本文承接博主的上一篇博文:
什么叫图像或轮廓的空间矩、中心矩、归一化中心矩?并利用OpenCV的类Moments计算轮廓的这几个矩和质心位置
继续介绍Hu矩的相关知识。
Hu矩是由二阶和三阶中心距计算得到七个不变矩,Hu矩具有旋转、平移和缩放不变性,因此在图像具有旋转和放缩的情况下Hu矩具有更广泛的应用领域。
在博主的上一篇博文中介绍了归一化的中心矩的计算式。我们回顾一下:
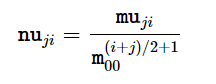
我们令
n
u
j
i
=
η
j
i
nu_{ji}=η_{ji}
nuji?=ηji? ,则有Hu矩的七个矩的计算式如下:
h
u
[
0
]
=
η
20
+
η
02
h
u
[
1
]
=
(
η
20
?
η
02
)
2
+
4
η
11
2
h
u
[
2
]
=
(
η
30
?
3
η
12
)
2
+
(
3
η
21
?
η
03
)
2
h
u
[
3
]
=
(
η
30
+
η
12
)
2
+
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
2
h
u
[
4
]
=
(
η
30
?
3
η
12
)
(
η
30
+
η
12
)
[
(
η
30
+
η
12
)
2
?
3
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
2
]
+
(
3
η
21
?
η
03
)
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
[
3
(
η
30
+
η
12
)
2
?
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
2
]
h
u
[
5
]
=
(
η
20
?
η
02
)
[
(
η
30
+
η
12
)
2
?
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
2
]
+
4
η
11
(
η
30
+
η
12
)
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
h
u
[
6
]
=
(
3
η
21
?
η
03
)
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
[
3
(
η
30
+
η
12
)
2
?
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
2
]
?
(
η
30
?
3
η
12
)
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
[
3
(
η
30
+
η
12
)
2
?
(
η
21
+
η
03
)
2
]
\begin{array}{l} hu[0]= \eta _{20}+ \eta _{02} \\ hu[1]=( \eta _{20}- \eta _{02})^{2}+4 \eta _{11}^{2} \\ hu[2]=( \eta _{30}-3 \eta _{12})^{2}+ (3 \eta _{21}- \eta _{03})^{2} \\ hu[3]=( \eta _{30}+ \eta _{12})^{2}+ ( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03})^{2} \\ hu[4]=( \eta _{30}-3 \eta _{12})( \eta _{30}+ \eta _{12})[( \eta _{30}+ \eta _{12})^{2}-3( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03})^{2}]+(3 \eta _{21}- \eta _{03})( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03})[3( \eta _{30}+ \eta _{12})^{2}-( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03})^{2}] \\ hu[5]=( \eta _{20}- \eta _{02})[( \eta _{30}+ \eta _{12})^{2}- ( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03})^{2}]+4 \eta _{11}( \eta _{30}+ \eta _{12})( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03}) \\ hu[6]=(3 \eta _{21}- \eta _{03})( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03})[3( \eta _{30}+ \eta _{12})^{2}-( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03})^{2}]-( \eta _{30}-3 \eta _{12})( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03})[3( \eta _{30}+ \eta _{12})^{2}-( \eta _{21}+ \eta _{03})^{2}] \\ \end{array}
hu[0]=η20?+η02?hu[1]=(η20??η02?)2+4η112?hu[2]=(η30??3η12?)2+(3η21??η03?)2hu[3]=(η30?+η12?)2+(η21?+η03?)2hu[4]=(η30??3η12?)(η30?+η12?)[(η30?+η12?)2?3(η21?+η03?)2]+(3η21??η03?)(η21?+η03?)[3(η30?+η12?)2?(η21?+η03?)2]hu[5]=(η20??η02?)[(η30?+η12?)2?(η21?+η03?)2]+4η11?(η30?+η12?)(η21?+η03?)hu[6]=(3η21??η03?)(η21?+η03?)[3(η30?+η12?)2?(η21?+η03?)2]?(η30??3η12?)(η21?+η03?)[3(η30?+η12?)2?(η21?+η03?)2]?
这7个不变矩构成一组特征量,Hu.M.K在1962年证明了他们具有旋转,缩放和平移不变性。
实际上,在对图片中物体的识别过程中,只有hu[0]和hu[1]不变性保持的比较好,其他的几个不变矩带来的误差比较大。有学者认为只有基于二阶矩的不变矩对二维物体的描述才是真正的具有旋转、缩放和平移不变性(hu[0]和hu[1]刚好都是由二阶矩组成的)。
由Hu矩组成的特征量对图片进行识别,优点就是速度很快(因为计算量小嘛),缺点是识别率比较低。有人用它来做过手势识别,对于已经分割好的手势轮廓图,识别率也就30%左右,对于纹理比较丰富的图片,识别率更是不堪入眼,只有10%左右。主要原因是由于Hu不变矩只用到低阶矩(最多也就用到三阶矩),对于图像的细节未能很好的描述出来,导致对图像的描述不够完整。
Hu不变矩一般用来识别图像中大的物体,对于物体的形状描述得比较好,图像的纹理特征不能太复杂,像识别水果的形状,或者对于车牌中的简单字符的识别效果会相对好一些。
OpenCV提供了函数HuMoments()来计算图像或轮廓的Hu矩的七个矩。
其C++原型有两个,分别如下:
void cv::HuMoments( const Moments & moments,
double hu[7] )
void cv::HuMoments( const Moments & m,
OutputArray hu )
参数意义如下:
moments或m—Input moments computed with moments .(输入的类Moments的实例化对象,通过我的上一篇博文大家可以知道里面其实包含图像或轮廓的三阶以下空间矩、中心矩和归一化的中心矩)
hu—Output Hu invariants.(计算得到的Hu矩,包含七个分量)
函数HuMoments()的使用示例代码如下:
代码中用到的图像下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ZfOReFRyeMDLhk3PjJXGwA?pwd=aes8
//博主微信/QQ 2487872782
//有问题可以联系博主交流
//有图像处理需求也可联系博主
//图像处理技术交流QQ群 271891601
//OpenCV版本:3.0
//VS版本:2013
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgcodecs/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Mat srcGary = imread("F:/material/images/P0045-ellipse-02.jpg", 0);
imshow("srcGary", srcGary);
// 阈值化操作
Mat threMat;
int thresh = 128;
threshold(srcGary, threMat, thresh, 255, THRESH_BINARY);
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
// find Contours
findContours(threMat, contours, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
cout << "检测到的轮廓个数为:" << (int)contours.size() << endl << endl;
// draw Contours
Mat contours_img(srcGary.size(), CV_8U, Scalar(0));
drawContours(contours_img, contours, -1, Scalar(255), 1);
imshow("contours_img", contours_img);
//计算Hu矩
Moments moments_1 = moments(contours[0]);
Mat hu_1;
HuMoments(moments_1, hu_1);
cout << "图像的七个Hu矩的值如下:\n" << hu_1<< endl << endl;
waitKey();
return(0);
}
运行结果如下:

接下来,我们利用Hu矩来进行英文大写字母的轮廓匹配。
OpenCV中专门提供了函数matchShapes()来计算两个图像或轮廓Hu矩的差异程度,其原型如下:
double cv::matchShapes( InputArray contour1,
InputArray contour2,
int method,
double parameter
)
其参数意义如下:
contour1—First contour or grayscale image.
contour2—Second contour or grayscale image.
method—Comparison method.
parameter—Method-specific parameter (not supported now).(这个参数目前无意义,不用管它)
上面的英文很简单,就不翻译了。
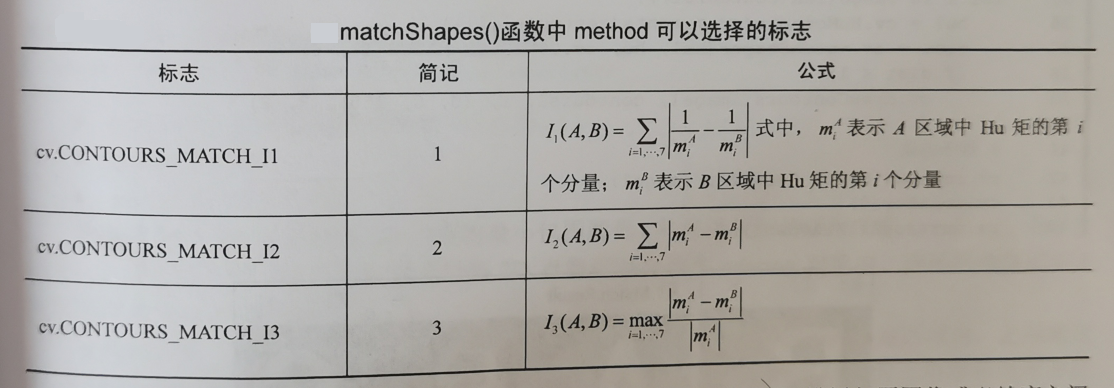
第三个参数method的可取值及意义如下:

中文版如下:
接下来上使用轮廓的Hu矩匹配英文大写字母B的示例代码:
代码中用到的两张图片下载链接:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1iOPs4EQ985bWfYxmcfJMbA?pwd=dk14
//博主微信/QQ 2487872782
//有问题可以联系博主交流
//有图像处理需求也可联系博主
//图像处理技术交流QQ群 271891601
//OpenCV版本:3.0
//VS版本:2013
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgcodecs/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void findcontours(Mat &image, vector<vector<Point>> &contours)
{
Mat gray, binary;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
//图像灰度化
cvtColor(image, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//图像二值化
threshold(gray, binary, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY | THRESH_OTSU);
//寻找轮廓
findContours(binary, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
}
int main()
{
Mat img = imread("F:/material/images/Hu_Match/ABC.png");
Mat img_B = imread("F:/material/images/Hu_Match/B-rotate30-zoom_in.png");
if (img.empty() || img_B.empty())
{
cout << "请确认图像文件名称是否正确" << endl;
return -1;
}
imshow("ABC", img);
imshow("B", img_B);
// 轮廓提取
vector<vector<Point>> contours1;
vector<vector<Point>> contours2;
findcontours(img, contours1);
findcontours(img_B, contours2);
// hu矩计算
Moments mm2 = moments(contours2[0]);
Mat hu2;
HuMoments(mm2, hu2);
// 轮廓匹配
for (int n = 0; n < contours1.size(); n++)
{
Moments mm = moments(contours1[n]);
Mat hum;
HuMoments(mm, hum);
//Hu矩匹配
double dist;
dist = matchShapes(hum, hu2, CV_CONTOURS_MATCH_I1, 0);
if (dist < 0.5)
{
drawContours(img, contours1, n, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3, 8);
}
}
imshow("match result", img);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
代码说明:
图片ABC.png中有三个字母,分别为A、B、C,如下图所示:

图片B-rotate30-zoom_in.png把上面的字母B进行了30度旋转,并且进行了放大处理,如下图所示:

我们以图片B-rotate30-zoom_in.png提取的轮廓B为模板,来匹配图片ABC.png中的B。
运行结果如下图所示:
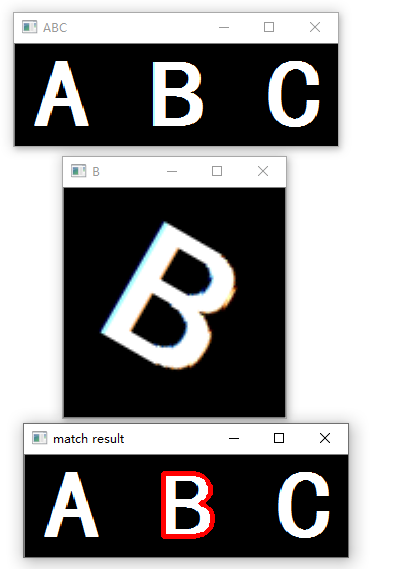
从运行结果可以看出,用Hu矩匹配到了大写字母B,这表明了Hu矩具有旋转、平移和缩放不变性。
