今天向分享一下轻量化网络GhostNet,从原理和代码上做一点个人见解,直接上原理和源码。
官方代码链接
论文链接
Ghost Module原理与代码解析

下图是GHost模块处理过程,图中写为了网络,实质是GHost模块。
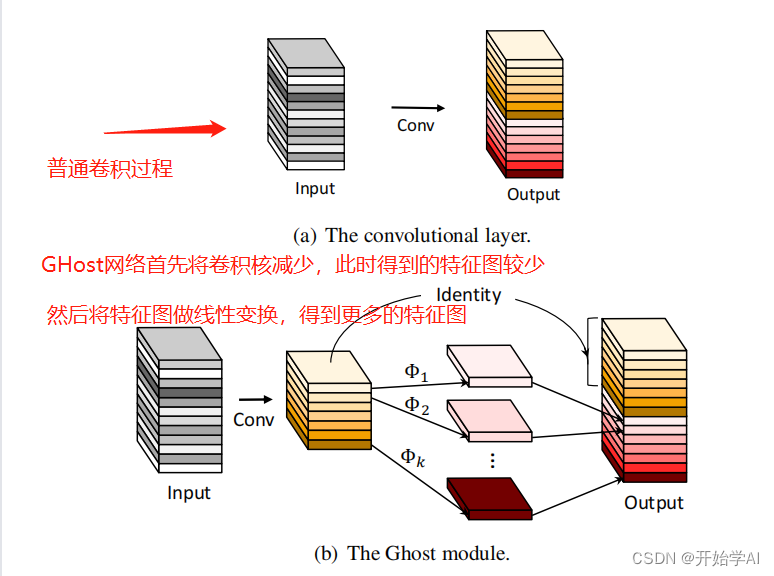
GhostModule的定义如下,实质廉价操作指的是通过深度可分离卷积实现线性变换
'''
GhostModule 类似一个即插即用的模块 输出尺寸不变 通道数改变了
'''
class GhostModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, kernel_size=1, ratio=2, dw_size=3, stride=1, relu=True):
super(GhostModule, self).__init__()
self.oup = oup
init_channels = math.ceil(oup / ratio) # 向上取整 压缩通道数
new_channels = init_channels*(ratio-1) # new_channels < oup
'''
if oup / ratio is integer:
init_channels + new_channels = oup
if oup / ratio is float:
init_channels + new_channels > oup
'''
self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, init_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False), # 尺寸不变
nn.BatchNorm2d(init_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(init_channels, new_channels, dw_size, 1, dw_size//2, groups=init_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.primary_conv(x)
x2 = self.cheap_operation(x1)
out = torch.cat([x1,x2], dim=1)
return out[:,:self.oup,:,:] # 由于拼接后的通道 大于等于 oup,所以这里只取oup
拆开cheap_operation 来看,实质就是采用深度可分离卷积进行操作,每一组对应一个通道。
self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,new_channels,kernel_size=dw_size,stride=1, padding=dw_size//2, groups=in_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential()
)
然后再将基础卷积与深度可分离卷积两种结果相加,由于深度可分离卷积参数小,所以GHost模块的参数量小于使用两层基础卷积的参数量。
Ghost Bottlenecks代码解析
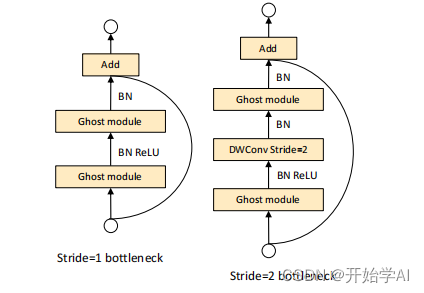
随后,作者设计了Ghost Bottlenecks,结构与ResNet的残差块相似,主要包括两个堆叠的Ghost 模块,第一个Ghost 模块用于扩张通道数,第二个Ghost 模块用于减少通道数,以匹配short cut路径上的通道数。
实现如下:
class GhostBottleneck(nn.Module):
""" Ghost bottleneck w/ optional SE"""
def __init__(self, in_chs, mid_chs, out_chs, dw_kernel_size=3,
stride=1, act_layer=nn.ReLU, se_ratio=0.):
super(GhostBottleneck, self).__init__()
has_se = se_ratio is not None and se_ratio > 0.
self.stride = stride
# Point-wise expansion
self.ghost1 = GhostModule(in_chs, mid_chs, relu=True)
# Depth-wise convolution
if self.stride > 1:
self.conv_dw = nn.Conv2d(mid_chs, mid_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2,
groups=mid_chs, bias=False)
self.bn_dw = nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_chs)
# Squeeze-and-excitation
if has_se:
self.se = SqueezeExcite(mid_chs, se_ratio=se_ratio)
else:
self.se = None
# Point-wise linear projection
self.ghost2 = GhostModule(mid_chs, out_chs, relu=False)
# shortcut
if (in_chs == out_chs and self.stride == 1):
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
else:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_chs, in_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2, groups=in_chs, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_chs),
nn.Conv2d(in_chs, out_chs, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chs),
)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
# 1st ghost bottleneck
x = self.ghost1(x)
# Depth-wise convolution
if self.stride > 1:
x = self.conv_dw(x)
x = self.bn_dw(x)
# Squeeze-and-excitation
if self.se is not None:
x = self.se(x)
# 2nd ghost bottleneck
x = self.ghost2(x)
x += self.shortcut(residual)
return x
可以看出GhostBottleneck模块,会将通道数指定设置到out_chs上,并且可以通过设置stride的大小对特征图的H、W进行改变,shortcut路径用于调整通道数和特征图的高和宽,方便做相加操作。并且所有操作均以深度可分离卷积进行,减少参数量。
以下简要在forward中进行数据流分析:
def forward(self,x):
residual = x # [B,C,H,W]
x = self.ghost1(x) # [B,mid_chs,H,W]
if self.stride > 1: # H,W 会根据stride的设置而改变
x = self.conv_dw(x)
x = self.bn_dw(x) # [B,mid_chs,H,W] -----> [B.mid_chs,h,w]
if self.se is not None:
x = self.se(x) #[B,mid_chs,h,w]
x = self.ghost2(x) #[B,out_chs,h,w]
x += self.shortcut(residual) #[B,out_chs,h,w]
return x
GhostNet构建
class GhostNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,cfgs,width=1.0,dropout=0.2):
super(GhostNet,self).__init__()
self.cfgs = cfgs
self.dropout = dropout
output_channel = _make_divisible(16*width,4)
self.conv_stem = nn.Conv2d(3,output_channel,kernel_size=3,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channel)
self.act1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
input_channel = output_channel
self.out_chs=[]
stages = []
block = GhostBottleneck
for cfg in self.cfgs:
layers = []
for k, exp_size, c, se_ratio, s in cfg:
output_channel = _make_divisible(c*width,4) #按width扩张通道,并返回相近的能被4整除的值
hidden_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size*width,4)
layers.append(block(in_chs=input_channel, mid_chs = hidden_channel, out_chs=output_channel, dw_kernel_size=k,
stride=s, se_ratio=se_ratio))
input_channel = output_channel
in_ch = layers[-1].output_channel
self.out_chs.append(in_ch)
stages.append(nn.Sequential(*layers))
output_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size*width,4)
self.out_chs.append(output_channel)
stages.append(nn.Sequential(ConvBnAct(input_channel, output_channel,kernel_size=1)))
input_channel = output_channel
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*stages)
print(self.out_chs)
self.out_channels = []
for i in range(6):
if i in [1,2,3,5]:
self.out_channels.append(self.out_chs[i])
print(self.out_channels)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv_stem(x) # 下采样了一倍
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
# print(self.blocks)
outputs = []
for i in range(6):
x = self.blocks[i](x)
if i in [1,2,3,5]:
outputs.append(x)
return outputs
def ghostnet(**kwargs):
"""
Constructs a GhostNet model
"""
cfgs = [
# k, t, c, SE, s
# stage1
[[3, 16, 16, 0, 1]],
# stage2
[[3, 48, 24, 0, 2],
[3, 72, 24, 0, 1]],
# stage3
[[5, 72, 40, 0.25, 2],
[5, 120, 40, 0.25, 1]],
# stage4
[[3, 240, 80, 0, 2],
[3, 200, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 480, 112, 0.25, 1],
[3, 672, 112, 0.25, 1]
],
# stage5
[[5, 672, 160, 0.25, 2],
[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0.25, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0.25, 1]
]
]
return GhostNet(cfgs, **kwargs)
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(2,3,640,640)
model = ghostnet()
y = model(x)
for out in y:
print(out.shape)
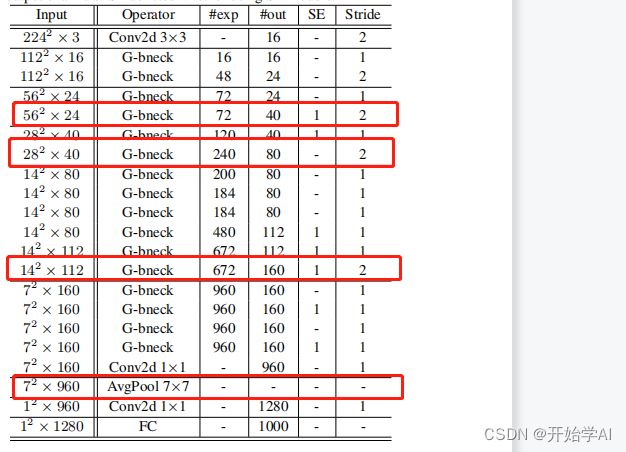
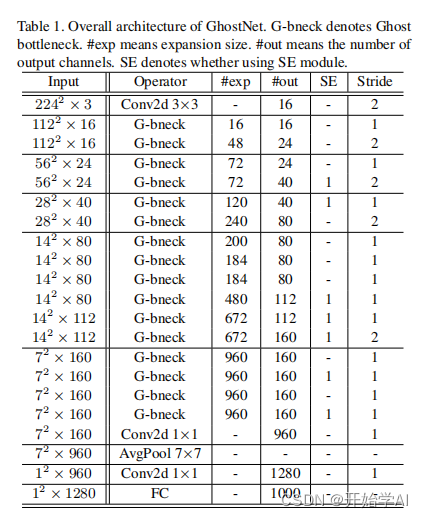
按如上参数表构建,便可以实现GHostNet,在上述代码中,我组合了以下特征图进行输出,方便项目使用。