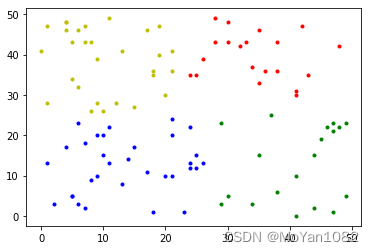
What are clustering algorithms used for?
We want to divide the data into several different types(different clusters) without labels. Data in the same cluster have some similar features for a given dataset.
We might as well define tihs similarities as distance. Therefore, our goal is to find a partition such that the intra-cluster distance is small and the inter-cluster distance is large.

we need to determine the appropriate distance measure based on the samples. Here we will use Euclidean distance as a similarity measure.
E u c l i d e a n ? d i s t a n c e : ∑ u = 1 n ∥ x i u ? x j u ∥ 2 Euclidean\ distance: \sqrt{\sum_{u=1}^n\|x_{iu}-x_{ju}\|^2} Euclidean?distance:u=1∑n?∥xiu??xju?∥2?
The problem we need to optimize
Divide the dataset { x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x M } \{x_1,x_2,...,x_M\} {x1?,x2?,...,xM?} into disjoint sets { S 1 , S 2 , . . . , S K } \{S_1,S_2,...,S_K\} {S1?,S2?,...,SK?}. For each set S k S_k Sk?, the representative point is chosen as μ k \mu_k μk?.
The loss function can be defined as:
E
(
S
1
,
.
.
.
,
S
K
;
μ
1
,
.
.
.
,
μ
K
)
=
1
N
∑
m
=
1
M
∑
k
=
1
K
[
[
x
m
∈
S
k
]
]
∥
x
m
?
μ
k
∥
2
E(S_1,...,S_K;\mu_1,...,\mu_K)=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{m=1}^M\sum_{k=1}^K[[x_m\in S_k]]\|x_m-\mu_k\|^2
E(S1?,...,SK?;μ1?,...,μK?)=N1?m=1∑M?k=1∑K?[[xm?∈Sk?]]∥xm??μk?∥2
Therefore, our goal is to find an optimal partition that minimizes
E
E
E.
min
?
S
1
,
.
.
.
,
S
K
;
μ
1
,
.
.
.
,
μ
K
E
(
S
1
,
.
.
.
,
S
K
;
μ
1
,
.
.
.
,
μ
K
)
\min_{S_1,...,S_K;\mu_1,...,\mu_K}E(S_1,...,S_K;\mu_1,...,\mu_K)
S1?,...,SK?;μ1?,...,μK?min?E(S1?,...,SK?;μ1?,...,μK?)
(Note: Going directly to find the optimal solution of E E E is an NP-hard problem.)
K-Means
- Assuming that μ 1 , . . . , μ k \mu_1,...,\mu_k μ1?,...,μk? have been determined, then for each sample x m x_m xm?, x m x_m xm? can be divided into a certain cluster that minimizes ∑ k = 1 K [ [ x m ∈ S k ] ] ∥ x m ? μ k ∥ 2 \sum_{k=1}^K[[x_m\in S_k]]\|x_m-\mu_k\|^2 ∑k=1K?[[xm?∈Sk?]]∥xm??μk?∥2. (The representative point μ k \mu_k μk? closest to x m x_m xm?).
- Assuming that
S
1
,
.
.
.
,
S
K
S_1,...,S_K
S1?,...,SK? have been determined, then for each cluster
S
k
S_k
Sk?, we can find a certain representative point
μ
k
\mu_k
μk? to minimize
E
k
=
∑
x
∈
S
k
∥
x
?
μ
k
∥
2
E_k=\sum_{x\in S_k}\|x-\mu_k\|^2
Ek?=∑x∈Sk??∥x?μk?∥2.
d E k d μ k = ∑ n 1 2 ( x n 1 ? μ k ) ( ? 1 ) + ∑ n 2 2 ( μ k ? x n 2 ) = 2 ( ∣ S k ∣ μ k ? ∑ x ∈ S k x ) \frac{d E_k}{d \mu_k}=\sum_{n_1}2(x_{n_1}-\mu_k)(-1)+\sum_{n_2}2(\mu_k-x_{n_2})=2(|S_k| \mu_k-\sum_{x\in S_k}x) dμk?dEk??=n1?∑?2(xn1???μk?)(?1)+n2?∑?2(μk??xn2??)=2(∣Sk?∣μk??x∈Sk?∑?x)
So, when μ k = 1 ∣ S k ∣ ∑ x ∈ S k x \mu_k=\frac{1}{|S_k|}\sum_{x\in S_k}x μk?=∣Sk?∣1?∑x∈Sk??x, the derivative of E k E_k Ek? with respect to μ k \mu_k μk? is 0. (The μ k \mu_k μk? also called the means vector for cluster S k S_k Sk?) - Steps 1 and 2 are repeated until the representative points μ \mu μ no longer change.
When we do the above operations, the value of
E
E
E is updated to
E
′
E'
E′,
E
′
≤
E
E'\le E
E′≤E, and
E
E
E has a lower bound
E
≥
0
E\ge 0
E≥0.
Therefore, it has been proved that the loss function must converge.
(Note: the loss function will eventually converge to a local extremum, not necessarily a global minimum.)
This also can be proved by EM(Expectation-Maximization) algorithm.
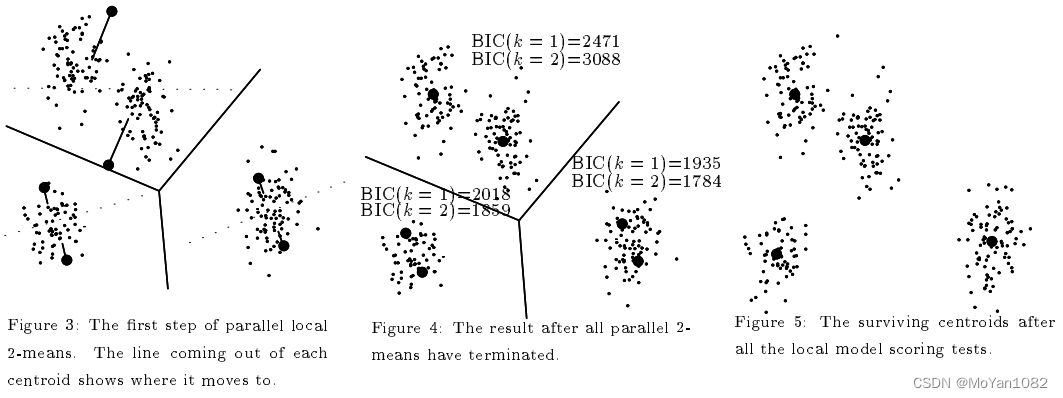
X-means
In the K-means algorithm, the value of K K K is fixed. However, it is often difficult to choose the best K K K.
For the X-means algorithm, users can choose a range of
K
K
K, and the X-means first runs the ordinary K-means algorithm according to the lower limit of the range. According to the value of BIC(Bayesian information criterion), the X-means algorithm determines whether to divide each cluster into two.
PDF: X-means: Extending K-means with Efficient Estimation of the Number of Clusters
Hierarchical Clustering
Hierarchical clustering provides another idea to help users interpret the appropriate number of clusters.
Take AGNES(AGglomerative NESting) as an example:
- Consider each sample as a cluster.
- Merge the two clusters with the smallest distance. (inter-cluster distance)
- Steps 1 and 2 are repeated until all clusters are merged into one single cluster including all points.

Users can observe the distance between clusters and choose an optimal K K K by themselves.
Code(K-means)
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
data = np.random.randint(0,50,size=[100,2])
K = 4 # fix the value of K
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=K, random_state=0).fit(data)
subCenter = list(kmeans.labels_)
# drawing
samples = [[] for i in range(K)]
for i in range(np.shape(data)[0]):
tmp = [data[i][0], data[i][1]]
samples[subCenter[i]].append(tmp)
plt.plot(np.array(samples[0])[:, :1], np.array(samples[0])[:, 1:], 'b.')
plt.plot(np.array(samples[1])[:, :1], np.array(samples[1])[:, 1:], 'r.')
plt.plot(np.array(samples[2])[:, :1], np.array(samples[2])[:, 1:], 'y.')
plt.plot(np.array(samples[3])[:, :1], np.array(samples[3])[:, 1:], 'g.')
plt.show()