LSTM与GRU
长短期记忆(LSTM)
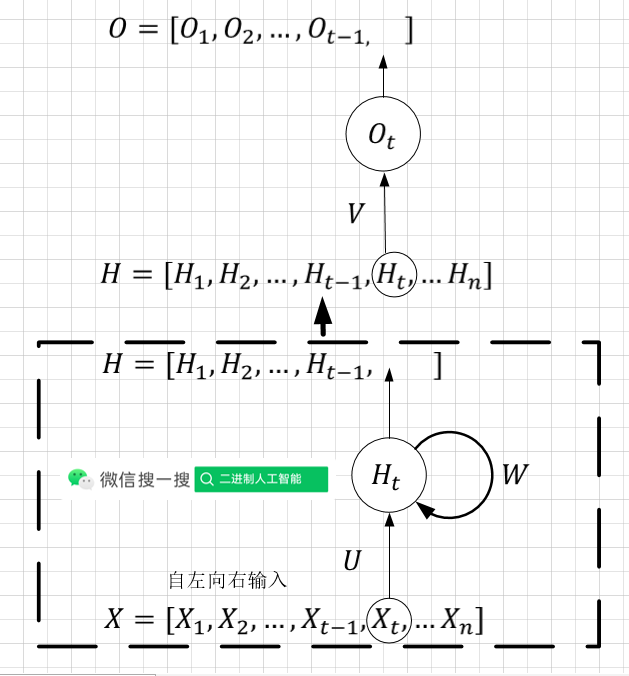
LSTM(Long short-term memory )是1997年提出的。与普通RNN一样,下面以”序列动,网络不动“的角度画出示意图。
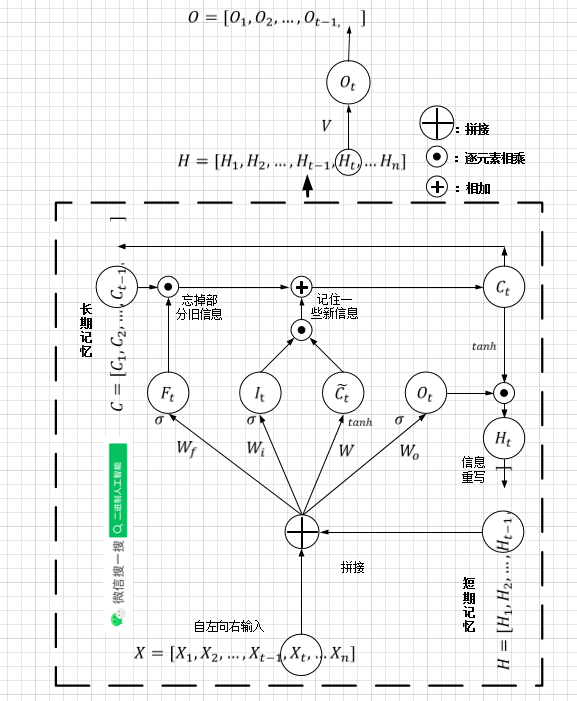

图片来源[1]。 σ : sigmoid \sigma:\text{sigmoid} σ:sigmoid,注意 sigmoid \text{sigmoid} sigmoid的“遗忘”特性
门控循环单元(GRU)
GRU(Gate Recurrent Unit)是2014年提出的,它用了更少的参数实现了与LSTM相当的效果。
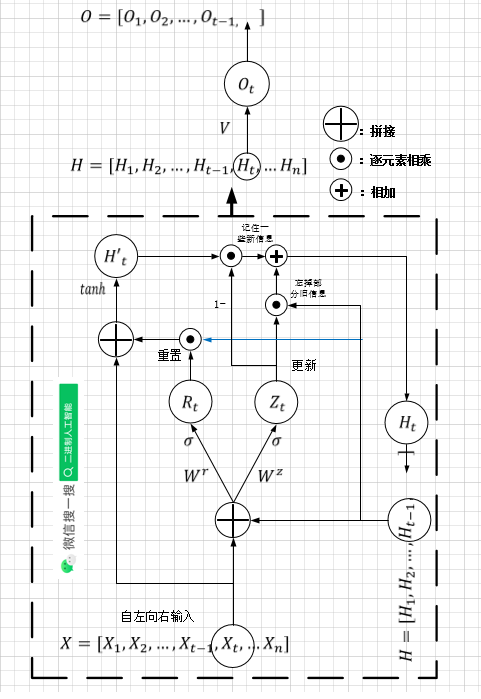
说明:目前网上流传的两个版本,一个是(原论文)
H
t
=
H
t
′
⊙
(
1
?
Z
t
)
+
H
t
?
1
⊙
Z
t
H_t=H'_t\odot(1-Z_t)+H_{t-1}\odot Z_t
Ht?=Ht′?⊙(1?Zt?)+Ht?1?⊙Zt?
另一个是:
H
t
=
H
t
′
⊙
Z
t
+
H
t
?
1
⊙
(
1
?
Z
t
)
H_t=H'_t\odot Z_t+H_{t-1}\odot (1-Z_t)
Ht?=Ht′?⊙Zt?+Ht?1?⊙(1?Zt?)
pytorch实现正弦波预测
LSTM
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import torch.optim as optim
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
torch.manual_seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 150
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(device)
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, output_size):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(
input_size=input_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
batch_first=True,
bidirectional=False,
)
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, inputs, h0, c0):
# x: [batch_size, seq_len, input_size]
# h0: [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
# c0: [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
outputs, (hn, cn) = self.rnn(inputs, (h0, c0))
# out: [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size]
# hn: [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
# cn: [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
# [batch, seq_len, hidden_size] => [batch * seq_len, hidden_size]
outputs = outputs.view(-1, self.hidden_size)
# [batch_size * seq_len, hidden_size] => [batch_size * seq_len, output_size]
outputs = self.linear(outputs)
# [batch_size * seq_len, output_size] => [batch_size, seq_len, output_size]
outputs = outputs.view(inputs.size())
return outputs, hn,cn
def test(model, seq_len, h0, c0):
input = torch.tensor(0, dtype=torch.float)
predictions = []
for _ in range(seq_len):
input = input.view(1, 1, 1)
prediction, hn, cn= model(input, h0, c0)
input = prediction
h0 = hn
c0 = cn
predictions.append(prediction.detach().numpy().ravel()[0])
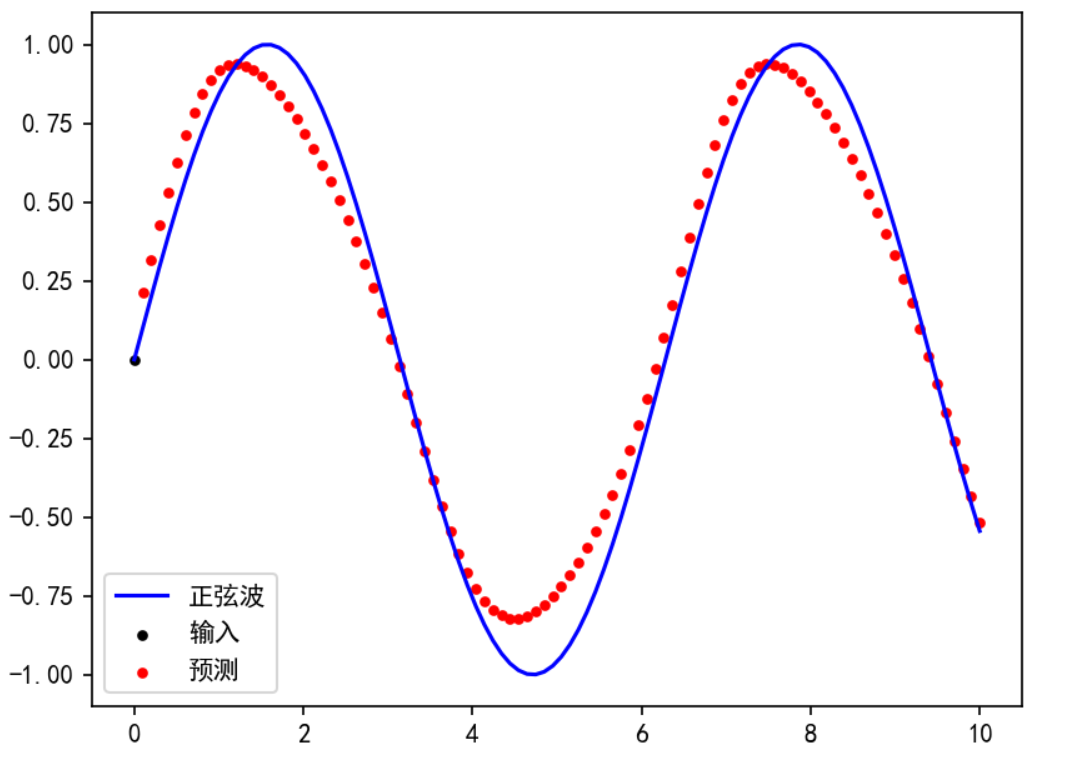
# 画图
time_steps = np.linspace(0, 10, seq_len)
data = np.sin(time_steps)
a, = plt.plot(time_steps, data, color='b')
b = plt.scatter(time_steps[0], 0, color='black', s=10)
c = plt.scatter(time_steps[1:], predictions[1:], color='red', s=10)
plt.legend([a, b, c], ['正弦波', '输入', '预测'])
plt.show()
def train():
seq_len = 100
input_size = 1
hidden_size = 16
output_size = 1
num_layers = 1
lr = 0.01
model = RNN(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, output_size)
loss_function = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr)
h0 = torch.zeros(num_layers, input_size, hidden_size)
c0 = torch.zeros(num_layers, input_size, hidden_size)
for i in range(300):
# 训练的数据:batch_size=1
time_steps = np.linspace(0, 10, seq_len + 1)
data = np.sin(time_steps)
data = data.reshape(seq_len + 1, 1)
# 去掉最后一个元素,作为输入
inputs = torch.tensor(data[:-1]).float().view(1, seq_len, 1)
# 去掉第一个元素,作为目标值 [batch_size, seq_len, input_size]
target = torch.tensor(data[1:]).float().view(1, seq_len, 1)
output, hn,cn = model(inputs, h0, c0)
# 与上一个批次的计算图分离 https://www.cnblogs.com/catnofishing/p/13287322.html
hn.detach()
loss = loss_function(output, target)
model.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if i % 100 == 0:
print("迭代次数: {} loss {}".format(i, loss.item()))
test(model, seq_len, h0, c0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
GRU
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import torch.optim as optim
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
torch.manual_seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 150
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(device)
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, output_size):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnn = nn.GRU(
input_size=input_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
batch_first=True,
bidirectional=False,
)
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, inputs, h0):
# x: [batch_size, seq_len, input_size]
# h0: [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
outputs, hn = self.rnn(inputs, h0)
# out: [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size]
# hn: [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
# [batch, seq_len, hidden_size] => [batch * seq_len, hidden_size]
outputs = outputs.view(-1, self.hidden_size)
# [batch_size * seq_len, hidden_size] => [batch_size * seq_len, output_size]
outputs = self.linear(outputs)
# [batch_size * seq_len, output_size] => [batch_size, seq_len, output_size]
outputs = outputs.view(inputs.size())
return outputs, hn
def test(model, seq_len, h0):
input = torch.tensor(0, dtype=torch.float)
predictions = []
for _ in range(seq_len):
input = input.view(1, 1, 1)
prediction, hn = model(input, h0)
input = prediction
h0 = hn
predictions.append(prediction.detach().numpy().ravel()[0])
# 画图
time_steps = np.linspace(0, 10, seq_len)
data = np.sin(time_steps)
a, = plt.plot(time_steps, data, color='b')
b = plt.scatter(time_steps[0], 0, color='black', s=10)
c = plt.scatter(time_steps[1:], predictions[1:], color='red', s=10)
plt.legend([a, b, c], ['正弦波', '输入', '预测'])
plt.show()
def train():
seq_len = 100
input_size = 1
hidden_size = 16
output_size = 1
num_layers = 1
lr = 0.01
model = RNN(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, output_size)
loss_function = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr)
h0 = torch.zeros(num_layers, input_size, hidden_size)
for i in range(300):
# 训练的数据:batch_size=1
time_steps = np.linspace(0, 10, seq_len + 1)
data = np.sin(time_steps)
data = data.reshape(seq_len + 1, 1)
# 去掉最后一个元素,作为输入
inputs = torch.tensor(data[:-1]).float().view(1, seq_len, 1)
# 去掉第一个元素,作为目标值 [batch_size, seq_len, input_size]
target = torch.tensor(data[1:]).float().view(1, seq_len, 1)
output, hn = model(inputs, h0)
# 与上一个批次的计算图分离 https://www.cnblogs.com/catnofishing/p/13287322.html
hn.detach()
loss = loss_function(output, target)
model.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if i % 100 == 0:
print("迭代次数: {} loss {}".format(i, loss.item()))
test(model, seq_len, h0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
对比(训练迭代300次)
| 普通RNN | LSTM | GRU |
|---|---|---|
 |  | 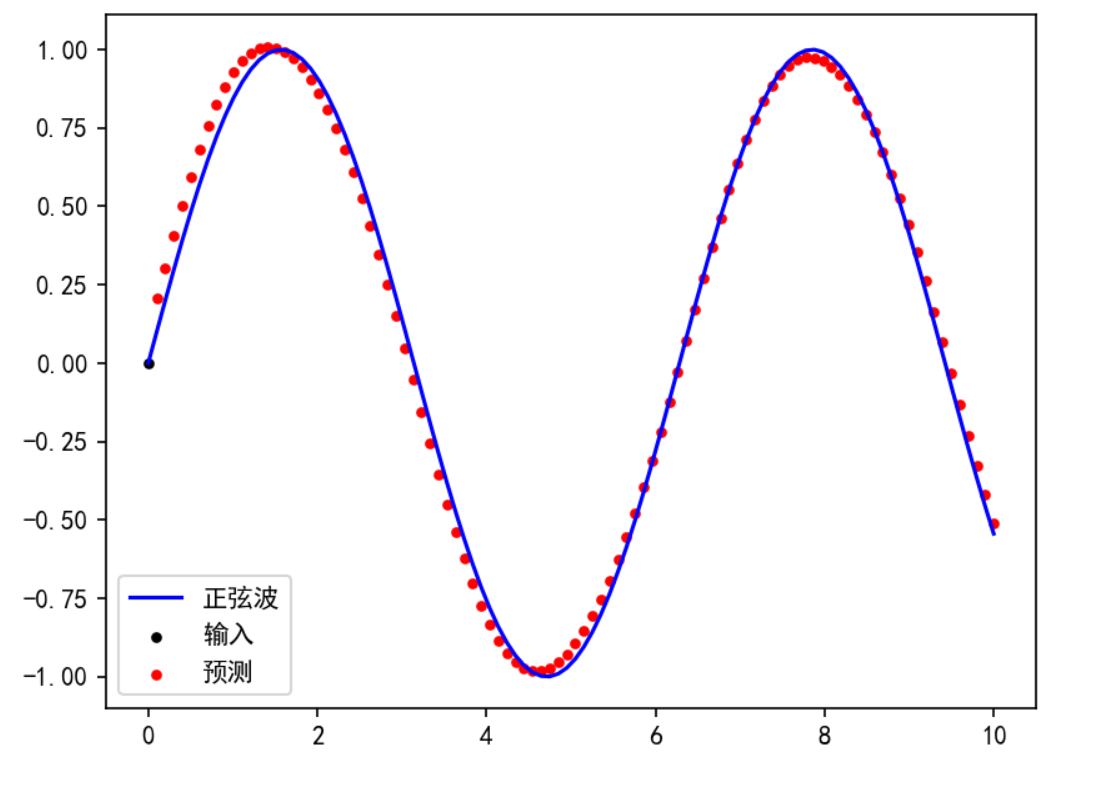 |
nn.LSTM
CLASStorch.nn.LSTM(*args, **kwargs)
参数说明:
input_size:输入序列单元 x t x_t xt?的维度。hidden_size:隐藏层神经元个数,或者也叫输出的维度num_layers:网络的层数,默认为1bias:是否使用偏置batch_first:输入数据的形式,默认是False,形式为(seq, batch, feature),也就是将序列长度放在第一位,batch 放在第二位。如果为True,则为(batch, seq, feature)dropout:dropout率, 默认为0,即不使用。如若使用将其设置成一个0-1的数字即可。birdirectional:是否使用两层的双向的 rnn,默认是Falseproj_size: 默认值:0 https://arxiv.org/abs/1402.1128
记:
N = batch?size L = ?sequence?length? D = 2 ?if?bidirectional=True?otherwise? 1 H in = ?input_size? H c e l l = ?hidden_size? H o u t = proj_size , 如 果 proj_size > 0 ; 否 则 = ?hidden_size? \begin{aligned} N &=\text{batch size} \\ L &=\text { sequence length } \\ D &=2 \text { if bidirectional=True otherwise } 1 \\ H_{\text {in}}&=\text{ input\_size } \\ H_{cell} &=\text { hidden\_size }\\ H_{out} &= \text{proj\_size}, 如果\text {proj\_size} > 0; 否则 = \text { hidden\_size } \end{aligned} NLDHin?Hcell?Hout??=batch?size=?sequence?length?=2?if?bidirectional=True?otherwise?1=?input_size?=?hidden_size?=proj_size,如果proj_size>0;否则=?hidden_size??
输入:input, (h_0, c_0)
(1) input(输入序列)
非批量: ( L , H i n ) (L,H_{in}) (L,Hin?)
批量:如果batch_first=False,
(
L
,
N
,
H
i
n
)
(L,N,H_{in})
(L,N,Hin?);如果batch_first=True,
(
N
,
L
,
H
i
n
)
(N,L,H_{in})
(N,L,Hin?)
(2) h_0(每一层网络的初始状态。如果未提供,则默认为零。)
非批量: ( D × num_layers , H o u t ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},H_{out}) (D×num_layers,Hout?)
批量: ( D × num_layers , N , H o u t ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},N,H_{out}) (D×num_layers,N,Hout?)
(3) c_0(默认为零。)
非批量: ( D × num_layers , H c e l l ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},H_{cell}) (D×num_layers,Hcell?)
批量: ( D × num_layers , N , H c e l l ) (D\times\text{num\_layers},N,H_{cell}) (D×num_layers,N,Hcell?)
输出,output, (h_n, c_n)
(1)output:
非批量: ( L , D × H o u t ) (L,D\times H_{out}) (L,D×Hout?)
批量:如果batch_first=False,
(
L
,
N
,
H
o
u
t
)
(L,N,H_{out})
(L,N,Hout?);如果batch_first=True,
(
N
,
L
,
H
o
u
t
)
(N,L,H_{out})
(N,L,Hout?)
(2)h_n:
非批量: ( D × num_layers , H o u t ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},H_{out}) (D×num_layers,Hout?)
批量: ( D × num_layers , N , H o u t ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},N,H_{out}) (D×num_layers,N,Hout?)
(3)c_n
非批量: ( D × num_layers , H c e l l ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},H_{cell}) (D×num_layers,Hcell?)
批量: ( D × num_layers , N , H c e l l ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},N,H_{cell}) (D×num_layers,N,Hcell?)
权重和偏置初始化:
从均匀分布 U ( ? k , k ) U(-\sqrt{k},\sqrt{k}) U(?k?,k?)采样,其中 k = 1 hidden_size k=\frac{1}{\text{hidden\_size}} k=hidden_size1?
nn.GRU
CLASS torch.nn.GRU(*args, **kwargs)
参数说明:
input_size:输入序列单元 x t x_t xt?的维度。hidden_size:隐藏层神经元个数,或者也叫输出的维度num_layers:网络的层数,默认为1nonlinearity:激活函数,默认为tanhbias:是否使用偏置batch_first:输入数据的形式,默认是False,形式为(seq, batch, feature),也就是将序列长度放在第一位,batch 放在第二位。如果为True,则为(batch, seq, feature)dropout:dropout率, 默认为0,即不使用。如若使用将其设置成一个0-1的数字即可。birdirectional:是否使用两层的双向的 rnn,默认是False
记:
N = batch?size L = ?sequence?length? D = 2 ?if?bidirectional=True?otherwise? 1 H in = ?input_size? H o u t = ?hidden_size? \begin{aligned} N &=\text{batch size} \\ L &=\text { sequence length } \\ D &=2 \text { if bidirectional=True otherwise } 1 \\ H_{\text {in}}&=\text{ input\_size } \\ H_{o u t} &=\text { hidden\_size } \end{aligned} NLDHin?Hout??=batch?size=?sequence?length?=2?if?bidirectional=True?otherwise?1=?input_size?=?hidden_size??
输入:input, h_0
(1)input(输入序列)
非批量: ( L , H i n ) (L,H_{in}) (L,Hin?)
批量:如果batch_first=False,
(
L
,
N
,
H
i
n
)
(L,N,H_{in})
(L,N,Hin?);如果batch_first=True,
(
N
,
L
,
H
i
n
)
(N,L,H_{in})
(N,L,Hin?)
(2) h_0(每一层网络的初始状态。如果未提供,则默认为零。)
非批量: ( D × num_layers , H o u t ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},H_{out}) (D×num_layers,Hout?)
批量: ( D × num_layers , N , H o u t ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},N,H_{out}) (D×num_layers,N,Hout?)
输出,output,hn:
(1)output:
非批量: ( L , D × H o u t ) (L,D\times H_{out}) (L,D×Hout?)
批量:如果batch_first=False,
(
L
,
N
,
H
o
u
t
)
(L,N,H_{out})
(L,N,Hout?);如果batch_first=True,
(
N
,
L
,
H
o
u
t
)
(N,L,H_{out})
(N,L,Hout?)
(2)h_n:状态
非批量: ( D × num_layers , H o u t ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},H_{out}) (D×num_layers,Hout?)
批量: ( D × num_layers , N , H o u t ) (D\times \text{num\_layers},N,H_{out}) (D×num_layers,N,Hout?)
权重和偏置初始化:
从均匀分布 U ( ? k , k ) U(-\sqrt{k},\sqrt{k}) U(?k?,k?)采样,其中 k = 1 h i d d e n _ s i z e k=\frac{1}{hidden\_size} k=hidden_size1?
[1] https://www.zjujournals.com/eng/article/2019/1008-973X/G181044wanghongxia-1.jpg.html
