本文目录
1. Data Prepation
1.1 加载数据集
# load data in folder datasets
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('datasets', one_hot=False)
train_data = mnist.train.images.astype(np.float32)
val_data = mnist.validation.images.astype(np.float32)
test_data = mnist.test.images.astype(np.float32)
train_labels = mnist.train.labels
val_labels = mnist.validation.labels
test_labels = mnist.test.labels
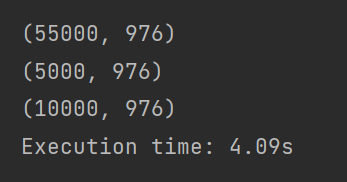
train_data_shape:55000,784
val_data_shape:5000,784
test_data_shape:1000,784
train_label_shape:55000
解释:训练集共计55000张图片,每张图片都是28*28的,每个特征的数值是01型。所有的数组类型都为ndarray型数组
1.2 构造图
1.2.1 构造大小为m的网格
def grid(m, dtype=np.float32):
"""Return coordinates of grid points"""
M = m**2 # 784=28*28
x = np.linspace(0,1,m, dtype=dtype) # 生成大小为784的0-1之间的等间距的小数数组x
y = np.linspace(0,1,m, dtype=dtype) # 生成大小为784的0-1之间的等间距的小数数组y
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y) # shape(28,28)
z = np.empty((M,2), dtype) # shape(784,2)
z[:,0] = xx.reshape(M)
z[:,1] = yy.reshape(M)
return z
np.linspace(start, stop, num, endpoint, retstep, dtype)
star和stop为起始和终止位置,均为标量
num为包括start和stop的间隔点总数,默认为50
endpoint为bool值,为False时将会去掉最后一个点计算间隔
restep为bool值,为True时会同时返回数据列表和间隔值
dtype默认为输入变量的类型,给定类型后将会把生成的数组类型转为目标类型
这是一个可以生成等间距数组的的一个函数,还是蛮常用的,最重要的就是前三个参数
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y) 代表的是将x中每一个数据和y中每一个数据组合生成很多点,然后将这些点的x坐标放入到X中,y坐标放入Y中,并且相应位置是对应的
np.empty() 函数语法如下:
empty(shape[, dtype, order])
依给定的shape, 和数据类型 dtype, 返回一个一维或者多维数组,数组的元素不为空,为随机产生的数据。
其中参数解释如下:
shape: 整数或者整型元组定义的返回数组的形状。
dtype:数据类型, 定义返回数组的类型,可选。 如dtype = int
order: {‘C’, ‘F’}, 规定返回数组元素在内存的存储顺序。
1.2.2 计算成对距离
def distance_sklearn_metrics(z, k=4, metric='euclidean'):
"""Compute pairwise distances"""
d = sklearn.metrics.pairwise.pairwise_distances(z, metric=metric, n_jobs=1) # 计算z中两两行之间的距离,shape(784,784)
# k-NN
idx = np.argsort(d)[:,1:k+1] # 将每一行分别排序后获取排序后的下标,获取每一行中与其距离最近的8行,shape(784,8)
d.sort() # 将每一行分别排序
d = d[:,1:k+1] # 获取每一行与其距离最近的8行的距离值
return d, idx # 返回每一行中与其距离最近的8行的下标与距离值
sklearn.metrics.pairwise_distances(X, Y=None, metric=’euclidean’, n_jobs=None, **kwds)
根据向量数组X和可选的Y计算距离矩阵。
此方法采用向量数组或距离矩阵,然后返回距离矩阵。 如果输入是向量数组,则计算距离。 如果输入是距离矩阵,则将其返回。
如果给出了Y(默认值为None),则返回的矩阵是数组之间从X和Y开始的成对距离。
argsort(x)函数是将x中的元素从小到大排列,提取其对应的index(索引),然后返回
1.2.3 构造图的邻接稀疏权重矩阵
def adjacency(dist, idx):
"""Return adjacency matrix of a kNN graph"""
M, k = dist.shape
assert M, k == idx.shape
assert dist.min() >= 0
assert dist.max() <= 1
# Pairwise distances
sigma2 = np.mean(dist[:,-1])**2
dist = np.exp(- dist**2 / sigma2) # 将距离标准化
# Weight matrix
I = np.arange(0, M).repeat(k) #shape(784*8=6272,)
J = idx.reshape(M*k) #shape(784*8=6272,)
V = dist.reshape(M*k) #shape(784*8=6272,)
W = scipy.sparse.coo_matrix((V, (I, J)), shape=(M, M)) # 构造I*J的稀疏矩阵,对应非0的值为V
# No self-connections
W.setdiag(0) # 对角线的值设置为0
# Undirected graph
bigger = W.T > W
W = W - W.multiply(bigger) + W.T.multiply(bigger)
assert W.nnz % 2 == 0 # 判断非零个数是否为偶数
assert np.abs(W - W.T).mean() < 1e-10
assert type(W) is scipy.sparse.csr.csr_matrix
return W
1.2.4 构造网格图
def grid_graph(grid_side,number_edges,metric):
"""Generate graph of a grid"""
z = grid(grid_side)
dist, idx = distance_sklearn_metrics(z, k=number_edges, metric=metric)
A = adjacency(dist, idx) # shape(784, 784)的一个系数稀疏矩阵
print("nb edges: ",A.nnz) # 稀疏矩阵中有6396个零
return A # 返回邻接稀疏权重矩阵
1.3 计算粗话图
1.3.1 重边匹配HEM
def HEM(W, levels, rid=None):
"""
Coarsen a graph multiple times using the Heavy Edge Matching (HEM).
Input
W: symmetric sparse weight (adjacency) matrix
levels: the number of coarsened graphs
Output
graph[0]: original graph of size N_1
graph[2]: coarser graph of size N_2 < N_1
graph[levels]: coarsest graph of Size N_levels < ... < N_2 < N_1
parents[i] is a vector of size N_i with entries ranging from 1 to N_{i+1}
which indicate the parents in the coarser graph[i+1]
nd_sz{i} is a vector of size N_i that contains the size of the supernode in the graph{i}
Note
if "graph" is a list of length k, then "parents" will be a list of length k-1
"""
N, N = W.shape
if rid is None:
rid = np.random.permutation(range(N))
ss = np.array(W.sum(axis=0)).squeeze()
rid = np.argsort(ss)
parents = []
degree = W.sum(axis=0) - W.diagonal()
graphs = []
graphs.append(W)
print('Heavy Edge Matching coarsening with Xavier version')
for _ in range(levels):
weights = degree # graclus weights
weights = np.array(weights).squeeze()
# PAIR THE VERTICES AND CONSTRUCT THE ROOT VECTOR
idx_row, idx_col, val = scipy.sparse.find(W)
cc = idx_row
rr = idx_col
vv = val
if not (list(cc)==list(np.sort(cc))):
tmp=cc
cc=rr
rr=tmp
cluster_id = HEM_one_level(cc,rr,vv,rid,weights)
parents.append(cluster_id)
# COMPUTE THE EDGES WEIGHTS FOR THE NEW GRAPH
nrr = cluster_id[rr]
ncc = cluster_id[cc]
nvv = vv
Nnew = cluster_id.max() + 1
# CSR is more appropriate: row,val pairs appear multiple times
W = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix((nvv,(nrr,ncc)), shape=(Nnew,Nnew))
W.eliminate_zeros()
# Add new graph to the list of all coarsened graphs
graphs.append(W)
N, N = W.shape
# COMPUTE THE DEGREE (OMIT OR NOT SELF LOOPS)
degree = W.sum(axis=0)
# CHOOSE THE ORDER IN WHICH VERTICES WILL BE VISTED AT THE NEXT PASS
ss = np.array(W.sum(axis=0)).squeeze()
rid = np.argsort(ss)
return graphs, parents
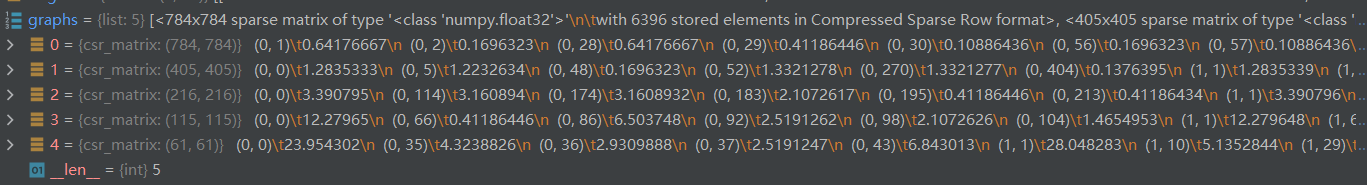
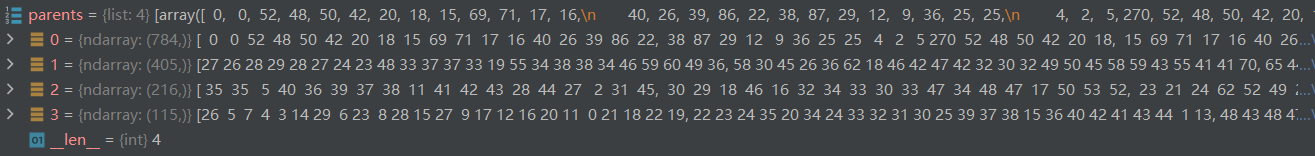
1.3.2 构造二叉树
def compute_perm(parents):
"""
Return a list of indices to reorder the adjacency and data matrices so
that the union of two neighbors from layer to layer forms a binary tree.
"""
# Order of last layer is random (chosen by the clustering algorithm).
indices = []
if len(parents) > 0:
M_last = max(parents[-1]) + 1
indices.append(list(range(M_last)))
for parent in parents[::-1]:
# Fake nodes go after real ones.
pool_singeltons = len(parent)
indices_layer = []
for i in indices[-1]:
indices_node = list(np.where(parent == i)[0])
assert 0 <= len(indices_node) <= 2
# Add a node to go with a singelton.
if len(indices_node) is 1:
indices_node.append(pool_singeltons)
pool_singeltons += 1
# Add two nodes as children of a singelton in the parent.
elif len(indices_node) is 0:
indices_node.append(pool_singeltons+0)
indices_node.append(pool_singeltons+1)
pool_singeltons += 2
indices_layer.extend(indices_node)
indices.append(indices_layer)
# Sanity checks.
for i,indices_layer in enumerate(indices):
M = M_last*2**i
# Reduction by 2 at each layer (binary tree).
assert len(indices[0] == M)
# The new ordering does not omit an indice.
assert sorted(indices_layer) == list(range(M))
return indices[::-1]
assert (compute_perm([np.array([4,1,1,2,2,3,0,0,3]),np.array([2,1,0,1,0])])
== [[3,4,0,9,1,2,5,8,6,7,10,11],[2,4,1,3,0,5],[0,1,2]])
1.3.3 构造聚类树
def perm_adjacency(A, indices):
"""
Permute adjacency matrix, i.e. exchange node ids,
so that binary unions form the clustering tree.
"""
if indices is None:
return A
M, M = A.shape
Mnew = len(indices)
A = A.tocoo()
# Add Mnew - M isolated vertices.
rows = scipy.sparse.coo_matrix((Mnew-M, M), dtype=np.float32)
cols = scipy.sparse.coo_matrix((Mnew, Mnew-M), dtype=np.float32)
A = scipy.sparse.vstack([A, rows])
A = scipy.sparse.hstack([A, cols])
# Permute the rows and the columns.
perm = np.argsort(indices)
A.row = np.array(perm)[A.row]
A.col = np.array(perm)[A.col]
assert np.abs(A - A.T).mean() < 1e-8 # 1e-9
assert type(A) is scipy.sparse.coo.coo_matrix
1.3.4 构造图拉普拉斯矩阵
def laplacian(W, normalized=True):
"""Return graph Laplacian"""
# Degree matrix.
d = W.sum(axis=0)
# Laplacian matrix.
if not normalized:
D = scipy.sparse.diags(d.A.squeeze(), 0)
L = D - W
else:
d += np.spacing(np.array(0, W.dtype))
d = 1 / np.sqrt(d)
D = scipy.sparse.diags(d.A.squeeze(), 0) # 构造对角稀疏矩阵
I = scipy.sparse.identity(d.size, dtype=W.dtype) # 构造单位矩阵
L = I - D * W * D # 构造标准化拉普拉斯矩阵
assert np.abs(L - L.T).mean() < 1e-9
assert type(L) is scipy.sparse.csr.csr_matrix
return L
1.3.5 使用重边匹配构造K个粗化图
def coarsen(A, levels):
graphs, parents = HEM(A, levels)
perms = compute_perm(parents)
laplacians = []
for i,A in enumerate(graphs):
M, M = A.shape
if i < levels:
A = perm_adjacency(A, perms[i])
A = A.tocsr() # 将矩阵转换为压缩形式
A.eliminate_zeros() # 删除零
Mnew, Mnew = A.shape
print('Layer {0}: M_{0} = |V| = {1} nodes ({2} added), |E| = {3} edges'.format(i, Mnew, Mnew-M, A.nnz//2))
L = laplacian(A, normalized=True)
laplacians.append(L) # 将当前图的拉普拉斯矩阵加入列表
return laplacians, perms[0] if len(perms) > 0 else None
perms存放的是进行边聚合后构造的二叉树,laplacians存放的是每一种粗化图对应的图拉普莱斯矩阵
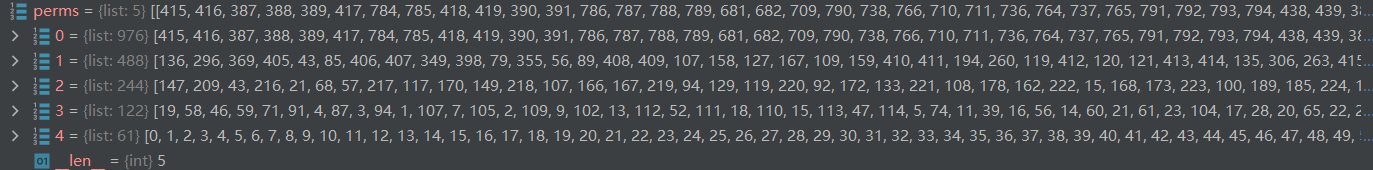
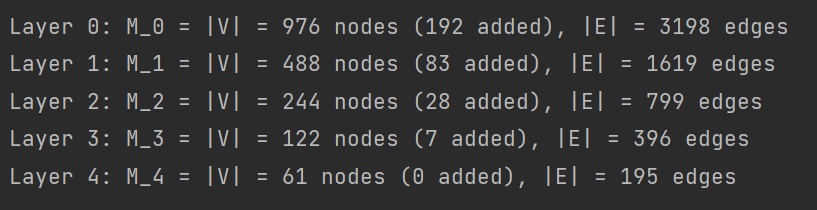
第一层代表总共有976个节点,其中192个节点是添加的呈中性的假节点(为构造二叉树用),原图真正的节点数976-192=784
1.4 计算每个粗话图的最大特征值
def lmax_L(L):
"""Compute largest Laplacian eigenvalue"""
return scipy.sparse.linalg.eigsh(L, k=1, which='LM', return_eigenvectors=False)[0]
scipy.sparse.linalg.eigsh(A, k=6, M=None, sigma=None, which=‘LM’, v0=None, ncv=None, maxiter=None, tol=0, return_eigenvectors=True, Minv=None, OPinv=None, mode=‘normal’)
功能:找到实对称方阵或复杂厄米特矩阵的k个特征值,特征向量
1.5 根据二叉树节点索引重新索引数据集的节点索引,构造数据集二叉树
# Reindex nodes to satisfy a binary tree structure
train_data = perm_data(train_data, perm)
val_data = perm_data(val_data, perm)
test_data = perm_data(test_data, perm)
print(train_data.shape)
print(val_data.shape)
print(test_data.shape)
print('Execution time: {:.2f}s'.format(time.time() - t_start))
del perm