数据清洗过程,将原始数据处理成可用于机器学习或者深度学习训练的数据。
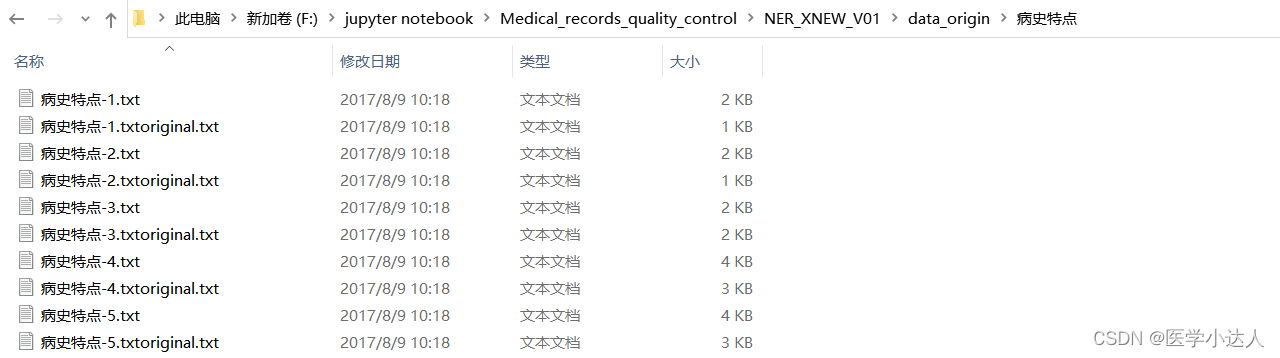
数据原始格式:
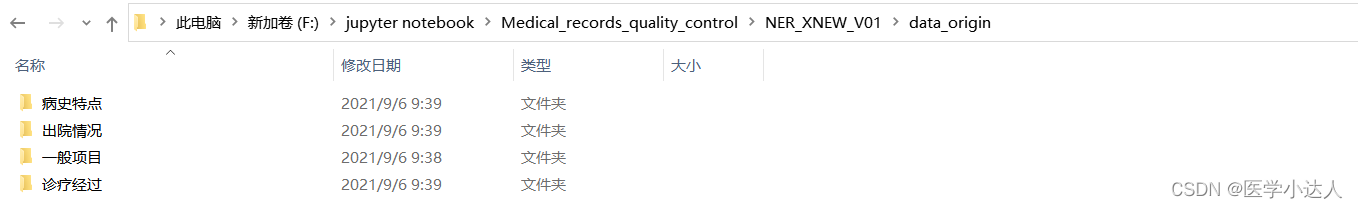
?
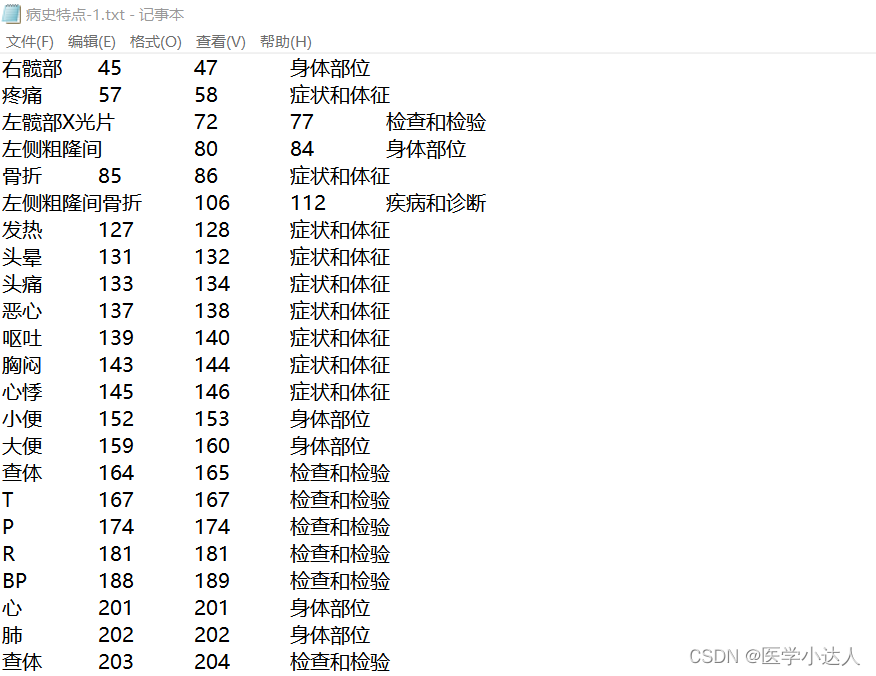
?
?
?数据和代码,参考了刘焕勇老师的数据和分享
1.导入需要的包(jupyter notebook)
import os
from collections import Counter2.事先定义好数据标签:(jupyter notebook)
label_dict = {
'检查和检验': 'CHECK',
'症状和体征': 'SIGNS',
'疾病和诊断': 'DISEASE',
'治疗': 'TREATMENT',
'身体部位': 'BODY'}
cate_dict ={
'O':0,
'TREATMENT-I': 1,
'TREATMENT-B': 2,
'BODY-B': 3,
'BODY-I': 4,
'SIGNS-I': 5,
'SIGNS-B': 6,
'CHECK-B': 7,
'CHECK-I': 8,
'DISEASE-I': 9,
'DISEASE-B': 10
}3.定位到文件夹路径,此文件夹为data(父文件夹),还有四个子文件夹,定位到data_transfer_process.ipynb这个python执行文件的绝对路径的上一层:(jupyter notebook)
cur = '\\'.join(os.path.abspath('data_transfer_process.ipynb').split('\\')[:-1])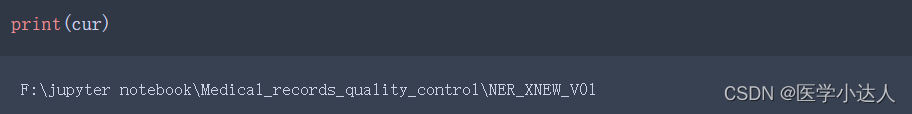 ?注意在windows系统中,路径是这样的,但是在服务器上,是这样的
?注意在windows系统中,路径是这样的,但是在服务器上,是这样的
cur_01 = '/'.join(os.path.abspath('data_transfer_process.ipynb').split('/')[:-1])要不然,split是切分不开的!
4.创建变量: 原始数据路径,输出数据路径(jupyter notebook)
#原始数据路径
origin_path = os.path.join(cur, 'data_origin')
#输出数据路径
train_filepath = os.path.join(cur, 'train.txt')5.数据处理过程:(jupyter notebook)
f = open(train_filepath, 'w+',encoding='utf-8')
for root,dirs,files in os.walk(origin_path):
# print('root:',root)
# print('dirs:',dirs)
# print('files:',files)
for file in files:
filepath = os.path.join(root, file)
if 'original' not in filepath:
continue
# print(type(filepath))
label_fliepath = filepath.replace('.txtoriginal','')
# print(filepath,'\n',label_fliepath)
content = open(filepath,encoding='utf-8').read().strip()
# print(content)
res_dict = {}
for line in open(label_fliepath,encoding='utf-8'):
res = line.strip().split('\t')
start = res[1]
end = res[2]
label = res[3]
label_id = label_dict.get(label)
for i in range(int(start),int(end)+1):
if i ==int(start):
label_cate = label_id + '-B'
else:
label_cate = label_id + '-I'
res_dict[i] = label_cate
# print('res:',res)
# print('res_dict:',res_dict)
# break
for indx,char in enumerate(content):
# print(indx,content)
char_label = res_dict.get(indx,'0')
print(indx,'\t',char,'\t',char_label)
f.write(char + '\t' + char_label + '\n')
# break
# break
f.close()6.完整代码(pycharm):
import os
from collections import Counter
class TransferData:
def __init__(self):
cur = '/'.join(os.path.abspath(__file__).split('/')[:-1])
self.label_dict = {
'检查和检验': 'CHECK',
'症状和体征': 'SIGNS',
'疾病和诊断': 'DISEASE',
'治疗': 'TREATMENT',
'身体部位': 'BODY'}
self.cate_dict ={
'O':0,
'TREATMENT-I': 1,
'TREATMENT-B': 2,
'BODY-B': 3,
'BODY-I': 4,
'SIGNS-I': 5,
'SIGNS-B': 6,
'CHECK-B': 7,
'CHECK-I': 8,
'DISEASE-I': 9,
'DISEASE-B': 10
}
self.origin_path = os.path.join(cur, 'data_origin')
self.train_filepath = os.path.join(cur, 'train.txt')
return
def transfer(self):
f = open(self.train_filepath, 'w+',encoding='utf-8')
count = 0
for root,dirs,files in os.walk(self.origin_path):
for file in files:
filepath = os.path.join(root, file)
if 'original' not in filepath:
continue
label_filepath = filepath.replace('.txtoriginal','')
print(filepath, '\t\t', label_filepath)
content = open(filepath,encoding='utf-8').read().strip()
print(content)
res_dict = {}
for line in open(label_filepath,encoding='utf-8'):
res = line.strip().split(' ')
start = int(res[1])
end = int(res[2])
label = res[3]
label_id = self.label_dict.get(label)
for i in range(start, end+1):
if i == start:
label_cate = label_id + '-B'
else:
label_cate = label_id + '-I'
res_dict[i] = label_cate
for indx, char in enumerate(content):
char_label = res_dict.get(indx, 'O')
print(char,'\t',char_label)
f.write(char + '\t' + char_label + '\n')
f.close()
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
handler = TransferData()
train_datas = handler.transfer()