论文:Multi-View Stereo for Community Photo Collections 5.1节
1.Global View Selection
For each reference view R, global view selection seeks a set N of neighboring views that are good candidates for stereo matching in terms of scene content, appearance, and scale.
对于每个参考视图 R,全局视图选择会寻找一组 N 个相邻视图,这些视图在场景内容、外观和比例方面是立体匹配的良好候选者。
在这里,我们描述了一个评分函数,旨在根据这些要求来衡量每个候选相邻视图的质量。
To first order, the number of shared feature points reconstructed in the SfM phase is a good indicator of the compatibility of a given view V with the reference view R. Indeed, images with many shared features generally cover a similar portion of the scene.
事实上,具有许多共享特征的图像通常覆盖场景的相似部分。
Moreover, success in SIFT matching is a good predictor that pixel-level matching will also succeed across much of the image. In particular, SIFT selects features with similar appearance, and thus images with many shared features tend to have similar appearance to each other, overall.
SIFT选择具有相似外观的特征,具有许多共享特征的图像总体上倾向于具有相似的外观。
转折来了
However, the number of shared feature points is not sufficient to ensure good reconstructions.
共享特征点数目不够多
First, the views with the most shared feature points tend to be nearly collocated and as such do not provide a large enough baseline for accurate reconstruction.
首先,具有最多共享特征点的视图往往几乎并置,因此不能提供足够大的基线来进行准确的重建。
Second, the scale invariance of the SIFT feature detector causes images of substantially different resolutions to match well, but such resolution differences are problematic for stereo matching.
其次,SIFT 特征检测器的尺度不变性导致分辨率差异很大的图像可以很好地匹配,但是这种分辨率差异对于立体匹配是有问题的。
?准备解决:

为候选邻域 N(包括 R)内的每个视图 V 计算全局分数 gR,作为与 R 共享的特征的加权和。FX是在视图X中观察到的特征点的集合。
?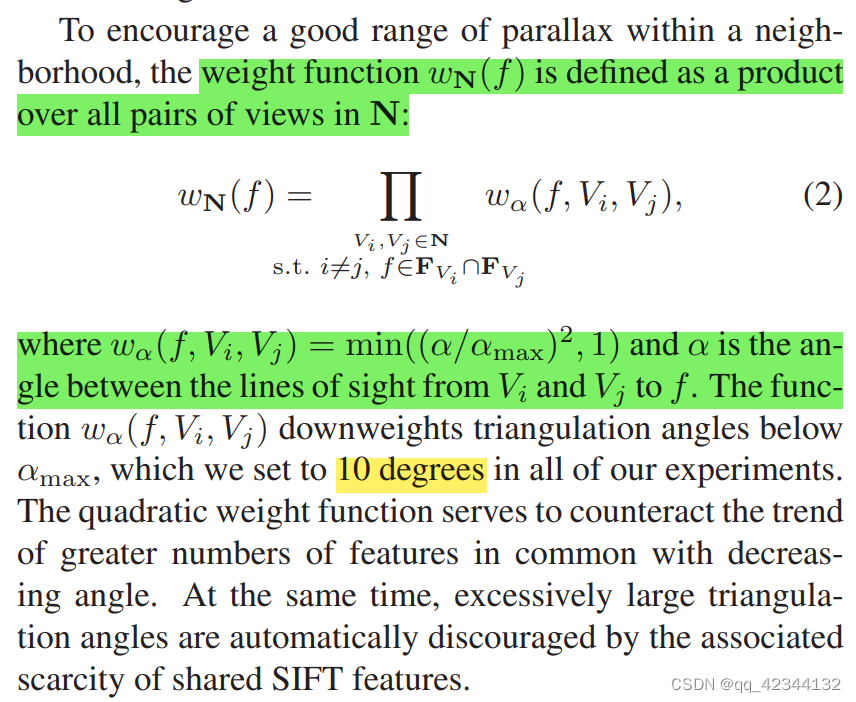
?为了鼓励邻域内的良好视差范围,权重函数 wN(f) 定义为 N 中所有视图对的乘积。
?α 是从 Vi 和 Vj 到 f 的视线之间的夹角。
函数 wα(f, Vi, Vj ) 将三角测量角降低到低于 αmax 的权重,我们在所有实验中将其设置为 10 度。二次权重函数用于抵消更多共同特征随着角度减小的趋势。 同时,由于共享 SIFT 特征的相关稀缺性,会自动阻止过大的三角剖分角度。
保证基线足够大。


?加权函数 ws(f) 测量图像 R 和 V 在特征 f 处的分辨率相似性。 为了估计特征 f 附近 V 的 3D 采样率,我们计算以 f 为中心的球体的直径 sV (f),其在 V 中的投影直径等于在 V 中的像素间距。我们类似地计算 R 的 sR(f) 并根据比率 r = sR(f)/sV (f) 定义尺度权重 ws 。
此权重函数偏爱与参考视图具有相同或更高分辨率的视图。
针对分辨率
?
?
定义了视图 V 和邻域 N 的全局分数后,我们现在可以根据视图分数 V ∈N gR(v) 的总和找到给定大小 P(通常 |N| = 10)的最佳 N。 为了提高效率,我们采用贪婪的方法,并通过在给定当前 N(最初仅包含 R)的情况下将得分最高的视图迭代添加到 N 来递增邻域。
?
