导读
之前看了ConvNext论文,我们知道了ConvNext是基于ResNet50改进而来,我们梦回初始看看ResNet是如何实现的
Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition发表于2015年,这是过去6、7年里用到最多的一篇文章,至今引用数量已经到了11w,虽然最开始resnet是用在CV领域,但是后来我们可以看到基本上所有的神经网络模型都有用到这篇文章的残差框架,只要网络深度达到一定数量的话,基本上都会到残差学习的思想放入到网络中使网络更好的训练
摘要首先写了写作的背景,指出当前领域面临的问题,第二句话提出了解决方案残差学习框架和目的,后面是细节的展开和比赛取的成绩
为了深层网络不差于浅层网络,让后面的层学习恒等变换,我们希望深层比浅层网络多出来的层数学习的函数y=x,也就是这些层没有起到任何的作用,这样深层网络至少和浅层网络一样好。
算法用论文的图2表示,论文核心的思想框架:
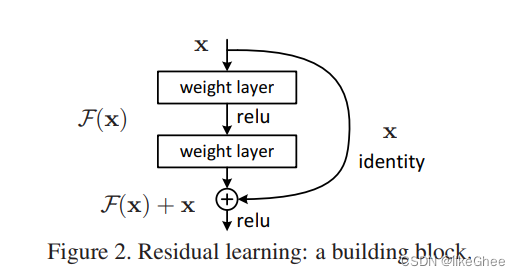
x输入象征浅层网络输出,下面视作深层网络,浅层网络输出添加一条路径连接深层网络输出,这样多出来的这些层学习的是y-x,学习的是残差,这样比直接去学y容易学
如果浅层网络足够的话,直接走连接深层网络路径就好
残差学习框架有几种变体,除开x和F(x)维度一致,还有另外一种是输入和输出通道数目不一致,直接做加法是加不了的,我们需要增加一个MLP变换层,但这样做会带来参数增加
论文中baseline选择模型是VGG-19,是之前在图像识别上主流的一个模型,基于此模型改造resnet
VGG-19结构:
图片经过几层卷积图片维度不变,通道数从3增加到64,之后经过下采样层对图片的长度和宽度进行下采样池化,同时对图片的通道数进行上采样,目的是保证每一层的计算量是差不多的,在经过两层卷积,再进一步下采样,之后也是一样,最终图片维度降到7,通道数增加到512,最后经过全连接层投影到要分类的概率分布上
resnet沿用了一些思想,不同的stage过渡时有空间的下采样,通道上用上采样,最后全局池化,投影到分类类别的概率分布上
resnet normal结构:
经过stem层,7×7卷积,通道数增至64,stride=2,padding=kernel_size/2=3,空间维度下采样1/2
(这里有个规律,stride=x,padding=kernel_size/2,那么图片将会缩小1/x)
stem层之后经过pool层,空间下采样1/2
之后是4层的stage,每个stage通道数分别是64,128,256,512,每个stage都是3×3的卷积,stride=1,padding=1,stage之间有一个下采样,通过卷积实现下采样,通道数从x增加到2x,空间维度降低1/2,为了实现这个下采样则参数为:kernel=3×3,
stride=2,padding=kernel_size/2=1
每个stage中每两个block使用残差连接,4层stage的block数目分别是6,8,12,6,论文图3中,实线连接表示x和F(x)维度一致,虚线部分两层卷积不一致,输入张量和输出张量维度不一致,这种情况我们需要通过一个变化把输入维度映射到输出维度上
最后是average pool连接fc,head层
resnet 瓶颈结构:
resnet50之后更大的网络,每个残差连接的block是三层的,三层block卷积核大小分别是1×1,3×3,1×1,1×1就是point-wise卷积目的是做通道融合,3×3用于处理更小的输入和输出维度并且做空间融合
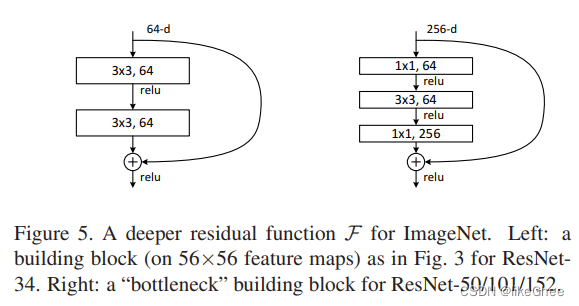
resnet18至resnet152各个模型结构:
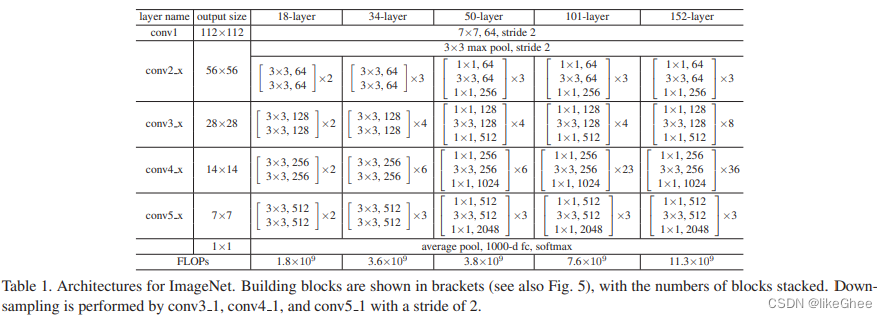
需要注意NormalBlock与BottleneckBlock下采样的位置,都是3×3卷积的地方做图片的下采样,而不是在1×1卷积处
论文地址
https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/papers/He_Deep_Residual_Learning_CVPR_2016_paper.pdf
实现代码
借助timm库学习resnet结构,我们导入timm库,使用creat_model函数,creat_model传入resnet50得到model实例化对象
第一个是一个stem层,每个卷积层后面都跟着一个批归一化和一个非线性激活函数
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), padding=(3, 3), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act1): ReLU(inplace=True)
第二层是一个最大池化,进行一个1/2空间的下采样,56×56
(maxpool): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
然后就是不同的stage,stage1是layer1,里面重复了3个block,所以有3个bottleneck,每个bottleneck就是一个block
来看stage1的第一个block,Bottleneck0里面有conv1,conv2,conv3,每个conv之后紧跟的两个batch norm和active函数,conv3后是下采样层
conv1:in_c=64, out_c=64,1×1,stride=1
conv2:in_c=64, out_c=64,3×3,stride=1,padding=1(输入输出维度一致)
conv3:in_c=64, out_c=256,1×1,stride=1
此时图片大小没有变化,仍是56×56,channel=256
为了去做残差连接,下采样层(残差连接变换层):把输入dim=64变换到256,用的是简单1×1的卷积去做的,in_c=64, out_c=256
在第二个block的时候,就没有这个变换层的问题了,输入dim=256,最后conv3的输出dim=256,所以可以直接做残差连接
第三个block也是一样的,conv1输入dim=256,最后conv3的输出dim=256
(layer1): Sequential(
(0): Bottleneck(
(conv1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv3): Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(downsample): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(1): Bottleneck(
(conv1): Conv2d(256, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv3): Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act3): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
(2): Bottleneck(
(conv1): Conv2d(256, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv3): Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act3): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
第一个stage的通道数是256,到了第二个stage,我们得经过一个卷积层变换到128,并且这个卷积做了一个空间的下采样,图片大小变成28×28
所以我们来看stage2的第一个block
conv1:in=256, out=128, 1×1,stride=1,通道数减少一半,图片大小不变
conv2:in=128, out=128, stride=2, padding=1, 3×3,图片大小减半,56×56变成28×28
conv3:in=128, out=512,1×1,stride=1,通道数上采样
同样的需要残差变化层,in=256, out=512, stride=2, 1×1, 让输入的56×56变成28×28,channel=512,让输入可以和conv3结果相加
其余都是差不多一样的步骤了
(layer2): Sequential(
(0): Bottleneck(
(conv1): Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv3): Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(downsample): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(1): Bottleneck(
(conv1): Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv3): Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act3): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
(2): Bottleneck(
(conv1): Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv3): Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act3): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
(3): Bottleneck(
(conv1): Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv3): Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act3): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
最后就是pool层和fc层
2d pool对h和w进行池化,
fc层做分类任务
(global_pool): SelectAdaptivePool2d (pool_type=avg, flatten=Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1))
(fc): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=1000, bias=True)
来看代码的实现,在models文件夹下的resnet.py中
先看核心的class ResNet如何实现,
我们进入到init函数中
第一步是是要实现stem层,1/2空间下采样
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
接着是最大池化层,也是1/2空间下采样
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
channel是写死的就是64,128,256,512
能改的就是每个stage重复多少遍
stage_modules添加到add_module函数,add_module函数接受两个参数,第一个是module_name,第二个model对象,所以stage_modules是由元组构成的列表
最后是head层,创建池化和FC
后面就是forward_features和forward函数了,很常规
因此核心部分是self.layer1,layer2,layer3,layer4的一个个block创建,函数用的是make_blocks,关键看make_blocks函数怎么实现
class ResNet(nn.Module):
"""注释太长删了,想看的自己去源码看吧
"""
def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000, in_chans=3,
cardinality=1, base_width=64, stem_width=64, stem_type='', replace_stem_pool=False,
output_stride=32, block_reduce_first=1, down_kernel_size=1, avg_down=False,
act_layer=nn.ReLU, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, aa_layer=None, drop_rate=0.0, drop_path_rate=0.,
drop_block_rate=0., global_pool='avg', zero_init_last_bn=True, block_args=None):
block_args = block_args or dict()
assert output_stride in (8, 16, 32)
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
# Stem
deep_stem = 'deep' in stem_type
inplanes = stem_width * 2 if deep_stem else 64
if deep_stem:
stem_chs = (stem_width, stem_width)
if 'tiered' in stem_type:
stem_chs = (3 * (stem_width // 4), stem_width)
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(*[
nn.Conv2d(in_chans, stem_chs[0], 3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
norm_layer(stem_chs[0]),
act_layer(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(stem_chs[0], stem_chs[1], 3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
norm_layer(stem_chs[1]),
act_layer(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(stem_chs[1], inplanes, 3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)])
else:
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(inplanes)
self.act1 = act_layer(inplace=True)
self.feature_info = [dict(num_chs=inplanes, reduction=2, module='act1')]
# Stem Pooling
if replace_stem_pool:
self.maxpool = nn.Sequential(*filter(None, [
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, inplanes, 3, stride=1 if aa_layer else 2, padding=1, bias=False),
aa_layer(channels=inplanes, stride=2) if aa_layer else None,
norm_layer(inplanes),
act_layer(inplace=True)
]))
else:
if aa_layer is not None:
self.maxpool = nn.Sequential(*[
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
aa_layer(channels=inplanes, stride=2)])
else:
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
# Feature Blocks
channels = [64, 128, 256, 512]
stage_modules, stage_feature_info = make_blocks(
block, channels, layers, inplanes, cardinality=cardinality, base_width=base_width,
output_stride=output_stride, reduce_first=block_reduce_first, avg_down=avg_down,
down_kernel_size=down_kernel_size, act_layer=act_layer, norm_layer=norm_layer, aa_layer=aa_layer,
drop_block_rate=drop_block_rate, drop_path_rate=drop_path_rate, **block_args)
for stage in stage_modules:
self.add_module(*stage) # layer1, layer2, etc
self.feature_info.extend(stage_feature_info)
# Head (Pooling and Classifier)
self.num_features = 512 * block.expansion
self.global_pool, self.fc = create_classifier(self.num_features, self.num_classes, pool_type=global_pool)
self.init_weights(zero_init_last_bn=zero_init_last_bn)
def init_weights(self, zero_init_last_bn=True):
for n, m in self.named_modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.ones_(m.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
if zero_init_last_bn:
for m in self.modules():
if hasattr(m, 'zero_init_last_bn'):
m.zero_init_last_bn()
def get_classifier(self):
return self.fc
def reset_classifier(self, num_classes, global_pool='avg'):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.global_pool, self.fc = create_classifier(self.num_features, self.num_classes, pool_type=global_pool)
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
return x
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.global_pool(x)
if self.drop_rate:
x = F.dropout(x, p=float(self.drop_rate), training=self.training)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
仔细看一下make_blocks函数,它把4个stage和每个stage中的blcok实例化好
第一个参数是block_fn,传入的是basicblock或者bottleneck类的实例化,定义是两层结构还是三层结构
关键参数是channels和block_repeats
一开始是一个for循环,for对stage的参数进行遍历,
for stage_idx, (planes, num_blocks, db) in enumerate(zip(channels, block_repeats, drop_blocks(drop_block_rate))):
list(zip(channels, block_repeats, drop_blocks(drop_block_rate)))的value是[(64, 3, None), (128, 4, None), (256, 6, None), (512, 3, None)],每个元组里的元素分别代表stage_idx, (planes, num_blocks, db)
stage_name就是在forward_features函数里面看到的self.layer1,layer2,layer3,layer4的由来,在最后面可以看到,stage_name是作为元组元素返回的
stage_name = f'layer{stage_idx + 1}' # never liked this name, but weight compat requires it
第一个stage的stride要设置成1,其他stage的stride设置成2,这是因为在进入stage1之前图片是经过max pool空间下采样变成56×56的了,stage1过渡到stage2才需要再做一次下采样
stride = 1 if stage_idx == 0 else 2
对block遍历,去创建block
for block_idx in range(num_blocks):
block_idx为0才用到downsample层,即输入维度变化层(为了残差连接),重复第二个和第二个往后的block就不需要设置downsample了
downsample = downsample if block_idx == 0 else None
stride = stride if block_idx == 0 else 1
block_fn是一个nn.Module子类(即BasicBlock类或者BottleNeck类)的实例化,通过__call__函数,构建block,创建好的block实例化添加到列表之中
inplanes表示下一个block的输入通道数,因为考虑到有瓶颈的结构,上一个block输出是有一个4倍的通道数的放大,对于常规的normal block是没有的,expansion=1
得到block列表,用星号*展开,作为Sequential函数输入,添加到stages列表中
最后返回stages
def make_blocks(
block_fn, channels, block_repeats, inplanes, reduce_first=1, output_stride=32,
down_kernel_size=1, avg_down=False, drop_block_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0., **kwargs):
stages = []
feature_info = []
net_num_blocks = sum(block_repeats)
net_block_idx = 0
net_stride = 4
dilation = prev_dilation = 1
for stage_idx, (planes, num_blocks, db) in enumerate(zip(channels, block_repeats, drop_blocks(drop_block_rate))):
stage_name = f'layer{stage_idx + 1}' # never liked this name, but weight compat requires it
stride = 1 if stage_idx == 0 else 2
if net_stride >= output_stride:
dilation *= stride
stride = 1
else:
net_stride *= stride
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or inplanes != planes * block_fn.expansion:
down_kwargs = dict(
in_channels=inplanes, out_channels=planes * block_fn.expansion, kernel_size=down_kernel_size,
stride=stride, dilation=dilation, first_dilation=prev_dilation, norm_layer=kwargs.get('norm_layer'))
downsample = downsample_avg(**down_kwargs) if avg_down else downsample_conv(**down_kwargs)
block_kwargs = dict(reduce_first=reduce_first, dilation=dilation, drop_block=db, **kwargs)
blocks = []
for block_idx in range(num_blocks):
downsample = downsample if block_idx == 0 else None
stride = stride if block_idx == 0 else 1
block_dpr = drop_path_rate * net_block_idx / (net_num_blocks - 1) # stochastic depth linear decay rule
blocks.append(block_fn(
inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, first_dilation=prev_dilation,
drop_path=DropPath(block_dpr) if block_dpr > 0. else None, **block_kwargs))
prev_dilation = dilation
inplanes = planes * block_fn.expansion
net_block_idx += 1
stages.append((stage_name, nn.Sequential(*blocks)))
feature_info.append(dict(num_chs=inplanes, reduction=net_stride, module=stage_name))
return stages, feature_info
来看看block的实现,先看简单的basic block
就是两层的卷积,再用一条路径连接输入和输出
init函数中,先实例化两层卷积,conv1和conv2
forward函数中,进入conv1,conv2
输出x在连接一个shortcut
x += shortcut
如果是每个stage的第一个block的话,那么可能有一个downsample层,第二个block和第二个往后就没有downsample层了
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, cardinality=1, base_width=64,
reduce_first=1, dilation=1, first_dilation=None, act_layer=nn.ReLU, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d,
attn_layer=None, aa_layer=None, drop_block=None, drop_path=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
assert cardinality == 1, 'BasicBlock only supports cardinality of 1'
assert base_width == 64, 'BasicBlock does not support changing base width'
first_planes = planes // reduce_first
outplanes = planes * self.expansion
first_dilation = first_dilation or dilation
use_aa = aa_layer is not None and (stride == 2 or first_dilation != dilation)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(
inplanes, first_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1 if use_aa else stride, padding=first_dilation,
dilation=first_dilation, bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(first_planes)
self.act1 = act_layer(inplace=True)
self.aa = aa_layer(channels=first_planes, stride=stride) if use_aa else None
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(
first_planes, outplanes, kernel_size=3, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation, bias=False)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(outplanes)
self.se = create_attn(attn_layer, outplanes)
self.act2 = act_layer(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
self.dilation = dilation
self.drop_block = drop_block
self.drop_path = drop_path
def zero_init_last_bn(self):
nn.init.zeros_(self.bn2.weight)
def forward(self, x):
shortcut = x
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
if self.drop_block is not None:
x = self.drop_block(x)
x = self.act1(x)
if self.aa is not None:
x = self.aa(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
if self.drop_block is not None:
x = self.drop_block(x)
if self.se is not None:
x = self.se(x)
if self.drop_path is not None:
x = self.drop_path(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
shortcut = self.downsample(shortcut)
x += shortcut
x = self.act2(x)
return x
最后是bottleNeck,一共有三层卷积,分别是1×1,3×3,1×1,同样地,可能有一个downsample层
forward函数写法和之前的basic写法差不多,经过conv1,conv2,conv3,如果有downsample层,经过downsample得到新的shortcut
再把shortcut加到x上
加完之后再经过激活函数
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, cardinality=1, base_width=64,
reduce_first=1, dilation=1, first_dilation=None, act_layer=nn.ReLU, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d,
attn_layer=None, aa_layer=None, drop_block=None, drop_path=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
width = int(math.floor(planes * (base_width / 64)) * cardinality)
first_planes = width // reduce_first
outplanes = planes * self.expansion
first_dilation = first_dilation or dilation
use_aa = aa_layer is not None and (stride == 2 or first_dilation != dilation)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, first_planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(first_planes)
self.act1 = act_layer(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(
first_planes, width, kernel_size=3, stride=1 if use_aa else stride,
padding=first_dilation, dilation=first_dilation, groups=cardinality, bias=False)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(width)
self.act2 = act_layer(inplace=True)
self.aa = aa_layer(channels=width, stride=stride) if use_aa else None
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(width, outplanes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = norm_layer(outplanes)
self.se = create_attn(attn_layer, outplanes)
self.act3 = act_layer(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
self.dilation = dilation
self.drop_block = drop_block
self.drop_path = drop_path
def zero_init_last_bn(self):
nn.init.zeros_(self.bn3.weight)
def forward(self, x):
shortcut = x
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
if self.drop_block is not None:
x = self.drop_block(x)
x = self.act1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
if self.drop_block is not None:
x = self.drop_block(x)
x = self.act2(x)
if self.aa is not None:
x = self.aa(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.bn3(x)
if self.drop_block is not None:
x = self.drop_block(x)
if self.se is not None:
x = self.se(x)
if self.drop_path is not None:
x = self.drop_path(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
shortcut = self.downsample(shortcut)
x += shortcut
x = self.act3(x)
return x