1. 粒子群算法的概念
粒子群优化算法(PSO:Particle swarm optimization)是一种进化计算技术(evolutionary computation)。源于对鸟群捕食的行为研究。粒子群优化算法的基本思想:是通过群体中个体之间的协作和信息共享来寻找最优解.
PSO的优势:在于简单容易实现并且没有许多参数的调节。目前已被广泛应用于函数优化、神经网络训练、模糊系统控制以及其他遗传算法的应用领域。
2. 粒子群算法分析
- 基本思想
粒子群算法通过设计一种无质量的粒子来模拟鸟群中的鸟,粒子仅具有两个属性:速度和位置,速度代表移动的快慢,位置代表移动的方向。每个粒子在搜索空间中单独的搜寻最优解,并将其记为当前个体极值,并将个体极值与整个粒子群里的其他粒子共享,找到最优的那个个体极值作为整个粒子群的当前全局最优解,粒子群中的所有粒子根据自己找到的当前个体极值和整个粒子群共享的当前全局最优解来调整自己的速度和位置。下面的动图很形象地展示了PSO算法的过程:
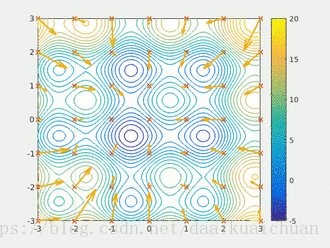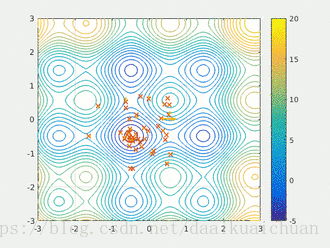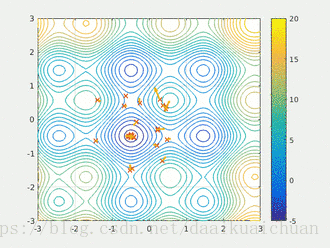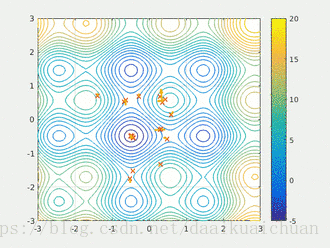
- 更新规则
PSO初始化为一群随机粒子(随机解)。然后通过迭代找到最优解。在每一次的迭代中,粒子通过跟踪两个“极值”(pbest,gbest)来更新自己。在找到这两个最优值后,粒子通过下面的公式来更新自己的速度和位置。
v i = v i + c 1 × r a n d ( ) × ( p b e s t i ? x i ) + c 2 × r a n d ( ) × ( g b e s t i ? x i ) (1) v_{i}=v_{i}+c_{1}\times\mathrm{rand}()\times(pbest_{i}-x_{i})+c_{2}\times\mathrm{rand}()\times(gbest_{i}-x_{i}) \tag{1} vi?=vi?+c1?×rand()×(pbesti??xi?)+c2?×rand()×(gbesti??xi?)(1)
x i = x i + v i (2) x_{i}=x_{i}+v_{i} \tag{2} xi?=xi?+vi?(2)
其中
i
=
1
,
2
,
?
?
,
N
i=1,2,\cdots,N
i=1,2,?,N,
N
N
N是此群中粒子的总数;
v
i
v_{i}
vi?是粒子的速度,
v
i
v_{i}
vi?的最大值为
V
max
?
>
0
V_{\max}>0
Vmax?>0,如果
v
i
>
V
max
?
v_{i}>V_{\max}
vi?>Vmax?,则
v
i
=
V
max
?
v_{i}=V_{\max}
vi?=Vmax?;
r
a
n
d
(
)
\mathrm{rand}()
rand()是介于(0,1)之间的随机数;
x
i
x_{i}
xi?为粒子的当前位置;
c
1
c_{1}
c1?和
c
2
c_{2}
c2?是学习因子,通常
c
1
=
c
2
=
2
c_{1}=c_{2}=2
c1?=c2?=2;
公式(1)的
- 第一部分称为记忆项,表示上次速度大小和方向的影响;
- 第二部分称为自身认知项,是从当前点指向粒子自身最好点的一个矢量,表示粒子的动作来源于自己经验的部分;
- 第三部分称为群体认知项,是一个从当前点指向种群最好点的矢量,反映了粒子间的协同合作和知识共享。粒子就是通过自己的经验和同伴中最好的经验来决定下一步的运动。
以上面两个公式为基础,形成了PSO的标准形式。
v i = ω × v i + c 1 × r a n d ( ) × ( p b e s t i ? x i ) + c 2 × r a n d ( ) × ( g b e s t i ? x i ) v_{i}=\omega\times v_{i}+c_{1}\times \mathrm{rand}()\times(pbest_{i}-x_{i})+c_{2}\times\mathrm{rand}()\times(gbest_{i}-x_{i}) vi?=ω×vi?+c1?×rand()×(pbesti??xi?)+c2?×rand()×(gbesti??xi?)
其中 ω \omega ω叫做惯性因子,其值为非负。其值较大,全局寻优能力强,局部寻优能力弱;其值较小,全局寻优能力弱,局部寻优能力强。动态 ω \omega ω能获得比固定值更好的寻优结果。动态 ω \omega ω可在PSO搜索过程中线性变化,也可以根据PSO性能的某个测度函数动态改变。
目前采用较多的是线性递减权值(Linear Decreasing Weight,LDW)策略:
ω ( t ) = ( ω i n i ? ω e n d ) ( G k ? g ) / G k + ω e n d \omega^{(t)}=(\omega_{ini}-\omega_{end})(G_{k}-g)/G_{k}+\omega_{end} ω(t)=(ωini??ωend?)(Gk??g)/Gk?+ωend?
其中
G
k
G_{k}
Gk?是最大迭代次数;
ω
i
n
i
\omega_{ini}
ωini?是初始惯性权值;
ω
e
n
d
\omega_{end}
ωend?是迭代至最大进化代数时的惯性权值;
典型权值为:
ω i n i = 0.9 , ω e n d = 0.4 \omega_{ini}=0.9,\omega_{end}=0.4 ωini?=0.9,ωend?=0.4
ω \omega ω的引入,使用PSO算法性能有了很大的提高,针对不同的搜索问题,可以调整全局和局部搜索能力,也使PSO算法有成功地应用于很多实际问题。
公式(2)(3)被视为标准PSO算法。
3. PSO算法的流程和伪代码
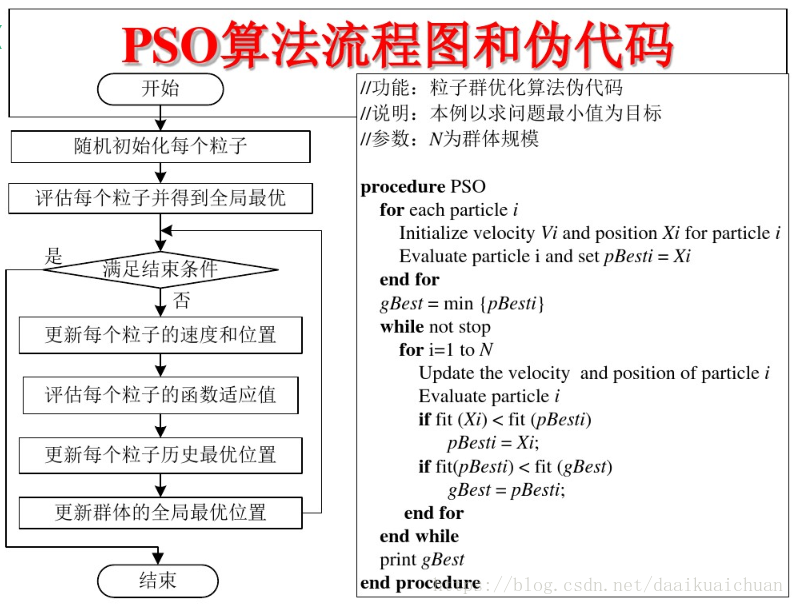
4. PSO算法举例

5. PSO算法的matlab实现
% PSO algorithm:
% velosity: vi=w*vi+c1*rand()*(pbesti-xi)+c2*rand()*(gbesti-xi);
% position: xi=xi+vi;
% Objective Funtion:y=f(x1,x2)=x1^2+x2^2,-10<=x1,x2<=10
%% -------------- set the weight of parameters ----------------
w=0.5; % the weight of velocity
c1=2; % the first weight of position
c2=2; % the second weight of position
N=1000; % the number of particles
NP=3; % the number of parameters per particle
Nstep=1000; % the step number of iteration
xmin=-100; % the upper limit for x
xmax=100; %the lower limit for x
vmax=1; % to be modified according to experience
%% -------------- initialize --------------------------
x=unifrnd(xmin,xmax,N,NP) % position
v=unifrnd(-vmax,vmax,N,NP) %velosity
pbest=x; % the best position
% f=x(:,1).^2+x(:,2).^2; % objective function
%f=(x-5).^2;
% f=(x(:,1)-5).^2+(x(:,2)-10).^2;
f=(x(:,1)-5).^2+(x(:,2)-10).^2+(x(:,3)-20).^2;
flbest=f; % the optimal value per particle
fgbest=min(flbest); % for optimal value all particle
[p1,p2]=find(flbest==fgbest); % the position of the global optimal value
p3=size(p1);
if p3(1)==1
p4=p1;
else
p4=p1(1);
end
gbest=pbest(p4,:); % the position of the global optimal value
%% ----------- to iterate PSO------------------------
for i=1:Nstep
gbesttemp=repmat(gbest,N,1); % extend 1D matrix into 2D matrix
vtemp=w*v+c1*rand()*(pbest-x)+c2*rand()*(gbest-x);
vtemp(vtemp>vmax)=vmax;
vtemp(vtemp<-vmax)=-vmax;
v=vtemp;
xtemp=x+v;
xtemp(xtemp>xmax)=xmax;
xtemp(xtemp<xmin)=xmin;
x=xtemp;
% f=x(:,1).^2+x(:,2).^2; % to be improved
% f=(x-5).^2;
% f=(x(:,1)-5).^2+(x(:,2)-10).^2;
f=(x(:,1)-5).^2+(x(:,2)-10).^2+(x(:,3)-20).^2;
flbest=min(f,flbest); % compare two matrix for the minimum value
[temp1,temp2]=find((flbest-f)==0); % the location of the optimal value change
if isempty(temp1)==0 % prevent null matrix
x(temp1,:);
pbest(temp1,:)=x(temp1,:);
end
fgbest=min(flbest); % for optimal value per particle's position
[p1,p2]=find(flbe
st==fgbest); %the position of the global optimal value
p3=size(p1);
if p3(1)==1 % prevent matrix elements from being greater than one
p4=p1;
else
p4=p1(1);
end
gbest=pbest(p4,:); %the position of the global optimal value
end
