GAN简介(Generative Adversarial Nets)
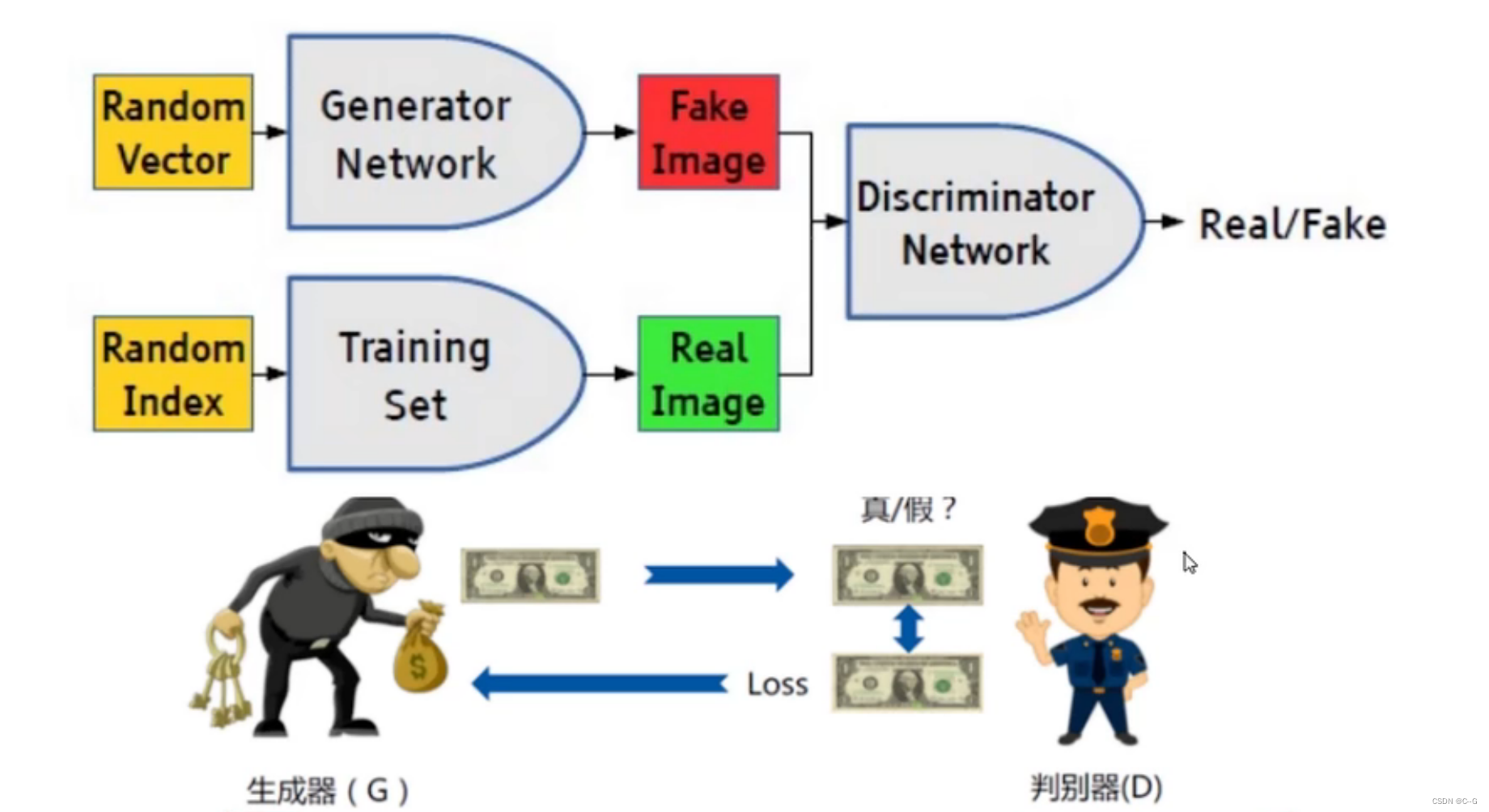
小偷(Generator Network)通过随机变量(Random Vector)生成假钱(Fake Image)存进银行(Discriminator Network),银行通过真钱(Real Image)、假钱(Fake Image)学习判断小偷的假钱,循环上述步骤。
小偷希望银行判断假钱为真钱,所以将假钱(标签值为真)交给银行判断,得到银行反馈的loss,以此进行更新迭代,优化造假技术
银行希望准确判断真假币,所以同时对小偷的假钱(标签值为假)、和训练的真钱(标签值为真)进行训练,以此进行更新迭代
损失函数
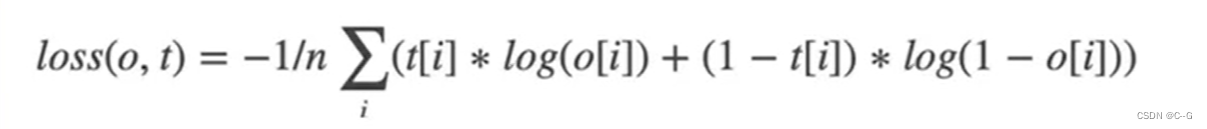
import torch
from torch import autograd
import torch.nn as nn
import math
input = autograd.Variable(torch.tensor([
[1.9072, 1.1079, 1.4906],
[-0.6548, -0.0512, 0.7608],
[-0.0614, 0.6583, 0.1095]
]))
print(input)
print('-' * 100)
m = nn.Sigmoid()
print(m(input))
print('-' * 100)
target = torch.FloatTensor([
[0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0]
])
print(target)
print('-' * 100)
r11 = 0 * math.log(0.8707) + (1 - 0) * math.log((1 - 0.8707))
r12 = 1 * math.log(0.7517) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.7517))
r13 = 1 * math.log(0.8162) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.8162))
r21 = 1 * math.log(0.3419) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.3419))
r22 = 1 * math.log(0.4872) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.4872))
r23 = 1 * math.log(0.6815) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.6815))
r31 = 0 * math.log(0.4847) + (1 - 0) * math.log((1 - 0.4847))
r32 = 0 * math.log(0.6589) + (1 - 0) * math.log((1 - 0.6589))
r33 = 0 * math.log(0.5273) + (1 - 0) * math.log((1 - 0.5273))
r1 = -(r11 + r12 + r13) / 3
r2 = -(r21 + r22 + r23) / 3
r3 = -(r31 + r32 + r33) / 3
bceloss = (r1 + r2 + r3) / 3
print(bceloss)
print('-' * 100)
# torch 需要Sigmoid
loss = nn.BCELoss()
print(loss(m(input), target))
print('-' * 100)
# torch 不需要Sigmoid
loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
print(loss(input, target))
print('-' * 100)

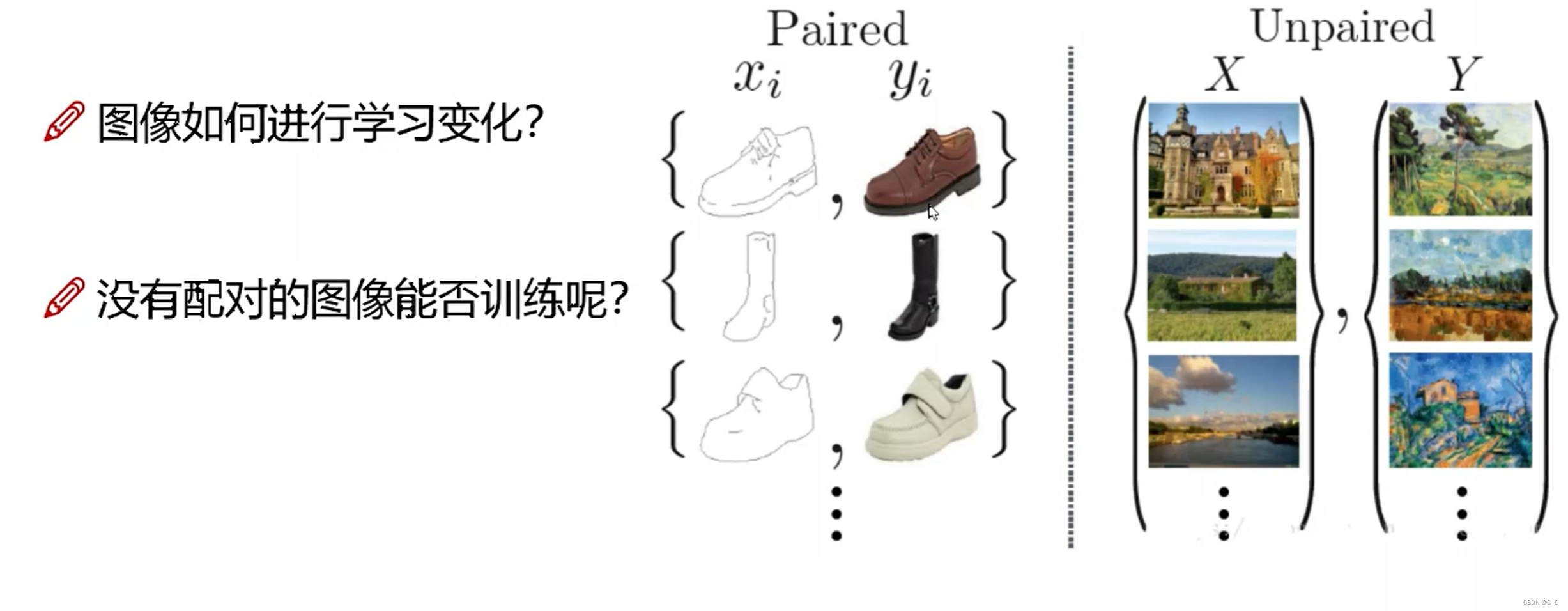
CycleGan
简介
- 实现效果
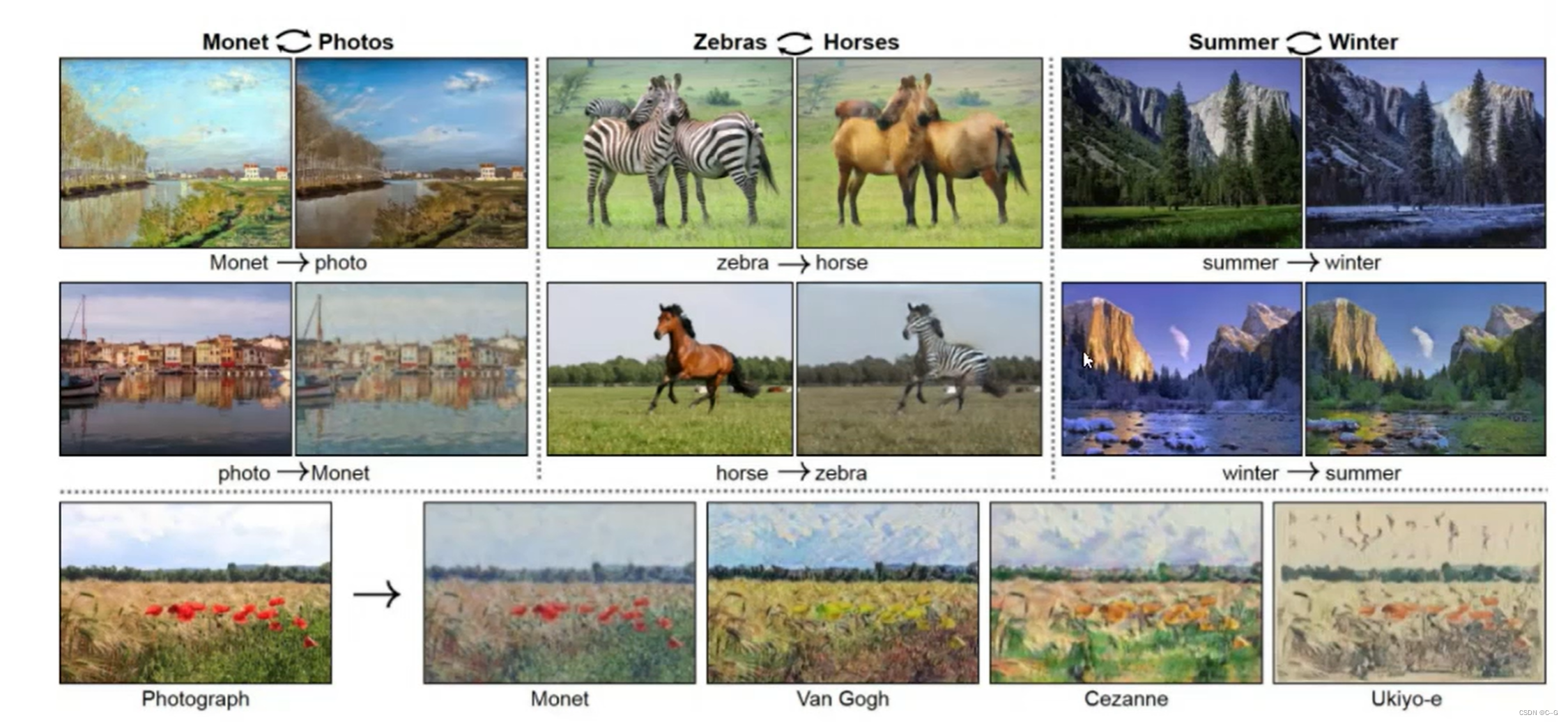

- 无须配对数据

-
如何学习
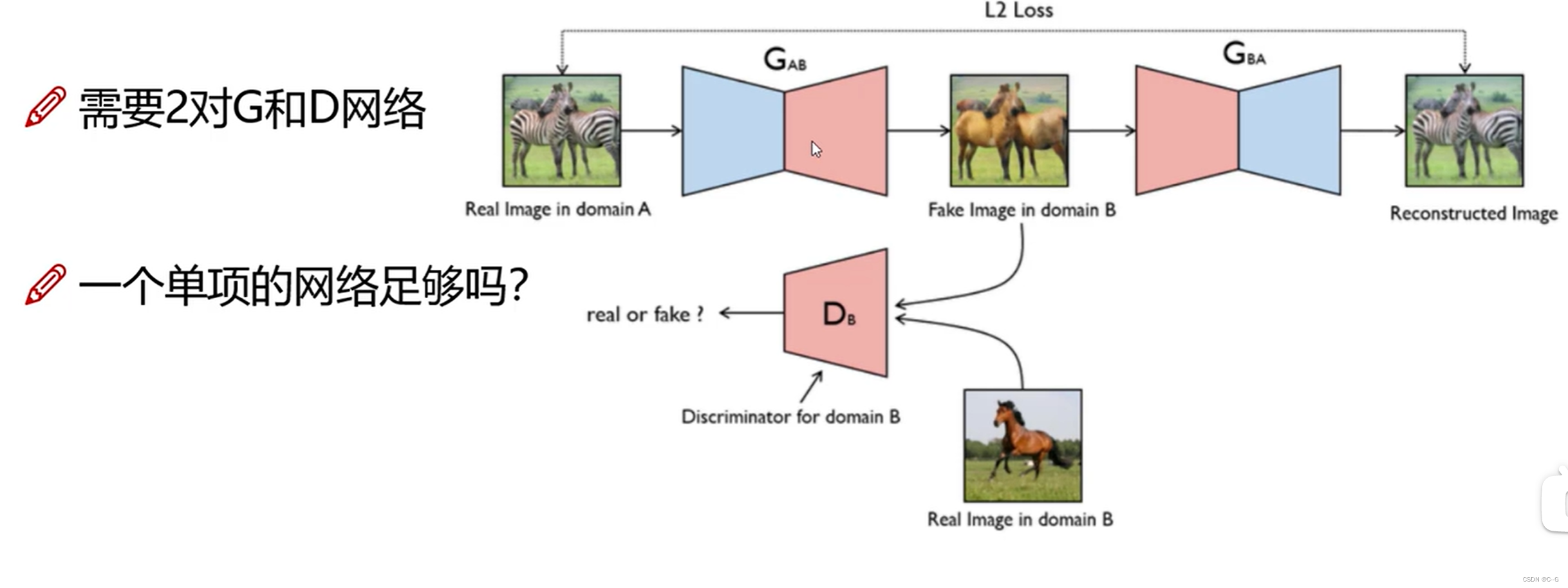
生成器Gab通过真斑马生成假马,假马通过Gba生成假斑马,假斑马与真斑马产生L2损失,迭代优化 -
整体网络架构
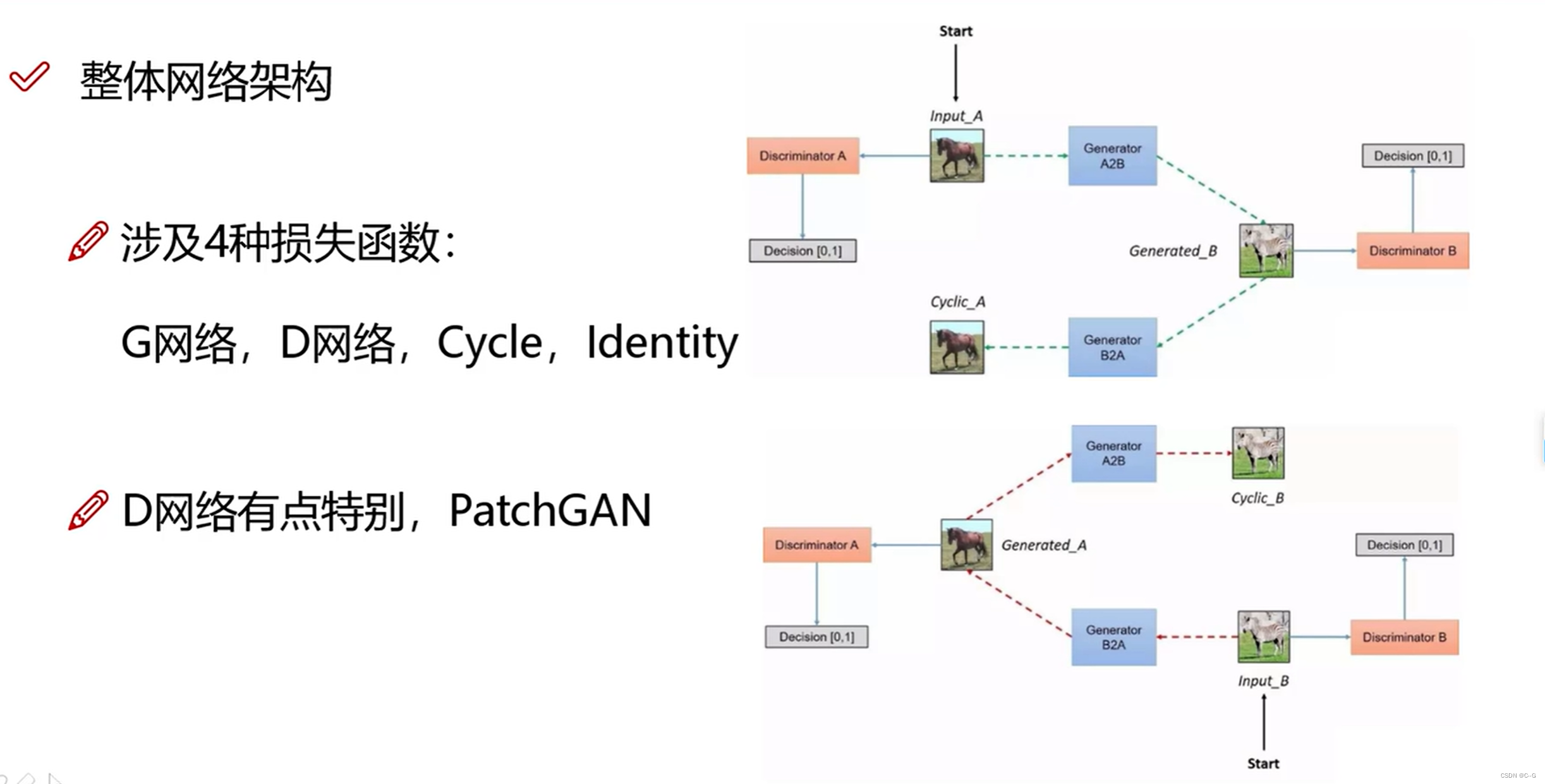
-
PatchGAN
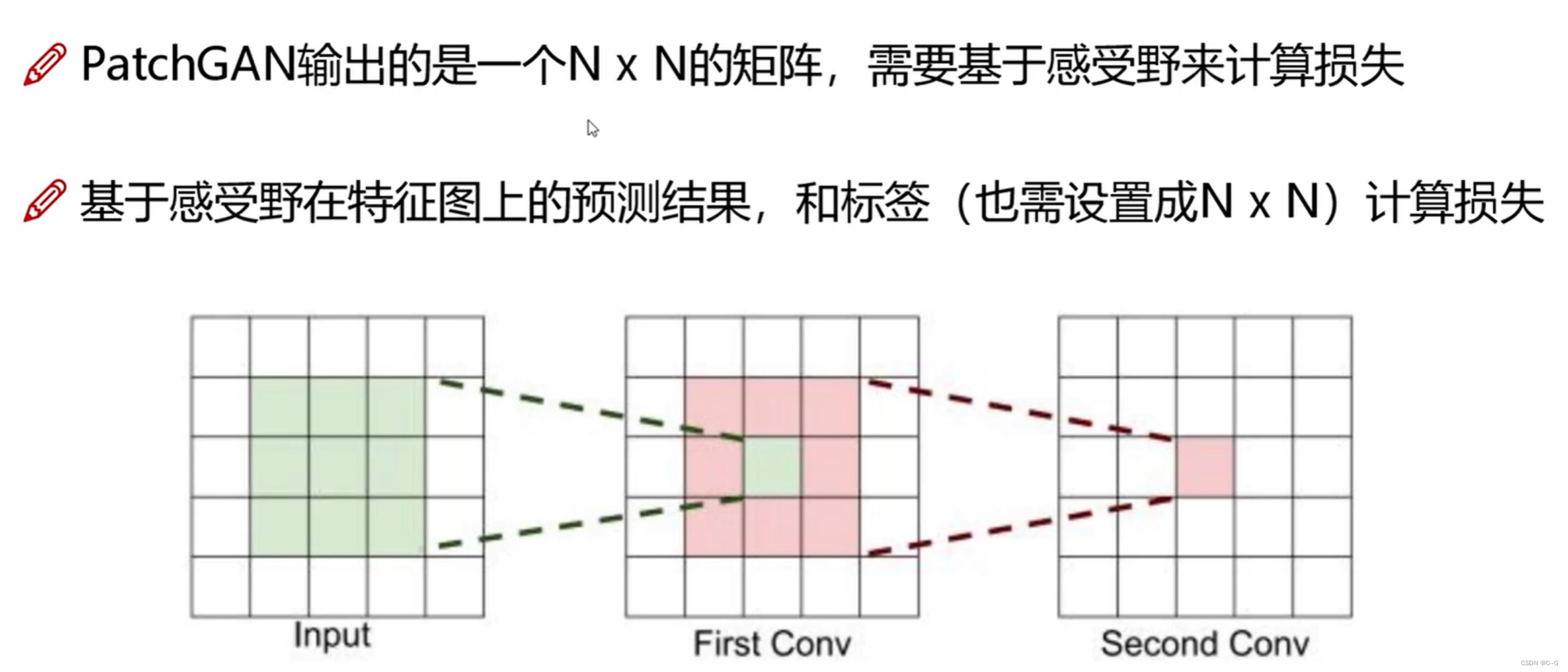
入门测试
- 源码地址
https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
- 数据下载
以文本形式打开文件
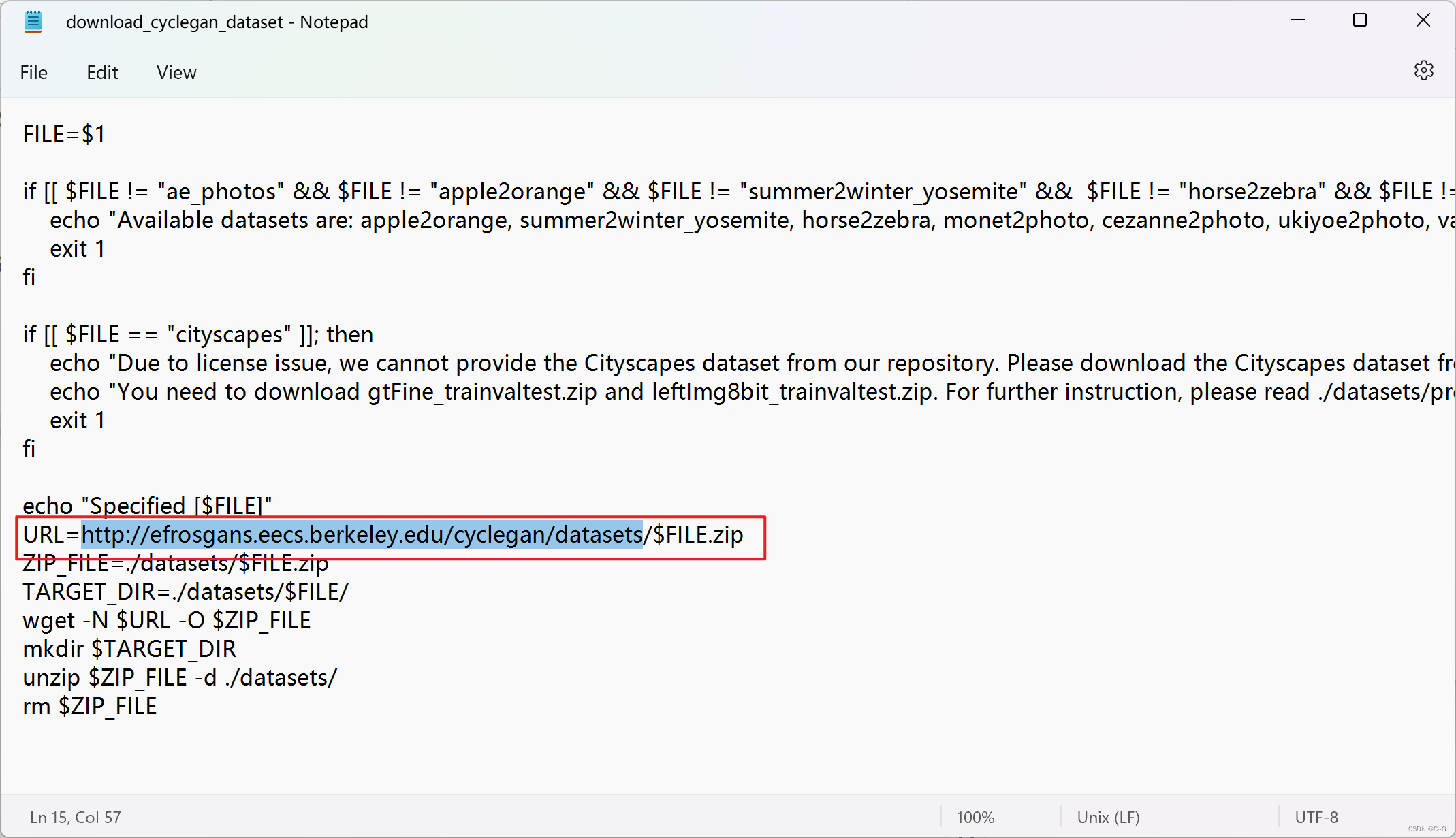
复制下载链接
- 训练好的参数权重
https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh#L3
http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/cyclegan/pretrained_models/
将下载好的horse2zebra.pth文件放到pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix-master\checkpoints\horse2zebra_pretrained下,并修改名称为latest_net_G.pth
- 启动测试
测试参数
--dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA
--name horse2zebra.pth_pretrained
--model test --no_dropout
# 使用cpu
--gpu_ids -1

在pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix-master\results\horse2zebra_pretrained\test_latest下保存结果
打开index.html

visdom
CycleGan训练时使用visdom作为可视化工具,训练前先启动visdom
pip install visdom
python -m visdom.server
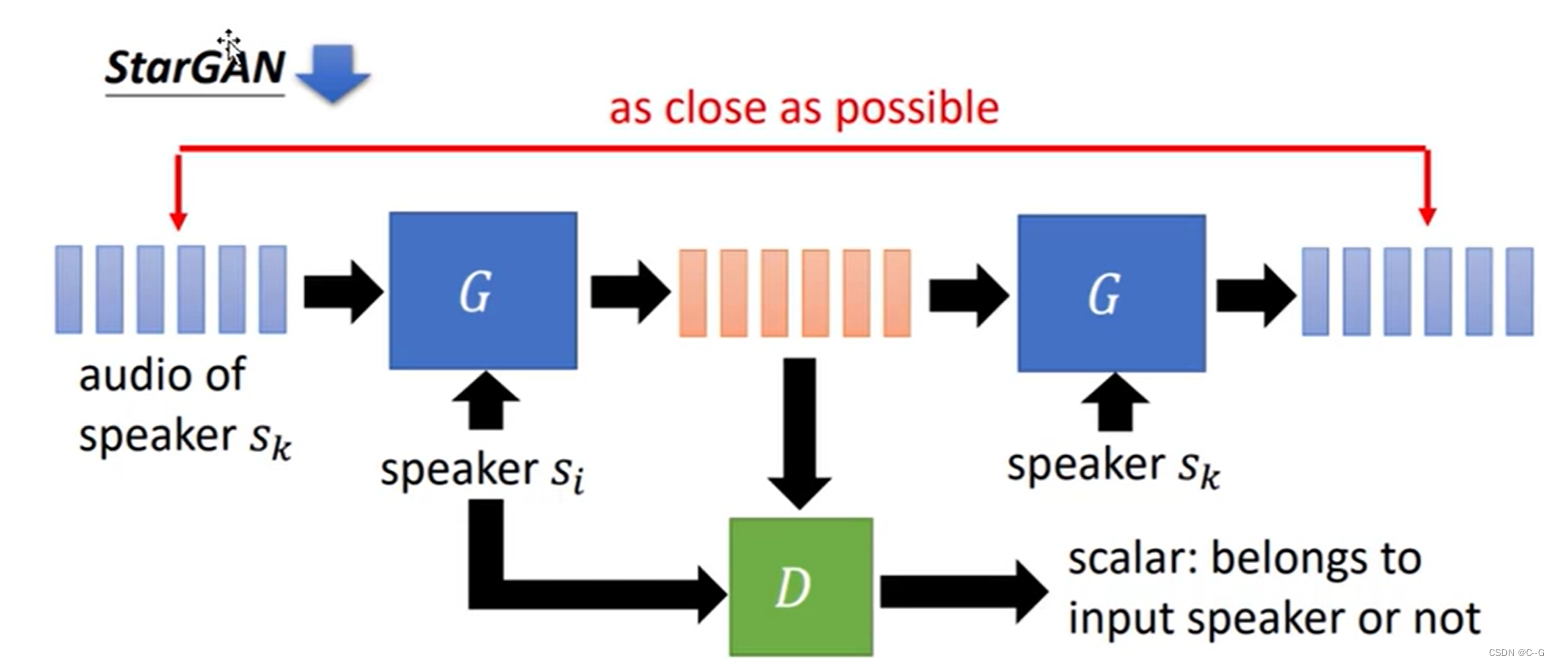
stargan

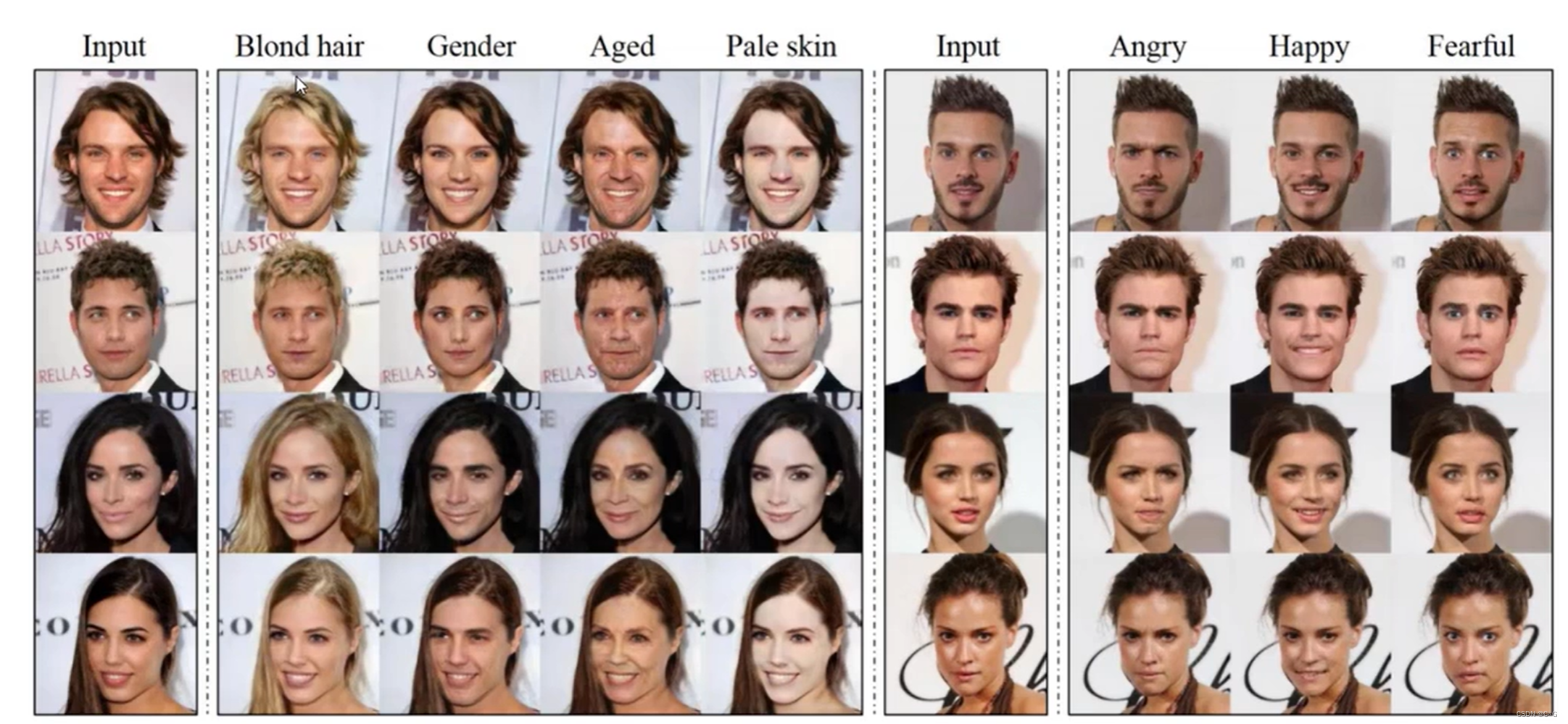
- 何为star
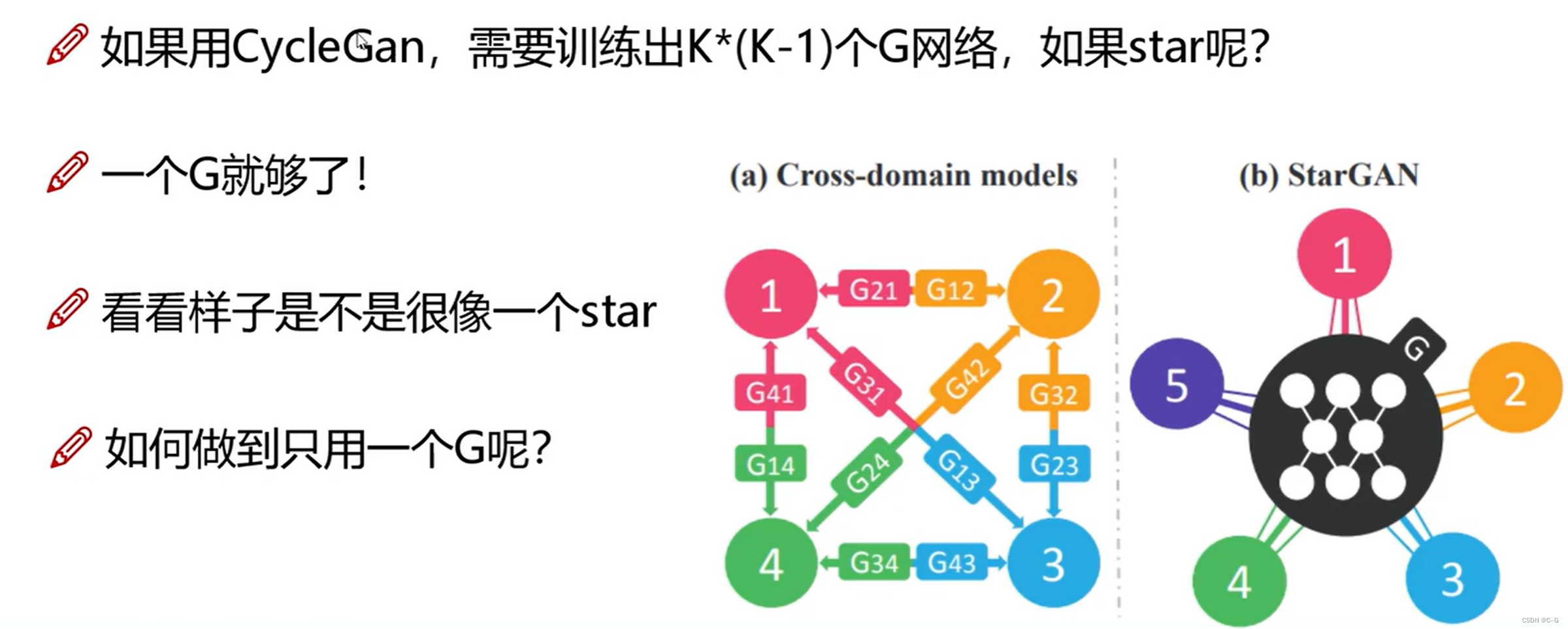
- 基本思路
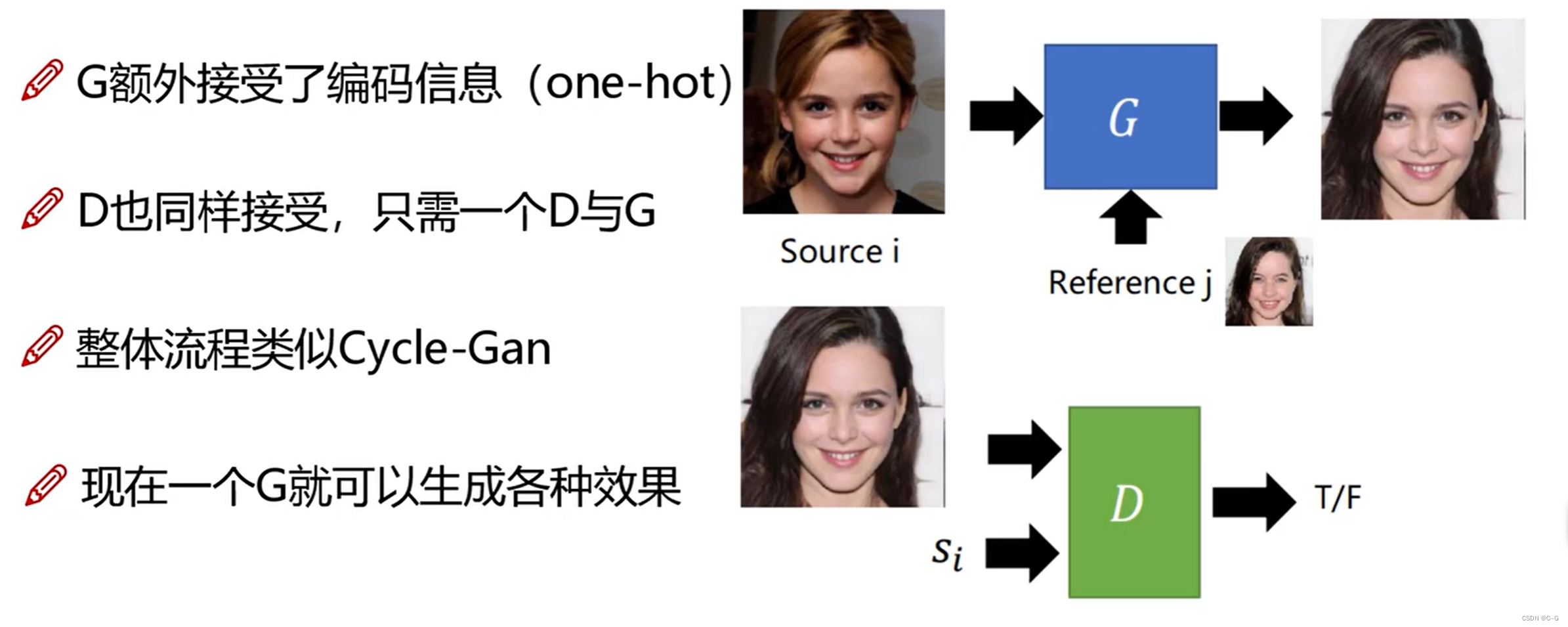
- 整体流程
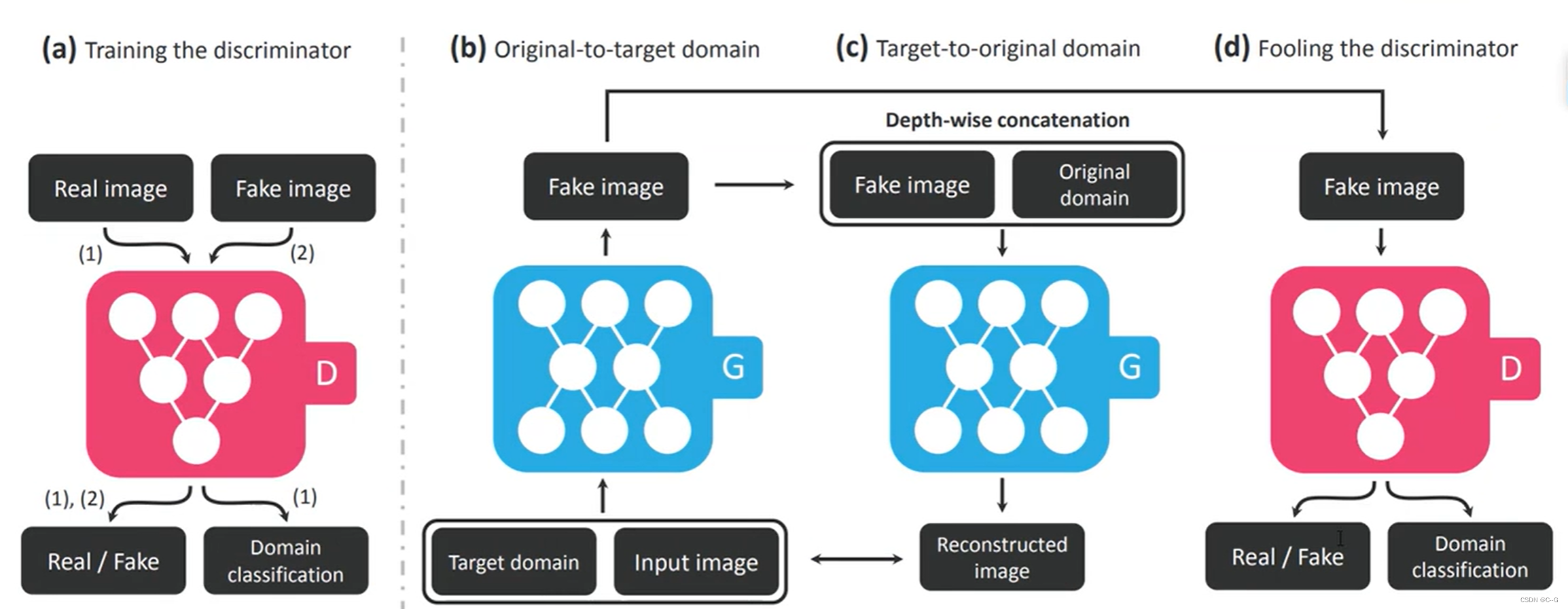

输入图片与编码特征,通过生成器得到假照片,再将假照片通过生成器得到真实照片,并与原图进行对比,缩小真实照片与原图的差距
stargan使用编码代替风格,特征性不强,没有参与计算
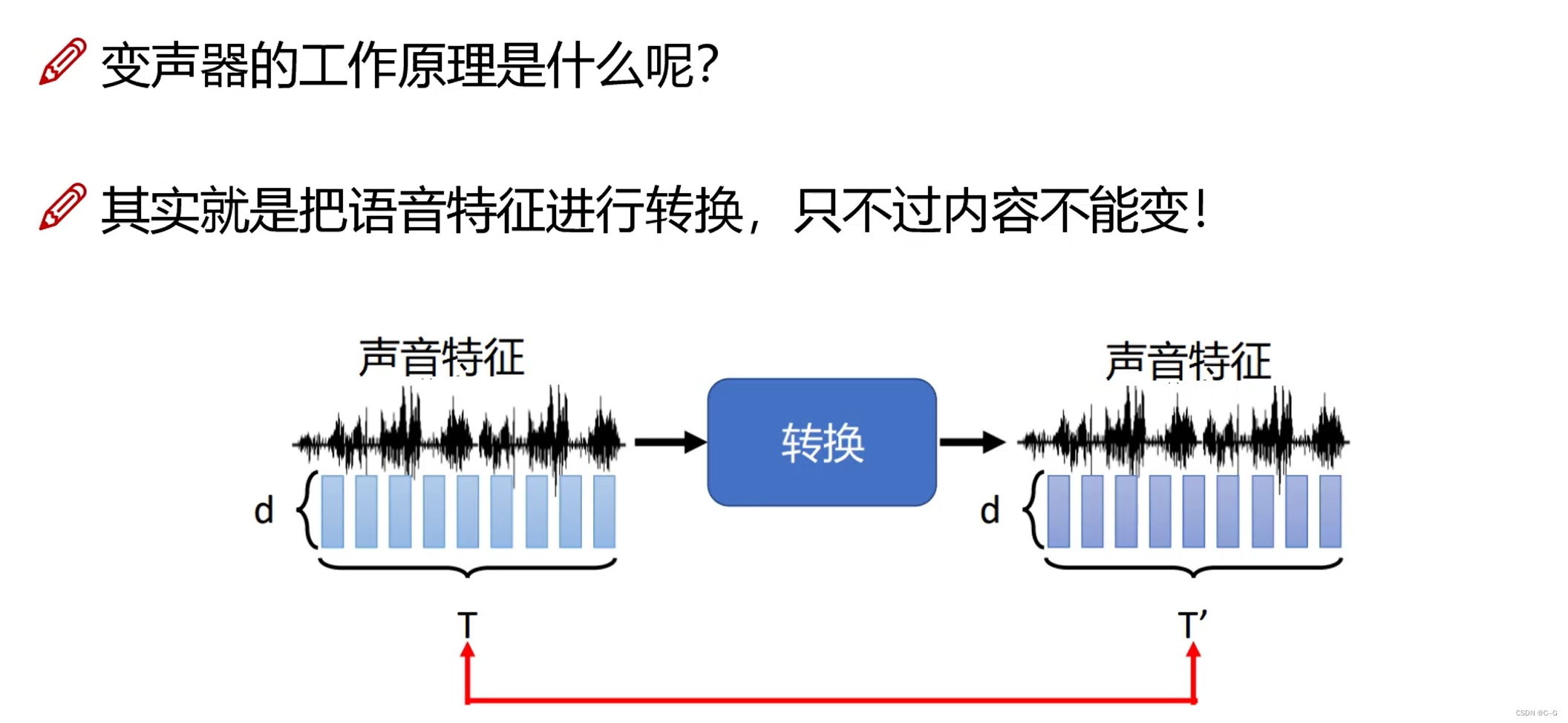
- 扩展:变声器
stargan-v2
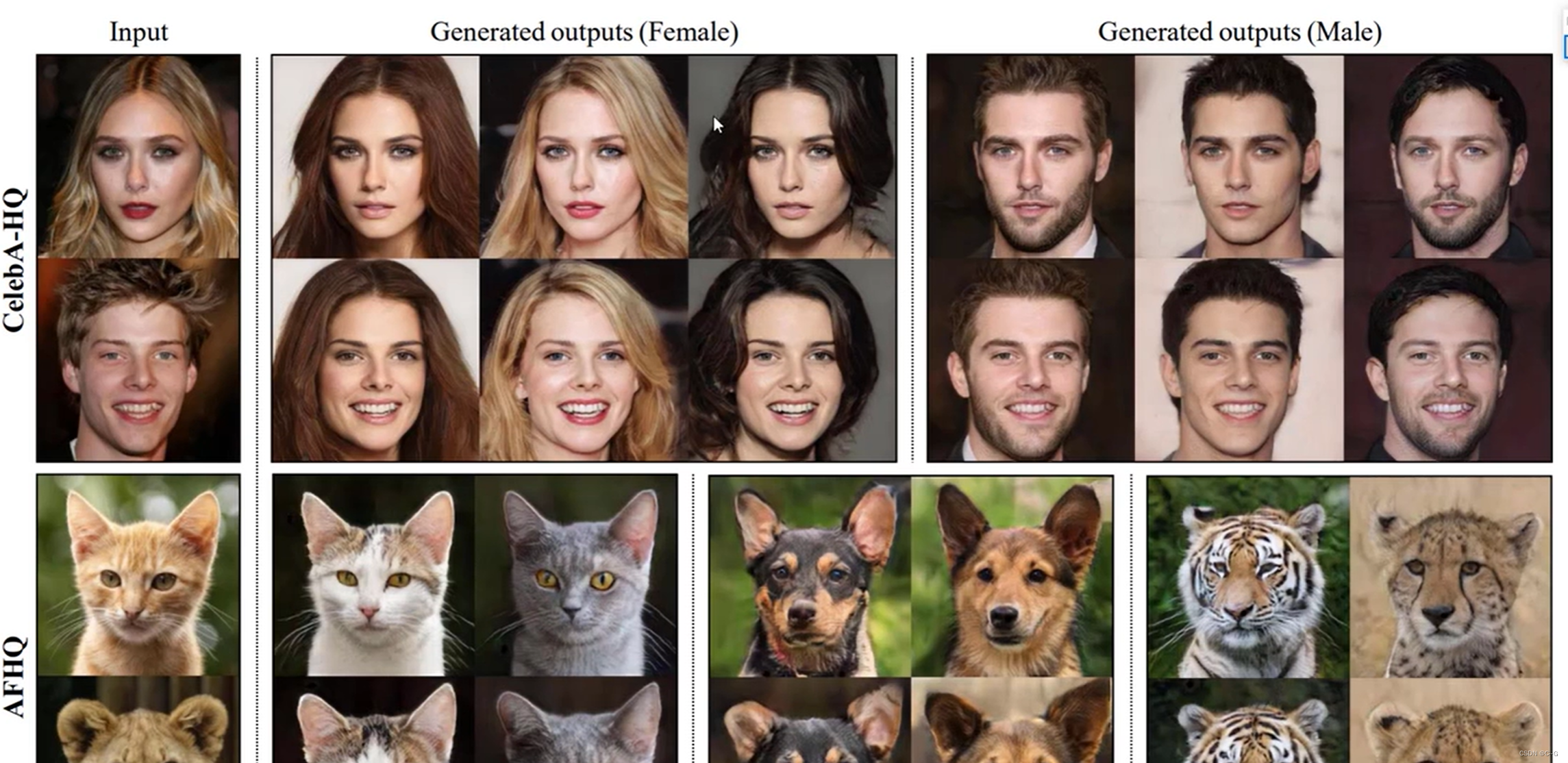


- 整体网络架构
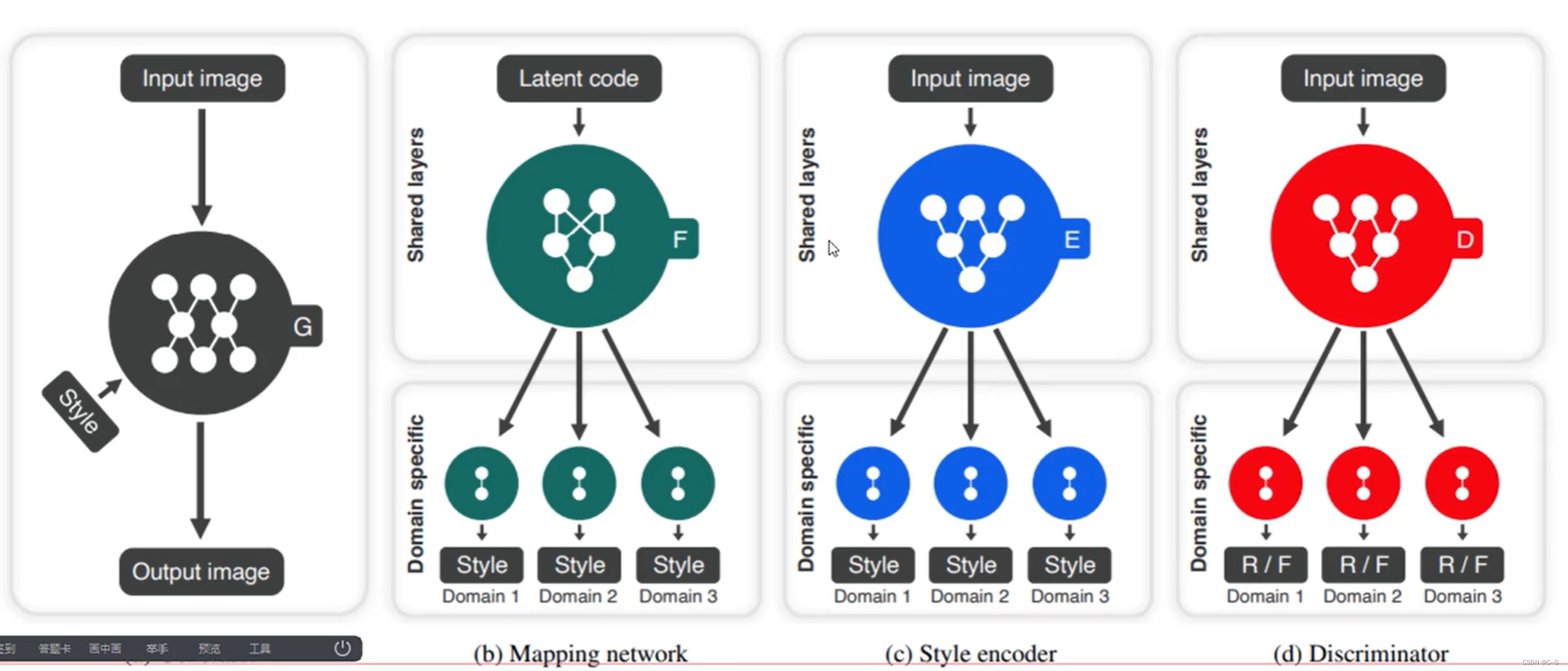
- 编码器训练(Style reconstruction)

- 多样化训练(Style diversification)

- cycle loss

代码分析
- 源码下载
https://github.com/clovaai/stargan-v2 - 导入必须的包
conda create -n stargan-v2 python=3.6.7
conda activate stargan-v2
conda install -y pytorch=1.4.0 torchvision=0.5.0 cudatoolkit=10.0 -c pytorch
conda install x264=='1!152.20180717' ffmpeg=4.0.2 -c conda-forge
pip install opencv-python==4.1.2.30 ffmpeg-python==0.2.0 scikit-image==0.16.2
pip install pillow==7.0.0 scipy==1.2.1 tqdm==4.43.0 munch==2.5.0
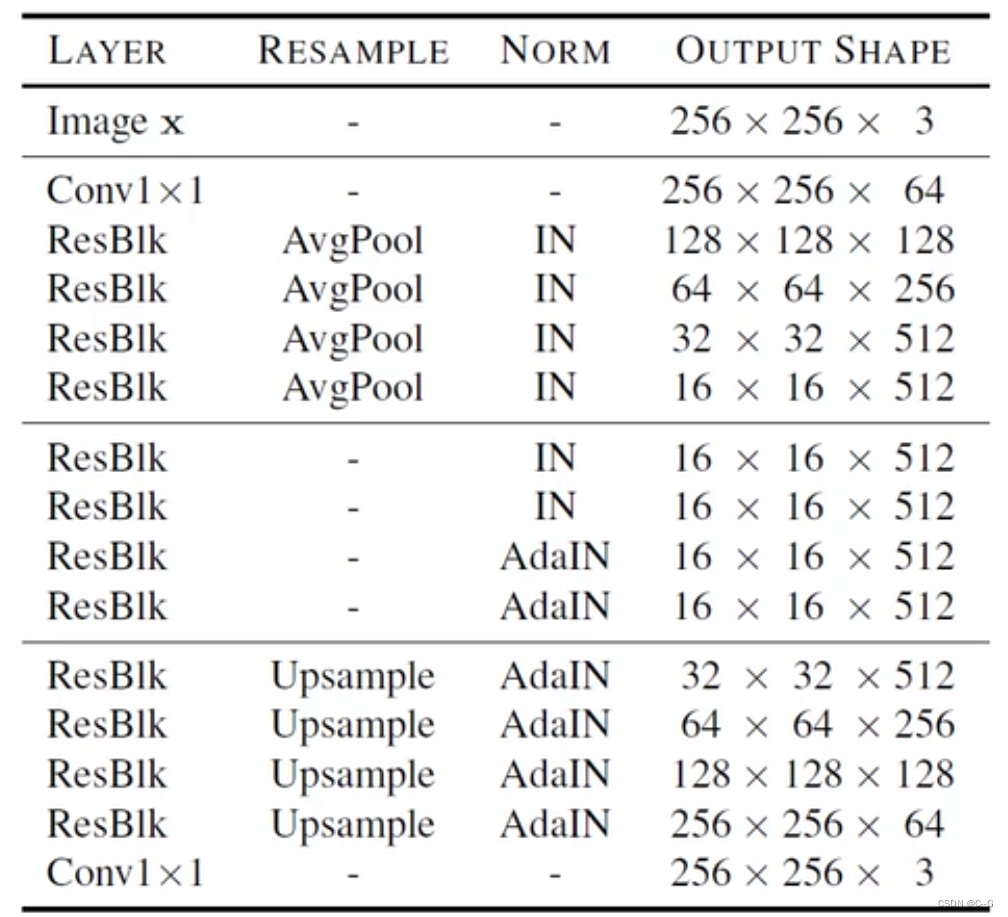
- 生成器
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=256, style_dim=64, max_conv_dim=512, w_hpf=1):
super().__init__()
dim_in = 2**14 // img_size
self.img_size = img_size
self.from_rgb = nn.Conv2d(3, dim_in, 3, 1, 1)
self.encode = nn.ModuleList()
self.decode = nn.ModuleList()
self.to_rgb = nn.Sequential(
nn.InstanceNorm2d(dim_in, affine=True),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Conv2d(dim_in, 3, 1, 1, 0))
# down/up-sampling blocks
repeat_num = int(np.log2(img_size)) - 4
if w_hpf > 0:
repeat_num += 1
for _ in range(repeat_num):
dim_out = min(dim_in*2, max_conv_dim)
self.encode.append(
ResBlk(dim_in, dim_out, normalize=True, downsample=True))
self.decode.insert(
0, AdainResBlk(dim_out, dim_in, style_dim,
w_hpf=w_hpf, upsample=True)) # stack-like
dim_in = dim_out
# bottleneck blocks
for _ in range(2):
self.encode.append(
ResBlk(dim_out, dim_out, normalize=True))
self.decode.insert(
0, AdainResBlk(dim_out, dim_out, style_dim, w_hpf=w_hpf))
if w_hpf > 0:
device = torch.device(
'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
self.hpf = HighPass(w_hpf, device)
def forward(self, x, s, masks=None):
x = self.from_rgb(x)
cache = {}
for block in self.encode:
if (masks is not None) and (x.size(2) in [32, 64, 128]):
cache[x.size(2)] = x
x = block(x)
for block in self.decode:
x = block(x, s)
if (masks is not None) and (x.size(2) in [32, 64, 128]):
mask = masks[0] if x.size(2) in [32] else masks[1]
mask = F.interpolate(mask, size=x.size(2), mode='bilinear')
x = x + self.hpf(mask * cache[x.size(2)])
return self.to_rgb(x)
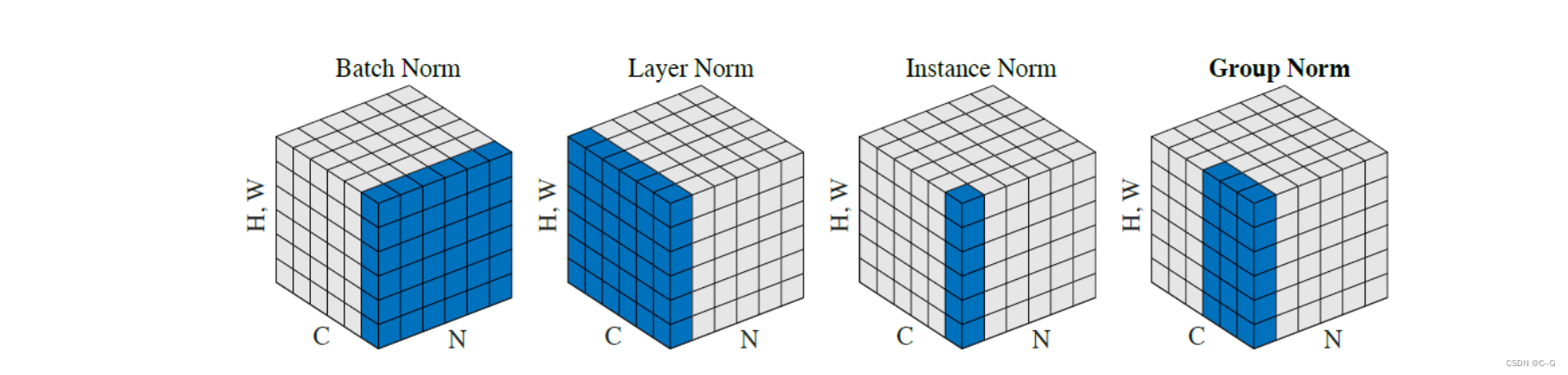
归一化层,目前主要有这几个方法,Batch Normalization(2015年)、Layer Normalization(2016年)、Instance Normalization(2017年)、Group Normalization(2018年)、Switchable Normalization(2018年);
将输入的图像shape记为[N, C, H, W],这几个方法主要的区别就是在,
- batchNorm是在batch上,对NHW做归一化,对小batchsize效果不好;
- layerNorm在通道方向上,对CHW归一化,主要对RNN作用明显;
- instanceNorm在图像像素上,对HW做归一化,用在风格化迁移;
- GroupNorm将channel分组,然后再做归一化;
- SwitchableNorm是将BN、LN、IN结合,赋予权重,让网络自己去学习归一化层应该使用什么方法。
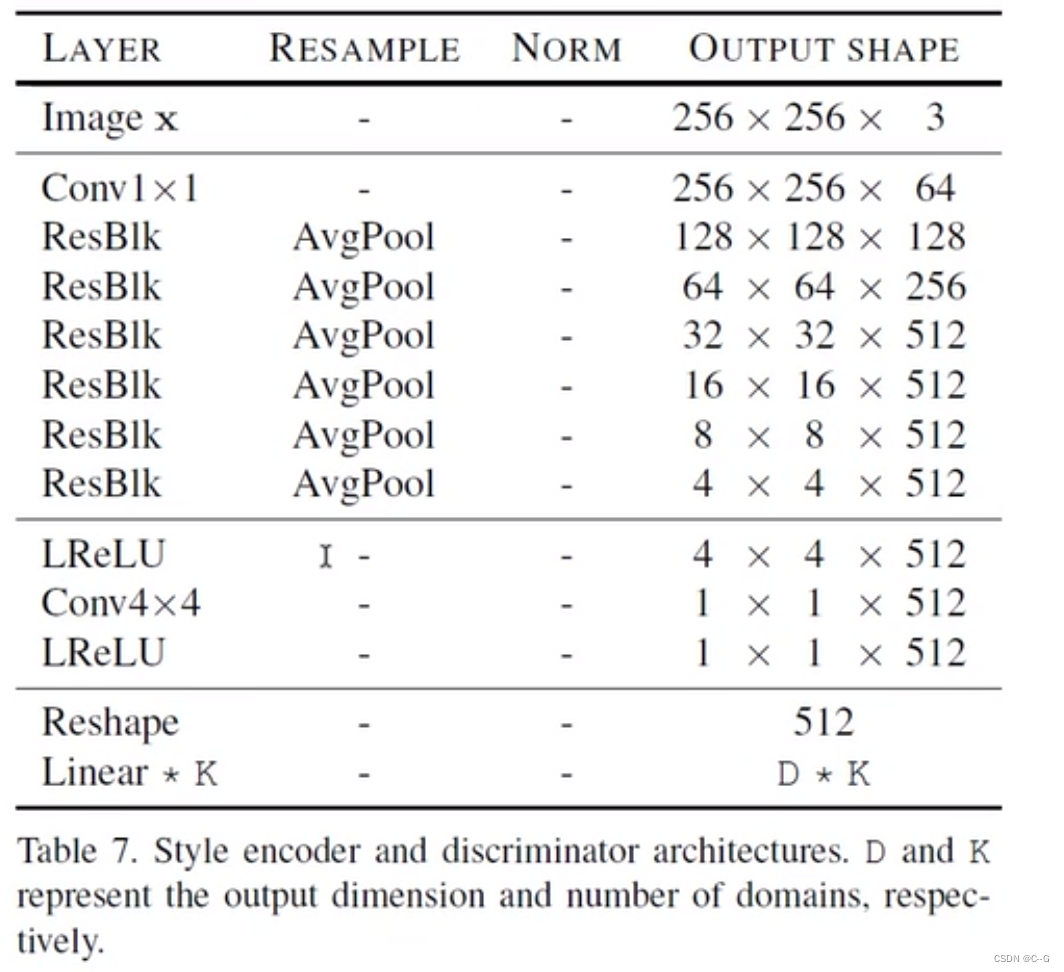
- 风格特征编码
class MappingNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, latent_dim=16, style_dim=64, num_domains=2):
super().__init__()
layers = []
layers += [nn.Linear(latent_dim, 512)]
layers += [nn.ReLU()]
for _ in range(3):
layers += [nn.Linear(512, 512)]
layers += [nn.ReLU()]
self.shared = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.unshared = nn.ModuleList()
for _ in range(num_domains):
self.unshared += [nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, style_dim))]
def forward(self, z, y):
h = self.shared(z)
out = []
for layer in self.unshared:
out += [layer(h)]
out = torch.stack(out, dim=1) # (batch, num_domains, style_dim)
idx = torch.LongTensor(range(y.size(0))).to(y.device)
s = out[idx, y] # (batch, style_dim)
return s

- 判别器
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=256, num_domains=2, max_conv_dim=512):
super().__init__()
dim_in = 2**14 // img_size
blocks = []
blocks += [nn.Conv2d(3, dim_in, 3, 1, 1)]
repeat_num = int(np.log2(img_size)) - 2
for _ in range(repeat_num):
dim_out = min(dim_in*2, max_conv_dim)
blocks += [ResBlk(dim_in, dim_out, downsample=True)]
dim_in = dim_out
blocks += [nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)]
blocks += [nn.Conv2d(dim_out, dim_out, 4, 1, 0)]
blocks += [nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)]
blocks += [nn.Conv2d(dim_out, num_domains, 1, 1, 0)]
self.main = nn.Sequential(*blocks)
def forward(self, x, y):
out = self.main(x)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) # (batch, num_domains)
idx = torch.LongTensor(range(y.size(0))).to(y.device)
out = out[idx, y] # (batch)
return out
stargan-vc2
http://www.kecl.ntt.co.jp/people/kaneko.takuhiro/projects/stargan-vc2/index.html
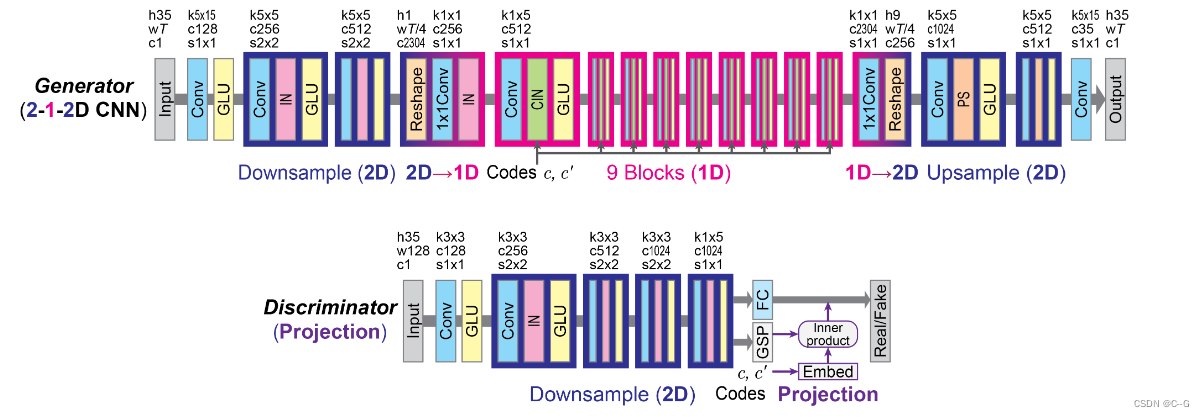
- 变声器

-
输入数据

-
预处理

-
特征汇总

-
MFCC

-
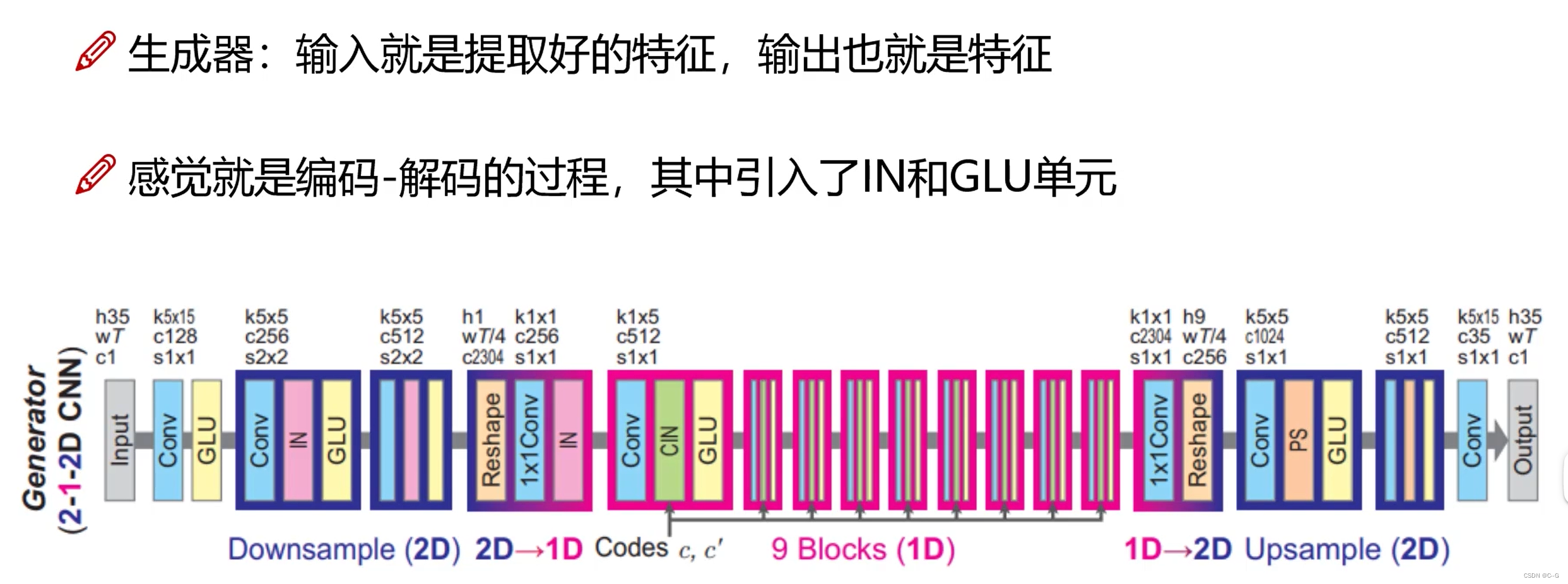
生成器
-
语言数据包含的成分
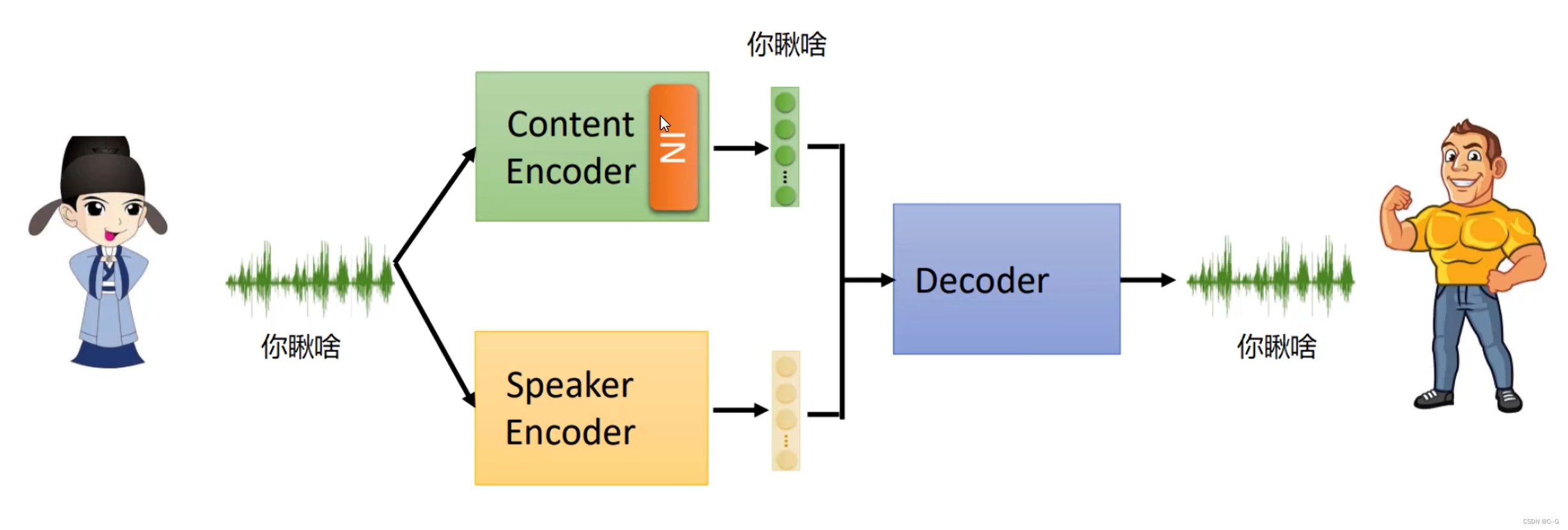
-
Instance Normalization 和 Adaptive Instance Normalization

-
Instance Normalization
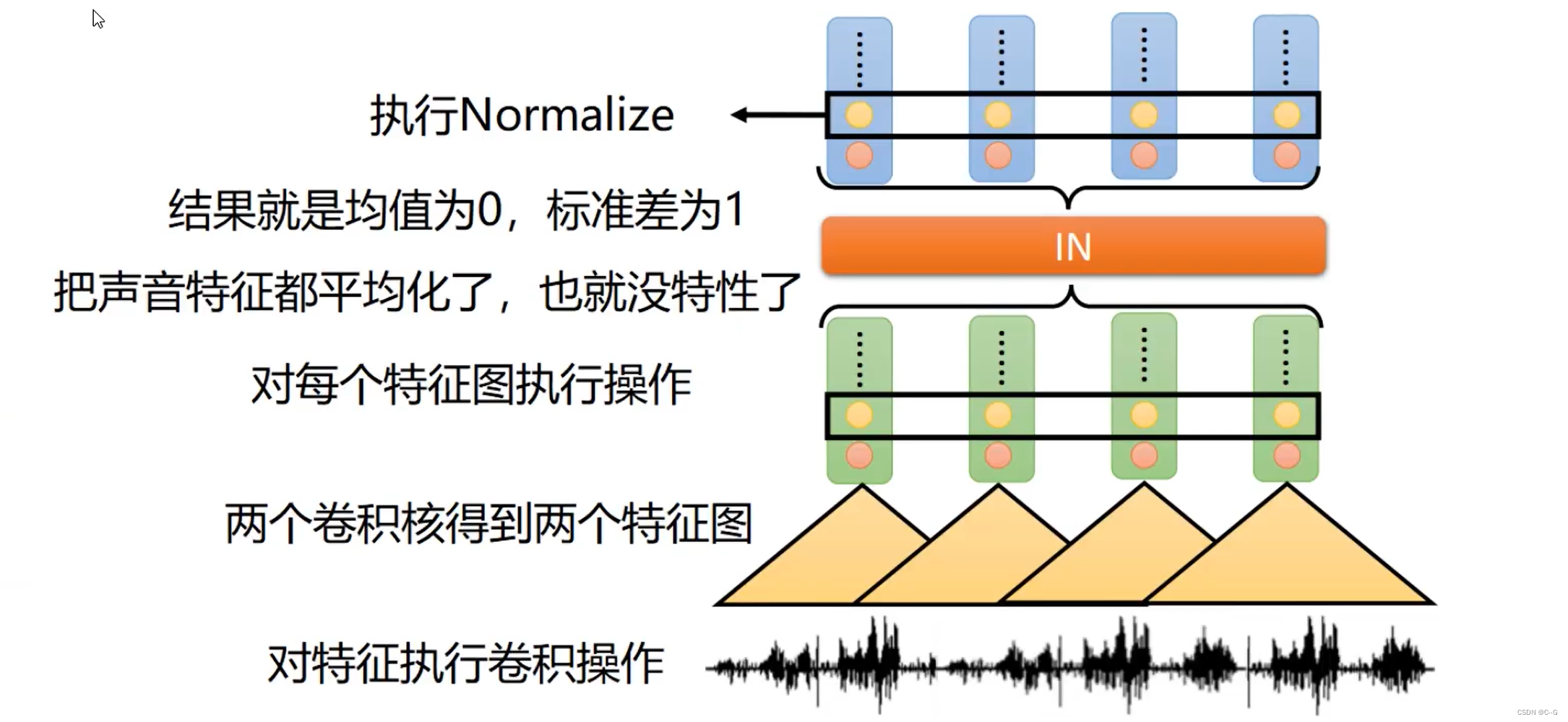
内容编码器只需要内容,不需要语言特征,所以使用Instance Normalization对每个特征图进行归一化,将声音特征平均化,去掉语言特性 -
AdaIn
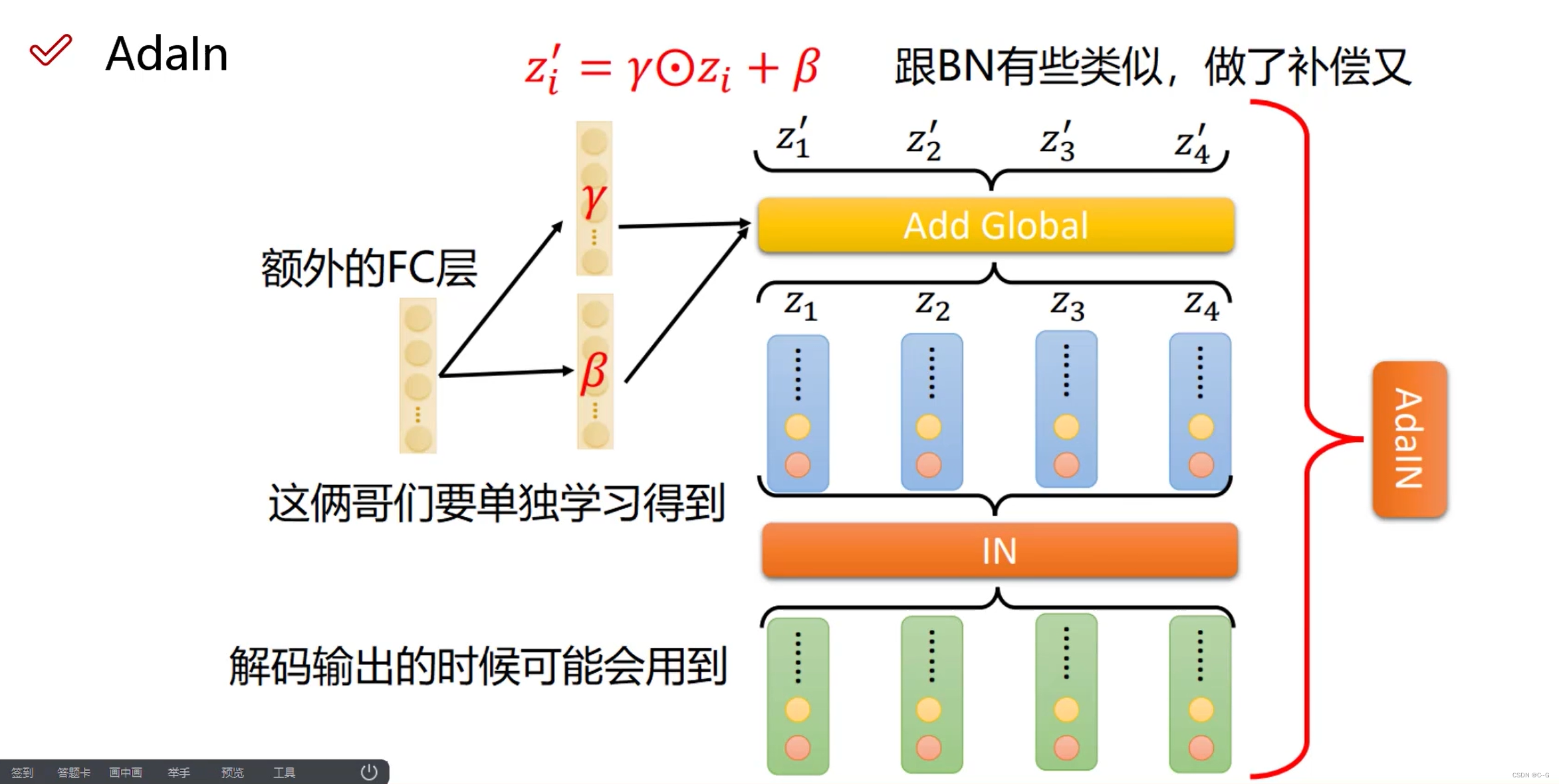
In归一化去掉了语言特征,AdaIn则是通过额外的FC层赋予语言特征 -
PixelShuffle
上采样与下采样:都是老路子,stride=2来下采样,反卷积来上采样
**PixelShuffle层又名亚像素卷积层,是论文Real-Time Single Image and Video Super-Resolution Using an Efficient Sub-Pixel Convolutional Neural Network中介绍的一种应用于超分辨率重建应用的具有上采样功能的卷积层。这篇ESPCN论文介绍了这种层的功能,sub-pixel convolution layer以stride = 1 r stride=\frac{1}{r}stride= r1 (r rr为SR的放大倍数upscaling factor)去提取feature map,虽然称之为卷积,但是其并没用用到任何需要学习的参数,它的原理也很简单,就是将输入feature map进行像素重组,也就是说亚像素卷积层虽用卷积之名,但却没有做任何乘加计算,只是用了另一种方式去提取特征罢了:
**
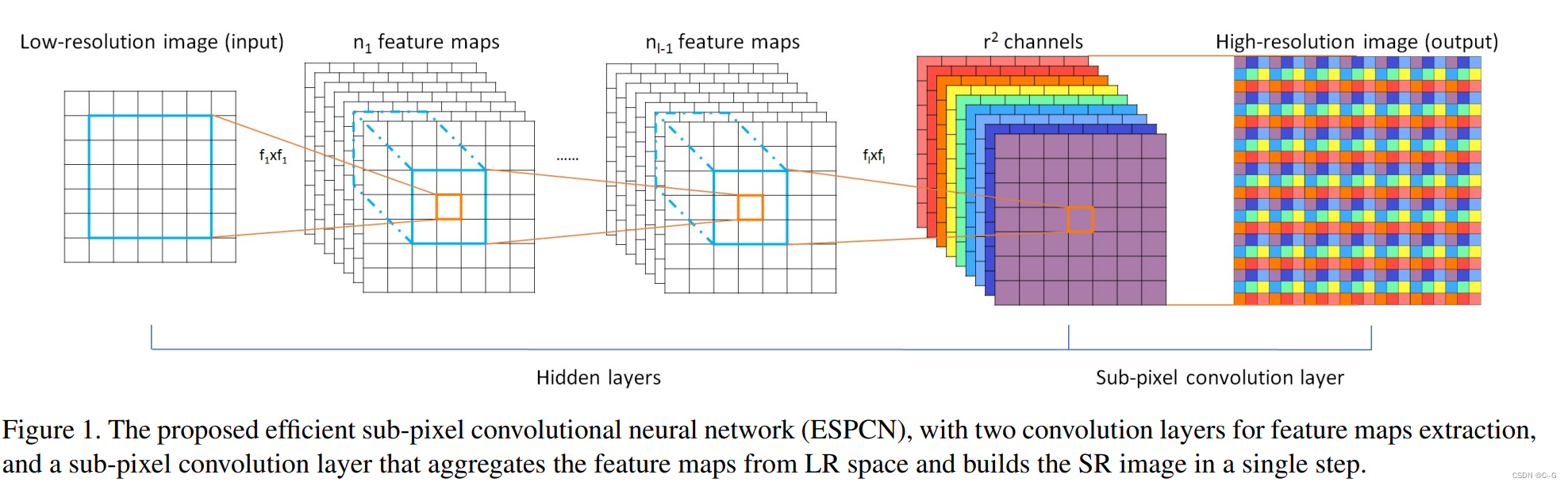
如上图所示的最后一层就是亚像素卷积层,它就是将输入格式为( b a t c h , r 2 C , H , W ) (batch,r^2C, H, W)(batch,r 2C,H,W)的feature map中同一通道的像素提取出来作为输出feature map的一小块,遍历整个输入feature map就可以得到最后的输出图像。整体来看,就好像是用1r\frac{1}{r}r1的步长去做卷积一样,这样就造成了不是对整像素点做卷积,而是对亚像素做卷积,故称之为亚像素卷积层,最后的输出格式就是( b a t c h , 1 , r H , r W ) (batch,1, rH,rW)(batch,1,rH,rW)。
因此,简单一句话,PixelShuffle层做的事情就是将输入feature map像素重组输出高分辨率的feature map,是一种上采样方法,具体表达为
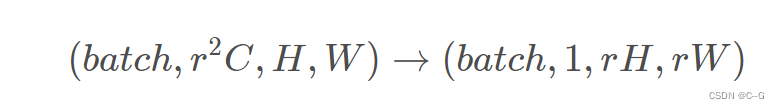
其中r为上采样倍率(上图中r = 3)
- 判别器
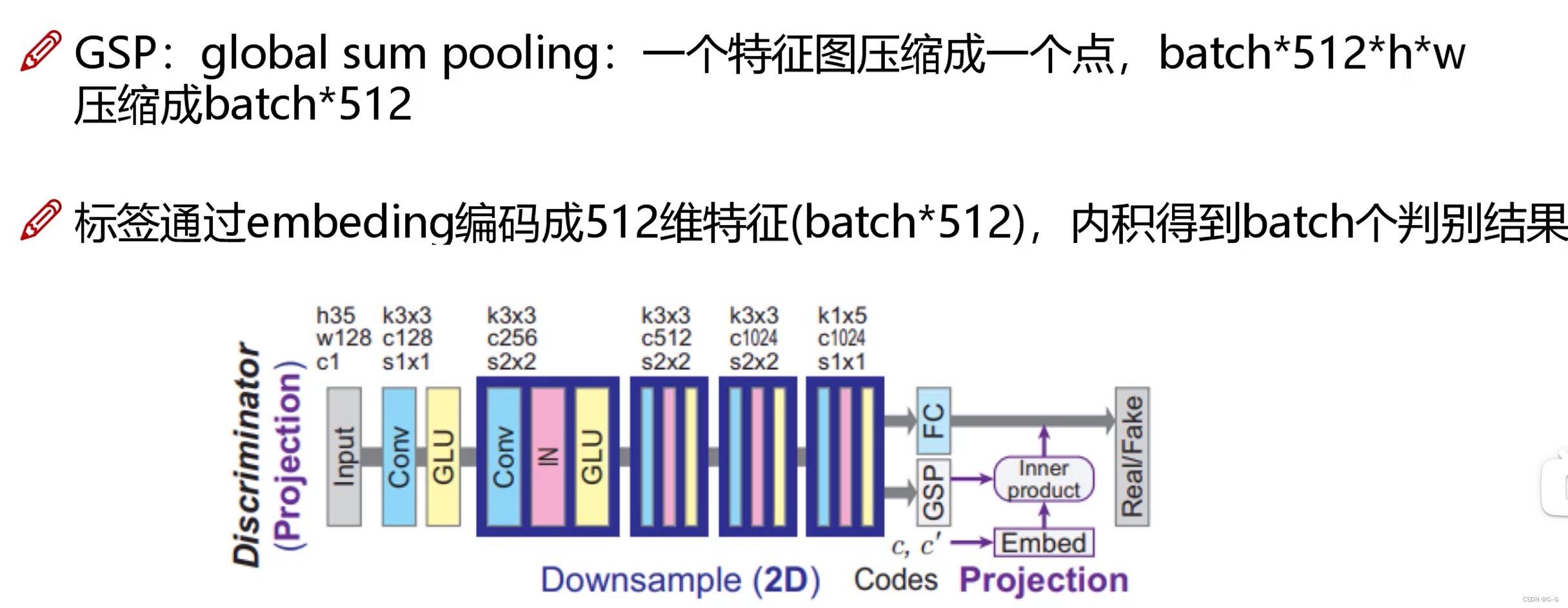
图像超分辨率重构(SPGAN)
- 网络架构
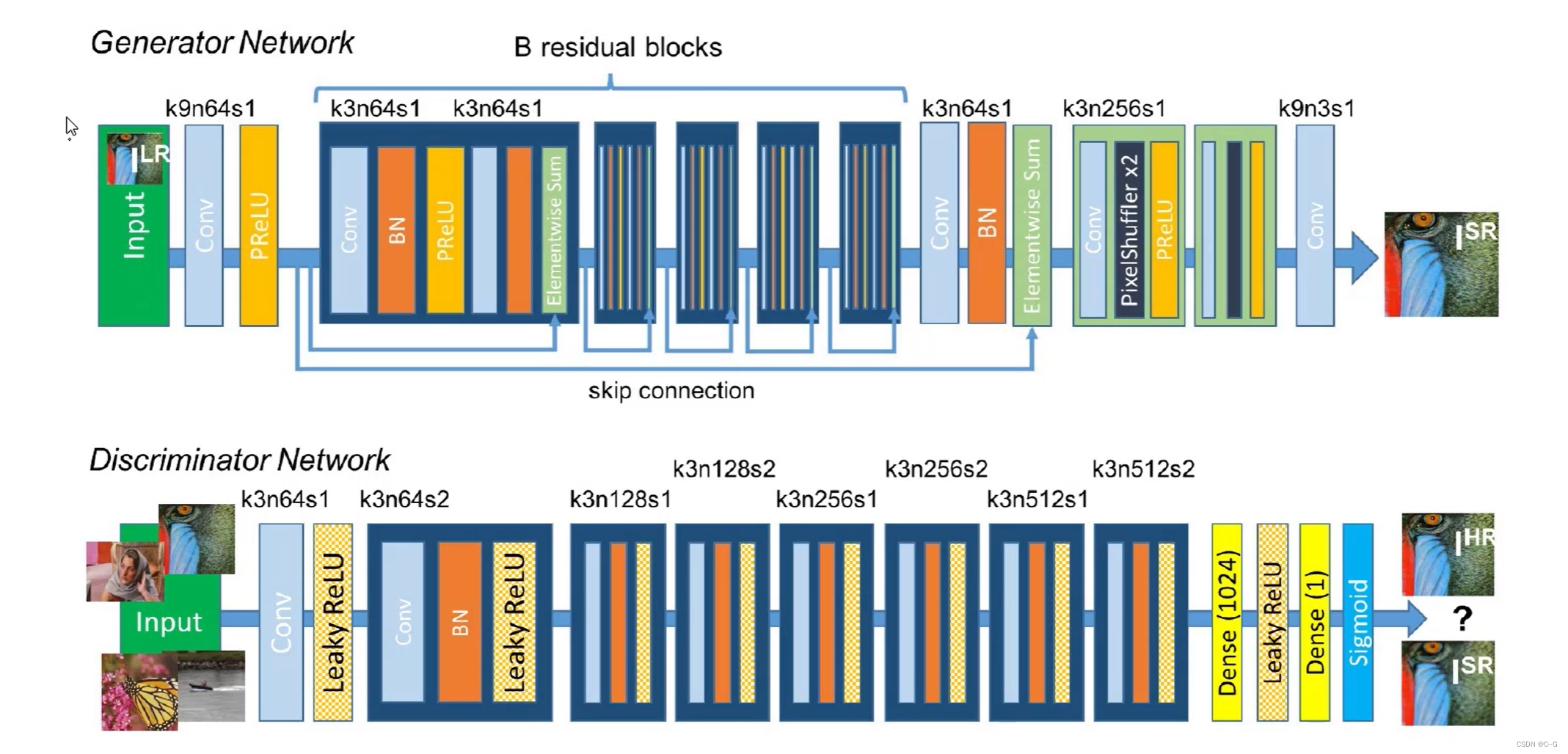
- 基本思路
基本的GAN网络思想,其中生成器使用了PixelShuffle实现超分辨率重建,同时为了提升细节效果,引入vgg19,将生成器生成的假图和真图放入vgg19模型提取特征,并提取最后一层特征图进行损失计算,将该损失加入到生成器损失
- 工具
图像补全
论文:Globally and Locally Consistent Image Completion
-
网络架构
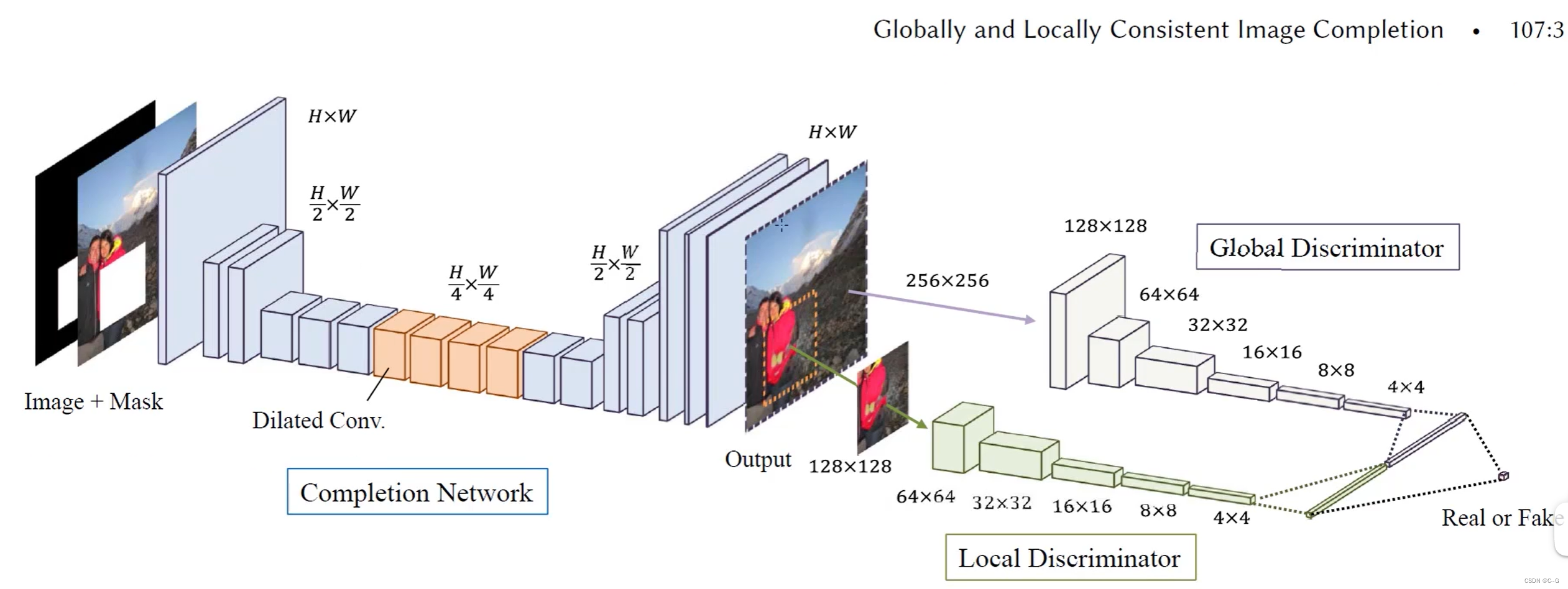
-
全卷积网络,不限制输入图片大小
-
Dilated Conv 空洞卷积 增大感受野 替代pooling
-
Local Discriminator 局部判别网络 收集局部信息
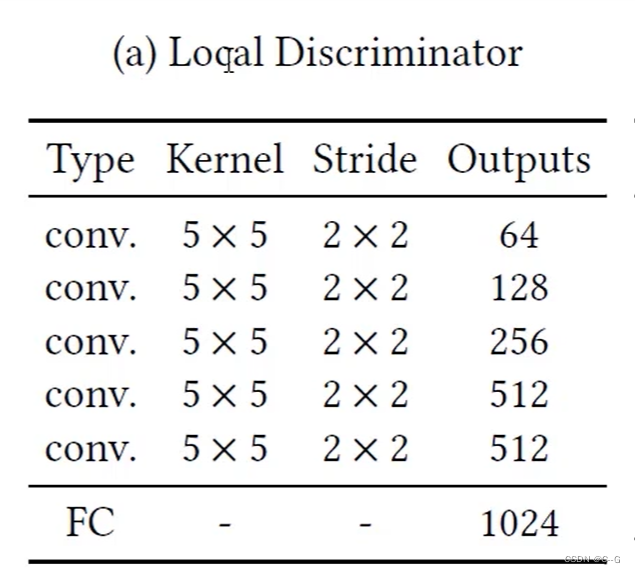
-
Global Discriminator 全局判别网络 收集全局信息
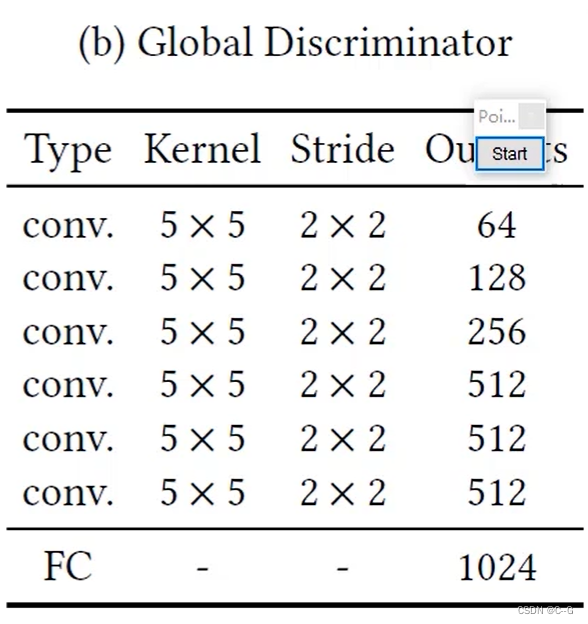
-
图像生成网络
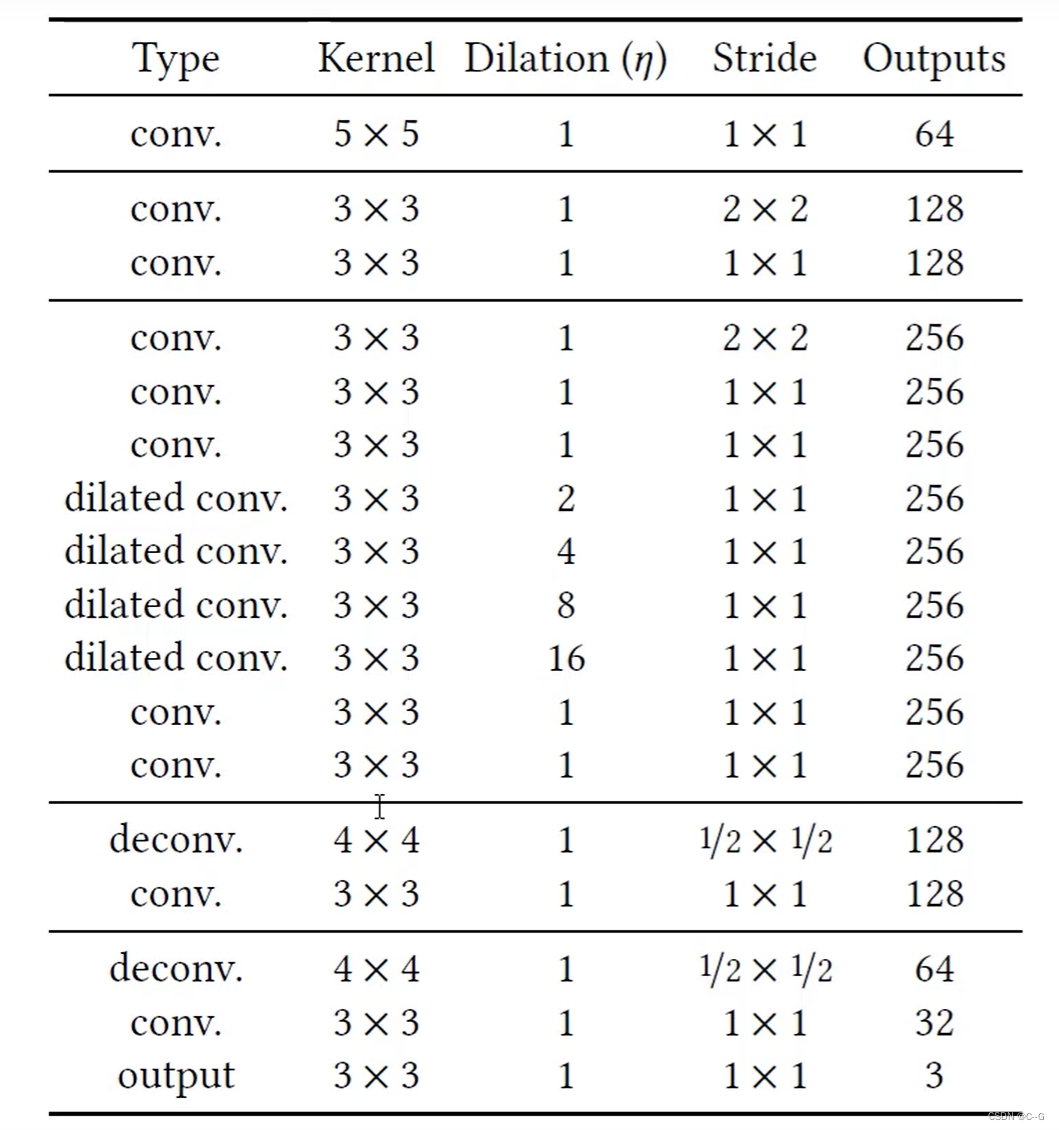
-
最后的合成网络
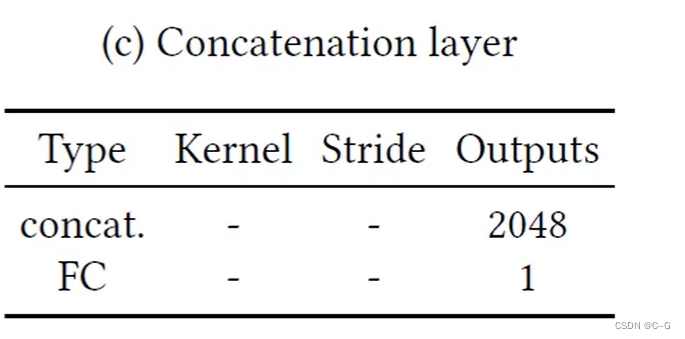
-
MSE损失

通过生成图像与原图的MSE损失,避免过度依赖判别器的特征判断 -
分步计算损失

前Tc次迭代只计算MSE损失,当t大于TC小于Tc+Td时计算判别器损失,当t大于Tc+Td时计算MSE和判别器损失
