RRT_Star结合OMPL实现三维点云的路径规划
文章目录
OMPL中文名为最优规划,比如 R R T ? RRT^{\ast} RRT?。采用OMPL为基本框架,在三维点云中实现 R R T ? RRT^{\ast} RRT?算法。
1.OMPL安装
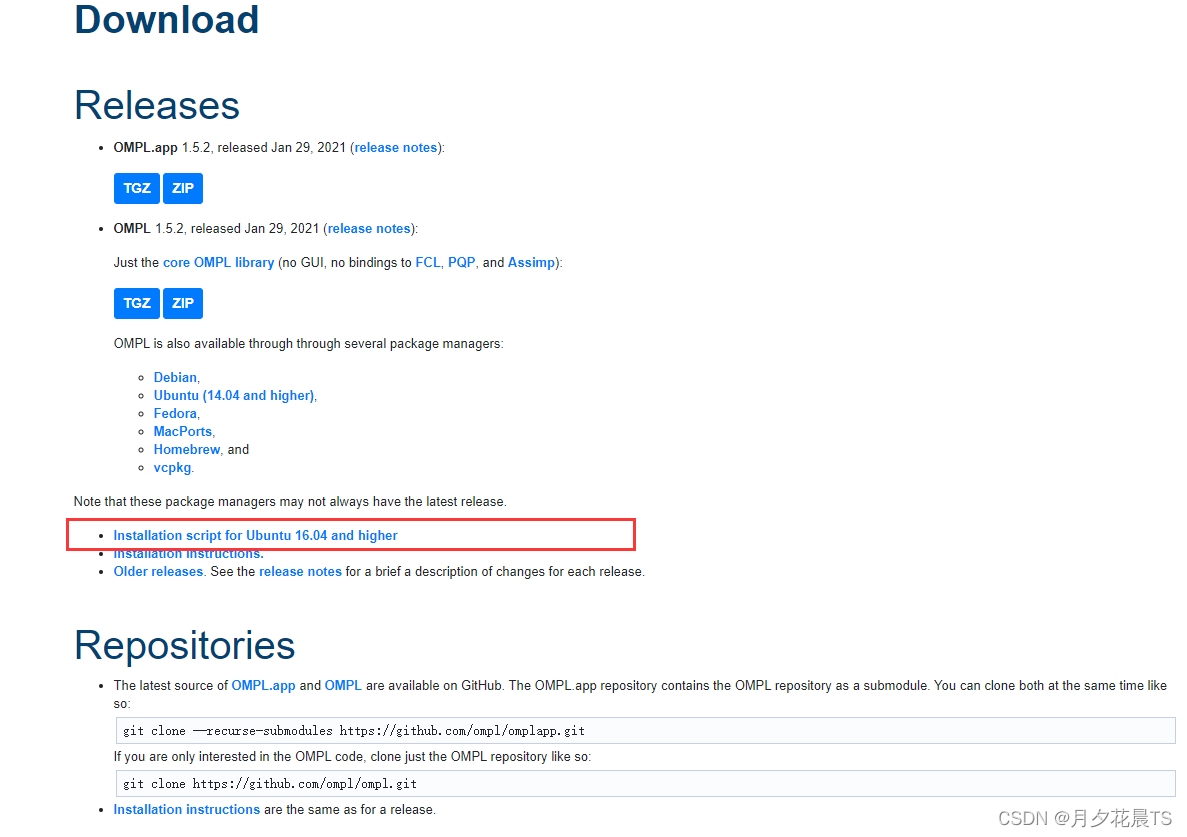
网址:https://ompl.kavrakilab.org/download.html
推荐使用脚本安装,下载脚本后
sudo chmod 777 install-ompl-ubuntn.sh
./install-ompl-ubuntn.sh
注意:1.如果在安装脚本的过程中,需要下载ros中的一些东西,此时最好在安装角本前,更换ros源。 ros源更换参考:ROS换源(除了清华之外的ROS源)
? ROS wiki
? 2.安装ompl可能会出现电脑分辨率的发生变化,并且此时会弹出Patch the file(我记得是这样),此时先不要管,一路回车即可。最终再在电脑设置中更改分辨率。
2.OMPL使用
2.1创建机器人的状态空间
因为是在有限点云空间中进行路径规划,因此机器人的状态空间为3,其次需要为空间设置一个边界。
ob::StateSpacePtr space(new ob::RealVectorStateSpace(3));
//将空间的边界设置为[0,1]。
ob::RealVectorBounds bounds(3);
bounds.setLow(0, - _x_size * 0.5);
bounds.setLow(1, - _y_size * 0.5);
bounds.setLow(2, 0.0);
bounds.setHigh(0, + _x_size * 0.5);
bounds.setHigh(1, + _y_size * 0.5);
bounds.setHigh(2, _z_size);
space->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace>()->setBounds(bounds);
2.2 构造一个空间实例
ob::SpaceInformationPtr si(new ob::SpaceInformation(space));
//设置用于检查空间中哪些状态有效的对象
si->setStateValidityChecker(ob::StateValidityCheckerPtr(new ValidityChecker(si)));
si->setup();
其中ValidityChecker为自定义的类,目的时继承ompl下的StateValidityChecker,并重写有效性函数isValid(ompl无法对该点状态做有效性(安全性)判断)。
class ValidityChecker : public ob::StateValidityChecker
{
public:
ValidityChecker(const ob::SpaceInformationPtr& si) :ob::StateValidityChecker(si) {}
//返回给定状态的位置是否与圆形障碍物重叠
bool isValid(const ob::State* state) const
{
//在本例中使用的是RealVectorStateSpace,因此需要将状态转换为特定类型。
const ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType* state3D =state->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>();
auto x=(*state3D)[0];
auto y=(*state3D)[1];
auto z=(*state3D)[2];
return _RRTstar_preparatory->isObsFree(x, y, z);
}
};
2.3 创建问题实例,并设置一些参数
auto pdef(std::make_shared<ob::ProblemDefinition>(si));
//设置开始和目标状态
pdef->setStartAndGoalStates(start, goal);
//设置优化目标
pdef->setOptimizationObjective(getPathLengthObjective(si));
其中getPathLengthObjective函数为自定义函数,目的是为ompl提供优化阈值。如果阈值为0.0,表示希望能够找到最好的路线,不设置默认为0.0。阈值通过**obj->setCostThreshold(ob::Cost())**进行设置。
ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr getPathLengthObjective(const ob::SpaceInformationPtr& si)
{
ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr obj(new ob::PathLengthOptimizationObjective(si));
#obj->setCostThreshold(ob::Cost(1.51));
return obj;
}
2.4 构建优化器
使用RRT算法构建优化器
ob::PlannerPtr optimizingPlanner(new og::RRTstar(si));
optimizingPlanner->setProblemDefinition(pdef);
optimizingPlanner->setup();
2.5 ompl进行求解
其中参数1.0表示希望在1s中得出路径规划结果
ob::PlannerStatus solved = optimizingPlanner->solve(1.0);
2.6 ompl路径生成
if (solved)
{
//从问题定义中获取目标表示(与目标状态不同),并查询找到的路径
og::PathGeometric* path = pdef->getSolutionPath()->as<og::PathGeometric>();
vector<Vector3d> path_points;
for (size_t path_idx = 0; path_idx < path->getStateCount (); path_idx++)
{
const ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType *state = path->getState(path_idx)->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>();
auto x = (*state)[0];
auto y = (*state)[1];
auto z = (*state)[2];
Vector3d temp_mat(x,y,z);
path_points.push_back(temp_mat);
}
}
3.整体代码展示
3.1 代码框架修改
在章的基础上进行修改,修改如下
在src文件夹下,新建rrt.cpp,rrt_demo.cpp
在include文件夹下,新建rrt.h
在launch文件夹下,新建rrt_demo.launch
修改CMakeLists.txt内容
3.1.1 rrt.h
#ifndef _GRID_SEARCHER_H_
#define _GRID_SEARCHER_H_
#include <iostream>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <ros/console.h>
#include <Eigen/Eigen>
#include "backward.hpp"
#include "node.h"
class RRTstarPreparatory
{
private:
protected:
uint8_t * data;
GridNodePtr *** GridNodeMap;
int GLX_SIZE, GLY_SIZE, GLZ_SIZE;
int GLXYZ_SIZE, GLYZ_SIZE;
double resolution, inv_resolution;
double gl_xl, gl_yl, gl_zl;
double gl_xu, gl_yu, gl_zu;
Eigen::Vector3d gridIndex2coord(const Eigen::Vector3i & index);
Eigen::Vector3i coord2gridIndex(const Eigen::Vector3d & pt);
public:
RRTstarPreparatory(){};
~RRTstarPreparatory(){};
void initGridMap(double _resolution, Eigen::Vector3d global_xyz_l, Eigen::Vector3d global_xyz_u, int max_x_id, int max_y_id, int max_z_id);
void setObs(const double coord_x, const double coord_y, const double coord_z);
bool isObsFree(const double coord_x, const double coord_y, const double coord_z);
Eigen::Vector3d coordRounding(const Eigen::Vector3d & coord);
};
#endif
3.1.2 rrt.cpp
#include <rrt.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
void RRTstarPreparatory::initGridMap(double _resolution, Vector3d global_xyz_l, Vector3d global_xyz_u, int max_x_id, int max_y_id, int max_z_id)
{
gl_xl = global_xyz_l(0);
gl_yl = global_xyz_l(1);
gl_zl = global_xyz_l(2);
gl_xu = global_xyz_u(0);
gl_yu = global_xyz_u(1);
gl_zu = global_xyz_u(2);
GLX_SIZE = max_x_id;
GLY_SIZE = max_y_id;
GLZ_SIZE = max_z_id;
GLYZ_SIZE = GLY_SIZE * GLZ_SIZE;
GLXYZ_SIZE = GLX_SIZE * GLYZ_SIZE;
resolution = _resolution;
inv_resolution = 1.0 / _resolution;
data = new uint8_t[GLXYZ_SIZE];
memset(data, 0, GLXYZ_SIZE * sizeof(uint8_t));
}
void RRTstarPreparatory::setObs(const double coord_x, const double coord_y, const double coord_z)
{
if( coord_x < gl_xl || coord_y < gl_yl || coord_z < gl_zl ||
coord_x >= gl_xu || coord_y >= gl_yu || coord_z >= gl_zu )
return;
int idx_x = static_cast<int>( (coord_x - gl_xl) * inv_resolution);
int idx_y = static_cast<int>( (coord_y - gl_yl) * inv_resolution);
int idx_z = static_cast<int>( (coord_z - gl_zl) * inv_resolution);
data[idx_x * GLYZ_SIZE + idx_y * GLZ_SIZE + idx_z] = 1;
}
bool RRTstarPreparatory::isObsFree(const double coord_x, const double coord_y, const double coord_z)
{
Vector3d pt;
Vector3i idx;
pt(0) = coord_x;
pt(1) = coord_y;
pt(2) = coord_z;
idx = coord2gridIndex(pt);
int idx_x = idx(0);
int idx_y = idx(1);
int idx_z = idx(2);
return (idx_x >= 0 && idx_x < GLX_SIZE && idx_y >= 0 && idx_y < GLY_SIZE && idx_z >= 0 && idx_z < GLZ_SIZE &&
(data[idx_x * GLYZ_SIZE + idx_y * GLZ_SIZE + idx_z] < 1));
}
Vector3d RRTstarPreparatory::gridIndex2coord(const Vector3i & index)
{
Vector3d pt;
pt(0) = ((double)index(0) + 0.5) * resolution + gl_xl;
pt(1) = ((double)index(1) + 0.5) * resolution + gl_yl;
pt(2) = ((double)index(2) + 0.5) * resolution + gl_zl;
return pt;
}
Vector3i RRTstarPreparatory::coord2gridIndex(const Vector3d & pt)
{
Vector3i idx;
idx << min( max( int( (pt(0) - gl_xl) * inv_resolution), 0), GLX_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (pt(1) - gl_yl) * inv_resolution), 0), GLY_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (pt(2) - gl_zl) * inv_resolution), 0), GLZ_SIZE - 1);
return idx;
}
Eigen::Vector3d RRTstarPreparatory::coordRounding(const Eigen::Vector3d & coord)
{
return gridIndex2coord(coord2gridIndex(coord));
}
上述代码的API接口和功能基本如Astar与C++可视化在RVIZ的三维点云地图,详情请见Astar与C++可视化在RVIZ的三维点云地图。
3.1.3 rrt_demo.cpp
该程序基本实现上述OMPL的使用和一些ROS基本框架,不在赘述。
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <math.h>
#include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <ros/console.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Path.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h>
#include <visualization_msgs/MarkerArray.h>
#include <visualization_msgs/Marker.h>
#include <ompl/config.h>
#include <ompl/base/StateSpace.h>
#include <ompl/base/Path.h>
#include <ompl/base/spaces/RealVectorBounds.h>
#include <ompl/base/spaces/RealVectorStateSpace.h>
#include <ompl/base/StateValidityChecker.h>
#include <ompl/base/OptimizationObjective.h>
#include <ompl/base/objectives/PathLengthOptimizationObjective.h>
#include <ompl/geometric/planners/rrt/RRTstar.h>
#include <ompl/geometric/SimpleSetup.h>
#include "rrt.h"
#include "backward.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
namespace ob = ompl::base;
namespace og = ompl::geometric;
namespace backward {
backward::SignalHandling sh;
}
double _resolution, _inv_resolution, _cloud_margin;
double _x_size, _y_size, _z_size;
bool _has_map = false;
Vector3d _start_pt;
Vector3d _map_lower, _map_upper;
int _max_x_id, _max_y_id, _max_z_id;
ros::Subscriber _map_sub, _pts_sub;
ros::Publisher _grid_map_vis_pub, _RRTstar_path_vis_pub;
RRTstarPreparatory * _RRTstar_preparatory = new RRTstarPreparatory();
void rcvWaypointsCallback(const nav_msgs::Path & wp);
void rcvPointCloudCallBack(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 & pointcloud_map);
void pathFinding(const Vector3d start_pt, const Vector3d target_pt);
void visRRTstarPath(vector<Vector3d> nodes );
void rcvWaypointsCallback(const nav_msgs::Path & wp)
{
if( wp.poses[0].pose.position.z < 0.0 || _has_map == false )
return;
Vector3d target_pt;
target_pt << wp.poses[0].pose.position.x,
wp.poses[0].pose.position.y,
wp.poses[0].pose.position.z;
ROS_INFO("[node] receive the planning target");
pathFinding(_start_pt, target_pt);
}
void rcvPointCloudCallBack(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 & pointcloud_map)
{
if(_has_map ) return;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_vis;
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 map_vis;
pcl::fromROSMsg(pointcloud_map, cloud);
if( (int)cloud.points.size() == 0 ) return;
pcl::PointXYZ pt;
for (int idx = 0; idx < (int)cloud.points.size(); idx++)
{
pt = cloud.points[idx];
// set obstalces into grid map for path planning
_RRTstar_preparatory->setObs(pt.x, pt.y, pt.z);
// for visualize only
Vector3d cor_round = _RRTstar_preparatory->coordRounding(Vector3d(pt.x, pt.y, pt.z));
pt.x = cor_round(0);
pt.y = cor_round(1);
pt.z = cor_round(2);
cloud_vis.points.push_back(pt);
}
cloud_vis.width = cloud_vis.points.size();
cloud_vis.height = 1;
cloud_vis.is_dense = true;
pcl::toROSMsg(cloud_vis, map_vis);
map_vis.header.frame_id = "/world";
_grid_map_vis_pub.publish(map_vis);
_has_map = true;
}
class ValidityChecker : public ob::StateValidityChecker
{
public:
ValidityChecker(const ob::SpaceInformationPtr& si) :ob::StateValidityChecker(si) {}
//返回给定状态的位置是否与圆形障碍物重叠
bool isValid(const ob::State* state) const
{
//在本例中使用的是RealVectorStateSpace,因此需要将状态转换为特定类型。
const ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType* state3D =state->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>();
auto x=(*state3D)[0];
auto y=(*state3D)[1];
auto z=(*state3D)[2];
return _RRTstar_preparatory->isObsFree(x, y, z);
}
};
//返回表示优化目标的结构,以用于优化运动规划。该方法返回一个目标,该目标试图最小化计算路径在配置空间中的长度。
ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr getPathLengthObjective(const ob::SpaceInformationPtr& si)
{
return ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr(new ob::PathLengthOptimizationObjective(si));
}
ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr getThresholdPathLengthObj(const ob::SpaceInformationPtr& si)
{
ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr obj(new ob::PathLengthOptimizationObjective(si));
obj->setCostThreshold(ob::Cost(1.51));
return obj;
}
void pathFinding(const Vector3d start_pt, const Vector3d target_pt)
{
//创建正在规划的机器人状态空间。
ob::StateSpacePtr space(new ob::RealVectorStateSpace(3));
//将空间的边界设置为[0,1]。
ob::RealVectorBounds bounds(3);
bounds.setLow(0, - _x_size * 0.5);
bounds.setLow(1, - _y_size * 0.5);
bounds.setLow(2, 0.0);
bounds.setHigh(0, + _x_size * 0.5);
bounds.setHigh(1, + _y_size * 0.5);
bounds.setHigh(2, _z_size);
space->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace>()->setBounds(bounds);
//为此状态空间构造一个空间信息实例
ob::SpaceInformationPtr si(new ob::SpaceInformation(space));
//设置用于检查空间中哪些状态有效的对象
si->setStateValidityChecker(ob::StateValidityCheckerPtr(new ValidityChecker(si)));
si->setup();
//设置机器人的开始状态
ob::ScopedState<> start(space);
start[0]=(&start_pt)->operator[](0);
start[1]=(&start_pt)->operator[](1);
start[2]=(&start_pt)->operator[](2);
//设置机器人的目标状态
ob::ScopedState<> goal(space);
goal[0]=(&target_pt)->operator[](0);
goal[1]=(&target_pt)->operator[](1);
goal[2]=(&target_pt)->operator[](2);
//创建问题实例,将变量定义为pdef
auto pdef(std::make_shared<ob::ProblemDefinition>(si));
//设置开始和目标状态
pdef->setStartAndGoalStates(start, goal);
//设置优化目标,可以选择的选项在前面已经定义:getPathLengthObjective()和getThresholdPathLengthObj()
pdef->setOptimizationObjective(getPathLengthObjective(si));
//使用RRTstar算法构建我们的优化计划器,将Variable定义为optimizingPlanner
ob::PlannerPtr optimizingPlanner(new og::RRTstar(si));
//为规划者提供解决问题的实例
optimizingPlanner->setProblemDefinition(pdef);
optimizingPlanner->setup();
// 尝试在一秒钟内解决规划问题
ob::PlannerStatus solved = optimizingPlanner->solve(1.0);
if (solved)
{
//从问题定义中获取目标表示(与目标状态不同),并查询找到的路径
og::PathGeometric* path = pdef->getSolutionPath()->as<og::PathGeometric>();
vector<Vector3d> path_points;
for (size_t path_idx = 0; path_idx < path->getStateCount (); path_idx++)
{
const ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType *state = path->getState(path_idx)->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>();
//将找到的路径从路径转换为rviz显示的路径点
auto x = (*state)[0];
auto y = (*state)[1];
auto z = (*state)[2];
Vector3d temp_mat(x,y,z);
path_points.push_back(temp_mat);
}
visRRTstarPath(path_points);
}
}
void visRRTstarPath(vector<Vector3d> nodes )
{
//点是绿色,线是绿色
visualization_msgs::Marker Points, Line;
Points.header.frame_id = "world";
Points.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
Points.ns = "demo_node/RRTstarPath";
Points.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD;
Points.pose.orientation.w = Line.pose.orientation.w = 1.0;
Points.id = 0;
Points.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::POINTS;
Points.scale.x = _resolution/2;
Points.scale.y = _resolution/2;
Points.color.g = 1.0f;
Points.color.a = 1.0;
Line.header.frame_id = "world";
Line.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
Line.ns = "demo_node/RRTstarPath";
Line.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD;
Line.id = 1;
Line.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::LINE_STRIP;
Line.scale.x = _resolution/2;
Line.color.b = 1.0;
Line.color.a = 1.0;
geometry_msgs::Point pt;
for(int i = 0; i < int(nodes.size()); i++)
{
Vector3d coord = nodes[i];
pt.x = coord(0);
pt.y = coord(1);
pt.z = coord(2);
Points.points.push_back(pt);
Line.points.push_back(pt);
}
_RRTstar_path_vis_pub.publish(Points);
_RRTstar_path_vis_pub.publish(Line);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "rrt_demo");
ros::NodeHandle nh("~");
_map_sub = nh.subscribe( "map", 1, rcvPointCloudCallBack );
_pts_sub = nh.subscribe( "waypoints", 1, rcvWaypointsCallback );
_grid_map_vis_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("grid_map_vis", 1);
_RRTstar_path_vis_pub = nh.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("rrt_star_path_vis",1);
nh.param("map/cloud_margin", _cloud_margin, 0.0);
nh.param("map/resolution", _resolution, 0.2);
nh.param("map/x_size", _x_size, 50.0);
nh.param("map/y_size", _y_size, 50.0);
nh.param("map/z_size", _z_size, 5.0 );
nh.param("planning/start_x", _start_pt(0), 0.0);
nh.param("planning/start_y", _start_pt(1), 0.0);
nh.param("planning/start_z", _start_pt(2), 0.0);
_map_lower << - _x_size/2.0, - _y_size/2.0, 0.0;
_map_upper << + _x_size/2.0, + _y_size/2.0, _z_size;
_inv_resolution = 1.0 / _resolution;
_max_x_id = (int)(_x_size * _inv_resolution);
_max_y_id = (int)(_y_size * _inv_resolution);
_max_z_id = (int)(_z_size * _inv_resolution);
_RRTstar_preparatory = new RRTstarPreparatory();
_RRTstar_preparatory -> initGridMap(_resolution, _map_lower, _map_upper, _max_x_id, _max_y_id, _max_z_id);
ros::Rate rate(100);
bool status = ros::ok();
while(status)
{
ros::spinOnce();
status = ros::ok();
rate.sleep();
}
delete _RRTstar_preparatory;
return 0;
}
3.1.4 rrt_demo.launch
基本与Astar与C++可视化在RVIZ的三维点云地图章类似,仅仅修改节点名称和rviz文件路径。
<launch>
<arg name="map_size_x" default="10.0"/>
<arg name="map_size_y" default="10.0"/>
<arg name="map_size_z" default=" 2.0"/>
<arg name="start_x" default=" 0.0"/>
<arg name="start_y" default=" 0.0"/>
<arg name="start_z" default=" 1.0"/>
<arg name="pcd_path" default="$(find grid_path_searcher)/pcd/map.pcd"/>
<node pkg="grid_path_searcher" type="rrt_demo" name="rrt_demo" output="screen" required = "true">
<remap from="~waypoints" to="/waypoint_generator/waypoints"/>
<remap from="~map" to="/complex_map/global_map"/>
<param name="map/margin" value="0.0" />
<param name="map/resolution" value="0.2" />
<param name="map/x_size" value="$(arg map_size_x)"/>
<param name="map/y_size" value="$(arg map_size_y)"/>
<param name="map/z_size" value="$(arg map_size_z)"/>
<param name="planning/start_x" value="$(arg start_x)"/>
<param name="planning/start_y" value="$(arg start_y)"/>
<param name="planning/start_z" value="$(arg start_z)"/>
</node>
<node pkg ="grid_path_searcher" name ="complex_map" type ="complex_map" output = "screen">
<param name="pcd_path" value="$(arg pcd_path)"/>
<param name="sensing/rate" value="0.5"/>
</node>
<node pkg="waypoint_generator" name="waypoint_generator" type="waypoint_generator" output="screen">
<remap from="~goal" to="/goal"/>
<param name="waypoint_type" value="manual-lonely-waypoint"/>
</node>
<node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" args="-d $(find grid_path_searcher)/rviz/rrt.rviz" />
</launch>
3.1.5 CMakeLists.txt修改
主要增加OMPL包的依赖,如下图所示。
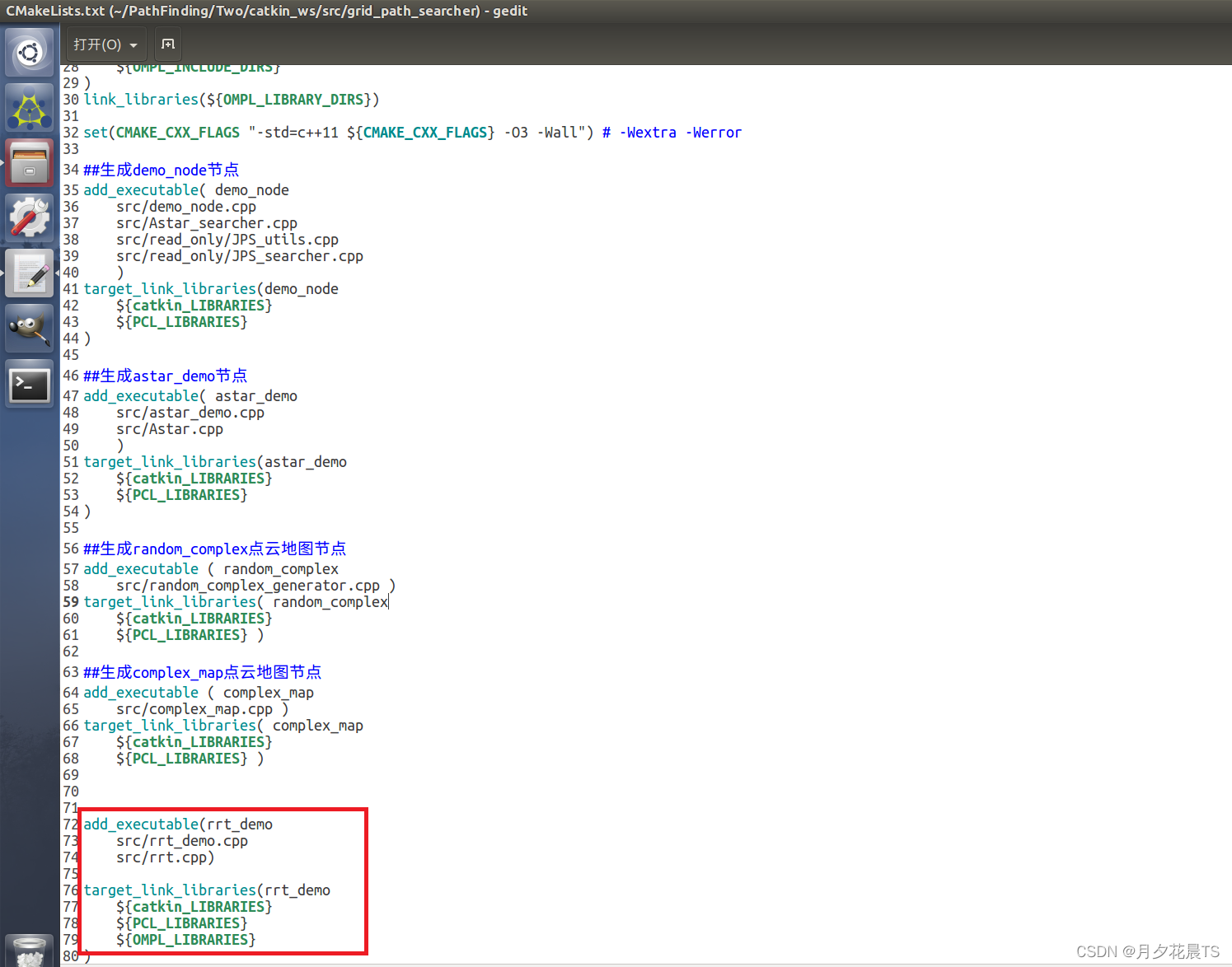
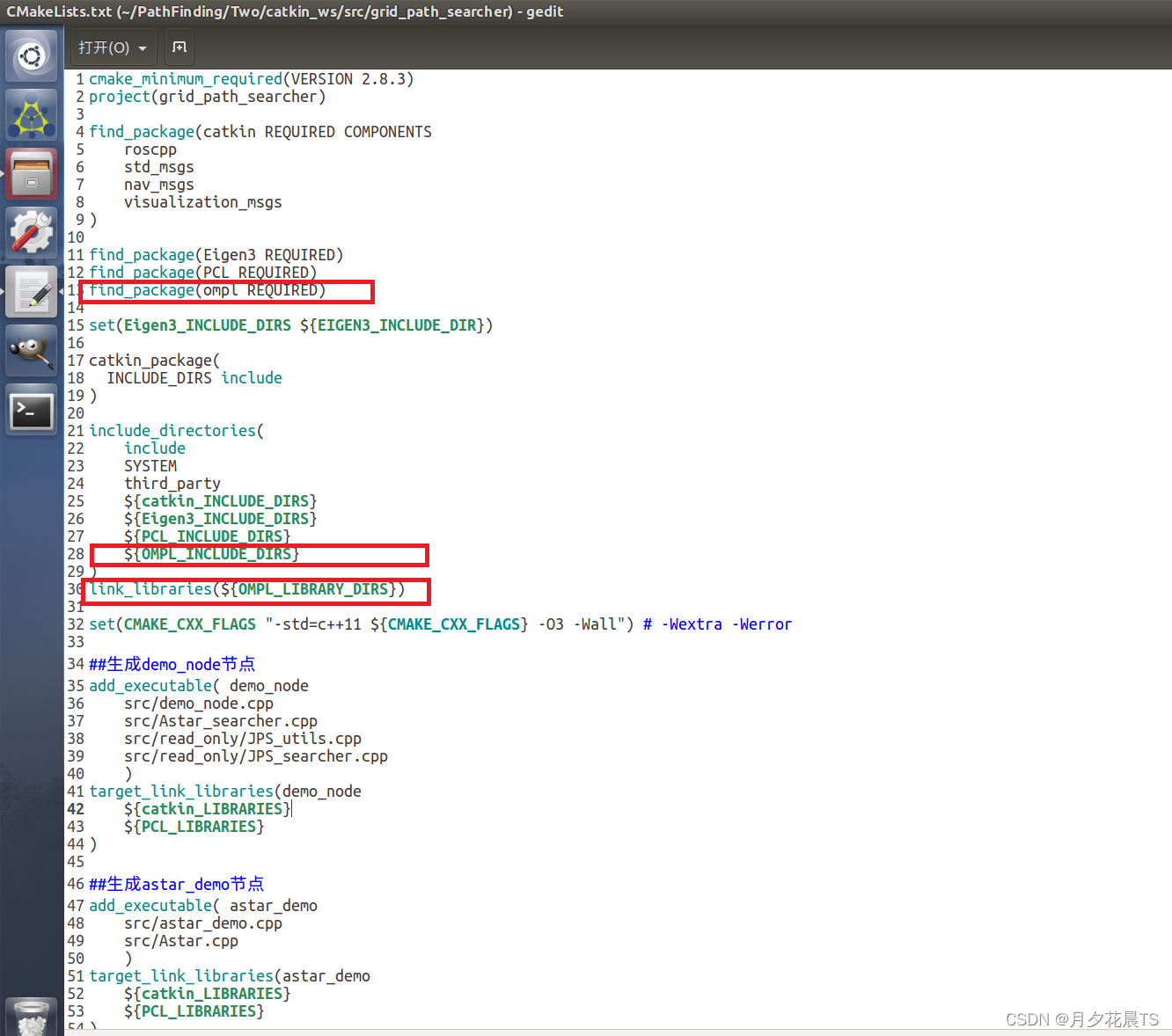
3.1.6 编译
问题1:
在编译的过程中若出现
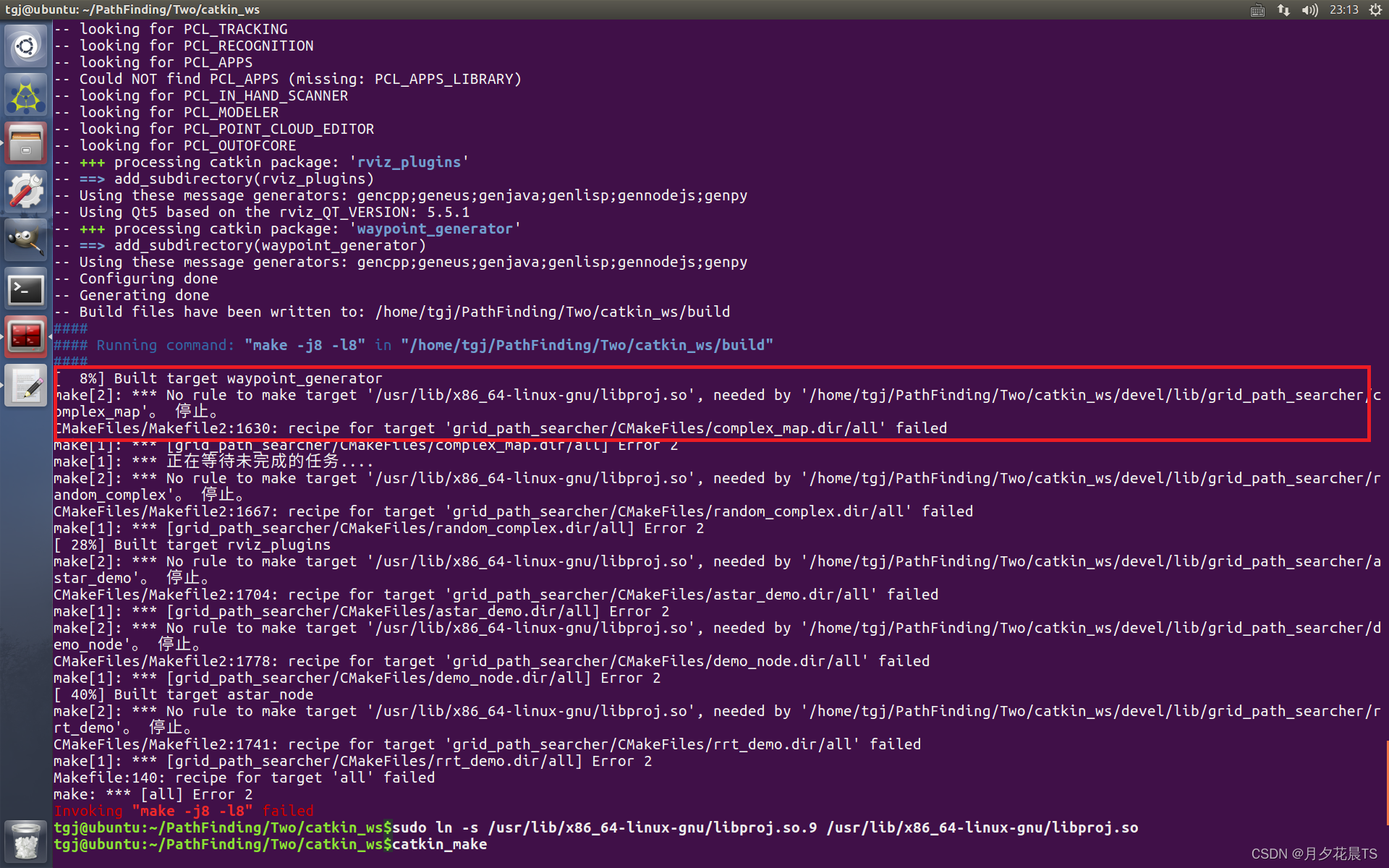
通过软链接来解决,指令如下
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproj.so.9 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproj.so
问题2:
编译过程中若出现缺少ompl-Config的问题,那是缺少ros的ompl包,因此通过
sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-ompl
3.2 代码展示
运行
roslaunch grid_path_searcher rrt_demo.launch
效果展示
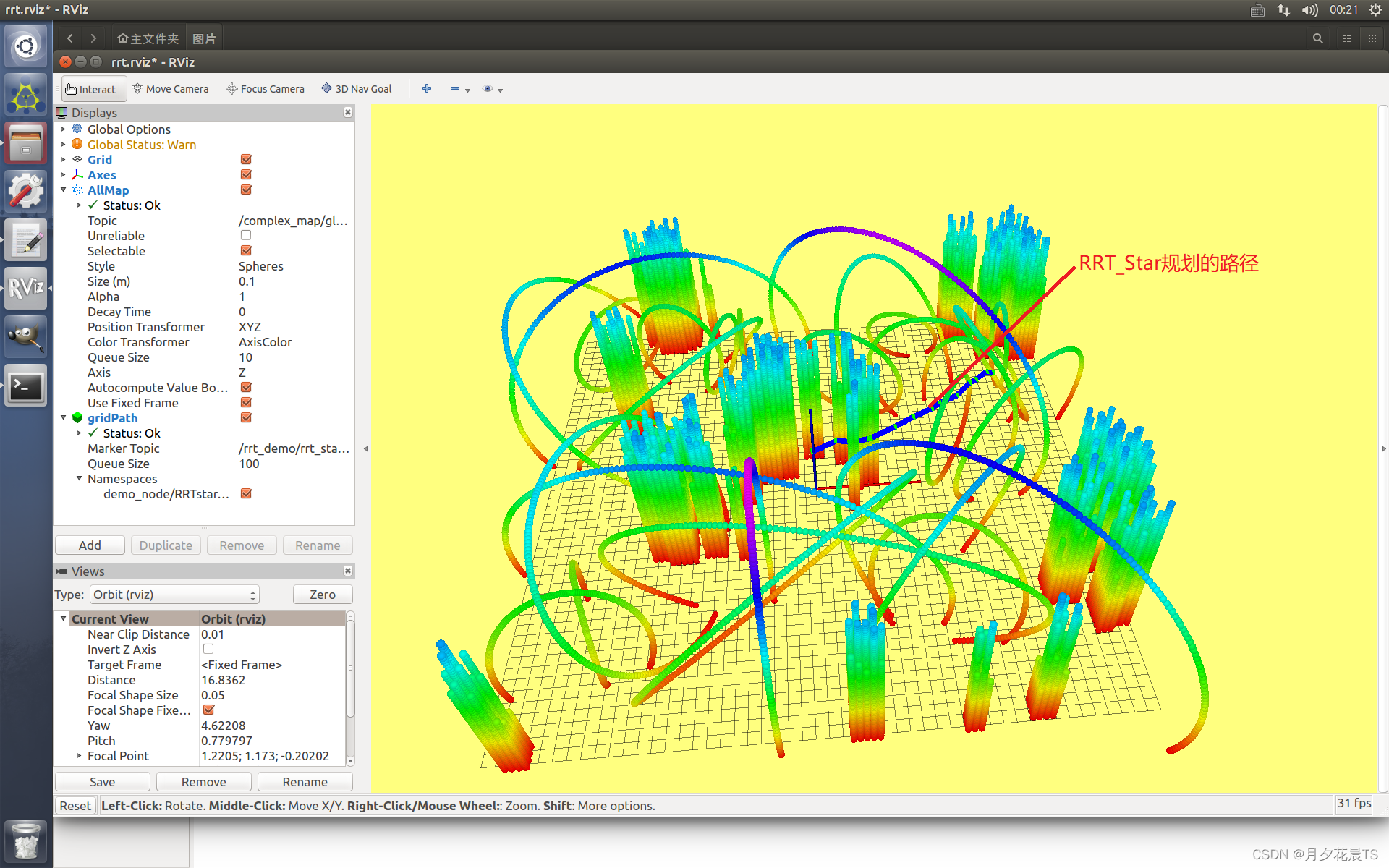
代码参考:
三维点云代码链接:https://github.com/KailinTong/Motion-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots
OMPL参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/mapleleaf98/article/details/124540749
