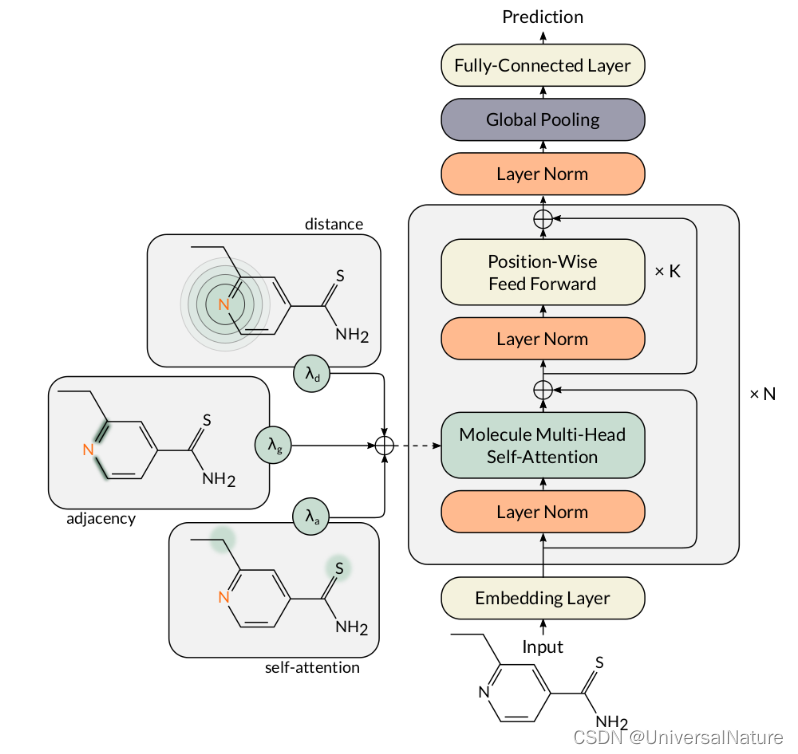
应用Transformer框架对分子属性进行预测,代码:MAT,原文:Molecule Attention Transformer。变量名,函数名很多来自The Annotated Transformer,在《深入浅出Embedding》一书中也做了讲解。本文主要从实例运行开始一步步看代码具体内容,整体模型如下:
文章目录
1.数据准备
from featurization.data_utils import load_data_from_df, construct_loader
batch_size = 64
# Formal charges are one-hot encoded to keep compatibility with the pre-trained weights.
# If you do not plan to use the pre-trained weights, we recommend to set one_hot_formal_charge to False.
X, y = load_data_from_df('../data/freesolv/freesolv.csv', one_hot_formal_charge=True)
data_loader = construct_loader(X, y, batch_size)
- 利用 load_data_from_df 读入原始数据,再用 construct_loader 将数据转化为 torch.utils.data.DataLoader 对象
1.1.load_data_from_df
def load_data_from_df(dataset_path, add_dummy_node=True, one_hot_formal_charge=False, use_data_saving=True):
"""Load and featurize data stored in a CSV file.
Args:
dataset_path (str): A path to the CSV file containing the data. It should have two columns:
the first one contains SMILES strings of the compounds,
the second one contains labels.
add_dummy_node (bool): If True, a dummy node will be added to the molecular graph. Defaults to True.
one_hot_formal_charge (bool): If True, formal charges on atoms are one-hot encoded. Defaults to False.
use_data_saving (bool): If True, saved features will be loaded from the dataset directory; if no feature file
is present, the features will be saved after calculations. Defaults to True.
Returns:
A tuple (X, y) in which X is a list of graph descriptors (node features, adjacency matrices, distance matrices),
and y is a list of the corresponding labels.
"""
feat_stamp = f'{"_dn" if add_dummy_node else ""}{"_ohfc" if one_hot_formal_charge else ""}'
feature_path = dataset_path.replace('.csv', f'{feat_stamp}.p')
if use_data_saving and os.path.exists(feature_path):
logging.info(f"Loading features stored at '{feature_path}'")
x_all, y_all = pickle.load(open(feature_path, "rb"))
return x_all, y_all
data_df = pd.read_csv(dataset_path)
data_x = data_df.iloc[:, 0].values
data_y = data_df.iloc[:, 1].values
if data_y.dtype == np.float64:
data_y = data_y.astype(np.float32)
x_all, y_all = load_data_from_smiles(data_x, data_y, add_dummy_node=add_dummy_node,
one_hot_formal_charge=one_hot_formal_charge)
if use_data_saving and not os.path.exists(feature_path):
logging.info(f"Saving features at '{feature_path}'")
pickle.dump((x_all, y_all), open(feature_path, "wb"))
return x_all, y_all
- feature_path 主要是判断是否利用已经保存的数据,可以跳过
- data_x 是 smiles 的序列数据,data_f 是标量数值,示例如下:
| data_x | data_y | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | CN?C(=O)c1ccc(cc1)OC | -1.874467 |
| 1 | CS(=O)(=O)Cl | -0.277514 |
| 2 | CC?C=C | 1.465089 |
| 3 | CCc1cnccn1 | -0.428367 |
| 4 | CCCCCCCO | -0.105855 |
- load_data_from_smiles 将 data_x 的 smiles 数据处理成 graph descriptors (node features, adjacency matrices, distance matrices),data_y 不变
- 得到特征 x_all 和 y_all 后返回,示例如下:
import numpy as np
np.asarray(X).shape,np.asarray(y).shape #((642, 3), (642, 1))
X[0],y[0]
"""
([array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.,
0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.,
0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.,
0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.,
0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.,
0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.,
0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.]]),
array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.]]),
array([[1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06,
1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06,
1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06,
1.00000000e+06, 1.00000000e+06],
...
[-1.8744674])
"""
X[0][0].shape,X[0][1].shape,X[0][2].shape #((14, 28), (14, 14), (14, 14))
X[1][0].shape,X[1][1].shape,X[1][2].shape #((6, 28), (6, 6), (6, 6))
- 每个分子原子数不同导致维度不一致,这里没有统一。每个原子用28维特征表示,可以在 featurize_mol 看出
1.1.1.load_data_from_smiles
def load_data_from_smiles(x_smiles, labels, add_dummy_node=True, one_hot_formal_charge=False):
"""Load and featurize data from lists of SMILES strings and labels.
Args:
x_smiles (list[str]): A list of SMILES strings.
labels (list[float]): A list of the corresponding labels.
add_dummy_node (bool): If True, a dummy node will be added to the molecular graph. Defaults to True.
one_hot_formal_charge (bool): If True, formal charges on atoms are one-hot encoded. Defaults to False.
Returns:
A tuple (X, y) in which X is a list of graph descriptors (node features, adjacency matrices, distance matrices),
and y is a list of the corresponding labels.
"""
x_all, y_all = [], []
for smiles, label in zip(x_smiles, labels):
try:
mol = MolFromSmiles(smiles)
try:
mol = Chem.AddHs(mol)
AllChem.EmbedMolecule(mol, maxAttempts=5000)
AllChem.UFFOptimizeMolecule(mol)
mol = Chem.RemoveHs(mol)
except:
AllChem.Compute2DCoords(mol)
afm, adj, dist = featurize_mol(mol, add_dummy_node, one_hot_formal_charge)
x_all.append([afm, adj, dist])
y_all.append([label])
except ValueError as e:
logging.warning('the SMILES ({}) can not be converted to a graph.\nREASON: {}'.format(smiles, e))
return x_all, y_all
- 先产生 mol 的3D构象,利用UFF力场优化,这是为了计算原子间距离,具体计算在 featurize_mol
1.1.2.featurize_mol
def featurize_mol(mol, add_dummy_node, one_hot_formal_charge):
"""Featurize molecule.
Args:
mol (rdchem.Mol): An RDKit Mol object.
add_dummy_node (bool): If True, a dummy node will be added to the molecular graph.
one_hot_formal_charge (bool): If True, formal charges on atoms are one-hot encoded.
Returns:
A tuple of molecular graph descriptors (node features, adjacency matrix, distance matrix).
"""
node_features = np.array([get_atom_features(atom, one_hot_formal_charge)
for atom in mol.GetAtoms()])
adj_matrix = np.eye(mol.GetNumAtoms())
for bond in mol.GetBonds():
begin_atom = bond.GetBeginAtom().GetIdx()
end_atom = bond.GetEndAtom().GetIdx()
adj_matrix[begin_atom, end_atom] = adj_matrix[end_atom, begin_atom] = 1
conf = mol.GetConformer()
pos_matrix = np.array([[conf.GetAtomPosition(k).x, conf.GetAtomPosition(k).y, conf.GetAtomPosition(k).z]
for k in range(mol.GetNumAtoms())])
dist_matrix = pairwise_distances(pos_matrix)
if add_dummy_node:
m = np.zeros((node_features.shape[0] + 1, node_features.shape[1] + 1))
m[1:, 1:] = node_features
m[0, 0] = 1.
node_features = m
m = np.zeros((adj_matrix.shape[0] + 1, adj_matrix.shape[1] + 1))
m[1:, 1:] = adj_matrix
adj_matrix = m
m = np.full((dist_matrix.shape[0] + 1, dist_matrix.shape[1] + 1), 1e6)
m[1:, 1:] = dist_matrix
dist_matrix = m
return node_features, adj_matrix, dist_matrix
- node_features 主要用 get_atom_features 得到
- 邻接矩阵 adj_matrix 原子相连为1,不连为0
- 距离矩阵 dist_matrix 主要用 pairwise_distances 得到,mol 传入前已处理,GetConformer获取原子坐标信息,pos_matrix 是 n × 3 n \times 3 n×3维矩阵,dist_matrix 得到的是 n × n n \times n n×n维对称矩阵
- add_dummy_node 默认是True,dummy_node 不与分子中的任何原子相连,它与其他原子的距离设为了 1 0 6 10^6 106,这样模型可以在什么 pattern 都找不到的时候跳过搜索,类似 BERT 中的 [SEP] 词元(原文中提到)。添加 dummy_node 后,node_feature 在第一个编码,邻接矩阵对应为0,距离矩阵对应设为1e6
pos_matrix=np.array([
[1,1,1],
[1,2,3]
])
print(pairwise_distances(pos_matrix))
"""
[[0. 2.23606798]
[2.23606798 0. ]]
"""
print(np.sqrt((1-1)**2+(1-2)**2+(1-3)**2)) #2.23606797749979
1.1.3.get_atom_features
def get_atom_features(atom, one_hot_formal_charge=True):
"""Calculate atom features.
Args:
atom (rdchem.Atom): An RDKit Atom object.
one_hot_formal_charge (bool): If True, formal charges on atoms are one-hot encoded.
Returns:
A 1-dimensional array (ndarray) of atom features.
"""
attributes = []
attributes += one_hot_vector(
atom.GetAtomicNum(),
[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 15, 16, 17, 35, 53, 999]
)
attributes += one_hot_vector(
len(atom.GetNeighbors()),
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
)
attributes += one_hot_vector(
atom.GetTotalNumHs(),
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
)
if one_hot_formal_charge:
attributes += one_hot_vector(
atom.GetFormalCharge(),
[-1, 0, 1]
)
else:
attributes.append(atom.GetFormalCharge())
attributes.append(atom.IsInRing())
attributes.append(atom.GetIsAromatic())
return np.array(attributes, dtype=np.float32)
- 每个原子的特征以28维 one-hot 表示,可以从原文中了解,0-11依据原子序数编码有机物常见原子(包括了dummy_node),12-17编码邻位原子的数目,18-22编码氢原子数,23-25编码原子电荷(one_hot_formal_charge为True),26编码原子是否位于环上,27编码是否是芳香性原子,此函数返回的实际是 27 维 one-hot,因为第一步实际没有编码 dummy_node,真正编码在 featurize_mol,下面的图可能有误导,实际 dummy_node 编码在第一列,而不是倒数第二列。

1.1.4…one_hot_vector
def one_hot_vector(val, lst):
"""Converts a value to a one-hot vector based on options in lst"""
if val not in lst:
val = lst[-1]
return map(lambda x: x == val, lst)
- 依据 lst 中的内容进行编码,如果不存在就以最后一位编码,例如不是有机物常见原子以[0,0,…1]表示
1.2.construct_loader
def construct_loader(x, y, batch_size, shuffle=True):
"""Construct a data loader for the provided data.
Args:
x (list): A list of molecule features.
y (list): A list of the corresponding labels.
batch_size (int): The batch size.
shuffle (bool): If True the data will be loaded in a random order. Defaults to True.
Returns:
A DataLoader object that yields batches of padded molecule features.
"""
data_set = construct_dataset(x, y)
loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=data_set,
batch_size=batch_size,
collate_fn=mol_collate_func,
shuffle=shuffle)
return loader
- 先构造 dataset,定义处理函数 mol_collate_func,传入 DataLoader 返回 loader 对象
1.2.1.construct_dataset
def construct_dataset(x_all, y_all):
"""Construct a MolDataset object from the provided data.
Args:
x_all (list): A list of molecule features.
y_all (list): A list of the corresponding labels.
Returns:
A MolDataset object filled with the provided data.
"""
output = [Molecule(data[0], data[1], i)
for i, data in enumerate(zip(x_all, y_all))]
return MolDataset(output)
- 构造Molecule 对象列表,再构造 MolDataset 类,Molecule 对象接收 数据索引,x,y
1.2.2.Molecule
class Molecule:
"""
Class that represents a train/validation/test datum
- self.label: 0 neg, 1 pos -1 missing for different target.
"""
def __init__(self, x, y, index):
self.node_features = x[0]
self.adjacency_matrix = x[1]
self.distance_matrix = x[2]
self.y = y
self.index = index
- 将 x,y,index 数据整合在一起的类
1.2.3.MolDataset
class MolDataset(Dataset):
"""
Class that represents a train/validation/test dataset that's readable for PyTorch
Note that this class inherits torch.utils.data.Dataset
"""
def __init__(self, data_list):
"""
@param data_list: list of Molecule objects
"""
self.data_list = data_list
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data_list)
def __getitem__(self, key):
if type(key) == slice:
return MolDataset(self.data_list[key])
return self.data_list[key]
- 继承 torch.utils.data.Dataset,需要实现这里列出的三个方法
1.2.4.mol_collate_func
def mol_collate_func(batch):
"""Create a padded batch of molecule features.
Args:
batch (list[Molecule]): A batch of raw molecules.
Returns:
A list of FloatTensors with padded molecule features:
adjacency matrices, node features, distance matrices, and labels.
"""
adjacency_list, distance_list, features_list = [], [], []
labels = []
max_size = 0
for molecule in batch:
if type(molecule.y[0]) == np.ndarray:
labels.append(molecule.y[0])
else:
labels.append(molecule.y)
if molecule.adjacency_matrix.shape[0] > max_size:
max_size = molecule.adjacency_matrix.shape[0]
for molecule in batch:
adjacency_list.append(pad_array(molecule.adjacency_matrix, (max_size, max_size)))
distance_list.append(pad_array(molecule.distance_matrix, (max_size, max_size)))
features_list.append(pad_array(molecule.node_features, (max_size, molecule.node_features.shape[1])))
return [FloatTensor(features) for features in (adjacency_list, features_list, distance_list, labels)]
- 第一个 for 循环得到 batch 中分子最多原子数和 labels 的列表,以 max_size 为基准 padding
- 第二个 for 循环对 x 的三个数据矩阵 padding,pad_array 参数是数据矩阵和矩阵维度限定
1.2.5.pad_array
def pad_array(array, shape, dtype=np.float32):
"""Pad a 2-dimensional array with zeros.
Args:
array (ndarray): A 2-dimensional array to be padded.
shape (tuple[int]): The desired shape of the padded array.
dtype (data-type): The desired data-type for the array.
Returns:
A 2-dimensional array of the given shape padded with zeros.
"""
padded_array = np.zeros(shape, dtype=dtype)
padded_array[:array.shape[0], :array.shape[1]] = array
return padded_array
- 在规定维度之外的部分补0
1.3.总结
- 数据准备阶段输出 dataloader 对象,每次迭代一个 batch。经过了 mol_collate_func 的处理,不同 batch 原子数并没有统一,只有一个 batch 内原子数才恒定。data[0] 是邻接矩阵,data[1] 是 node_features,data[2] 是 距离矩阵
batch_size=2
cnt=1
for data in data_loader:
print(data[0].shape)
print(data[1].shape)
print(data[2].shape)
print(data[3].shape)
cnt+=1
if (cnt==3):break
"""
torch.Size([2, 13, 13])
torch.Size([2, 13, 28])
torch.Size([2, 13, 13])
torch.Size([2, 1])
torch.Size([2, 9, 9])
torch.Size([2, 9, 28])
torch.Size([2, 9, 9])
torch.Size([2, 1])
"""
