算法介绍
首先我们从Random sample consensus - Wikipedia上找到RANSAC原理的介绍。
RANSAC算法的中文名称是随机抽样一致算法(Random Sample Consenus),简单的说,通过RANSAC算法,我们将数据分为inliers和outliers,inliers是对于模型拟合有效的点,也称之为内点;outliers是对于模型拟合无效的点,也就是错误的数据点,称之为外点。而我们在使用观测数据拟合模型的过程中,外点的存在对于使用数据拟合模型是有害的,那么我们该如何剔除这些外点呢?RANSAC算法就是能够剔除外点的一个迭代性的算法。
举例
下图所示就是RANSAC算法的作用:剔除外点,使模型估计更加准确,参考Robust line model estimation using RANSAC — skimage v0.19.2 docs (scikit-image.org)
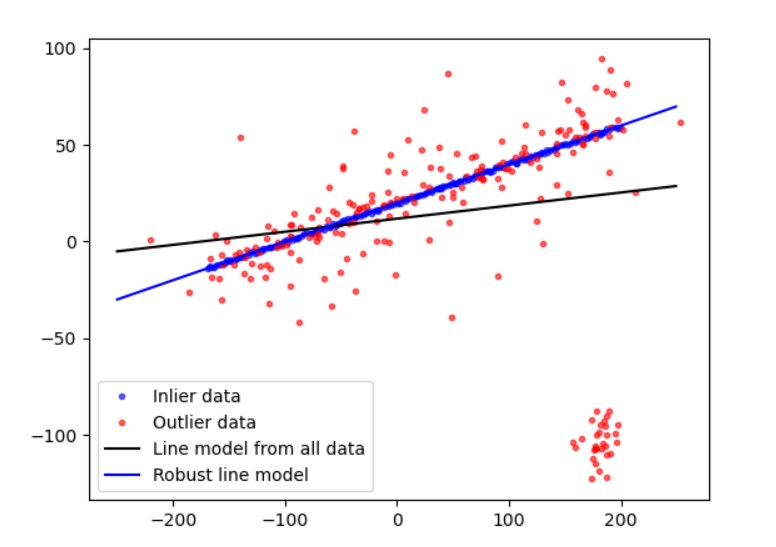
算法的基本思想和流程
算法的实现流程:
- 选择出估计模型的最小数据样本(对于二维和三维直线拟合来说,确定一条直线最少需要2个点;对于三维平面拟合来说,确定一个三维平面最少需要3个点)
- 使用这个最小的数据样本,算出拟合的模型。(也就是直线方程或者平面方程)
- 将所有的模型带入这个拟合的模型,计算出内点 的数量。(数据点和拟合的模型的误差在一定阈值范围内的数据点的数量)
- 比较当前模型和之前迭代的得到的最好的模型的内点数量(内点数量越多,模型越好),记录最大的内点数的模型参数和内点数量。
- 重复1-4步,直到达到迭代终止条件(例如达到最大迭代数、内点数量达到迭代终止条件)
迭代次数的推导
假设内点在数据中所占的比例为
t
t
t
t
=
n
i
n
l
i
e
r
s
n
i
n
l
i
e
r
s
+
n
o
u
t
l
i
e
r
s
t=\frac{n_{inliers}}{n_{inliers}+n_{outliers}}
t=ninliers?+noutliers?ninliers??
如果我们每次迭代都需要
N
N
N个点,那么每次迭代至少有一个外点的概率是:
P
1
=
1
?
t
N
P_{1}=1-t^N
P1?=1?tN
那么我们如果迭代
k
k
k次,所有的
k
k
k次迭代都至少有一个外点的概率为
P
1
k
P_{1}^{k}
P1k?,那么这
k
k
k次迭代,能够采样到正确的
N
N
N个内点去计算模型的概率就是上述概率的补集。
P
=
1
?
P
1
k
=
1
?
(
1
?
t
N
)
k
P=1-P_{1}^{k}=1-(1-t^{N})^{k}
P=1?P1k?=1?(1?tN)k
通过上式,我们可以求得
k
=
l
o
g
(
1
?
P
)
l
o
g
(
1
?
t
N
)
k=\frac{log(1-P)}{log(1-t^{N})}
k=log(1?tN)log(1?P)?
注意:内点的概率
t
t
t是一个先验值,如果我们一开始不知道这个先验值
t
t
t,可以采用自适应迭代的方法,用当前的内点的比值来当成
t
t
t来估算迭代的次数。然后通过不断迭代,内点的比值也逐渐增大,再用新的更大的内点比值去代替
t
t
t的值;对于
P
P
P来说,一般会取一个定值0.99,等式(4)可以看出,当
P
P
P不变时,
t
t
t越大,
k
k
k越小,
t
t
t越小,
k
k
k越大。
算法的实现
Given:
data – A set of observations.
model – A model to explain observed data points.
n – Minimum number of data points required to estimate model parameters.
k – Maximum number of iterations allowed in the algorithm.
t – Threshold value to determine data points that are fit well by model.
d – Number of close data points required to assert that a model fits well to data.
Return:
bestFit – model parameters which best fit the data (or null if no good model is found)
iterations = 0
bestFit = null
bestErr = something really large
while iterations < k do
maybeInliers := n randomly selected values from data
maybeModel := model parameters fitted to maybeInliers
alsoInliers := empty set
for every point in data not in maybeInliers do
if point fits maybeModel with an error smaller than t
add point to alsoInliers
end if
end for
if the number of elements in alsoInliers is > d then
// This implies that we may have found a good model
// now test how good it is.
betterModel := model parameters fitted to all points in maybeInliers and alsoInliers
thisErr := a measure of how well betterModel fits these points
if thisErr < bestErr then
bestFit := betterModel
bestErr := thisErr
end if
end if
increment iterations
end while
return bestFit
python代码实现
以下代码参考scikit-image/fit.py at v0.19.2 · scikit-image/scikit-image (github.com),也就是skimage的源码。
def _dynamic_max_trials(n_inliers, n_samples, min_samples, probability):
if n_inliers == 0:
return np.inf
if probability == 1:
return np.inf
if n_inliers == n_samples:
return 1
nom = math.log(1 - probability)
denom = math.log(1 - (n_inliers / n_samples) ** min_samples)
return int(np.ceil(nom / denom))
def ransac(data, model_class, min_samples, residual_threshold,
is_data_valid=None, is_model_valid=None,
max_trials=100, stop_sample_num=np.inf, stop_residuals_sum=0,
stop_probability=1, random_state=None, initial_inliers=None):
best_inlier_num = 0
best_inlier_residuals_sum = np.inf
best_inliers = []
validate_model = is_model_valid is not None
validate_data = is_data_valid is not None
random_state = np.random.default_rng(random_state)
# in case data is not pair of input and output, male it like it
if not isinstance(data, (tuple, list)):
data = (data, )
num_samples = len(data[0])
if not (0 < min_samples < num_samples):
raise ValueError(f"`min_samples` must be in range (0, {num_samples})")
if residual_threshold < 0:
raise ValueError("`residual_threshold` must be greater than zero")
if max_trials < 0:
raise ValueError("`max_trials` must be greater than zero")
if not (0 <= stop_probability <= 1):
raise ValueError("`stop_probability` must be in range [0, 1]")
if initial_inliers is not None and len(initial_inliers) != num_samples:
raise ValueError(
f"RANSAC received a vector of initial inliers (length "
f"{len(initial_inliers)}) that didn't match the number of "
f"samples ({num_samples}). The vector of initial inliers should "
f"have the same length as the number of samples and contain only "
f"True (this sample is an initial inlier) and False (this one "
f"isn't) values.")
# for the first run use initial guess of inliers
spl_idxs = (initial_inliers if initial_inliers is not None
else random_state.choice(num_samples, min_samples,
replace=False))
# estimate model for current random sample set
model = model_class()
for num_trials in range(max_trials):
# do sample selection according data pairs
samples = [d[spl_idxs] for d in data]
# for next iteration choose random sample set and be sure that
# no samples repeat
spl_idxs = random_state.choice(num_samples, min_samples, replace=False)
# optional check if random sample set is valid
if validate_data and not is_data_valid(*samples):
continue
success = model.estimate(*samples)
# backwards compatibility
if success is not None and not success:
continue
# optional check if estimated model is valid
if validate_model and not is_model_valid(model, *samples):
continue
residuals = np.abs(model.residuals(*data))
# consensus set / inliers
inliers = residuals < residual_threshold
residuals_sum = residuals.dot(residuals)
# choose as new best model if number of inliers is maximal
inliers_count = np.count_nonzero(inliers)
if (
# more inliers
inliers_count > best_inlier_num
# same number of inliers but less "error" in terms of residuals
or (inliers_count == best_inlier_num
and residuals_sum < best_inlier_residuals_sum)):
best_inlier_num = inliers_count
best_inlier_residuals_sum = residuals_sum
best_inliers = inliers
dynamic_max_trials = _dynamic_max_trials(best_inlier_num,
num_samples,
min_samples,
stop_probability)
if (best_inlier_num >= stop_sample_num
or best_inlier_residuals_sum <= stop_residuals_sum
or num_trials >= dynamic_max_trials):
break
# estimate final model using all inliers
if any(best_inliers):
# select inliers for each data array
data_inliers = [d[best_inliers] for d in data]
model.estimate(*data_inliers)
if validate_model and not is_model_valid(model, *data_inliers):
warn("Estimated model is not valid. Try increasing max_trials.")
else:
model = None
best_inliers = None
warn("No inliers found. Model not fitted")
return model, best_inliers
下一篇我们将重点讲解使用RANSAC拟合直线的例子,请移步RANSAC算法与原理(二)
References
Random sample consensus - Wikipedia
RANSAC算法详解(附Python拟合直线模型代码) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
Robust line model estimation using RANSAC — skimage v0.19.2 docs (scikit-image.org)
scikit-image/fit.py at v0.19.2 · scikit-image/scikit-image (github.com)
