在《学习OpenCV3,O'Reilly系列丛书》中的第11章常见的图像变换中讲到的“任意映射”,Remap函数。函数cv::remap通常用来纠正校准的立体图像,包括图像变形和图像扭曲。其实这个函数在无人机拍摄延时摄影(使用电子防抖算法)合成视频时也是常用到的函数。主要是处理无人机悬停或者行进中拍摄的照片出现比较大的形变。
remap( )函数解析
remap( )函数会根据我们指定的映射形式,将源图像进行重映射几何变换,基于的式子如下:
?
需要注意,此函数不支持就地(in-place)操作。看看其原型和参数。
| void cv::remap | ( | InputArray | src, |
| OutputArray | dst, | ||
| InputArray | map1, | ||
| InputArray | map2, | ||
| int? | interpolation, | ||
| int? | borderMode?=?BORDER_CONSTANT, | ||
| const?Scalar?&? | borderValue?=?Scalar()? | ||
| ) |
?Parameters
| src | Source image. |
| dst | Destination image. It has the same size as map1 and the same type as src . |
| map1 | The first map of either (x,y) points or just x values having the type CV_16SC2 , CV_32FC1, or CV_32FC2. See convertMaps for details on converting a floating point representation to fixed-point for speed. |
| map2 | The second map of y values having the type CV_16UC1, CV_32FC1, or none (empty map if map1 is (x,y) points), respectively. |
| interpolation | 插值方式, Interpolation method (see?InterpolationFlags). The method?INTER_AREA?is not supported by this function. |
| borderMode | 图像边界处理方式 Pixel extrapolation method (see?BorderTypes). When borderMode=BORDER_TRANSPARENT, it means that the pixels in the destination image that corresponds to the "outliers" in the source image are not modified by the function. |
| borderValue | Value used in case of a constant border. By default, it is 0. |
使用OpenCV-3.4中的samples/cpp/tutorial_code/ImgTrans/Remap_Demo.cpp进行演示。
update_map函数中的参数ind意义:
ind=0表示提取源图像的25%~75%显示,1%~24%和76%~100%填充。
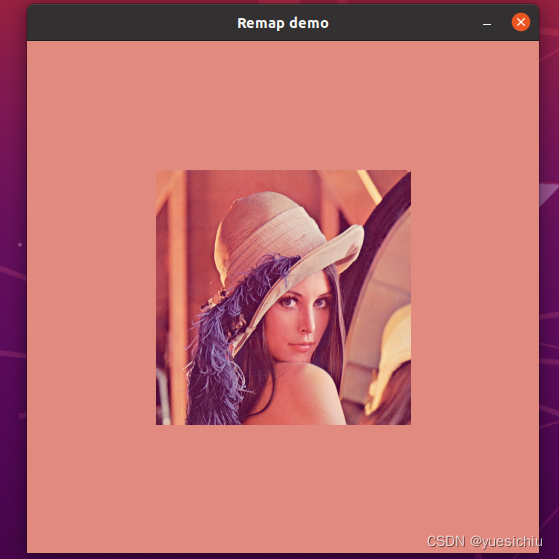
?
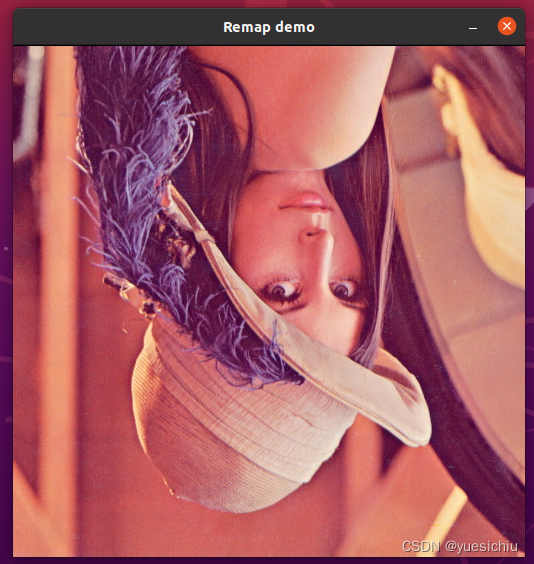
ind=1表示关于沿着x轴翻转(上下翻转)
ind=2表示关于沿着Y轴翻转(左右翻转)
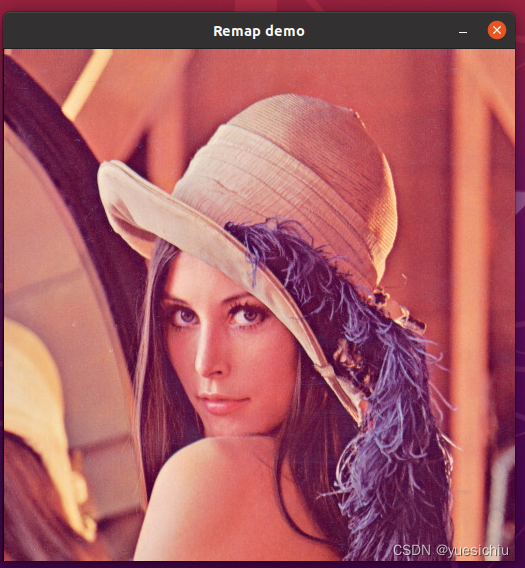
?
ind=3表是上下和左右同时翻转。
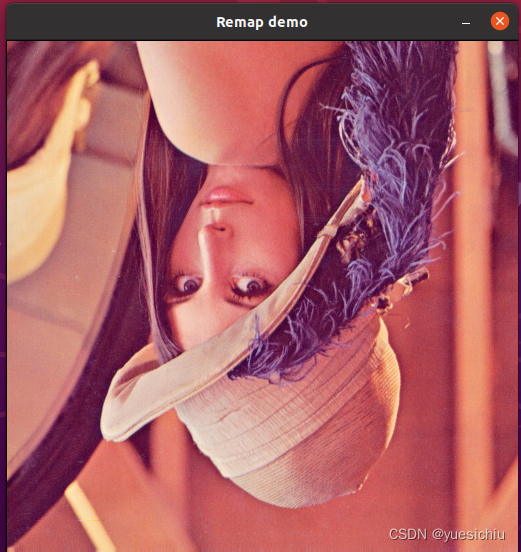
/**
* @function Remap_Demo.cpp
* @brief Demo code for Remap
* @author Ana Huaman
*/
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
/// Function Headers
void update_map( int &ind, Mat &map_x, Mat &map_y );
/**
* @function main
*/
int main(int argc, const char** argv)
{
CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, "{@image |chicky_512.png|input image name}");
std::string filename = parser.get<std::string>(0);
//! [Load]
/// Load the image
Mat src = imread( samples::findFile( filename ), IMREAD_COLOR );
if (src.empty())
{
std::cout << "Cannot read image: " << filename << std::endl;
return -1;
}
//! [Load]
//! [Create]
/// Create dst, map_x and map_y with the same size as src:
Mat dst(src.size(), src.type());
Mat map_x(src.size(), CV_32FC1);
Mat map_y(src.size(), CV_32FC1);
//! [Create]
//! [Window]
/// Create window
const char* remap_window = "Remap demo";
namedWindow( remap_window, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
//! [Window]
//! [Loop]
/// Index to switch between the remap modes
int ind = 0;
for(;;)
{
/// Update map_x & map_y. Then apply remap
update_map(ind, map_x, map_y);
remap( src, dst, map_x, map_y, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar(0, 0, 0) );
/// Display results
imshow( remap_window, dst );
/// Each 1 sec. Press ESC to exit the program
char c = (char)waitKey( 1000 );
if( c == 27 )
{
break;
}
}
//! [Loop]
return 0;
}
/**
* @function update_map
* @brief Fill the map_x and map_y matrices with 4 types of mappings
*/
//! [Update]
void update_map( int &ind, Mat &map_x, Mat &map_y )
{
for( int i = 0; i < map_x.rows; i++ )
{
for( int j = 0; j < map_x.cols; j++ )
{
switch( ind )
{
case 0:
if( j > map_x.cols*0.25 && j < map_x.cols*0.75 && i > map_x.rows*0.25 && i < map_x.rows*0.75 )
{
map_x.at<float>(i, j) = 2*( j - map_x.cols*0.25f ) + 0.5f;
map_y.at<float>(i, j) = 2*( i - map_x.rows*0.25f ) + 0.5f;
}
else
{
map_x.at<float>(i, j) = 0;
map_y.at<float>(i, j) = 0;
}
break;
case 1://行翻转
map_x.at<float>(i, j) = (float)j;
map_y.at<float>(i, j) = (float)(map_x.rows - i);
break;
case 2: //列翻转
map_x.at<float>(i, j) = (float)(map_x.cols - j);
map_y.at<float>(i, j) = (float)i;
break;
case 3: //上下左右均翻转
map_x.at<float>(i, j) = (float)(map_x.cols - j);
map_y.at<float>(i, j) = (float)(map_x.rows - i);
break;
default:
break;
} // end of switch
}
}
ind = (ind+1) % 4;
}