocks = self.stage1_cfg['NUM_BLOCKS'][0]
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_channels, num_blocks)
stage1_out_channel = block.expansion * num_channels
# stage 2
self.stage2_cfg = cfg['STAGE2']
num_channels = self.stage2_cfg['NUM_CHANNELS']
block = blocks_dict[self.stage2_cfg['BLOCK']]
num_channels = [
num_channels[i] * block.expansion for i in range(len(num_channels))]
self.transition1 = self._make_transition_layer(
[stage1_out_channel], num_channels)
self.stage2, pre_stage_channels = self._make_stage(
self.stage2_cfg, num_channels)
# stage 3
self.stage3_cfg = cfg['STAGE3']
num_channels = self.stage3_cfg['NUM_CHANNELS']
block = blocks_dict[self.stage3_cfg['BLOCK']]
num_channels = [
num_channels[i] * block.expansion for i in range(len(num_channels))]
self.transition2 = self._make_transition_layer(
pre_stage_channels, num_channels)
self.stage3, pre_stage_channels = self._make_stage(
self.stage3_cfg, num_channels)
# stage 4
self.stage4_cfg = cfg['STAGE4']
num_channels = self.stage4_cfg['NUM_CHANNELS']
block = blocks_dict[self.stage4_cfg['BLOCK']]
num_channels = [
num_channels[i] * block.expansion for i in range(len(num_channels))]
self.transition3 = self._make_transition_layer(
pre_stage_channels, num_channels)
self.stage4, pre_stage_channels = self._make_stage(
self.stage4_cfg, num_channels, multi_scale_output=True)
last_inp_channels = np.int_(np.sum(pre_stage_channels))
self.last_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=last_inp_channels,
out_channels=last_inp_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0),
self.norm_layer(last_inp_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=last_inp_channels,
out_channels=19,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
)
def _make_transition_layer(
self, num_channels_pre_layer, num_channels_cur_layer):
num_branches_cur = len(num_channels_cur_layer)
num_branches_pre = len(num_channels_pre_layer)
transition_layers = []
for i in range(num_branches_cur):
if i < num_branches_pre:
if num_channels_cur_layer[i] != num_channels_pre_layer[i]:
transition_layers.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_channels_pre_layer[i],
num_channels_cur_layer[i],
3,
1,
1,
bias=False),
self.norm_layer(num_channels_cur_layer[i]),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)))
else:
transition_layers.append(None)
else:
conv3x3s = []
for j in range(i + 1 - num_branches_pre):
inchannels = num_channels_pre_layer[-1]
outchannels = num_channels_cur_layer[i] \
if j == i - num_branches_pre else inchannels
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
inchannels, outchannels, 3, 2, 1, bias=False),
self.norm_layer(outchannels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)))
transition_layers.append(nn.Sequential(*conv3x3s))
return nn.ModuleList(transition_layers)
def _make_layer(self, block, inplanes, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
self.norm_layer(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, norm_layer=self.norm_layer))
inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(inplanes, planes, norm_layer=self.norm_layer))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _make_stage(self, layer_config, num_inchannels,
multi_scale_output=True):
num_modules = layer_config['NUM_MODULES']
num_branches = layer_config['NUM_BRANCHES']
num_blocks = layer_config['NUM_BLOCKS']
num_channels = layer_config['NUM_CHANNELS']
block = blocks_dict[layer_config['BLOCK']]
fuse_method = layer_config['FUSE_METHOD']
modules = []
for i in range(num_modules):
# multi_scale_output is only used last module
if not multi_scale_output and i == num_modules - 1:
reset_multi_scale_output = False
else:
reset_multi_scale_output = True
modules.append(
HighResolutionModule(num_branches,
block,
num_blocks,
num_inchannels,
num_channels,
fuse_method,
reset_multi_scale_output,
norm_layer=self.norm_layer)
)
num_inchannels = modules[-1].get_num_inchannels()
return nn.Sequential(*modules), num_inchannels
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x_list = []
for i in range(self.stage2_cfg['NUM_BRANCHES']):
if self.transition1[i] is not None:
x_list.append(self.transition1[i](x))
else:
x_list.append(x)
y_list = self.stage2(x_list)
x_list = []
for i in range(self.stage3_cfg['NUM_BRANCHES']):
if self.transition2[i] is not None:
if i < self.stage2_cfg['NUM_BRANCHES']:
x_list.append(self.transition2[i](y_list[i]))
else:
x_list.append(self.transition2[i](y_list[-1]))
else:
x_list.append(y_list[i])
y_list = self.stage3(x_list)
x_list = []
for i in range(self.stage4_cfg['NUM_BRANCHES']):
if self.transition3[i] is not None:
if i < self.stage3_cfg['NUM_BRANCHES']:
x_list.append(self.transition3[i](y_list[i]))
else:
x_list.append(self.transition3[i](y_list[-1]))
else:
x_list.append(y_list[i])
x = self.stage4(x_list)
# Upsampling
x0_h, x0_w = x[0].size(2), x[0].size(3)
x1 = F.interpolate(x[1], size=(x0_h, x0_w), mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
x2 = F.interpolate(x[2], size=(x0_h, x0_w), mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
x3 = F.interpolate(x[3], size=(x0_h, x0_w), mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
x = torch.cat([x[0], x1, x2, x3], 1)
x = self.last_layer(x)
return x
cfg = {
"hrnet48": {
"FINAL_CONV_KERNEL": 1,
"STAGE1": {
"NUM_MODULES": 1,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 1,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [64],
"BLOCK": 'BOTTLENECK',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
},
"STAGE2": {
"NUM_MODULES": 1,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 2,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4, 4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [48, 96],
"BLOCK": 'BASIC',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
},
"STAGE3": {
"NUM_MODULES": 4,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 3,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4, 4, 4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [48, 96, 192],
"BLOCK": 'BASIC',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
},
"STAGE4": {
"NUM_MODULES": 3,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 4,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4, 4, 4, 4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [48, 96, 192, 384],
"BLOCK": 'BASIC',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
}
},
"hrnet32": {
"FINAL_CONV_KERNEL": 1,
"STAGE1": {
"NUM_MODULES": 1,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 1,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [64],
"BLOCK": 'BOTTLENECK',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
},
"STAGE2": {
"NUM_MODULES": 1,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 2,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4, 4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [32, 64],
"BLOCK": 'BASIC',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
},
"STAGE3": {
"NUM_MODULES": 4,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 3,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4, 4, 4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [32, 64, 128],
"BLOCK": 'BASIC',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
},
"STAGE4": {
"NUM_MODULES": 3,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 4,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4, 4, 4, 4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [32, 64, 128, 256],
"BLOCK": 'BASIC',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
}
},
"hrnet18": {
"FINAL_CONV_KERNEL": 1,
"STAGE1": {
"NUM_MODULES": 1,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 1,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [64],
"BLOCK": 'BOTTLENECK',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
},
"STAGE2": {
"NUM_MODULES": 1,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 2,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4, 4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [18, 36],
"BLOCK": 'BASIC',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
},
"STAGE3": {
"NUM_MODULES": 4,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 3,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4, 4, 4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [18, 36, 72],
"BLOCK": 'BASIC',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
},
"STAGE4": {
"NUM_MODULES": 3,
"NUM_BRANCHES": 4,
"NUM_BLOCKS": [4, 4, 4, 4],
"NUM_CHANNELS": [18, 36, 72, 144],
"BLOCK": 'BASIC',
"FUSE_METHOD": 'SUM'
}
}
}
def _hrnet(arch, pretrained, progress, **kwargs):
model = HighResolutionNet(cfg[arch], **kwargs)
# if pretrained:
# model_url = model_urls[arch]
# state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url(model_url,
# progress=progress)
# model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
return model
def hrnet18(pretrained=False, progress=False, **kwargs):
r"""HRNet-18 model
"""
return _hrnet('hrnet18', pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)
def hrnet32(pretrained=False, progress=False, **kwargs):
r"""HRNet-32 model
"""
return _hrnet('hrnet32', pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)
def hrnet48(pretrained=False, progress=False, **kwargs):
r"""HRNet-48 model
"""
return _hrnet('hrnet48', pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)
if __name__ == '__main__':
images = torch.randn(size=(2, 3, 512, 512))
print(images.shape)
model = hrnet18()
# torch.Size([2, 19, 128, 128])
out = model(images)
print(out.shape)
参考资料
HRNet源代码结构解析_菜鸟_peng的博客-CSDN博客_hrnet代码
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36382582/article/details/119541890
HRNet 源代码结构详解 - 简书 (jianshu.com)
保持高分辨率:HRNet(v1,v2,v2p)论文笔记及代码简读(hrnet+ocr分割版本) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
