参考资料
1. 算法简介
-
曲线插值的方法是按照车辆在某些特定条件(安全、快速、高效)下, 进行路径的曲线拟合,常见的有多项式曲线、双圆弧段曲线、正弦函数曲线、贝塞尔曲线、 B样条曲线等。
-
曲线插值法的核心思想就是基于预先构造的曲线类型,根据车辆期望达到的状态(比如要求车辆到达某点的速度和加速度为期望值),将此期望值作为边界条件代入曲线类型进行方程求解,获得曲线的相关系数(简单地说就是待定系数法!)。
-
曲线所有的相关系数一旦确定,轨迹规划随之完成。
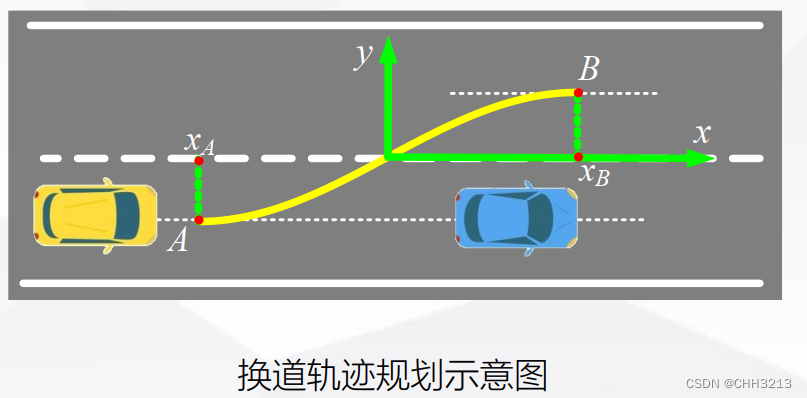
2. 算法精讲
2.1 多项式曲线
下面以多项式曲线为例讲解曲线插值法轨迹规划。
多项式曲线分为三次多项式曲线、 五次多项式曲线、 七次多项式曲线
- 针对三次多项式曲线,最多能确定每一个期望点的两个维度的期望状态,一般来说就是位置和速度。
{ x ( t ) = a 0 + a 1 t + a 2 t 2 + a 3 t 3 y ( t ) = b 0 + b 1 t + b 2 t 2 + b 3 t 3 (1) \tag{1} \left\{\begin{array}{l} x(t)=a_{0}+a_{1} t+a_{2} t^{2}+a_{3} t^{3} \\ y(t)=b_{0}+b_{1} t+b_{2} t^{2}+b_{3} t^{3} \end{array}\right. {x(t)=a0?+a1?t+a2?t2+a3?t3y(t)=b0?+b1?t+b2?t2+b3?t3?(1)
- 针对五次多项式曲线,最多能确定每一个期望点的三个维度的期望状态,一般来说就是位置、速度、加速度。
{ x ( t ) = a 0 + a 1 t + a 2 t 2 + a 3 t 3 + a 4 t 4 + a 5 t 5 y ( t ) = b 0 + b 1 t + b 2 t 2 + b 3 t 3 + b 4 t 4 + b 5 t 5 (2) \tag{2} \left\{\begin{array}{l} x(t)=a_{0}+a_{1} t+a_{2} t^{2}+a_{3} t^{3}+a_{4} t^{4}+a_{5} t^{5} \\ y(t)=b_{0}+b_{1} t+b_{2} t^{2}+b_{3} t^{3}+b_{4} t^{4}+b_{5} t^{5} \end{array}\right. {x(t)=a0?+a1?t+a2?t2+a3?t3+a4?t4+a5?t5y(t)=b0?+b1?t+b2?t2+b3?t3+b4?t4+b5?t5?(2)
- 针对七次多项式曲线,最多能确定每一个期望点的四个维度的期望状态,一般来说就是位置、速度、 加速度、加加速度(加加速度称为
jerk,加加加速度称为snap,无人机轨迹规划中有用到snap)
{ x ( t ) = a 0 + a 1 t + a 2 t 2 + a 3 t 3 + a 4 t 4 + a 5 t 5 + a 6 t 6 + a 7 t 7 y ( t ) = b 0 + b 1 t + b 2 t 2 + b 3 t 3 + b 4 t 4 + b 5 t 5 + b 6 t 6 + b 7 t 7 (3) \tag{3} \left\{\begin{array}{l} x(t)=a_{0}+a_{1} t+a_{2} t^{2}+a_{3} t^{3}+a_{4} t^{4}+a_{5} t^{5}+a_{6} t^{6}+a_{7} t^{7} \\ y(t)=b_{0}+b_{1} t+b_{2} t^{2}+b_{3} t^{3}+b_{4} t^{4}+b_{5} t^{5}+b_{6} t^{6}+b_{7} t^{7} \end{array}\right. {x(t)=a0?+a1?t+a2?t2+a3?t3+a4?t4+a5?t5+a6?t6+a7?t7y(t)=b0?+b1?t+b2?t2+b3?t3+b4?t4+b5?t5+b6?t6+b7?t7?(3)
2.2 示例——五次多项式曲线
以五次多项式曲线为例讲解曲线揷值法轨迹规划。
设 t 0 t_0 t0?为初始时间,位置、速度、加速度均已知,显然 x 和 y x和y x和y方向分别有以下三个方程:
- 位置
{ x ( t 0 ) = a 0 + a 1 t 0 + a 2 t 0 2 + a 3 t 0 3 + a 4 t 0 4 + a 5 t 0 5 y ( t 0 ) = b 0 + b 1 t 0 + b 2 t 0 2 + b 3 t 0 3 + b 4 t 0 4 + b 5 t 0 5 (4) \tag{4} \left\{\begin{array}{l}x\left(t_{0}\right)=a_{0}+a_{1} t_{0}+a_{2} t_{0}^{2}+a_{3} t_{0}^{3}+a_{4} t_{0}^{4}+a_{5} t_{0}^{5} \\ y\left(t_{0}\right)=b_{0}+b_{1} t_{0}+b_{2} t_{0}^{2}+b_{3} t_{0}^{3}+b_{4} t_{0}^{4}+b_{5} t_{0}^{5}\end{array} \quad\right. {x(t0?)=a0?+a1?t0?+a2?t02?+a3?t03?+a4?t04?+a5?t05?y(t0?)=b0?+b1?t0?+b2?t02?+b3?t03?+b4?t04?+b5?t05??(4) - 速度
{ x ′ ( t 0 ) = a 1 + 2 t 0 a 2 + 3 t 0 2 a 3 + 4 t 0 3 a 4 + 5 t 0 4 a 5 y ′ ( t 0 ) = b 1 + 2 t 0 b 2 + 3 t 0 2 b 3 + 4 t 0 3 b 4 + 5 t 0 4 b 5 (5) \tag{5} \left\{\begin{array}{l}x^{\prime}\left(t_{0}\right)=a_{1}+2 t_{0} a_{2}+3 t_{0}{ }^{2} a_{3}+4 t_{0}{ }^{3} a_{4}+5 t_{0}{ }^{4} a_{5} \\ y^{\prime}\left(t_{0}\right)=b_{1}+2 t_{0} b_{2}+3 t_{0}{ }^{2} b_{3}+4 t_{0}{ }^{3} b_{4}+5 t_{0}{ }^{4} b_{5}\end{array} \quad\right. {x′(t0?)=a1?+2t0?a2?+3t0?2a3?+4t0?3a4?+5t0?4a5?y′(t0?)=b1?+2t0?b2?+3t0?2b3?+4t0?3b4?+5t0?4b5??(5) - 加速度
{ x ′ ′ ( t 0 ) = 2 a 2 + 6 t 0 a 3 + 12 t 0 2 a 4 + 20 t 0 3 a 5 y ′ ′ ( t 0 ) = 2 b 2 + 6 t 0 b 3 + 12 t 0 2 b 4 + 20 t 0 3 b 5 (6) \tag{6} \left\{\begin{array}{l}x^{\prime \prime}\left(t_{0}\right)=2 a_{2}+6 t_{0} a_{3}+12 t_{0}{ }^{2} a_{4}+20 t_{0}{ }^{3} a_{5} \\ y^{\prime \prime}\left(t_{0}\right)=2 b_{2}+6 t_{0} b_{3}+12 t_{0}{ }^{2} b_{4}+20 t_{0}{ }^{3} b_{5}\end{array} \quad\right. {x′′(t0?)=2a2?+6t0?a3?+12t0?2a4?+20t0?3a5?y′′(t0?)=2b2?+6t0?b3?+12t0?2b4?+20t0?3b5??(6)

定义换道终点时间为 t 1 t_1 t1? ,横纵向(即 x , y x,y x,y方向)均有期望的位置、速度、 加速度,又分别可以得到以下三个方程:
- 位置
{ x ( t 1 ) = a 0 + a 1 t 1 + a 2 t 1 2 + a 3 t 1 3 + a 4 t 1 4 + a 5 t 1 5 y ( t 1 ) = b 0 + b 1 t 1 + b 2 t 1 2 + b 3 t 1 3 + b 4 t 1 4 + b 5 t 1 5 (7) \tag{7} \left\{\begin{array}{l}x\left(t_{1}\right)=a_{0}+a_{1} t_{1}+a_{2} t_{1}^{2}+a_{3} t_{1}^{3}+a_{4} t_{1}^{4}+a_{5} t_{1}^{5} \\ y\left(t_{1}\right)=b_{0}+b_{1} t_{1}+b_{2} t_{1}^{2}+b_{3} t_{1}^{3}+b_{4} t_{1}^{4}+b_{5} t_{1}^{5}\end{array} \quad\right. {x(t1?)=a0?+a1?t1?+a2?t12?+a3?t13?+a4?t14?+a5?t15?y(t1?)=b0?+b1?t1?+b2?t12?+b3?t13?+b4?t14?+b5?t15??(7) - 速度
{ x ′ ( t 1 ) = a 1 + 2 t 1 a 2 + 3 t 1 2 a 3 + 4 t 1 3 a 4 + 5 t 1 4 a 5 y ′ ( t 1 ) = b 1 + 2 t 1 b 2 + 3 t 1 2 b 3 + 4 t 1 3 b 4 + 5 t 1 4 b 5 (8) \tag{8} \left\{\begin{array}{l}x^{\prime}\left(t_{1}\right)=a_{1}+2 t_{1} a_{2}+3 t_{1}{ }^{2} a_{3}+4 t_{1}{ }^{3} a_{4}+5 t_{1}{ }^{4} a_{5} \\ y^{\prime}\left(t_{1}\right)=b_{1}+2 t_{1} b_{2}+3 t_{1}{ }^{2} b_{3}+4 t_{1}{ }^{3} b_{4}+5 t_{1}{ }^{4} b_{5}\end{array} \quad\right. {x′(t1?)=a1?+2t1?a2?+3t1?2a3?+4t1?3a4?+5t1?4a5?y′(t1?)=b1?+2t1?b2?+3t1?2b3?+4t1?3b4?+5t1?4b5??(8) - 加速度
{ x ′ ′ ( t 1 ) = 2 a 2 + 6 t 1 a 3 + 12 t 1 2 a 4 + 20 t 1 3 a 5 y ′ ′ ( t 1 ) = 2 b 2 + 6 t 1 b 3 + 12 t 1 2 b 4 + 20 t 1 3 b 5 (9) \tag{9} \left\{\begin{array}{l}x^{\prime \prime}\left(t_{1}\right)=2 a_{2}+6 t_{1} a_{3}+12 t_{1}{ }^{2} a_{4}+20 t_{1}{ }^{3} a_{5} \\ y^{\prime \prime}\left(t_{1}\right)=2 b_{2}+6 t_{1} b_{3}+12 t_{1}{ }^{2} b_{4}+20 t_{1}{ }^{3} b_{5}\end{array} \quad\right. {x′′(t1?)=2a2?+6t1?a3?+12t1?2a4?+20t1?3a5?y′′(t1?)=2b2?+6t1?b3?+12t1?2b4?+20t1?3b5??(9)
把起末两点的横纵向方程统一用矩阵表达为:
X
=
[
x
0
x
0
′
x
0
′
′
x
1
x
1
′
x
1
′
′
]
=
[
t
0
5
t
0
4
t
0
3
t
0
2
t
0
1
5
t
0
4
4
t
0
3
3
t
0
2
2
t
0
1
0
20
t
0
3
12
t
0
2
6
t
0
2
0
0
t
1
5
t
1
4
t
1
3
t
1
2
t
1
1
5
t
1
4
4
t
1
3
3
t
1
2
2
t
1
1
0
20
t
1
3
12
t
1
2
6
t
1
2
0
0
]
[
a
5
a
4
a
3
a
2
a
1
a
0
]
=
T
×
A
Y
=
[
y
0
y
0
′
y
0
′
′
y
1
y
1
′
y
1
′
′
]
=
[
t
0
5
t
0
4
t
0
3
t
0
2
t
0
1
5
t
0
4
4
t
0
3
3
t
0
2
2
t
0
1
0
20
t
0
3
12
t
0
2
6
t
0
2
0
0
t
1
5
t
1
4
t
1
3
t
1
2
t
1
1
5
t
1
4
4
t
1
3
3
t
1
2
2
t
1
1
0
20
t
1
3
12
t
1
2
6
t
1
2
0
0
]
[
b
5
b
4
b
3
b
2
b
1
b
0
]
=
T
×
B
(10)
\tag{10} \begin{aligned} &X=\left[\begin{array}{l} x_{0} \\ x_{0}^{\prime} \\ x_{0}^{\prime \prime} \\ x_{1} \\ x_{1}^{\prime} \\ x_{1}^{\prime \prime} \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{llllll} t_{0}{ }^{5} & t_{0}{ }^{4} & t_{0}{ }^{3} & t_{0}{ }^{2} & t_{0} & 1 \\ 5 t_{0}{ }^{4} & 4 t_{0}{ }^{3} & 3 t_{0}{ }^{2} & 2 t_{0} & 1 & 0 \\ 20 t_{0}{ }^{3} & 12 t_{0}{ }^{2} & 6 t_{0} & 2 & 0 & 0 \\ t_{1}^{5} & t_{1}{ }^{4} & t_{1}{ }^{3} & t_{1}{ }^{2} & t_{1} & 1 \\ 5 t_{1}^{4} & 4 t_{1}{ }^{3} & 3 t_{1}{ }^{2} & 2 t_{1} & 1 & 0 \\ 20 t_{1}{ }^{3} & 12 t_{1}{ }^{2} & 6 t_{1} & 2 & 0 & 0 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l} a_{5} \\ a_{4} \\ a_{3} \\ a_{2} \\ a_{1} \\ a_{0} \end{array}\right]=T \times A\\ \\ &Y=\left[\begin{array}{l} y_{0} \\ y_{0}^{\prime} \\ y_{0}^{\prime \prime} \\ y_{1} \\ y_{1}^{\prime} \\ y_{1}^{\prime \prime} \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{llllll} t_{0}{ }^{5} & t_{0}{ }^{4} & t_{0}{ }^{3} & t_{0}{ }^{2} & t_{0} & 1 \\ 5 t_{0}{ }^{4} & 4 t_{0}{ }^{3} & 3 t_{0}{ }^{2} & 2 t_{0} & 1 & 0 \\ 20 t_{0}{ }^{3} & 12 t_{0}{ }^{2} & 6 t_{0} & 2 & 0 & 0 \\ t_{1}^{5} & t_{1}{ }^{4} & t_{1}{ }^{3} & t_{1}{ }^{2} & t_{1} & 1 \\ 5 t_{1}^{4} & 4 t_{1}{ }^{3} & 3 t_{1}{ }^{2} & 2 t_{1} & 1 & 0 \\ 20 t_{1}{ }^{3} & 12 t_{1}{ }^{2} & 6 t_{1} & 2 & 0 & 0 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l} b_{5} \\ b_{4} \\ b_{3} \\ b_{2} \\ b_{1} \\ b_{0} \end{array}\right]=T \times B \end{aligned}
?X=?????????x0?x0′?x0′′?x1?x1′?x1′′???????????=?????????t0?55t0?420t0?3t15?5t14?20t1?3?t0?44t0?312t0?2t1?44t1?312t1?2?t0?33t0?26t0?t1?33t1?26t1??t0?22t0?2t1?22t1?2?t0?10t1?10?100100???????????????????a5?a4?a3?a2?a1?a0???????????=T×AY=?????????y0?y0′?y0′′?y1?y1′?y1′′???????????=?????????t0?55t0?420t0?3t15?5t14?20t1?3?t0?44t0?312t0?2t1?44t1?312t1?2?t0?33t0?26t0?t1?33t1?26t1??t0?22t0?2t1?22t1?2?t0?10t1?10?100100???????????????????b5?b4?b3?b2?b1?b0???????????=T×B?(10)
多项式曲线的自变量为时间 t t t,故一旦求解出系数矩阵 A , B A,B A,B,即可确定曲线方程(说白了,求系数的方法就是我们初中学过的待定系数法)。曲线唯一确定后, 则曲线上每一点的位置、速度等便确定了,轨迹即可求出。曲线上每一点的导数就代表了车辆经过该点时的速度,表明多项式曲线换道轨迹规划是路径+速度的耦合结果。
注意,五次多项式换道轨迹曲线特指横向位置/纵向位置是关于时间 t t t的五次多项式,而不是指纵向位置 y y y关于横向位置 x x x的五次多项式。
2.3 双圆弧段曲线
如图,对于双圆弧段换道轨迹,它由弧AC+线段CD+弧DF构成。
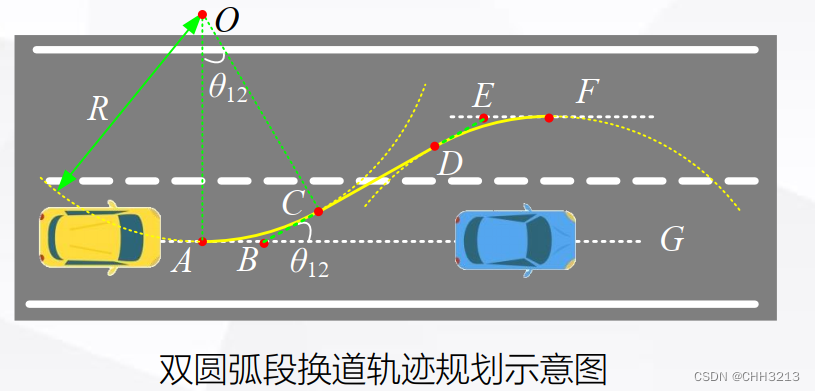
显然,在C点,轨迹曲率由弧AC段的定值突变为0,故为了让车辆能完全跟随轨迹, 考虑到方向盘转角是一个连续缓变过程,车辆行驶到在C点后必须速度为0, 让方向盘回正后才能继续行驶,因此无法应用于行车路径规划,而应用于泊车路径规划。
3. python代码实现
下面实现五次多项式曲线插值法轨迹规划
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
if __name__=="__main__":
# 场景定义
# 换道场景路段与车辆相关参数的定义
d = 3.5 # 道路标准宽度
len_line = 30 # 直线段长度
W = 1.75 # 车宽
L = 4.7 # 车长
# 车辆换道初始状态与终点期望状态
t0 = 0
t1 = 3
state_t0 = np.array([0, -d/2, 5, 0, 0, 0]) # 分别表示小车的x,y; vx,vy; ax,ay
state_t1 = np.array([20, d/2, 5, 0, 0, 0])
"""计算A和B两个系数矩阵"""
## 把起末两点的横纵向方程统一用矩阵表达
X = np.concatenate((np.array([state_t0[i] for i in range(6) if i%2==0]),np.array([state_t1[i] for i in range(6) if i%2==0])))
Y = np.concatenate((np.array([state_t0[i] for i in range(6) if i%2!=0]),np.array([state_t1[i] for i in range(6) if i%2!=0])))
#矩阵T表示
T = np.matrix([
[t0 ** 5,t0 ** 4,t0 ** 3,t0 ** 2,t0,1],
[5 * t0 ** 4,4 * t0 ** 3,3 * t0 ** 2,2 * t0,1,0],
[20 * t0 ** 3,12 * t0 ** 2,6 * t0,1,0,0],
[t1 ** 5,t1 ** 4,t1 ** 3,t1 ** 2,t1,1],
[5 * t1 ** 4,4 * t1 ** 3,3 * t1 ** 2,2 * t1,1,0],
[20 * t1 ** 3,12 * t1 ** 2,6 * t1,1,0,0]
])
# # 解法1
# A=np.linalg.pinv(T)@X
# B=np.linalg.pinv(T)@Y.T
# A=A.T
# B=B.T
# # 解法2
A = np.linalg.solve(T,X)
B = np.linalg.solve(T,Y)
# 将时间从t0到t1离散化,获得离散时刻的轨迹坐标
t = np.transpose((np.arange(t0,t1+0.05,0.05)))
path = np.zeros((len(t),4)) # 1-4列分别存放x,y,vx,vy
for i in range(len(t)):
# 纵向位置坐标
path[i,0] = np.array([t[i] ** 5,t[i] ** 4,t[i] ** 3,t[i] ** 2,t[i],1]) @ A # @符号是矩阵相乘的意思
# 横向位置坐标
path[i,1] = np.array([t[i] ** 5,t[i] ** 4,t[i] ** 3,t[i] ** 2,t[i],1]) @ B
# 纵向速度
path[i,2] = np.array([5 * t[i] ** 4,4 * t[i] ** 3,3 * t[i] ** 2,2 * t[i],1,0]) @ A
# 横向速度
path[i,3] = np.array([5 * t[i] ** 4,4 * t[i] ** 3,3 * t[i] ** 2,2 * t[i],1,0]) @ B
## 画场景示意图
plt.figure(1)
# 画灰色路面图
GreyZone = np.array([[- 5,- d - 0.5],[- 5,d + 0.5],[len_line,d + 0.5],[len_line,- d - 0.5]])
plt.fill(GreyZone[:,0],GreyZone[:,1],'gray')
# 画小车
plt.fill(np.array([state_t1[0],state_t1[0],state_t1[0] + L,state_t1[0] + L]),np.array([- d / 2 - W / 2,- d / 2 + W / 2,- d / 2 + W / 2,- d / 2 - W / 2]),'b')
plt.fill(np.array([state_t0[0],state_t0[0],state_t0[0] - L,state_t0[0] - L]),np.array([- d / 2 - W / 2,- d / 2 + W / 2,- d / 2 + W / 2,- d / 2 - W / 2]),'y')
# 画分界线
plt.plot(np.array([- 5,len_line]),np.array([0,0]),'w--')
plt.plot(np.array([- 5,len_line]),np.array([d,d]),'w')
plt.plot(np.array([- 5,len_line]),np.array([- d,- d]),'w')
# 设置坐标轴显示范围
plt.axis('equal')
plt.savefig("场景示意图.png")
# 画换道轨迹
plt.plot(path[:,0],path[:,1],'r--')
## 分析速度
# 横向速度
plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(t,path[:,3],'k')
plt.xlabel('time/s ')
plt.ylabel('m/s ')
plt.savefig("横向速度.png")
# 纵向速度
plt.figure(3)
plt.plot(t,path[:,2],'k')
plt.xlabel('time/s ')
plt.ylabel('m/s ')
plt.savefig("纵向速度.png")
plt.show()
结果如下:
-
换道轨迹

-
纵向速度

-
横向速度

代码仓库见github