不管学习什么,基础都是非常重要的,那想对深度学习模型进行创新来说,基础就是所有的经典模型,想要从模型角度进行创新,毫无疑问就需要了解不同类型模型的特点,然后在对每一类模型有一定基础的了解上,再进行创新,目前主要有的经典模型有 LeNet-AlexNet-ZFNet-VGGNets-GooLeNet-ResNet-DenseNet其中前四种属于对卷积层纵向改变,GooLeNet,开始对模型结构进行了横向的变化,接着为了解决网络退化问题,2015年便出现了有名的ResNet残差网络,2017年结GooLeNet的Inception结构和ResNet的残差结构诞生了具有稠密结构的DenseNet稠密网络。而我由于做的是一维信号的识别,所以用pytorch变复现了以上模型的一维版本。本文复现,部分参考《PyTorch深度学习实战-从新手小白到数据专家》
第一篇首先复现的是LeNet网络
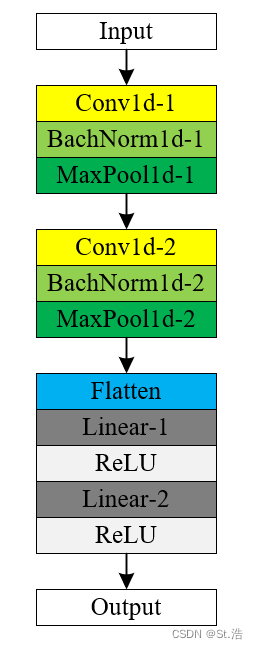
LetNet模型结构
LeNet网络是最早期的卷积神经网络只有2个卷积层,但却冥定了后期几乎所有卷积神经网络的基础卷积-池化-全连接的基本结构,在实际复现的过程中增加了一些应用性改动。
1.给每一个卷积层后加入批量标准化层,抑制梯度消失,提升样本初始分布对模型的抗干扰性
2.为了让不同通道数目,不同样本点大小的样本都可以在不对模型进行手动更改的情况下进行训练,所以对模型的最后的全连接部分进行了自适应处理,通过对输入数据的初始化,算出最后的全连接层的第一个参数的大小
3.在输入时检测样本维度大小,当数据维度大小输入错误时进行提示,新手友好
首先浅看一下LeNet的简简单单的模型的结构吧
因为给模型增加了自适应性所以输出的大小会根据输入数据的大小有不同的变化
表中我们命名输入批次为Batch,输入通道数为Channel,输入的样本点的数量为Sample
如输入的数据为1×1×224
则Batch=1,Channel=1,Sample=224
而经过卷积层和池化之后输出尺寸变化遵循以下公式
各层的参数如下
输出尺寸=(原尺寸+2×填充-核大小)//步幅 + 1
// → 双斜杠对应python中为向下取整操作 → 例: 5//2 = 2
例1:原尺寸Sample,经过了一个卷积核大小为5,步幅为1,填充为0的卷积层
则输出尺寸=(Sample + 2×0 - 5)//1 + 1 = (sample - 5)+1 = sample - 4
例2:原尺寸Sample,经过了一个池化核大小为5,步幅为2,填充为0的池化层
则输出尺寸=(Sample + 2×0 - 2)//2 + 1 = (sample - 2)//2+1 = sample//2 - 2//2 +1 = sample//2 - 1 +1 = sample//2
| 层号 | 层名 | 核大小 / 步长 / 填充 | 输出大小 |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | Input | - | Batch×Channel×Sample |
| 0 | Conv1d-1 | 5/1/0 | Batch × 20 × (Sample-4) |
| 1 | MaxPool1d-1 | 2/2/0 | Batch × 20 × ((Sample-4)//2) |
| 2 | BatchNorm1d-1 | - | Batch × 20 × ((Sample-4)//2) |
| 3 | Conv1d-2 | 5/1/0 | Batch × 50 × ((Sample-4)//2-4) |
| 4 | MaxPool1d-2 | 2/2/0 | Batch × 50 × (((Sample-4)//2-4)//2) |
| 5 | BatchNorm1d-1 | - | Batch × 50 × (((Sample-4)//2-4)//2) |
| 6 | Flatten | - | Batch × (50×((Sample-4)//2-4)//2) |
进行到第6层之后此时的Sample(当前样本点数量) = (50×((Sample-4)//2-4)//2)
| 层号 | 层名 | 池化层尺寸 | 输出大小 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Linear-1 | Sample×512 | Batch × 512 |
| 1 | ReLU | - | Batch × 512 |
| 2 | Linear-2 | 512×5 | Batch × 5 |
| 3 | ReLU | - | Batch × 5 |
LetNet代码实现
OK 好了接下来我们看代码实现的部分
import torch
class LeNet(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channels, input_sample_points, classes):
super(LeNet, self).__init__()
self.input_channels = input_channels
self.input_sample_points = input_sample_points
self.features = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv1d(input_channels, 20, kernel_size=5),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(20),
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(2),
torch.nn.Conv1d(20, 50, kernel_size=5),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(50),
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(2),
)
self.After_features_channels = 50
# 根据公式计算出通过所有的卷积层和池化层后输出的通道中样本点的数量
# self.After_features_sample_points = ((input_sample_points - 5 + 1) // 2 - 5 + 1) // 2
self.After_features_sample_points = ((input_sample_points-4)//2-4) // 2
self.classifier = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(self.After_features_channels * self.After_features_sample_points, 512),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(512, classes),
torch.nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
# 检查输入样本维度是否有错误
if x.size(1) != self.input_channels or x.size(2) != self.input_sample_points:
raise Exception(
'输入数据维度错误,输入维度应为[Batch_size,{},{}],实际输入维度为{}'.format(self.input_channels, self.input_sample_points,x.size()))
x = self.features(x)
x = x.view(-1, self.After_features_channels * self.After_features_sample_points)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = LeNet(input_channels=1, input_sample_points=224, classes=5)
input = torch.randn(size=(1, 1, 224))
output = model(input)
print(output.shape)
#torch.Size([1, 5])
可以看到如果在训练时设定模型参数和实际输入的维度相同时最后会正常输出结果
那如果输入的维度和设置好的尺寸不一样呢?把输入数据的通道数改成2试一试
input = torch.randn(size=(1, 2, 224))
则就会报如下的错误提示你得修改维度这样对于新手来说对维度这个麻烦事就可以有一个辅助了

然后我们打印模型看一下对应层的参数
print(model)

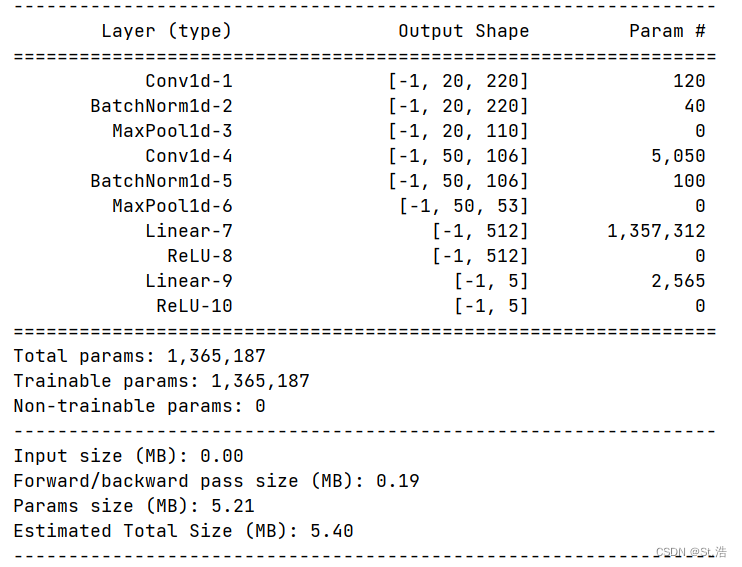
这里可以稍微关注一下classifier里第0层的in_features = 2650
这2650是怎么来的呢还记得我们设置的输入的样本点数量是224,则在进入分类器之前此时输出的样本维度为Batch × 50 × (((Sample-4)//2-4)//2)
(((Sample-4)//2-4)//2) = (((224-4)//2-4)//2) = (220//2 - 4)//2 = 106//2 = 53
则经过下面这个改变维度的代码也就是Flatten层之后
x = x.view(-1, self.After_features_channels * self.After_features_sample_points)
数据变为Batch × 50×(((Sample-4)//2-4)//2) = Batch × (50×63) = Batch × 2650
好了下一步再用torchsummary库看一下每一层的参数的数量,以及存储变量和计算所用到的内存空间的大小
from torchsummary import summary
summary(model=model,input_size=(1,224),device='cpu')
AlexNet
复现完了LeNet, 接下来复现AlexNet和LeNet,结构上并没有什么创新,对比LeNet主要是首先加深了网络,在处理二维数据时进行了数据增强,其次是引入了Dropout避免过拟合,然后是引用了LRN(Local Response Normalization)有的文章和书上翻译成了局部相应归一化,应该是翻译错了应该是局部相应标准化Normalization是标准化的意思。从有了BN Batch Normalization 之后研究人员发现LRN没什么用所以就去掉了。
import torch
class AlexNet(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_channels,input_sample_points,classes):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.input_channels = input_channels
self.input_sample_points = input_sample_points
self.features = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv1d(input_channels,64,kernel_size=11,stride=4,padding=2),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(64),
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
#torch.nn.LocalResponseNorm(size=5, alpha=0.0001, beta=0.75, k=2),
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=3,stride=2),
torch.nn.Conv1d(64, 192, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(192),
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
#torch.nn.LocalResponseNorm(size=5, alpha=0.0001, beta=0.75, k=2),
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
torch.nn.Conv1d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(384),
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
torch.nn.Conv1d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
torch.nn.Conv1d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
#自适应平均池化不管输入多少输出一定为6
torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(6),
)
self.classifier = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5),
torch.nn.Linear(1536,1024),
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5),
torch.nn.Linear(1024, 1024),
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
torch.nn.Linear(1024,classes),
)
def forward(self,x):
if x.size(1)!=self.input_channels or x.size(2)!=self.input_sample_points:
raise Exception('输入数据维度错误,输入维度应为[Batch_size,{},{}],实际输入维度为{}'.format(self.input_channels,self.input_sample_points,x.size()))
x = self.features(x)
x = x.view(-1,1536)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = AlexNet(input_channels=1, input_sample_points=224, classes=5)
input = torch.randn(size=(1, 1, 224))
output = model(input)
print(output.shape)
#torch.Size([1, 5])
ZFNet
ZFnet 将AlexNet的的第一个卷积核由于11变成7步长从4变成了2后面卷积层变为384,384,256复现ZFNet的时候提取特征部分又换回了普通的池化层
import torch
class ZFNet(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_channels,input_sample_points,classes):
super(ZFNet, self).__init__()
self.input_channels = input_channels
self.input_sample_points = input_sample_points
self.features = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv1d(input_channels,96,kernel_size=7,stride=2),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(96),
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=3,stride=2),
torch.nn.Conv1d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, stride=2),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
torch.nn.Conv1d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(384),
torch.nn.Conv1d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(384),
torch.nn.Conv1d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
self.After_features_channels = 256
self.After_features_sample_points = (((((((((input_sample_points-7)//2 + 1)-3)//2+1)-5)//2+1)-3)//2+1)-3)//2+1
self.classifier = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(self.After_features_channels*self.After_features_sample_points,1024),
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5),
torch.nn.Linear(1024, 1024),
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5),
torch.nn.Linear(1024,classes),
)
def forward(self,x):
if x.size(1)!=self.input_channels or x.size(2)!=self.input_sample_points:
raise Exception('输入数据维度错误,输入维度应为[Batch_size,{},{}],实际输入维度为{}'.format(self.input_channels,self.input_sample_points,x.size()))
x = self.features(x)
x = x.view(-1,self.After_features_channels*self.After_features_sample_points)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = ZFNet(input_channels=1, input_sample_points=224, classes=5)
input = torch.randn(size=(1, 1, 224))
output = model(input)
print(output.shape)
#torch.Size([1, 5])
总结
在复现一维模型的过程中报留了卷积层和池化层对应的尺寸,全连接层的尺寸做了相应的缩小,主要还是用作模型对比。
