1.Anchor-Free Person Search
Yichao Yan1 * ? , Jinpeng Li1*, Jie Qin1?, Song Bai2, Shengcai Liao1, Li Liu1, Fan Zhu1, and Ling Shao1
1 Inception Institute of Artificial Intelligence (IIAI), UAE 2 University of Oxford, UK
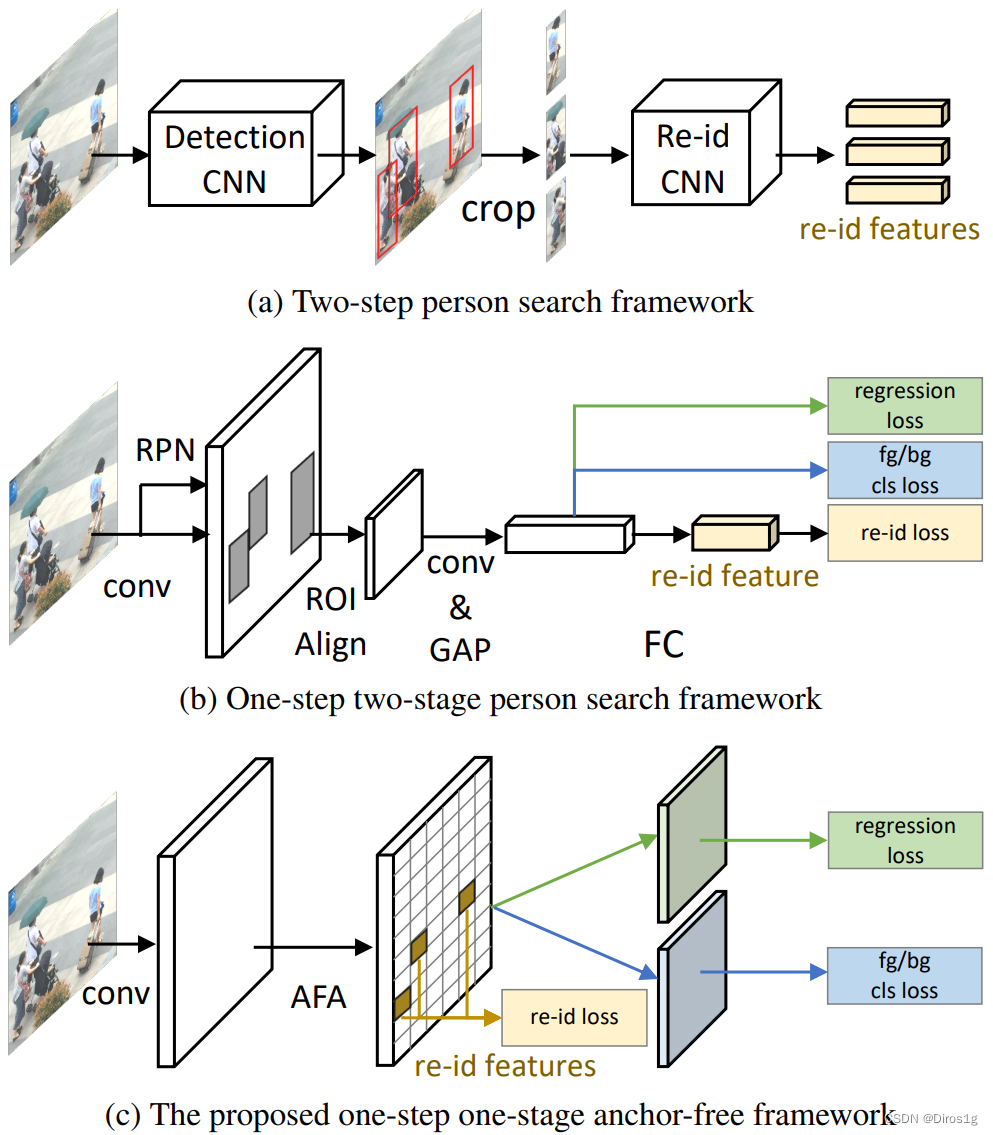
Person search任务的目的是:定位并识别目标行人。其包含了两个子任务:行人检测和行人重识别。现有方法主要分为两类:二步检索框架和一步二阶段检索框架。前者先通过目标检测算法定位行人位置,再裁切出行人进行重识别,这类方法比较耗时;后者实现了两种任务的端到端学习,通过ROI对齐层获取行人区域(如Faster-RCNN),这类方法存在密集anchor计算复杂的问题以及超参数敏感(anchor数量、尺寸等)的问题.
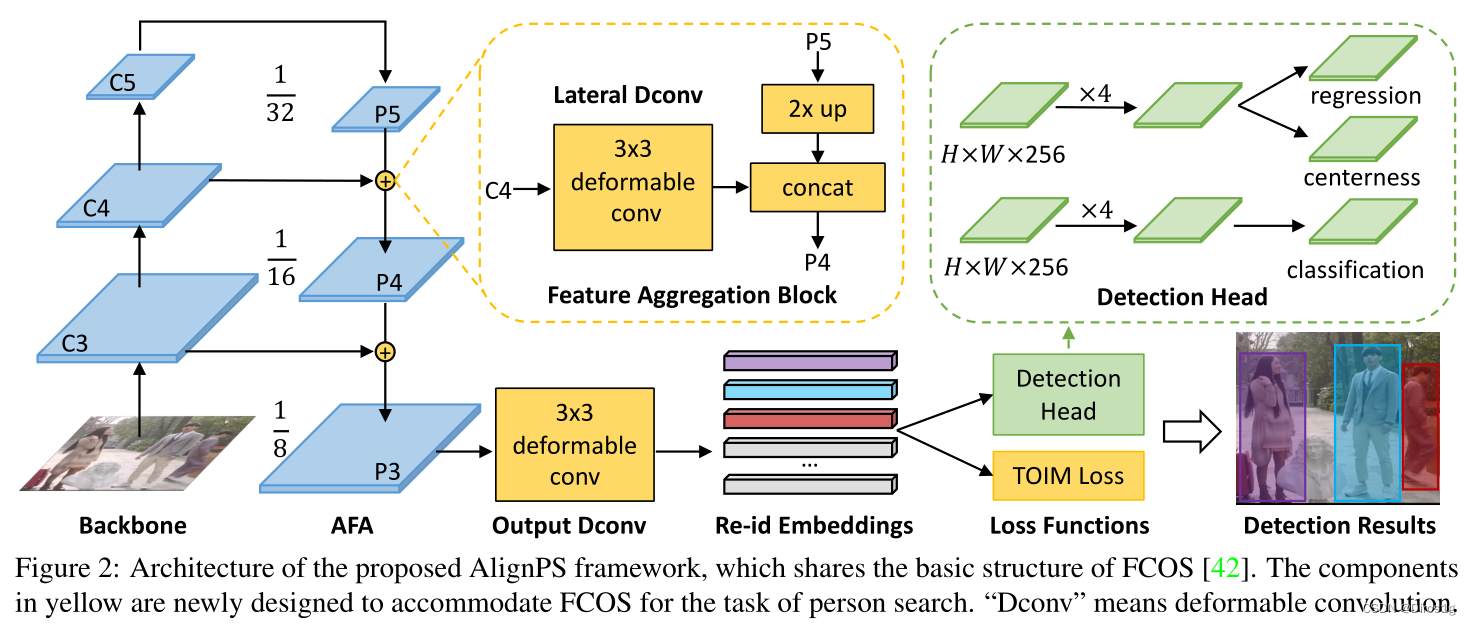
作者提出了anchor-free方法,作者设计了Feature Aligned Person Search Network (AlignPS)。其中设计了一个anchor-free检测模型以及一个aligned feature aggregation (AFA)模块:
AFA利用了可变卷积(deformable convolution)和特征融合来改造FPN,解决区域、尺寸的不对齐问题。
还提出新的损失:
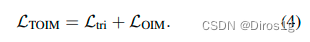
第一部分:
将行人中心周围的一组特征作为正样本,其他行人的一组特征为负样本,计算其三元组损失
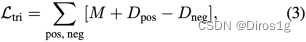
M代表正负样本间的边界大小,Dpos和Dneg分别代表正、负样本对之间的欧氏距离。最后,本文所提出的TOIM损失即为OIM和三元组损失函数的简单叠加。
第二部分:
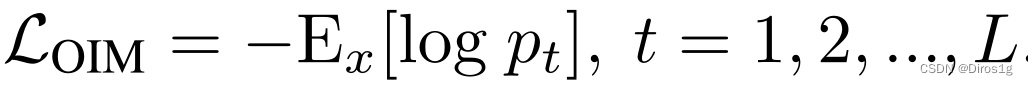
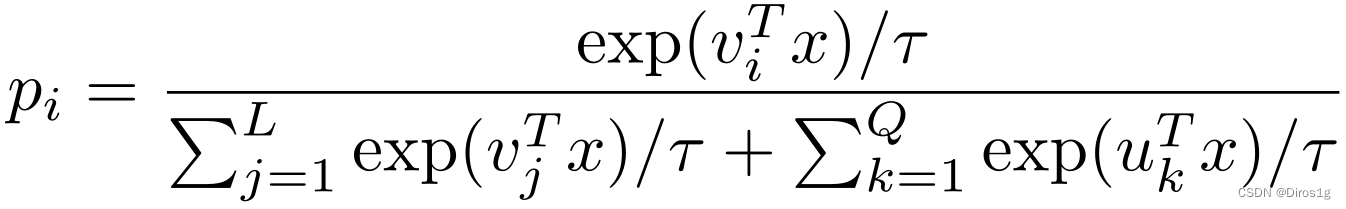
v代表有标签,u代表没标签
2.Spatial-Temporal Correlation and Topology Learning for Person Re-Identification in Videos
Jiawei Liu, Zheng-Jun Zha*, Wei Wu, Kecheng Zheng, Qibin Sun
University of Science and Technology of China, China
Spatial-Temporal Correlation and Topology Learning(CTL)利用 CNN 主干和关键点估计器,从人体中提取语义上的局部特征,作为图的节点,在多个颗粒度上进行提取。它通过考虑全局上下文信息和人体的物理连接,探索一种背景强化的拓扑结构来构建多尺度图。
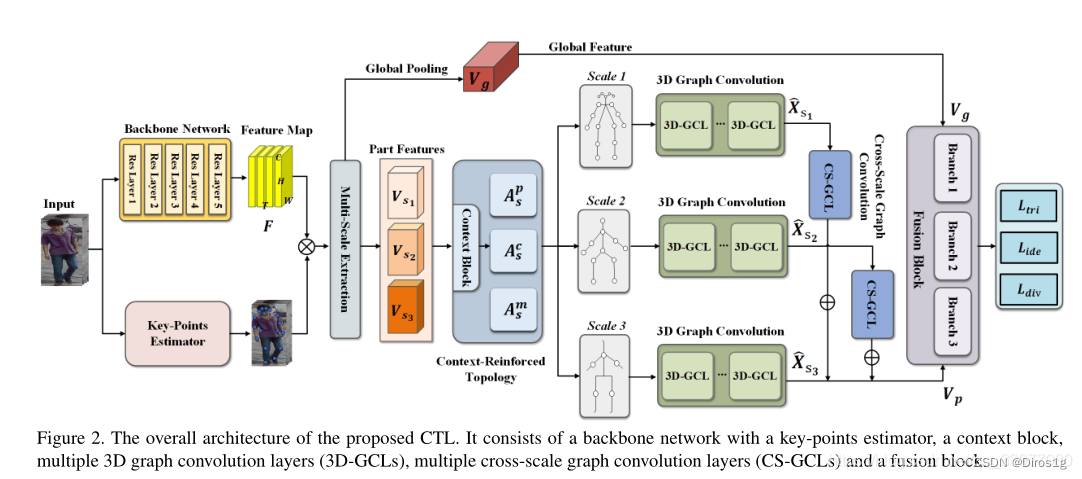
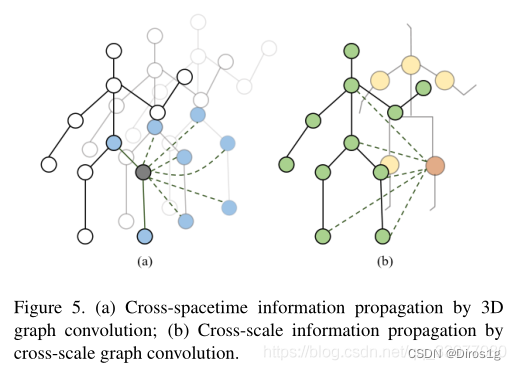
还设计一个三维图卷积和一个跨尺度图卷积,有利于直接跨时空和跨尺度的信息传播,以捕捉层次化的时空依赖和结构信息。通过联合进行这两种卷积,CTL有效地挖掘出与外观信息互补的综合线索,以提高表征能力。
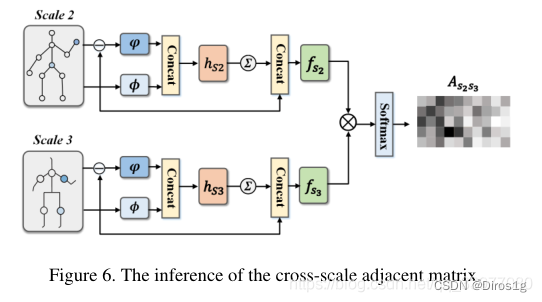
3.Partial Person Re-identification with Part-Part Correspondence Learning
Tianyu He1, Xu Shen1, Jianqiang Huang1, Zhibo Chen2, and Xian-Sheng Hua1
1DAMO Academy, Alibaba Group
2University of Science and Technology of China
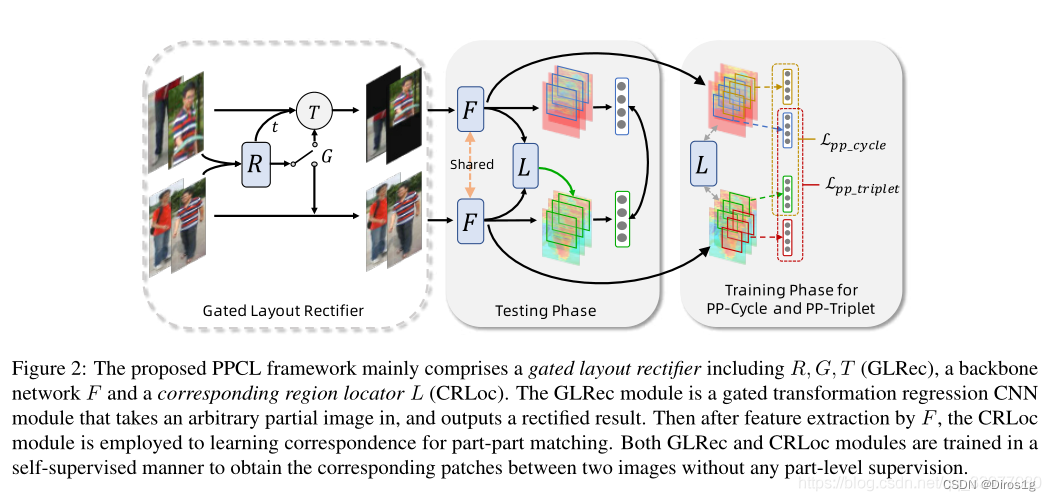
用GLRec模块生成一系列仿射变换系数,以指导局部图片的转换
用CRLoc模块,在PP-Cycle和PP-Triplet损失约束下,定位相应区域;
将重点放在识别部分(有缺陷的)输入,借助部分-部分对应学习(PPCL),这是以种自监督学习框架,无需任何额外的部分级监督即可学习图像块之间的对应关系。
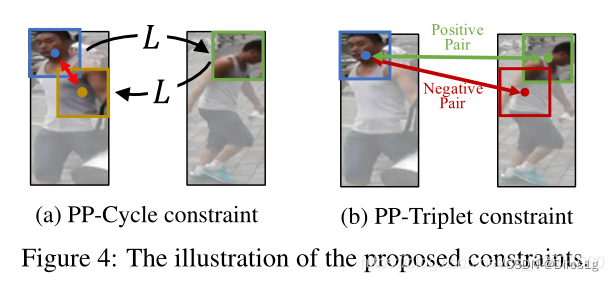
Part-Part Cycle constraint(PP-Cycle):利用功能的双重性来寻找相应的区域,假设如果CRLoc模块能够根据xr预测而y中相应的patch,那么它也能转换回xr
Part-Part Triplet constraint(PP-Triplet):对于给定的部分输入,利用两个图像块之间的最佳对应区域的唯一性。将给定的部分输入视为锚,CRLoc模块的输出视为正样本。和参考图像的随机采样的负样本,形成一个三元组约束。
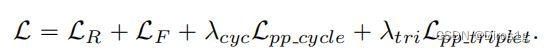
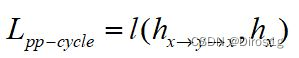
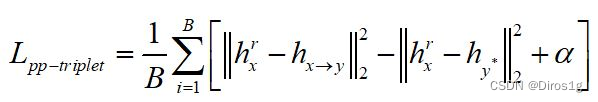
4.Person30K: A Dual-Meta Generalization Network for Person Re-Identification
Yan Bai1,4, Jile Jiao2, Wang Ce1, Jun Liu3, Yihang Lou1, Xuetao Feng2, and Ling-Y u Duan1,4,?
1Peking University, Beijing, China 2Alibaba Group, Beijing, China
3Singapore University of Technology and Design 4Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen, China
1.主要贡献
网络在已有的数据上检测结果可能较好,但是在不同条件下可能出现泛化能力下降的问题。
1.收集了一个新的数据集:Person30K,有三万个人,场景丰富
2.提出了一种区域泛化的ReID方法,dual-meta generalization network双元泛化网络(DMG-Net),以利用元学习在训练过程和度量空间学习方面的优点
2.算法流程
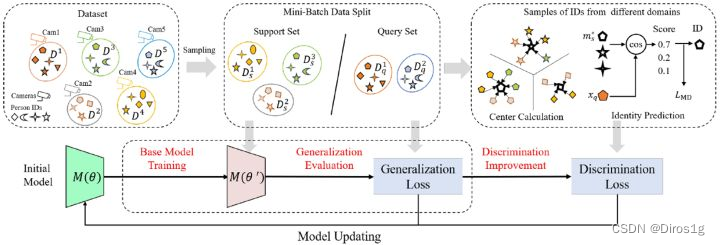
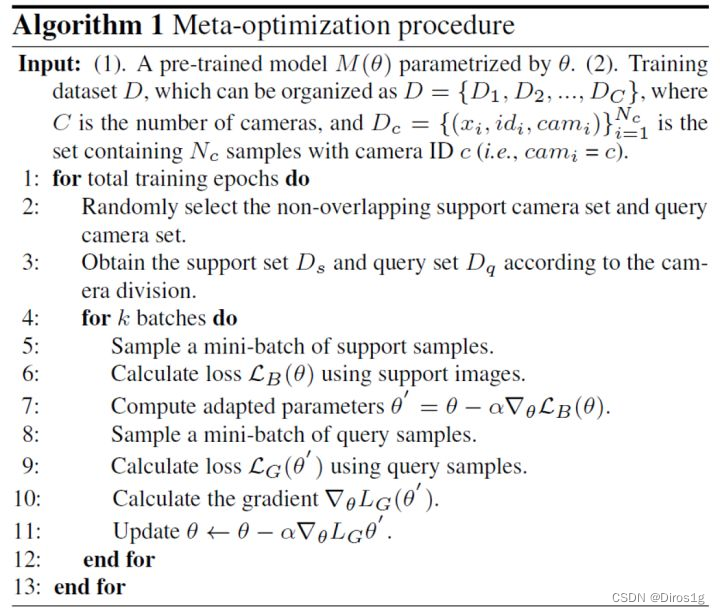
DMG-Net包括元泛化训练程序和元判别损失。元泛化首先在支持集(训练集)上训练基础模型,然后在查询集(测试集)上进行泛化评估。对于元判别损失,优化度量空间以改善模型判别。
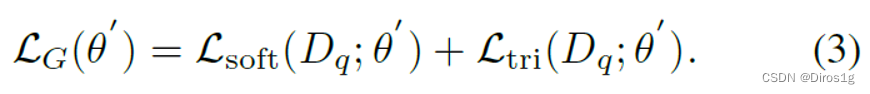
为了实现这种跨摄像头匹配,作者设计了一种新的P路分类器,它将查询样本分类为mini-batch内的P个支持ID
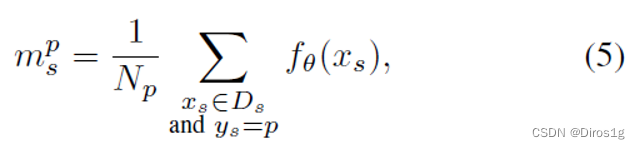
计算查询特征与哪个支持中心最为接近,然后根据相似度评分预测查询属于哪个支持ID。
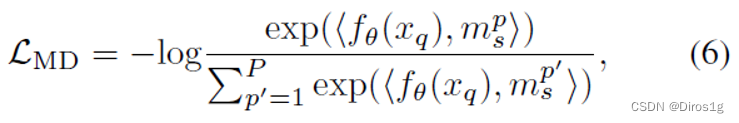
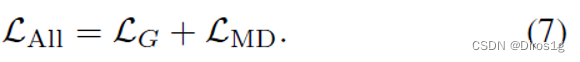
5.Learning 3D Shape Feature for Texture-insensitive Person Re-identification
Jiaxing Chen1,5#, Xinyang Jiang3#, Fudong Wang3, Jun Zhang3, Feng Zheng4, Xing Sun3, Wei-Shi Zheng1,2?
1School of Computer Science and Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, China
2Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen, China
3Y outu Lab, Tencent
4CSE, Southern University of Science and Technology
5Pazhou Lab, Guangzhou, China
1.主要贡献
人的再识别(person ReID)高度依赖于服装等视觉纹理信息,但大多数现有的ReID方法很少注意到纹理混淆的情况,如衣服的更换和人穿着相同的衣服
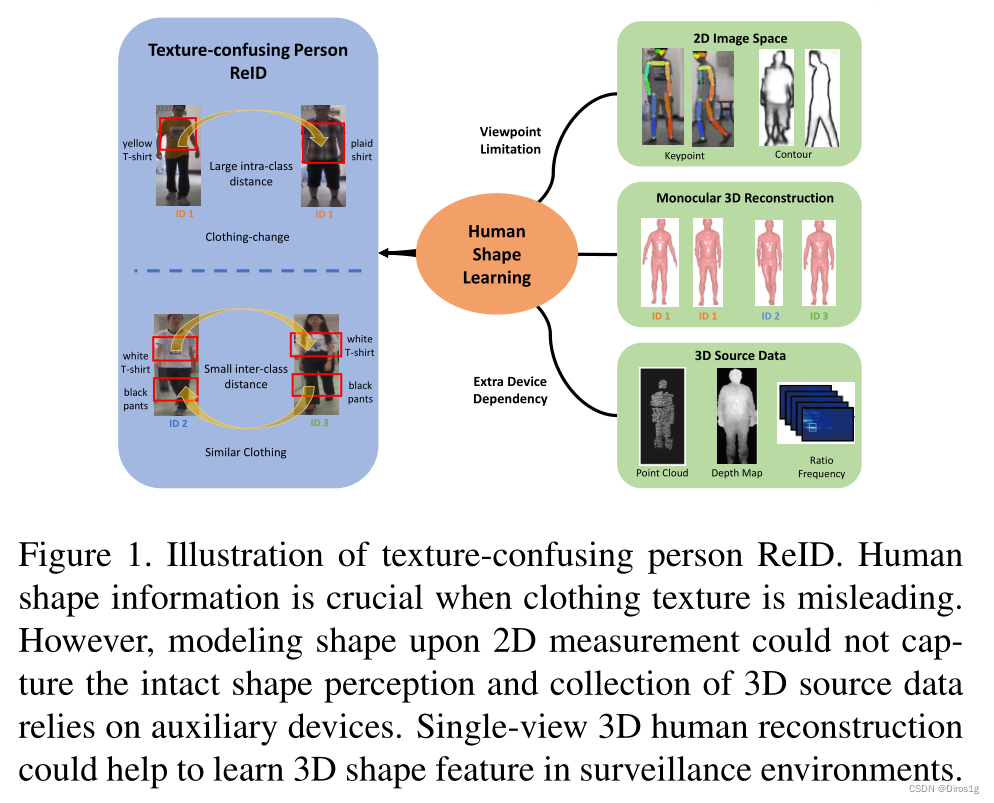
1.利用人的三维信息来提高,网络关于纹理信息方面的鲁棒性
据体,作者提出一个3d学习器3D Shape Learn-
ing,可以直接从2d图片上提取人的三维信息
2.由于没有gt,作者提出adversarial self-supervised pro-
jection (ASSP) 对抗性自我监督投射
2.算法流程
该模型由两个分支组成。一个是在三维人体重构的正则化下学习三维形状特征;另一个分支是通过从原始图像中学习纹理敏感的RGB特征。
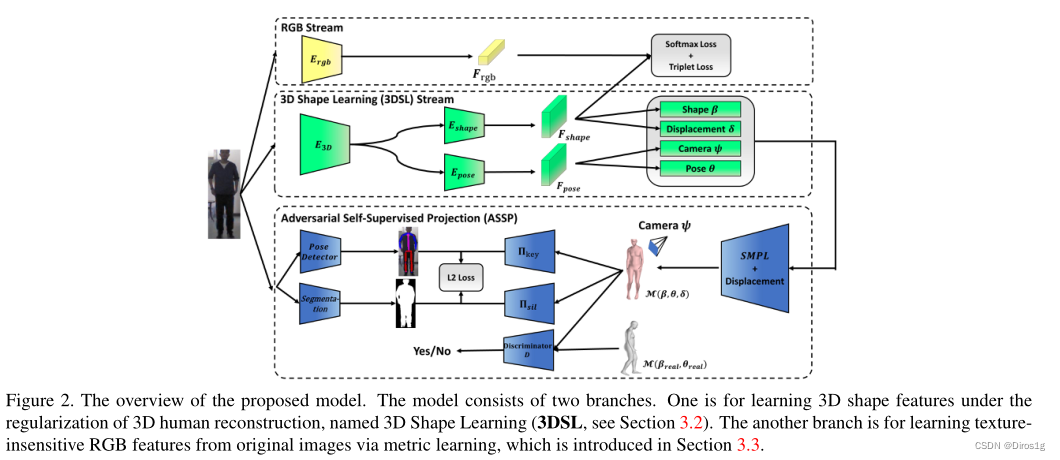
1.RGB Stream: 捕获其它有用的纹理不敏感的RGB特征:面部和其它一些局部特征
2.3DSL Stream:使用SMPL进行提取到包含所有3D信息的一般特征:形状相关和姿态相关
3.ASSP:对抗学习的目标是生成合理的3D人体模型,两部分信息:语义分割、骨干提取。通过对抗性学习确保粗略的 形体,并通过自监督从三维到二维来适应细致的身体细节。
6.Combined Depth Space based Architecture Search For Person Re-identification
Hanjun Li1,4, Gaojie Wu1, Wei-Shi Zheng1,2,3,*
1School of Computer Science and Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, China
2Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518005, China
3Key Laboratory of Machine Intelligence and Advanced Computing, Ministry of Education, China
4Pazhou Lab, Guangzhou, China
1.主要贡献
目前大多数关于ReID的工作利用了大型骨干网络,如ResNet(把工作的重心放在了目标检测方面),它是用于图像分类而不是ReID。
提出了一个轻型reid搜索空间Combined Depth Space和新的搜索策略称为Top-k Sample Search,得到高效的网络架构CDNet
2.算法流程
Combined Depth Space:
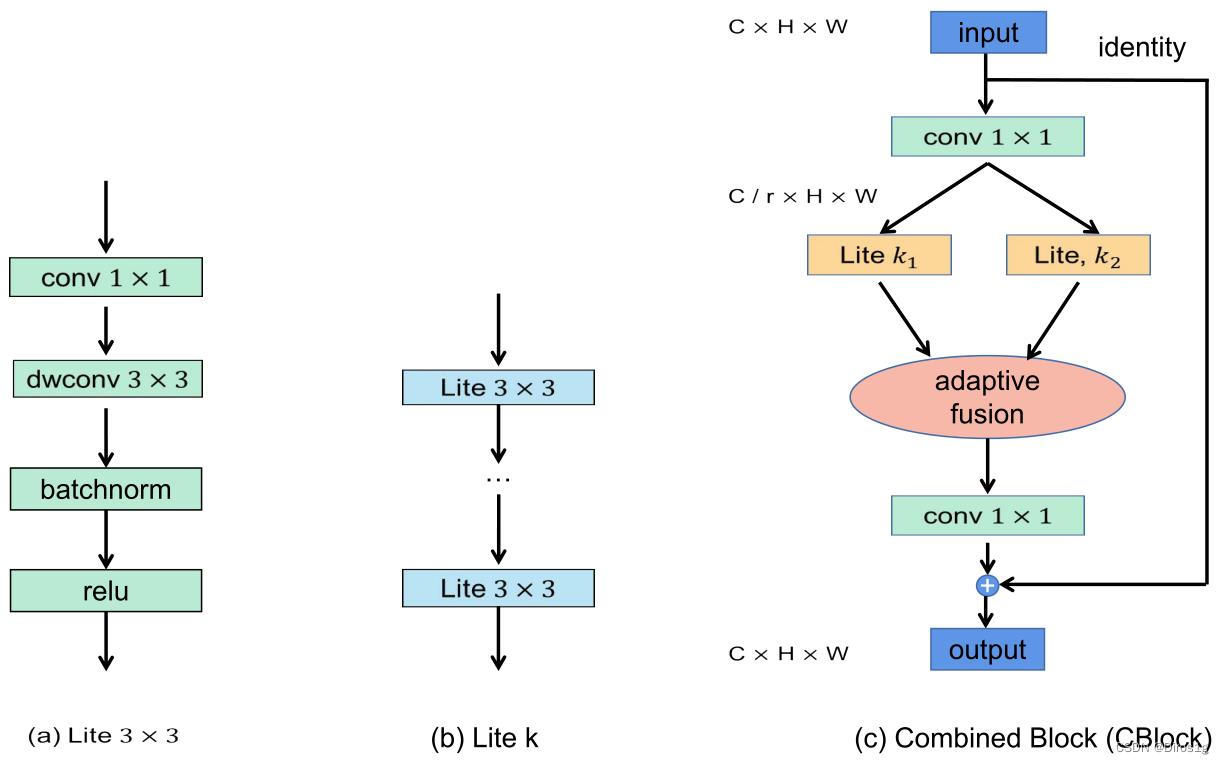
1.CBlock:CBlock采用了双分支Lite结构,设置组合为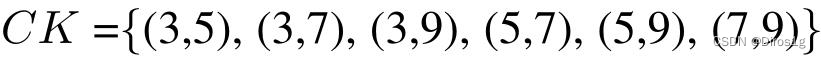
由此得到6中CBlock。两个Lite分支的融合过程引入了Adaptive Fusion Gate,在通道维度进行加权求和,最终通过1x1卷积恢复特征图尺寸
2.MBlock:
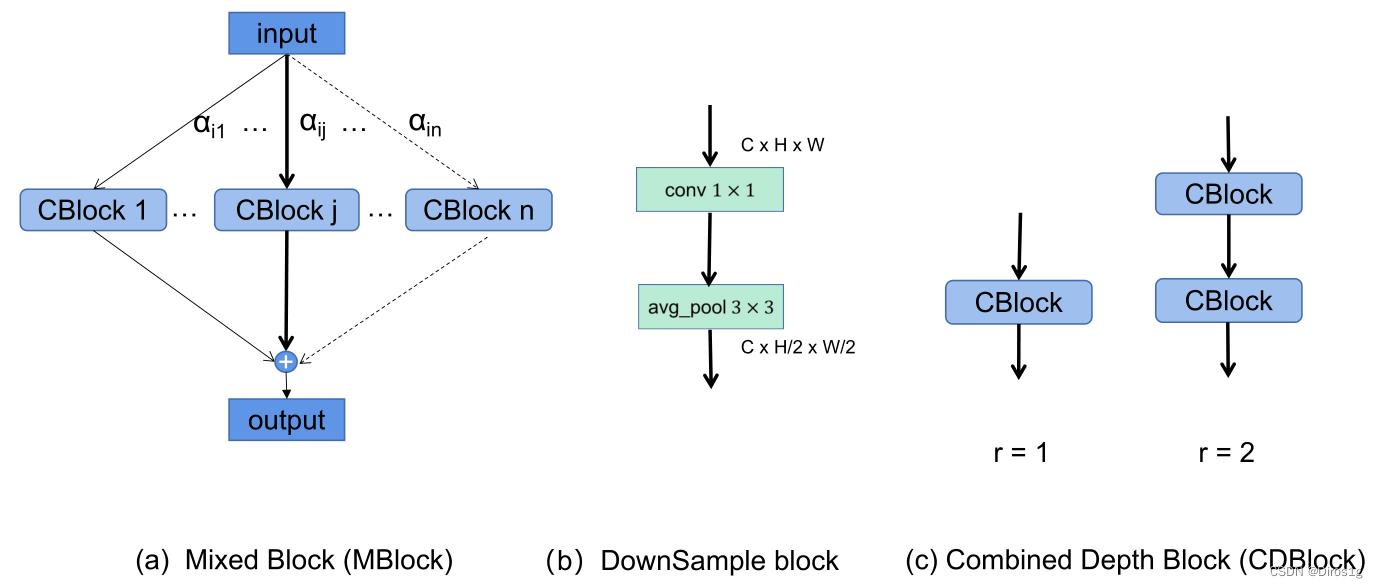
MBlock整合了上述CK中的6个不同卷积核尺寸的CBlock,每个分支赋予一个权重,表示该分支的重要性。
上述搜索空间称为Combined Space(CS),该搜索框架称为CNet,由于每个MBlock有6个候选分支,因此搜索空间大小66
3.CDBlock:
为了有效地加深网络,作者认为应该在每个阶段分配适量的MBlock,而不是随机或者均匀分配。
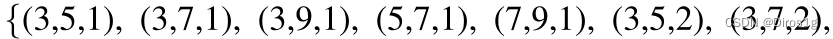
新的搜索空间大小为:126
7.Learning to Generalize Unseen Domains via Memory-based Multi-Source Meta-Learning for Person Re-Identification
Y uyang Zhao1*, Zhun Zhong2?, Fengxiang Yang1, Zhiming Luo1?, Yaojin Lin4, Shaozi Li1,3?, Nicu Sebe2
1 Department of Artificial Intelligence, School of Informatics, Xiamen University
2 Department of Information Engineering and Computer Science, University of Trento
3 Institute of Artificial Intelligence, Xiamen University
4 Minnan Normal University
1.主要贡献
目前的算法在新的场景鲁棒性比较差,因为我们的训练集不是完美的,作者在本文提出1.基于记忆的多元泛化模型Memory-based Multi-Source Meta-Learning (M3L)用于reid的源域泛化Domain generalization;
2.元批处理规范化层(MetaBN)
2.算法流程
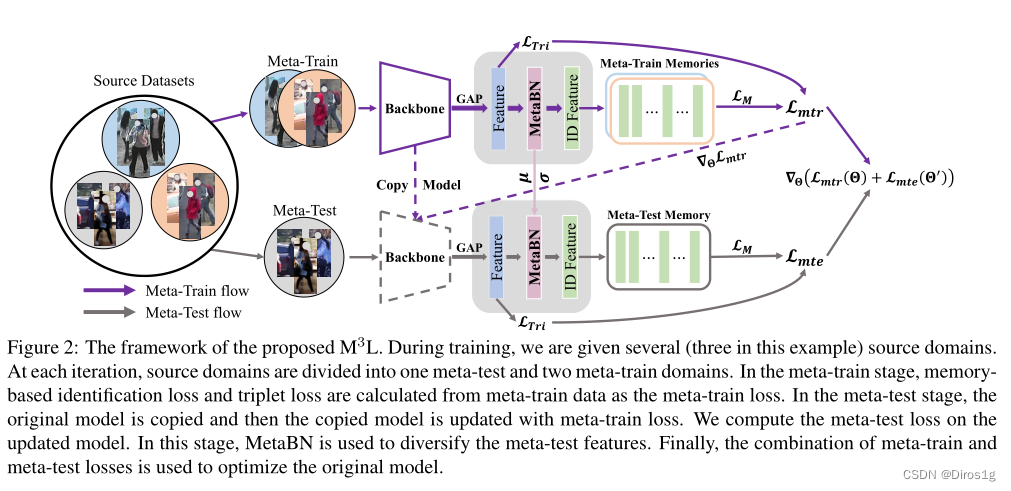
在训练期间,我们会得到三个源域。在每次迭代中,源域被划分为一个元测试和两个元训练域。在元训练阶段,根据元训练数据计算基于记忆的识别损失和三元组损失作为元训练损失。在元测试阶段,对原始模型进行复制,然后使用元训练损失更新复制的模型。
Memory-based Multi-Source Meta-Learning (M3L)的Multi-Source指的就是元学习的分割数据集策略:n 个源域随机划分为 n-1个域作为元训练,剩下的一个域作为元测试。元学习损失的计算过程包括元训练和元测试两个阶段:
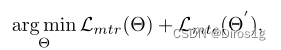
Θ指的是网络参数,Θ’是更新的后的参数,L_mte只用来更新Θ
Memory-based:使用的是lstm中的记忆策略:
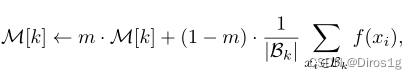
其中Bk表示属于第k个身份的样本,|Bk|表示当前小批量中属于第k个身份的样本数量。M∈[0,1]控制更新速率。
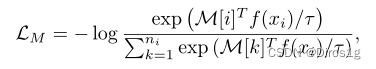
MetaBN:
