代码演示:
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
conv1 = nn.Conv1d(1,100,2,2)
x = torch.randn(2, 1, 1500)
input = x
#.permute(0,2,1)
input = Variable(input)
out = conv1(input)
out.shape
torch.Size([2, 100, 750])
手动计算(1500-2)/2 +1 = 1448/2 +1 =750
如果是text数据,
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
conv1 = nn.Conv1d(1500,100,2,2)
x = torch.randn(2,5,1500) # 2个batch,5个单词,1500embedding vector
input = x.permute(0,2,1)
input = Variable(input)
out = conv1(input)
# CONV1D中的参数in_channels 数目要和input的shape[1]维度一致
# 即in_channels = 1500
# 如果是自己的流量数据,那么in_channels = 1,因为input = batch,1,1500
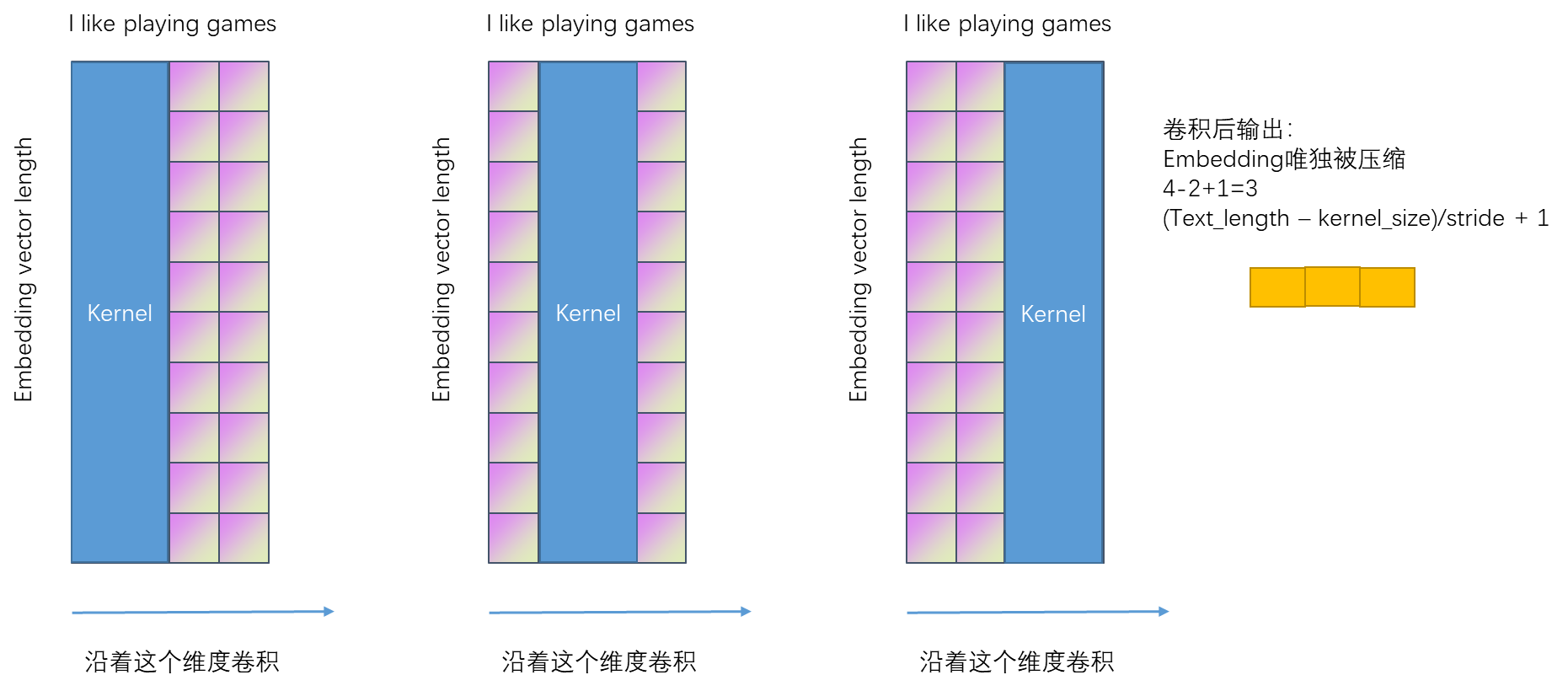
输出:batch,channels,2 = (5-2)/2 +1
torch.Size([2, 100, 2])
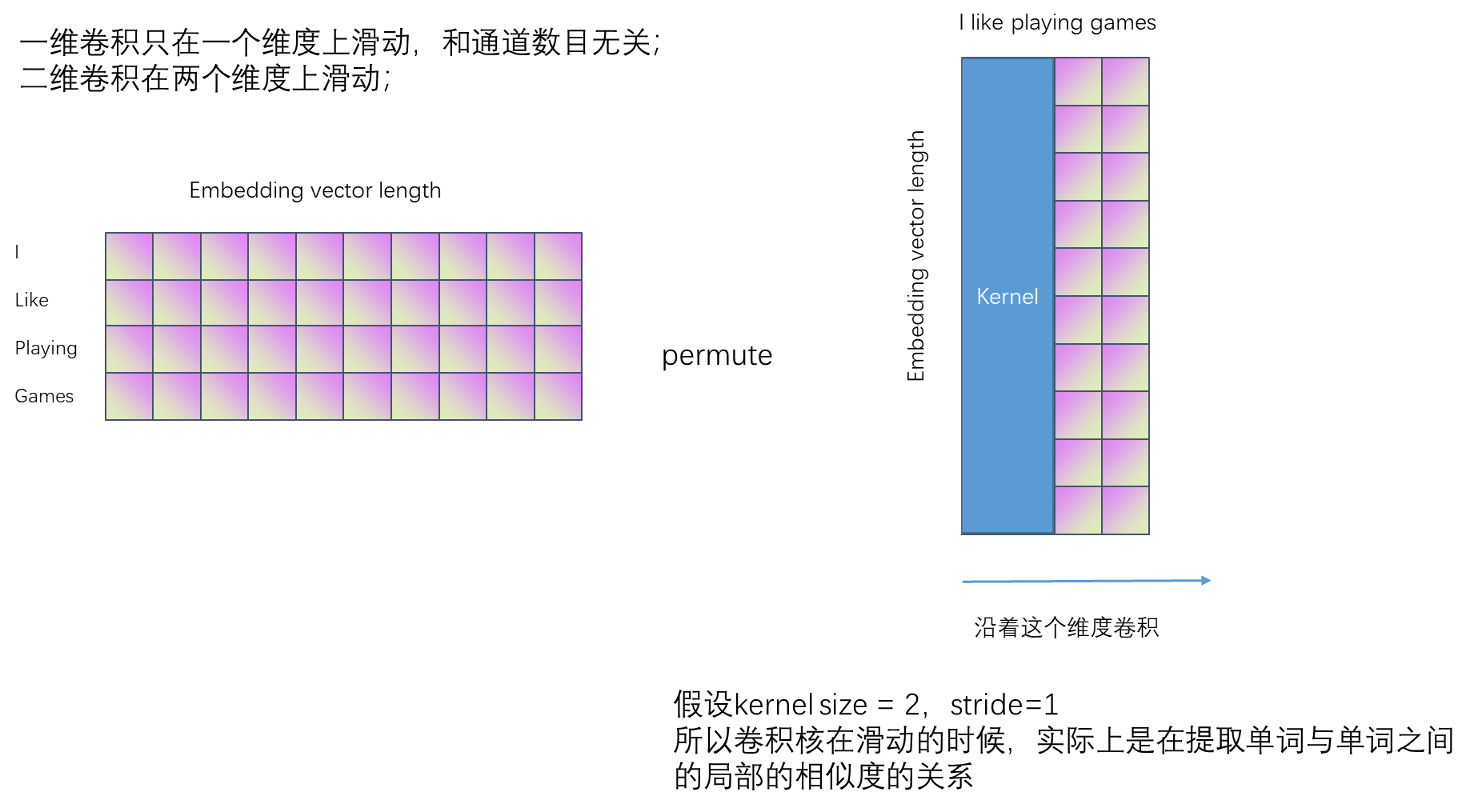
相当于降低了embeding的维度,2表示的是词语与词语之间的一个相似度的维度。
【总结】
nlp自然语言处理,数据与流量数据的类比;
batch,text_length,embeding_vector;这是原始的数据的存储的格式,输入到conv1d之前需要reshape下;
batch,embedding_vector,text_length;
输入到conv1d中的流量数据的格式:
batch, 1,1500;
所以,embedding_vector = 1,不需要再在另一个空间中对流量数据进行表示了;
text_length = 1500;
pytorch中conv1d在最后一个维度上进行卷积,也就是卷积核进行滑动,但是,在nlp中,滑动的过程是提取的一个句子中单词之间的相似度关系;
在流量数据中,滑动的过程提取的是1500个字节之间局部之间的相似度关系;