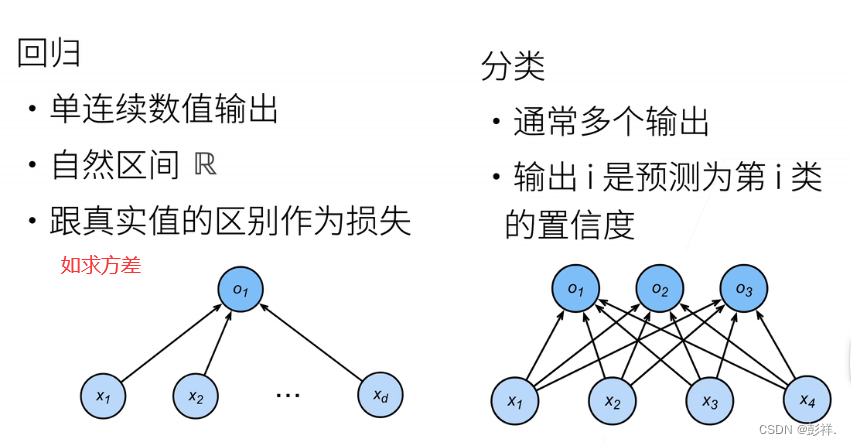
回归与分类的差别,回归是解决一个连续问题,估计一个连续值,如房价预测
而分类则是解决一个离散问题
常见的损失函数
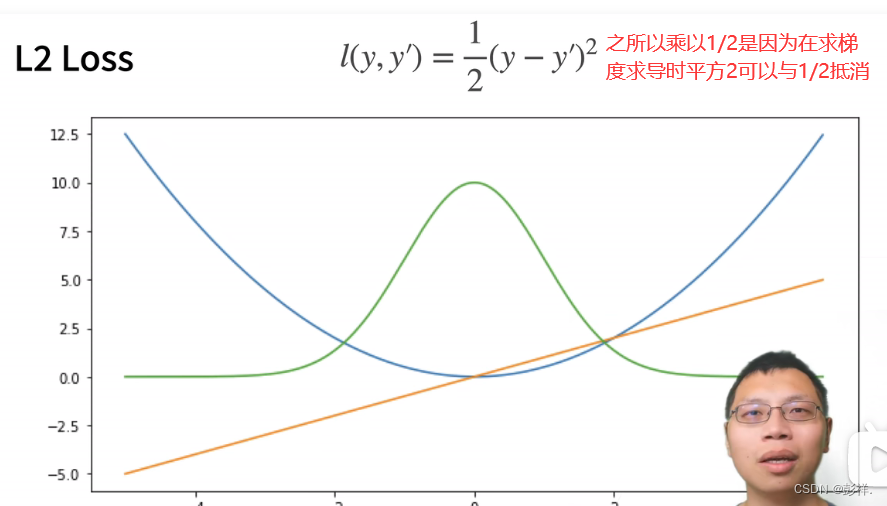
该函数作为损失函数可看到在临近导数为0时,即y与y’接近时,其变化(参数更新)幅度越小,这有可能导致我们的参数更新太剧烈,因此我们也可以采用下面这种绝对值函数作为我们的损失函数的方法
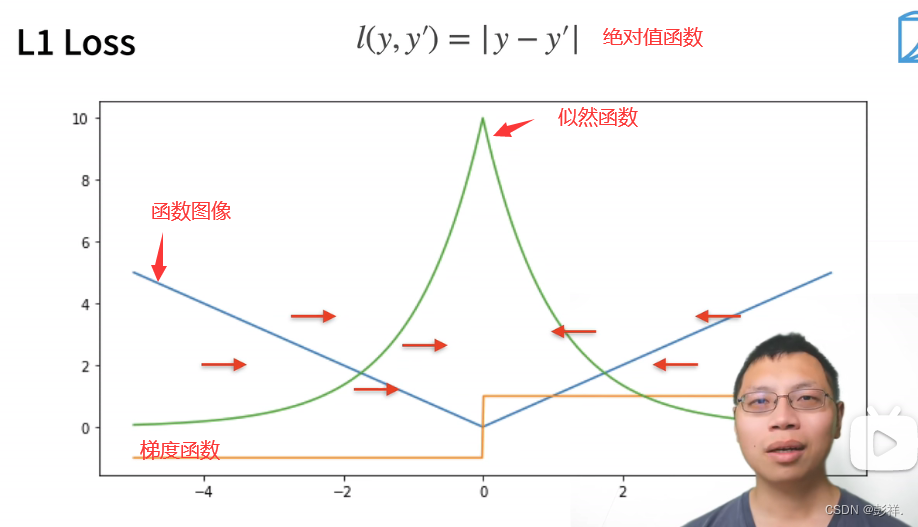
绝对值函数的梯度一直为常数,即变化是稳定的,但他也有缺点,即它在0处不可导,因此在0处取值波动大
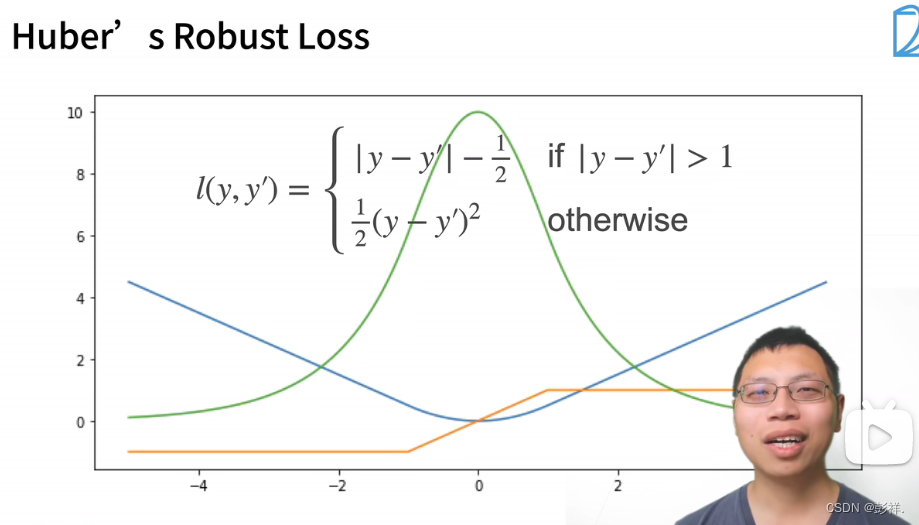
这种是吸取了上面两者损失函数的优缺点后改进的函数
图片分类数据集
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l#一些实现好的函数
import torchvision
from torch.utils import data
from torchvision import transforms#对数据进行操作的摸具
d2l.use_svg_display()#使用svg展示图片。清晰度高一些
# 通过ToTensor实例将图像数据从PIL类型变换成32位浮点数格式,
# 并除以255使得所有像素的数值均在0到1之间
#数据集并不大,几百M,直接读入内存即可
trans = transforms.ToTensor()#将图片转换为tensor
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="./data",#下载目录
train=True, #表面拿到的是训练集
transform=trans,#表面拿到的是转换为tensor的数据而不是一堆图片
download=True#默认网上下载,若已下载完成则无需指定
)
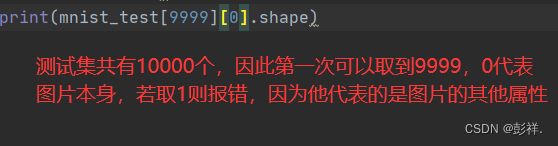
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="./data", train=False, transform=trans, download=True)
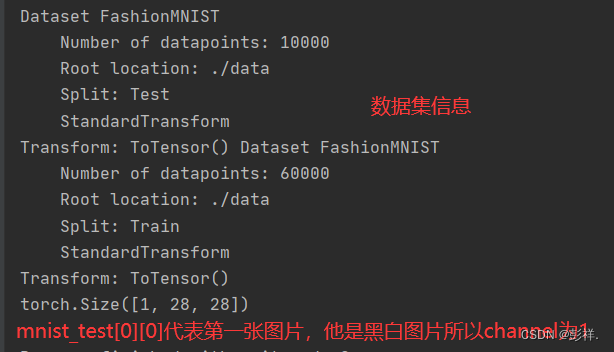
print(mnist_test,mnist_train)
#Fashion-MNIST中包含的10个类别,分别为t-shirt(T恤)、trouser(裤子)、pullover(套衫)、dress(连衣裙)
# 、coat(外套)、sandal(凉鞋)、shirt(衬衫)、sneaker(运动鞋)、bag(包)和ankle boot(短靴)。 以下函数用于在数字标签索引及其文本名称之间进行转换。
def get_fashion_mnist_labels(labels): #@save
"""返回Fashion-MNIST数据集的文本标签"""
text_labels = ['t-shirt', 'trouser', 'pullover', 'dress', 'coat',
'sandal', 'shirt', 'sneaker', 'bag', 'ankle boot']
return [text_labels[int(i)] for i in labels]
#创建一个函数来可视化这些样本
def show_images(imgs, num_rows, num_cols, titles=None, scale=1.5): #@save
"""绘制图像列表"""
figsize = (num_cols * scale, num_rows * scale)
_, axes = d2l.plt.subplots(num_rows, num_cols, figsize=figsize)
axes = axes.flatten()
for i, (ax, img) in enumerate(zip(axes, imgs)):
if torch.is_tensor(img):
# 图片张量
ax.imshow(img.numpy())
else:
# PIL图片
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
if titles:
ax.set_title(titles[i])
return axes
如果要展示这些图片还需要引入PIL
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
X, y = next(iter(data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size=18)))
plt.axes=show_images(X.reshape(18, 28, 28), 2, 9, titles=get_fashion_mnist_labels(y))
plt.show()

读取小批量
为了使我们在读取训练集和测试集时更容易,我们使用内置的数据迭代器,而不是从零开始创建。 回顾一下,在每次迭代中,数据加载器每次都会读取一小批量数据,大小为batch_size。 通过内置数据迭代器,我们可以随机打乱了所有样本,从而无偏见地读取小批量。
batch_size = 256
def get_dataloader_workers(): #@save,根据我们的cpu的进程数来确定,我的进程最大支持到4
"""使用4个进程来读取数据"""
return 2
train_iter = data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=get_dataloader_workers())
timer = d2l.Timer()
for X, y in train_iter:
continue
print(f'{timer.stop():.2f} sec')
将上面的所有代码进行封装以复用
def load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=None): #@save,resize是为了处理图片是否需要改大小,原本的是28*28
"""下载Fashion-MNIST数据集,然后将其加载到内存中"""
trans = [transforms.ToTensor()]
if resize:
trans.insert(0, transforms.Resize(resize))
trans = transforms.Compose(trans)
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="../data", train=True, transform=trans, download=True)
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="../data", train=False, transform=trans, download=True)
return (data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=get_dataloader_workers()),
data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=get_dataloader_workers()))
Softmax 从0开始实现
读取数据集
import torch
from IPython import display
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
初始化模型参数
softmax的输入是一个向量,原始数据集中的每个样本都是的图像。 在本节中,我们将展平每个图像,把它们看作长度为784的向量,偏置将构成一个1*10的行向量。 与线性回归一样,我们将使用正态分布初始化我们的权重W,偏置初始化为0。
import torch
from IPython import display
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
num_inputs = 784#28*28
num_outputs = 10#输出分类数10
W = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(num_inputs, num_outputs), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(num_outputs, requires_grad=True)
SoftMax实现

#此时的X不再是一个行向量,而是一个矩阵,对矩阵而言,我们就是用每一行来做softmax运算
def softmax(X):
X_exp = torch.exp(X)#求幂
partition = X_exp.sum(1, keepdim=True)
return X_exp / partition # 这里应用了广播机制
测试一下
该函数返回从单独的正态分布中提取的随机数的张量,该正态分布的均值是mean,标准差是std。
用法如下:我们从一个标准正态分布N~(0,1),提取一个2x5的矩阵
torch.normal(mean=0.,std=1.,size=(2,2))
#测试
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (2, 5))
X_prob = softmax(X)
print(X_prob, X_prob.sum(1))
和为1

定义模型
def net(X):
return softmax(torch.matmul(X.reshape((-1, W.shape[0])), W) + b)
定义损失函数
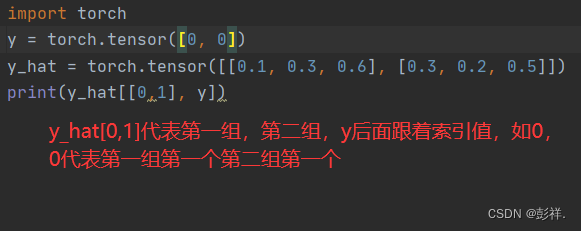
交叉熵采用真实标签的预测概率的负对数似然。 这里我们不使用Python的for循环迭代预测(这往往是低效的), 而是通过一个运算符选择所有元素。 下面,我们创建一个数据样本y_hat,其中包含2个样本在3个类别的预测概率, 以及它们对应的标签y。 有了y,我们知道在第一个样本中,第一类是正确的预测; 而在第二个样本中,第三类是正确的预测。 然后使用y作为y_hat中概率的索引, 我们选择第一个样本中第一个类的概率和第二个样本中第三个类的概率。
y = torch.tensor([0, 2])
y_hat = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.3, 0.6], [0.3, 0.2, 0.5]])
y_hat[[0, 1], y]
交叉熵损失函数

def cross_entropy(y_hat, y):
#y_hat为2*3的预测值,y为实际标签向量
return - torch.log(y_hat[range(len(y_hat)), y])
cross_entropy(y_hat, y)
完整代码
import torch
from IPython import display
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
num_inputs = 784#28*28
num_outputs = 10#输出分类数10
W = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(num_inputs, num_outputs), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(num_outputs, requires_grad=True)
#模拟矩阵运算求和
# X = torch.tensor([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]])
# X.sum(0, keepdim=True), X.sum(1, keepdim=True)
#此时的X不再是一个行向量,而是一个矩阵,对矩阵而言,我们就是用每一行来做softmax运算
def softmax(X):
X_exp = torch.exp(X)#做指数运算
partition = X_exp.sum(1, keepdim=True)#安装维度1求和,并保持原矩阵维度
return X_exp / partition # 这里应用了广播机制,对每一行都求】
#测试
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (2, 5))
X_prob = softmax(X)
print(X_prob, X_prob.sum(1))
def net(X):
return softmax(torch.matmul(X.reshape((-1, W.shape[0])), W) + b)
y = torch.tensor([0, 2])
y_hat = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.3, 0.6], [0.3, 0.2, 0.5]])
y_hat[[0, 1], y]
#交叉熵损失函数
def cross_entropy(y_hat, y):
return - torch.log(y_hat[range(len(y_hat)), y])
#损失值
cross_entropy(y_hat, y)
def accuracy(y_hat, y): #@save
"""计算预测正确的数量"""
if len(y_hat.shape) > 1 and y_hat.shape[1] > 1:
y_hat = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)
cmp = y_hat.type(y.dtype) == y
return float(cmp.type(y.dtype).sum())
#print(accuracy(y_hat, y) / len(y))
def evaluate_accuracy(net, data_iter): #@save
"""计算在指定数据集上模型的精度"""
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.eval() # 将模型设置为评估模式
metric = Accumulator(2) # 正确预测数、预测总数
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in data_iter:
metric.add(accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[1]
class Accumulator: #@save
"""在n个变量上累加"""
def __init__(self, n):
self.data = [0.0] * n
def add(self, *args):
self.data = [a + float(b) for a, b in zip(self.data, args)]
def reset(self):
self.data = [0.0] * len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.data[idx]
print(evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter))
def train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater): #@save
"""训练模型一个迭代周期(定义见第3章)"""
# 将模型设置为训练模式
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.train()
# 训练损失总和、训练准确度总和、样本数
metric = Accumulator(3)
for X, y in train_iter:
# 计算梯度并更新参数
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
if isinstance(updater, torch.optim.Optimizer):
# 使用PyTorch内置的优化器和损失函数
updater.zero_grad()
l.mean().backward()
updater.step()
else:
# 使用定制的优化器和损失函数
l.sum().backward()
updater(X.shape[0])
metric.add(float(l.sum()), accuracy(y_hat, y), y.numel())
# 返回训练损失和训练精度
return metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[2]
class Animator: #@save
"""在动画中绘制数据"""
def __init__(self, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None, xlim=None,
ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear',
fmts=('-', 'm--', 'g-.', 'r:'), nrows=1, ncols=1,
figsize=(3.5, 2.5)):
# 增量地绘制多条线
if legend is None:
legend = []
d2l.use_svg_display()
self.fig, self.axes = d2l.plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize=figsize)
if nrows * ncols == 1:
self.axes = [self.axes, ]
# 使用lambda函数捕获参数
self.config_axes = lambda: d2l.set_axes(
self.axes[0], xlabel, ylabel, xlim, ylim, xscale, yscale, legend)
self.X, self.Y, self.fmts = None, None, fmts
def add(self, x, y):
# 向图表中添加多个数据点
if not hasattr(y, "__len__"):
y = [y]
n = len(y)
if not hasattr(x, "__len__"):
x = [x] * n
if not self.X:
self.X = [[] for _ in range(n)]
if not self.Y:
self.Y = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i, (a, b) in enumerate(zip(x, y)):
if a is not None and b is not None:
self.X[i].append(a)
self.Y[i].append(b)
self.axes[0].cla()
for x, y, fmt in zip(self.X, self.Y, self.fmts):
self.axes[0].plot(x, y, fmt)
self.config_axes()
display.display(self.fig)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
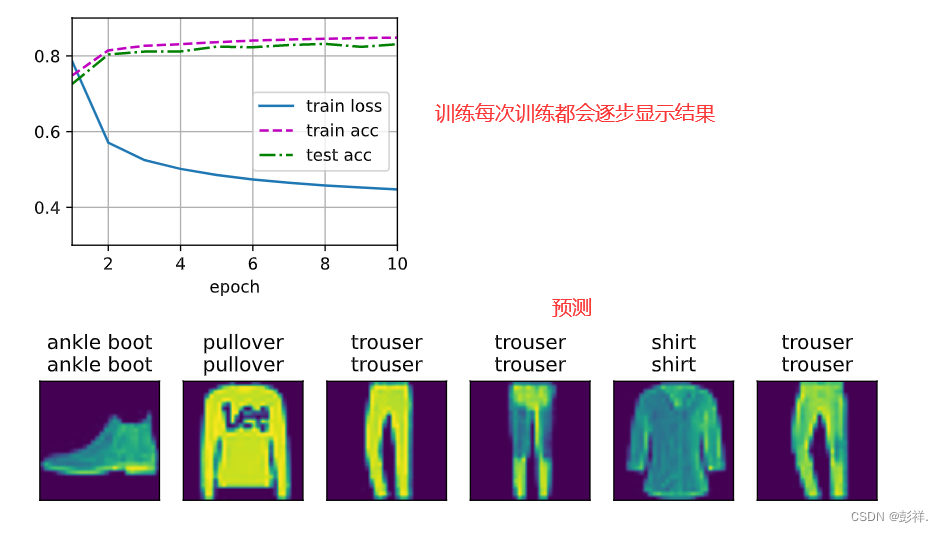
def train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater): #@save
"""训练模型(定义见第3章)"""
animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0.3, 0.9],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_metrics = train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater)
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, train_metrics + (test_acc,))
train_loss, train_acc = train_metrics
assert train_loss < 0.5, train_loss
assert train_acc <= 1 and train_acc > 0.7, train_acc
assert test_acc <= 1 and test_acc > 0.7, test_acc
lr = 0.1
def updater(batch_size):
return d2l.sgd([W, b], lr, batch_size)
num_epochs = 10
train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, cross_entropy, num_epochs, updater)
def predict_ch3(net, test_iter, n=6): #@save
"""预测标签(定义见第3章)"""
for X, y in test_iter:
break
trues = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(y)
preds = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(net(X).argmax(axis=1))
titles = [true +'\n' + pred for true, pred in zip(trues, preds)]
d2l.show_images(
X[0:n].reshape((n, 28, 28)), 1, n, titles=titles[0:n])
predict_ch3(net, test_iter)
SoftMax简易实现
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
# PyTorch不会隐式地调整输入的形状。因此,
# 我们在线性层前定义了展平层(flatten),来调整网络输入的形状
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 10))
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01)
net.apply(init_weights)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)
num_epochs = 10
from matplotlib import pyplot as pil
pil.axes=d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)
pil.show()