build_targets作用
build_targets函数用于网络训练时计算loss所需要的目标框,即正样本。
注意
- 与yolov3/yolov4不同,yolv5支持跨网格预测。即每一个bbox,正对于任何一个输出层,都可能有anchor与之匹配。
- 该函数输出的正样本框比传入的GT数目要多。
- 当前解读版本为6.1
可视化结果
- TODO
过程
- 首先通过bbox与当前层anchor做一遍过滤。对于任何一层计算当前bbox与当前层anchor的匹配程度,不采用IoU,而采用shape比例。如果anchor与bbox的宽高比差距大于4,则认为不匹配,保留下匹配的bbox。
r = t[..., 4:6] / anchors[:, None] # wh ratio
j = torch.max(r, 1 / r).max(2)[0] < self.hyp['anchor_t'] # compare
# j = wh_iou(anchors, t[:, 4:6]) > model.hyp['iou_t'] # iou(3,n)=wh_iou(anchors(3,2), gwh(n,2))
t = t[j] # filter
- 最后根据留下的bbox,在上下左右四个网格四个方向扩增采样。
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy
gxi = gain[[2, 3]] - gxy # inverse
j, k = ((gxy % 1 < g) & (gxy > 1)).T
l, m = ((gxi % 1 < g) & (gxi > 1)).T
j = torch.stack((torch.ones_like(j), j, k, l, m))
t = t.repeat((5, 1, 1))[j]
详细代码解读
准备
def build_targets(self, p, targets):
P是网络预测的输出。
p的shape为:(batch_size,anchor_num,grid_cell,grid_cell,xywh+obj_confidence+classes_num)

P[0]的shape

P[1]的shape

P[2]的shape

targets是经过数据增强(mosaic等)后总的bbox。
targets的shape为:[num_obj, 6] , that number 6 means -> (img_index, obj_index, x, y, w, h)
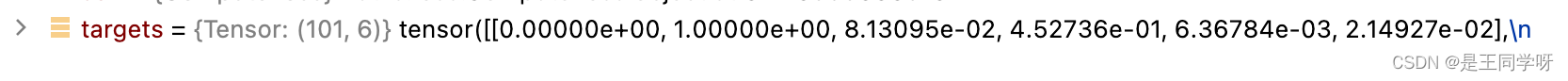
na, nt = self.na, targets.shape[0] # number of anchors, targets

tcls, tbox, indices, anch = [], [], [], []
tcls:用来存储类别。
tbox:用来存储bbox
indices:用来存储第几张图片,当前层的第几个anchor,以及当前层grid的下标。
gain = torch.ones(7, device=self.device) # normalized to gridspace gain
初始化为1,用来还原bbox为当前层的尺度大小。
ai = torch.arange(na, device=self.device).float().view(na, 1).repeat(1, nt) # same as .repeat_interleave(nt)
扩充anchor数量和当前bbox一样多。
ai是anchor的下标

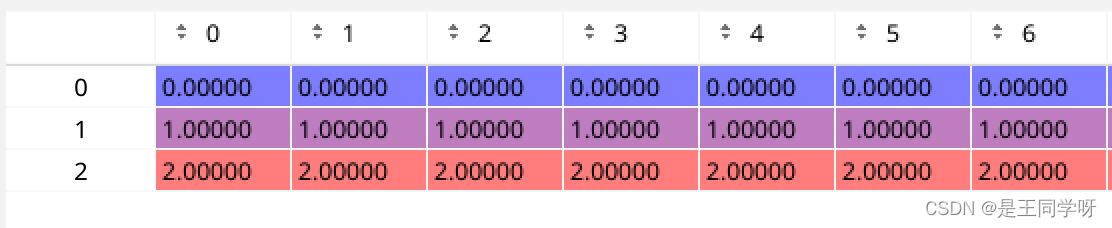
targets = torch.cat((targets.repeat(na, 1, 1), ai[..., None]), 2) # append anchor indices
targets的shape变为(3,101,7)。
targets[0]对应第一个anchor对应的(image_id, cls, center_x,center_y, w, h,第一个anchor)
targets[1]对应第一个anchor对应的(image_id, cls, center_x,center_y, w, h,第二个anchor)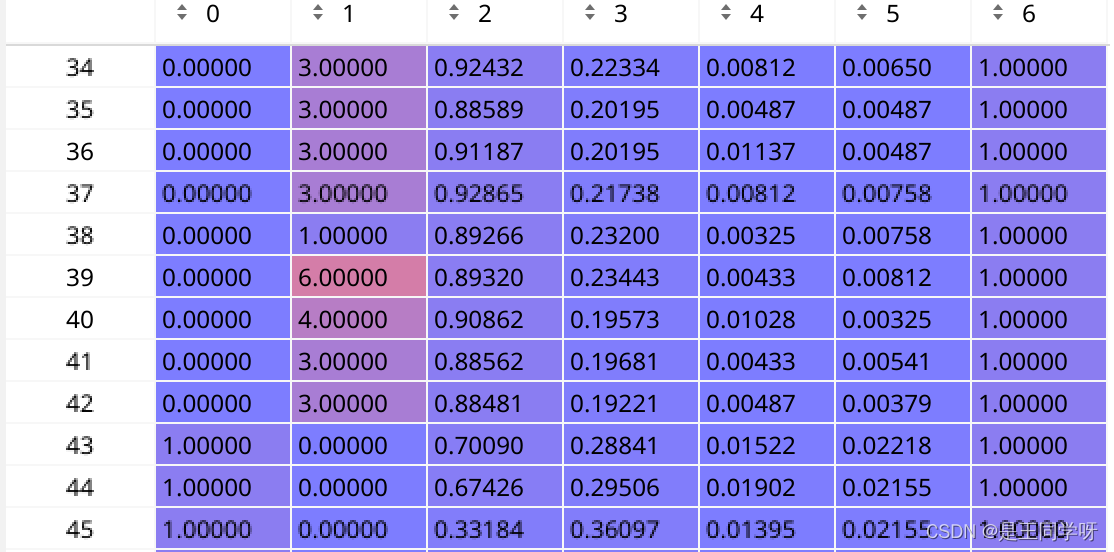
targets[2]对应第一个anchor对应的(image_id, cls, center_x,center_y, w, h,第三个anchor)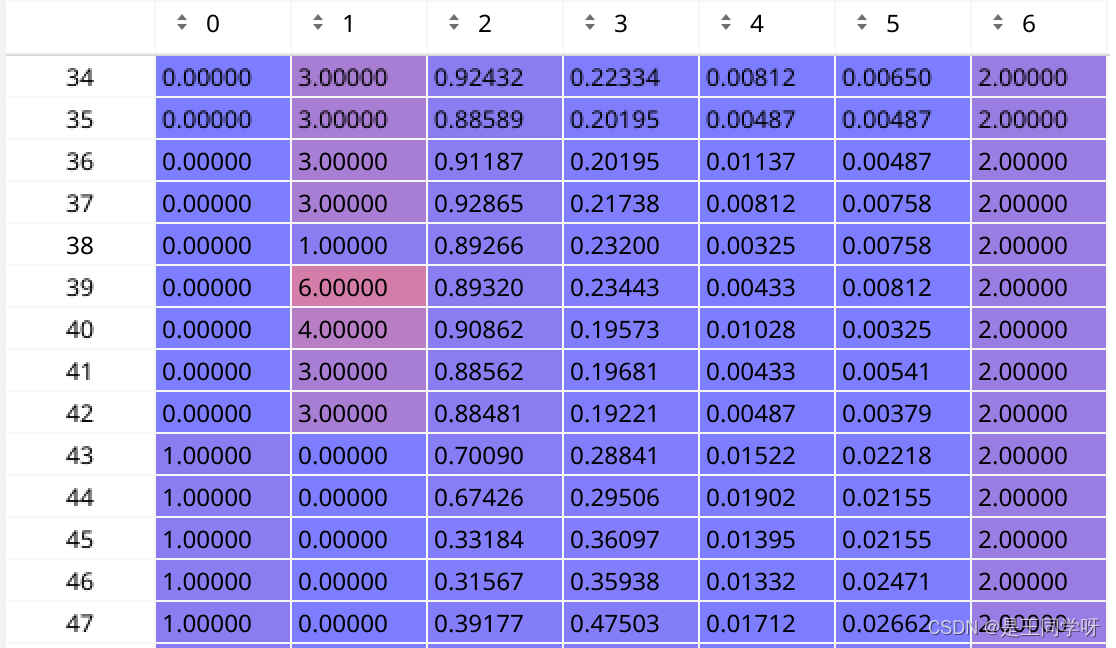
# 预定义的偏移量
g = 0.5 # bias
off = torch.tensor(
[
[0, 0],
[1, 0],
[0, 1],
[-1, 0],
[0, -1], # j,k,l,m
# [1, 1], [1, -1], [-1, 1], [-1, -1], # jk,jm,lk,lm
],
device=self.device).float() * g # offsets
for i in range(self.nl): # 枚举每一层
anchors = self.anchors[i] # 当前层anchor
self.anchors

self.anchors[0]得到第一层归一化后的anchor

乘8得到的
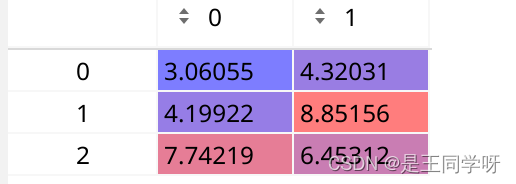
self.anchors[1]得到第二层归一化后的anchor
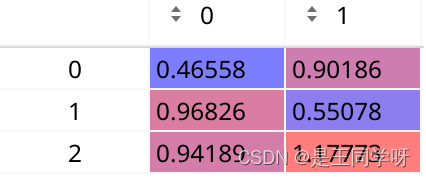
乘16得到的
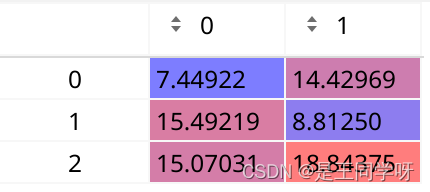
self.anchors[2]得到第三层归一化后的anchor
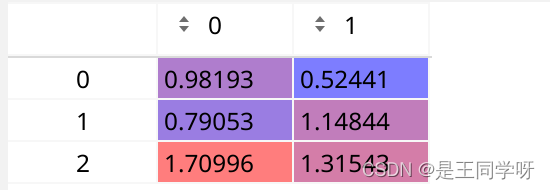
乘以32得到的
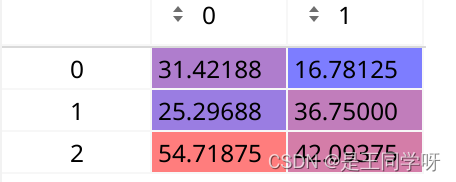
gain[2:6] = torch.tensor(p[i].shape)[[3, 2, 3, 2]] # xyxy gain
生成一个当前层的方格大小。
如果i=0

如果i=1,

如果i=2

t = targets * gain
将targets的大小映射到当前层,第六列是当前层的第几个anchor,第0列是位于哪张图片,第1列代表的是类别,2-5列是目标在当前层x,y,w,h。
下采样八倍的层
第一遍筛选
if nt: # 如果存在目标
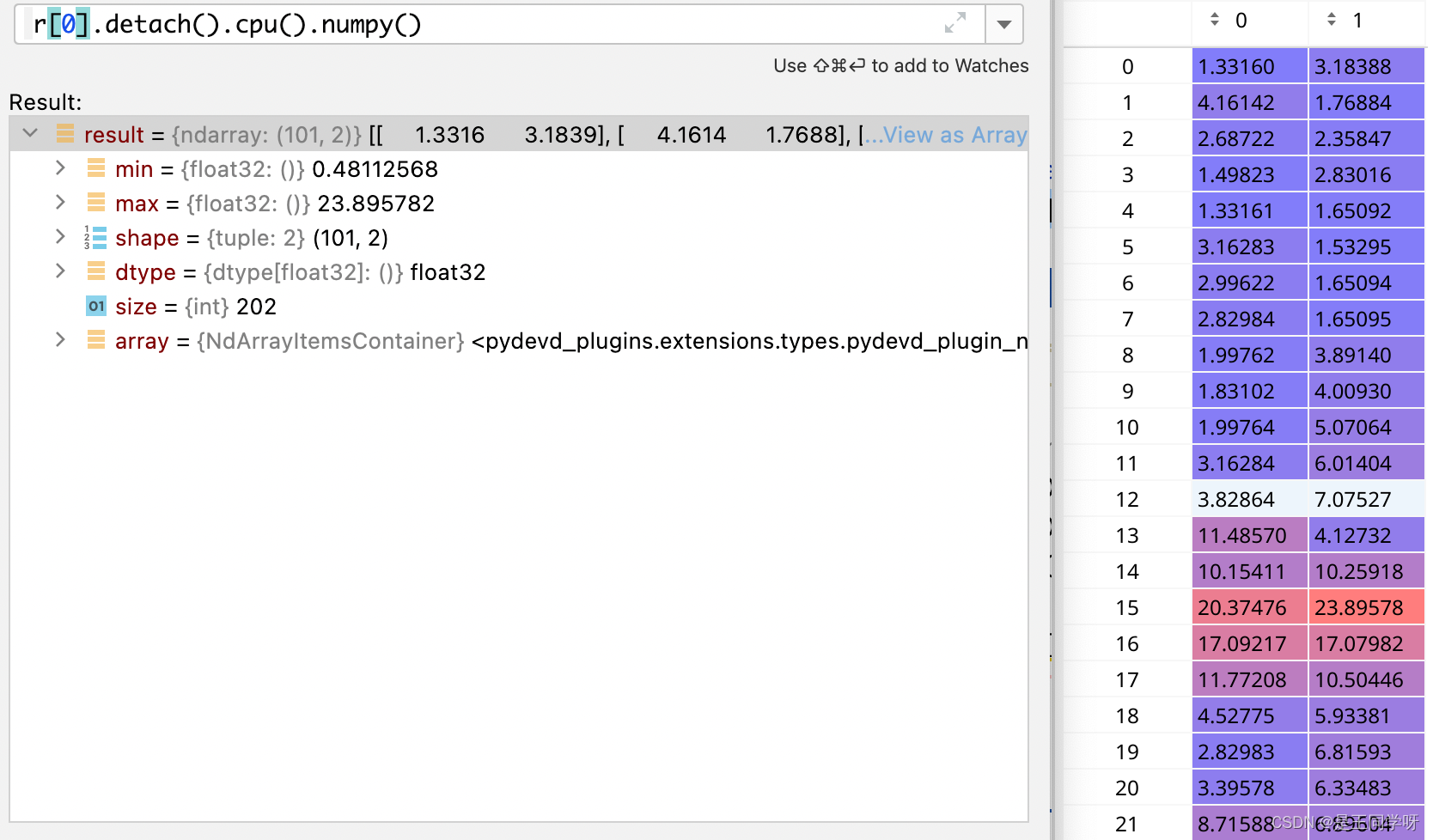
r = t[..., 4:6] / anchors[:, None]
r是指bbox与当前层三个anchor的高宽的比值。

r[0]
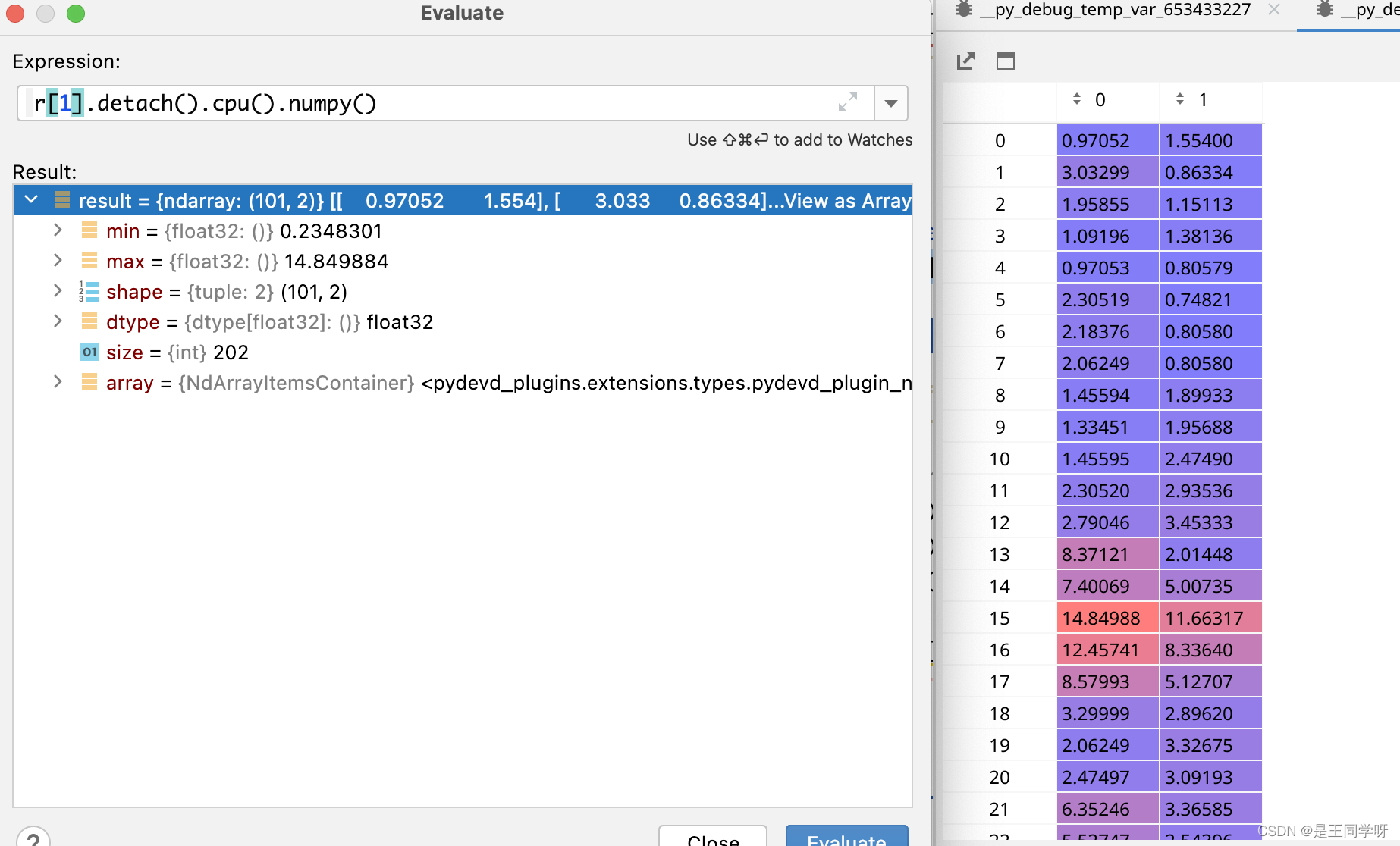
r[1]
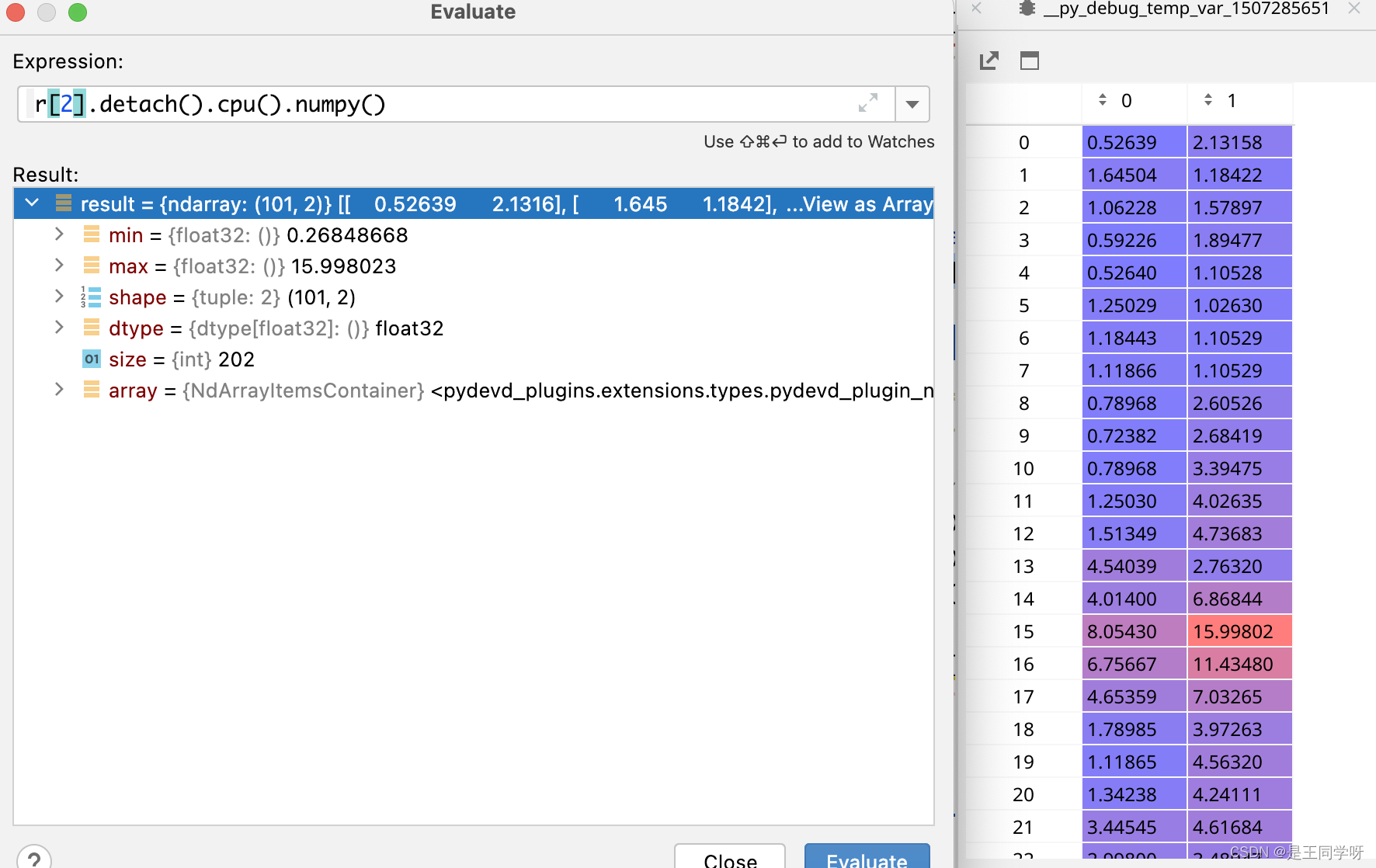
r[2]
j = torch.max(r, 1 / r).max(2)[0] < self.hyp['anchor_t'] # compare
torch.max(r, 1 / r).max(2)[0] 为什么是[0]不是[1].[0]代表的是value,[1]代表的index。

torch.max(r, 1 / r).max(2)[1]

torch.max(r, 1 / r).max(1)[0]
按行获取最大值。
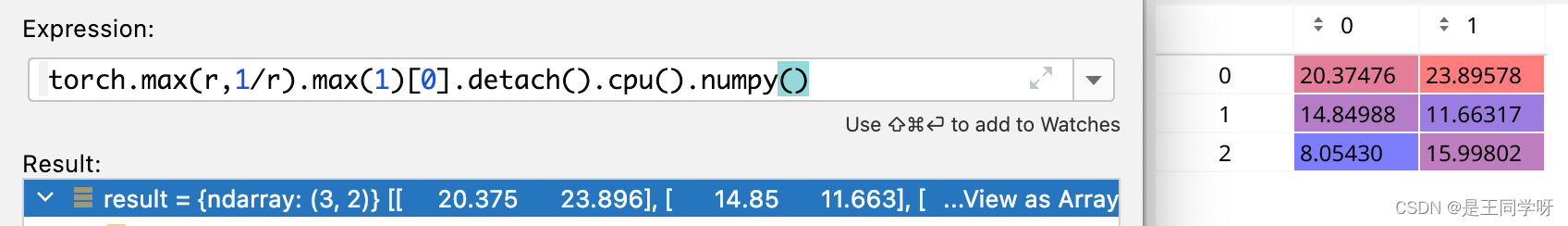
torch.max(r, 1 / r).max(1)[1]
按行获取最大值,返回索引。
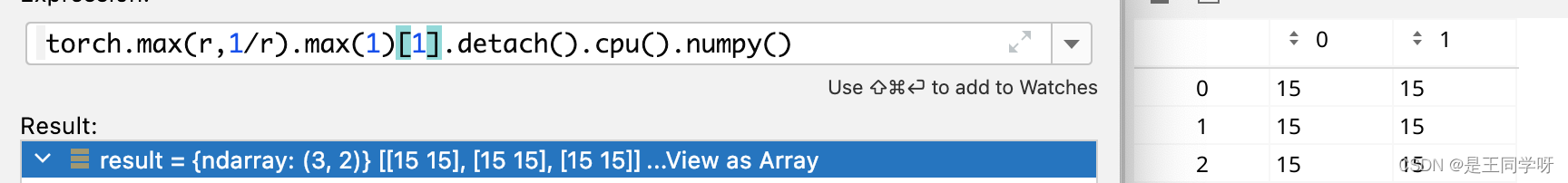
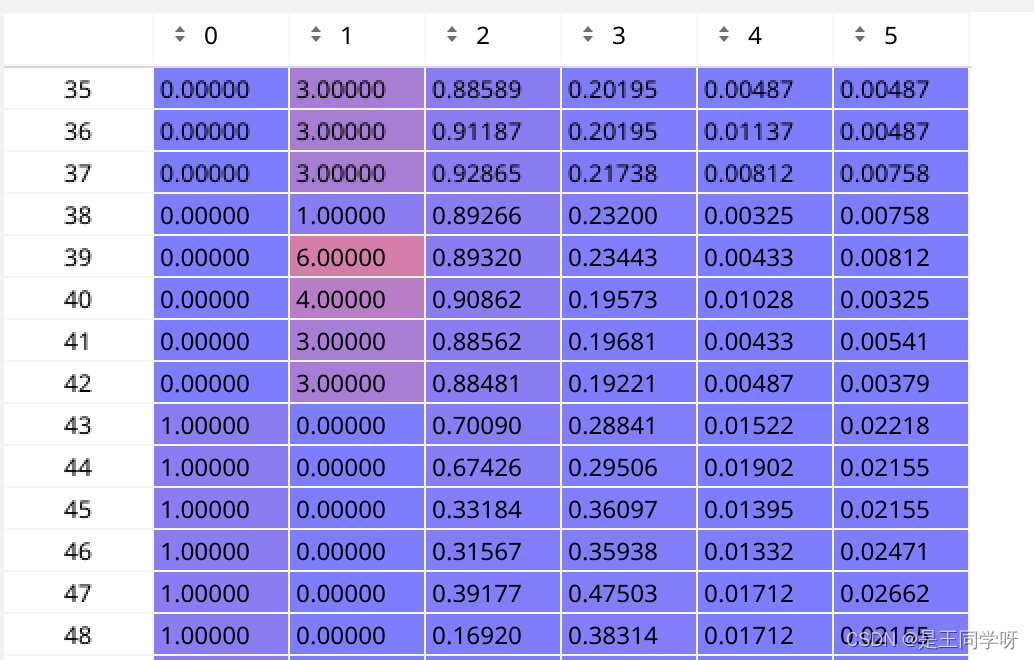
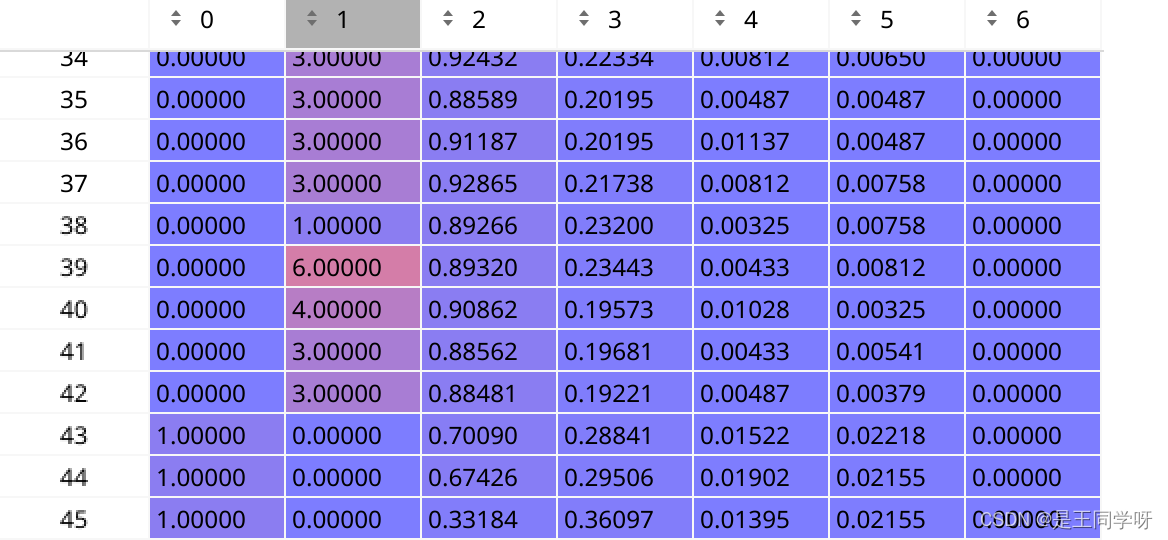
t = t[j] # filter
经过过滤后,全部汇总到来了一起。按照第六列anchor的顺序排列。
扩增正样本
接下来是扩增正样本
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy # 获取x,y
gxi = gain[[2, 3]] - gxy # inverse
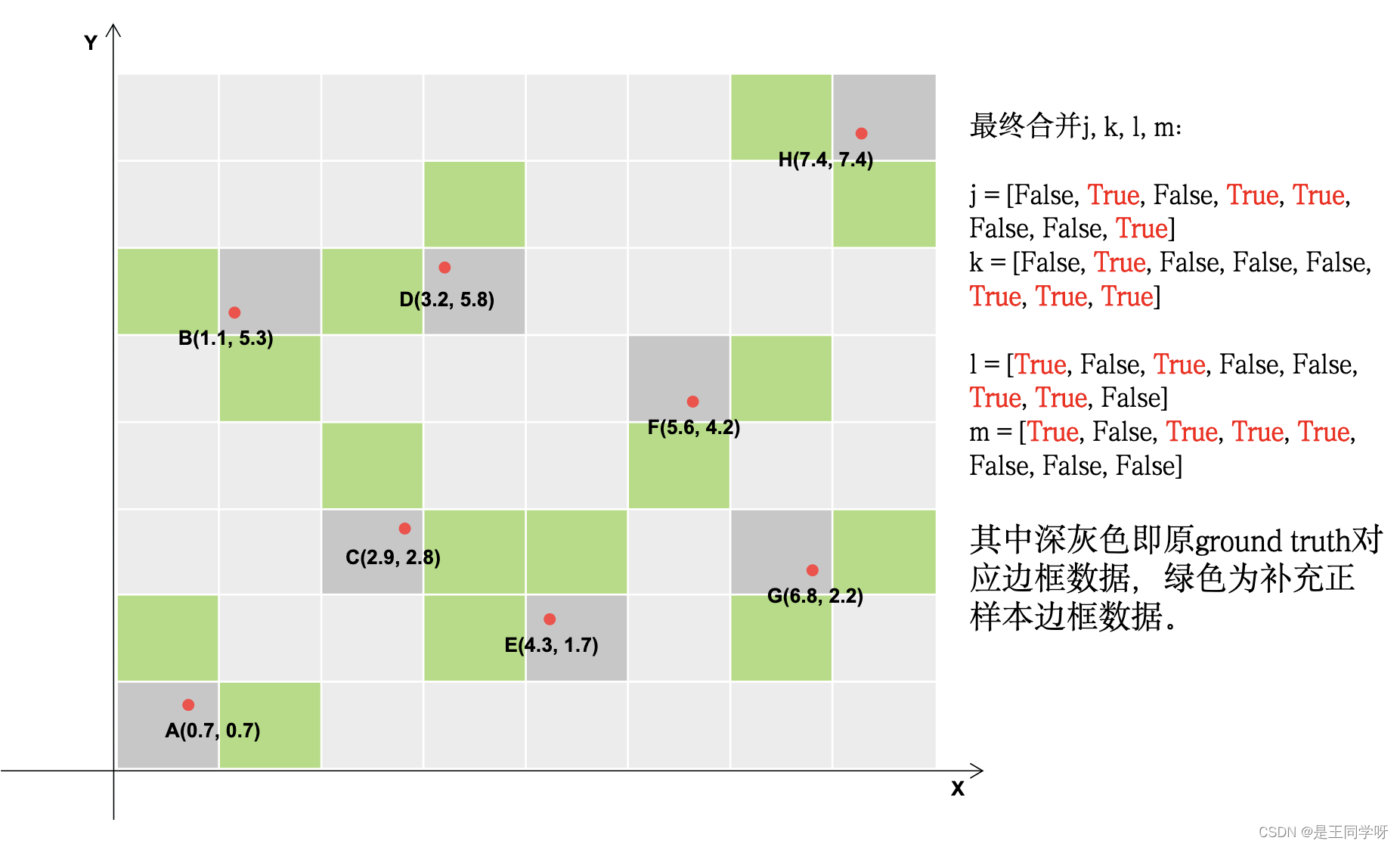
假设最后的特征图大小是8x8,有a-h8个目标边框如下。
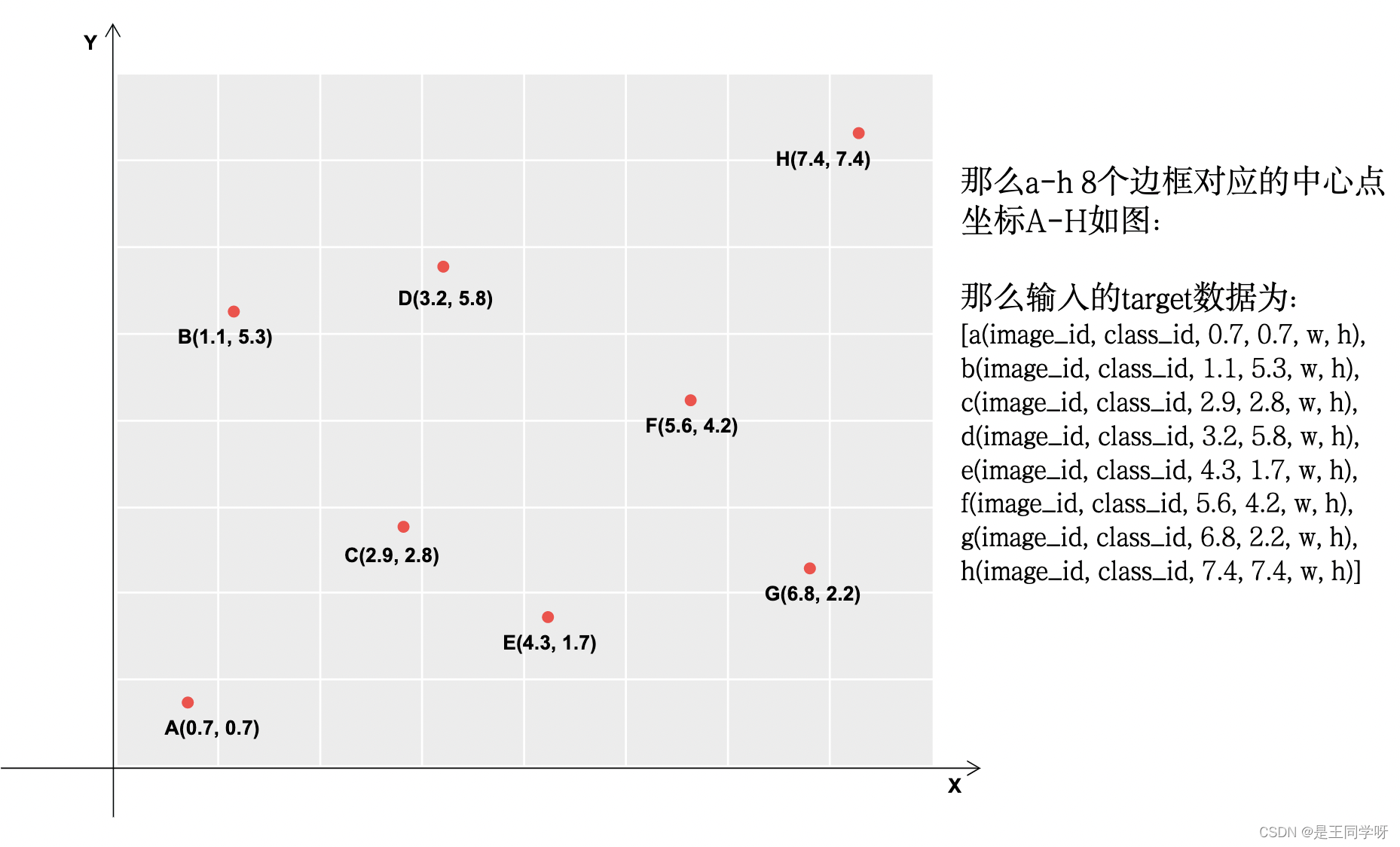
下图中深灰色的表示满足条件的。
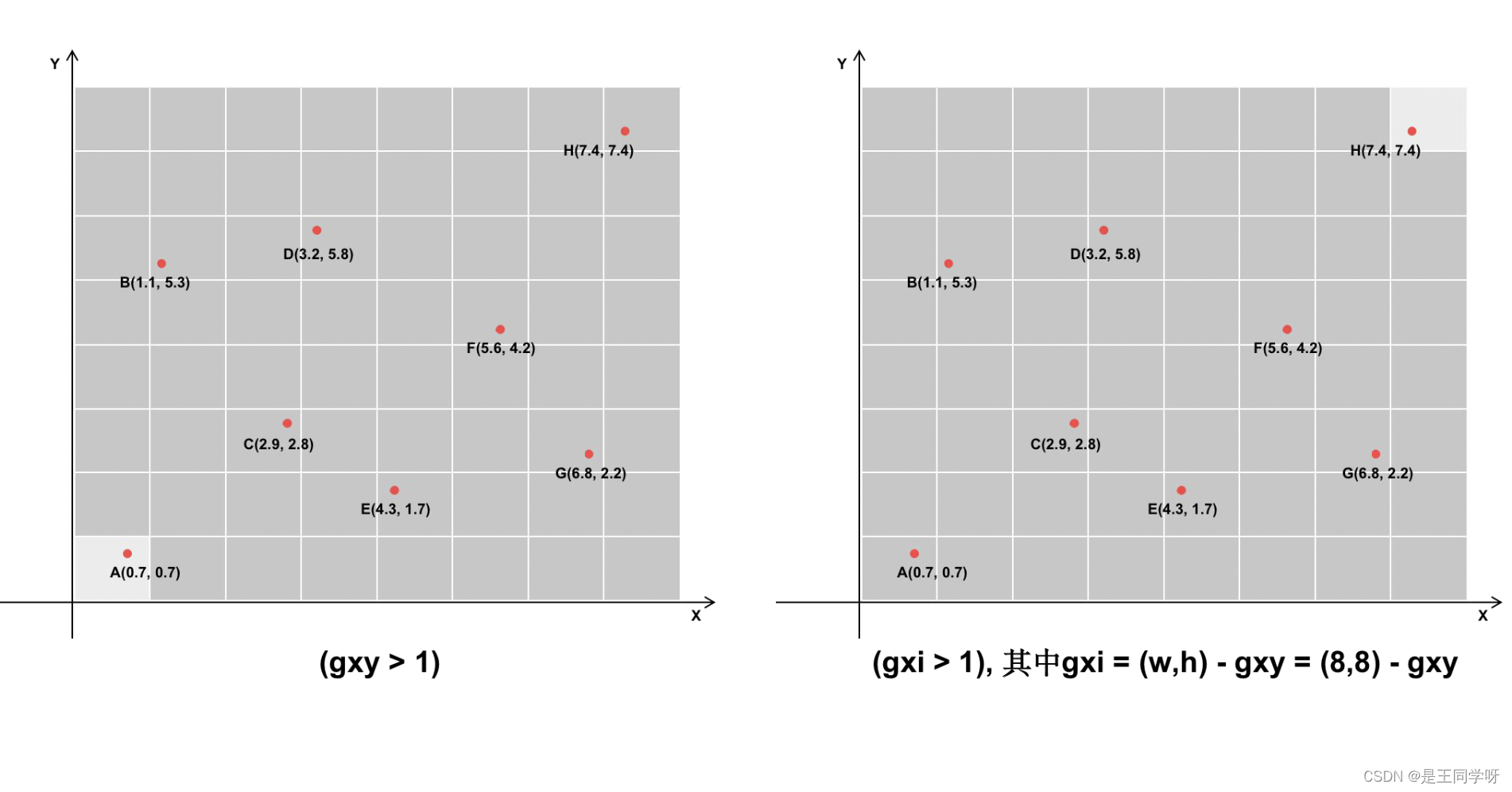
j, k = ((gxy % 1 < g) & (gxy > 1)).T
l, m = ((gxi % 1 < g) & (gxi > 1)).T
gxy % 1 < g和gxi % 1 < g包含两个方向,x和y方向。
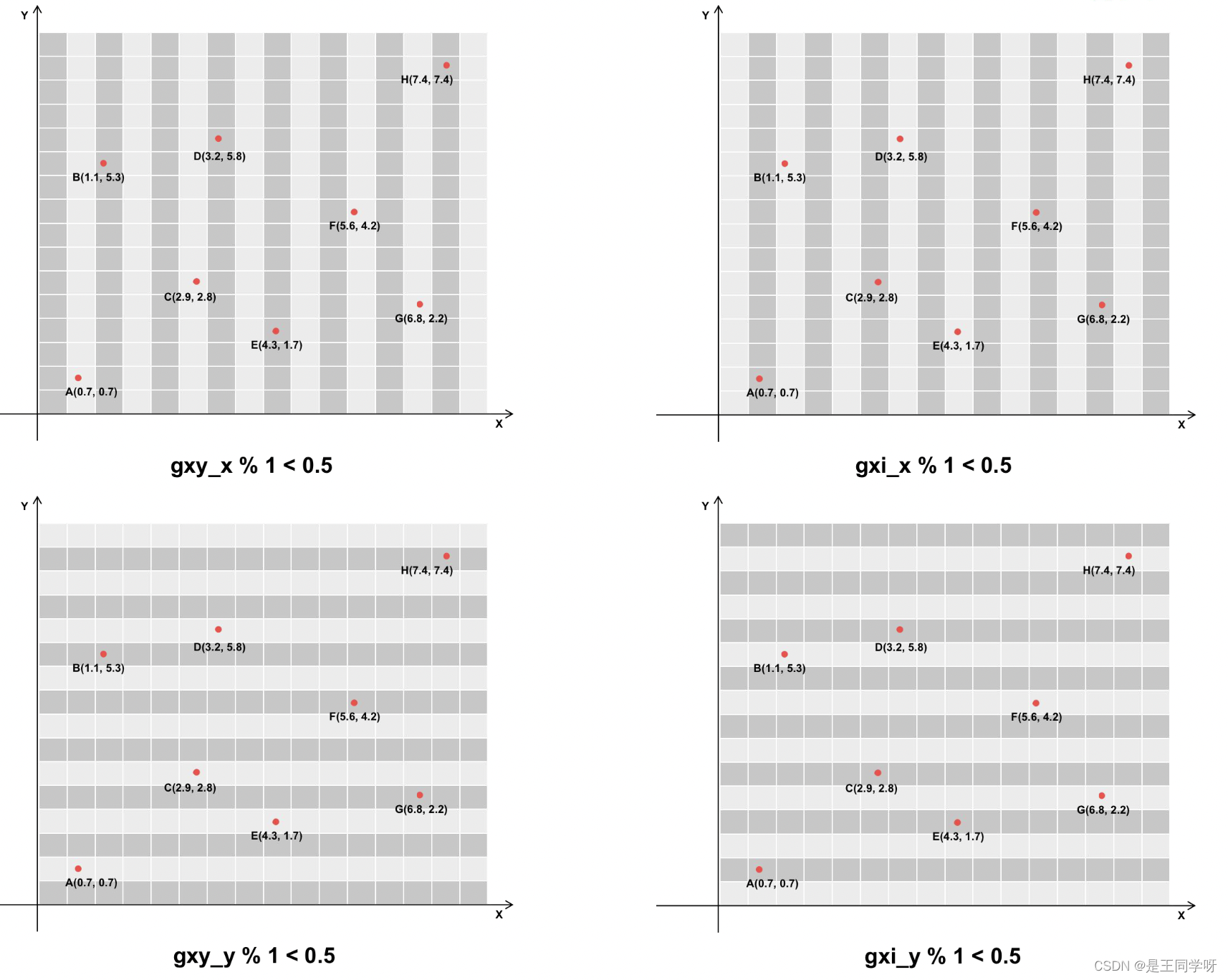
((gxy % 1 < g) & (gxy > 1)) #条件合并得到下图
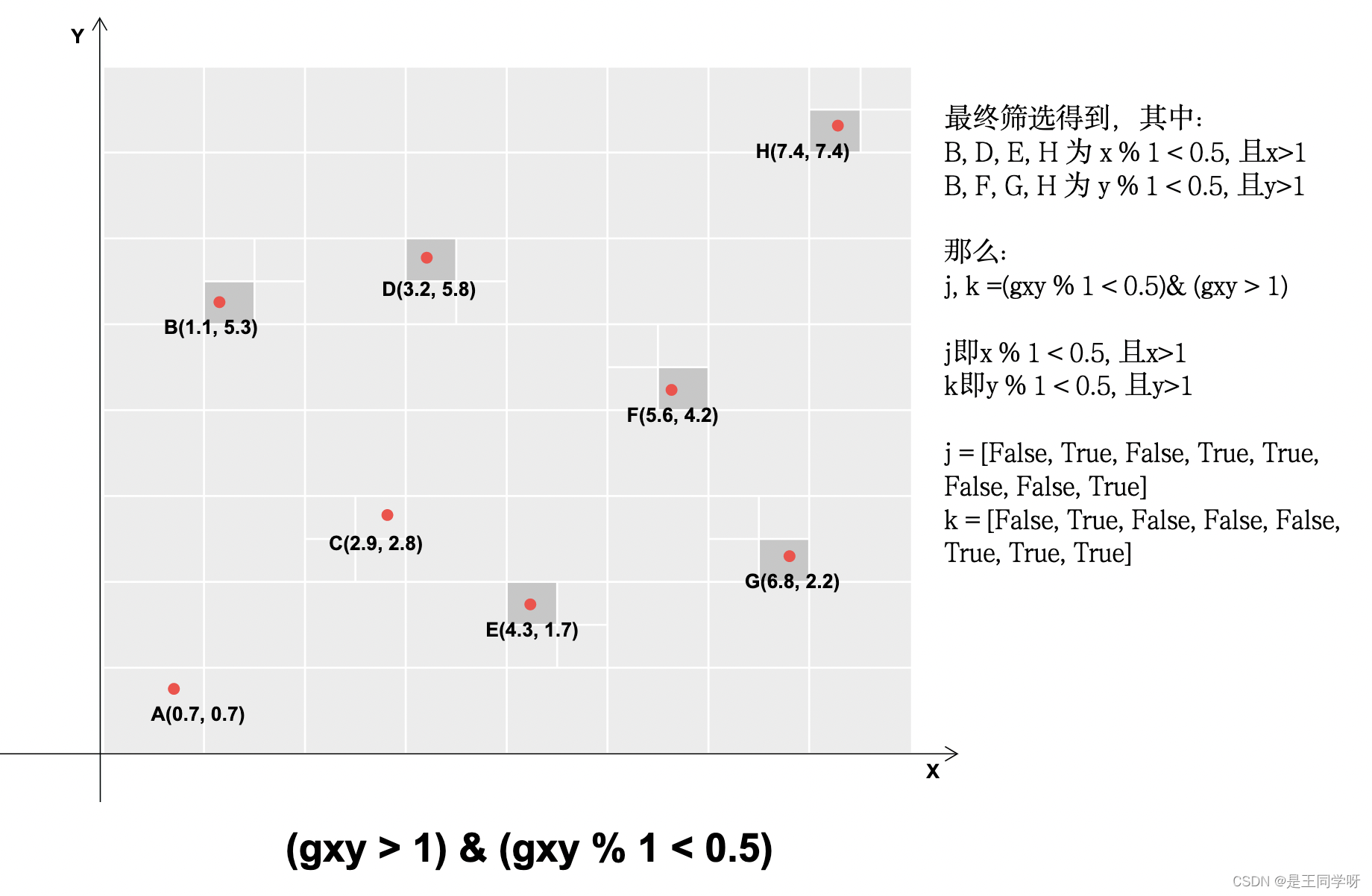
(gxi % 1 < g) & (gxi > 1) # 条件合并得到下图
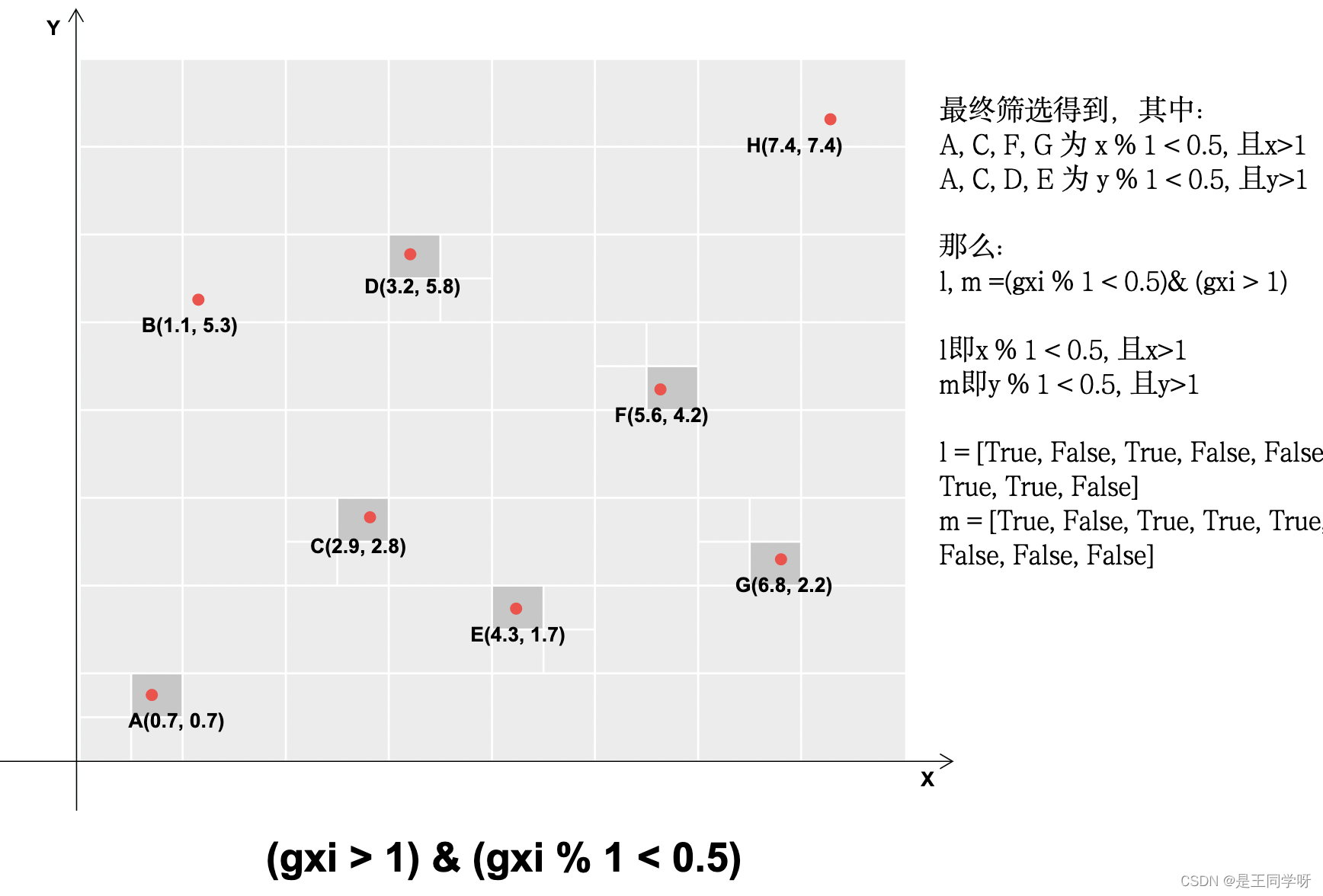
j = torch.stack((torch.ones_like(j), j, k, l, m))
t = t.repeat((5, 1, 1))[j]
# yolov5不仅用目标中心点所在的网格预测该目标,还采用了距目标中心点的最近两个网格
# 所以有五种情况,网格本身,上下左右
|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 这里将t复制5个,然后使用j来过滤 |
| 第一个t是保留经过第一步过滤留下的gtbox,因为上一步里面增加了一个全为true的维度|
| 第二个t保留了靠近方格左边的gtbox, |
| 第三个t保留了靠近方格上方的gtbox, |
| 第四个t保留了靠近方格右边的gtbox, |
| 第五个t保留了靠近方格下边的gtbox, |
|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
offsets = (torch.zeros_like(gxy)[None] + off[:, None])[j] # 生成偏移矩阵
j的第一行全为1,意思是指经过第一步保留下的bbox所在的grid_cell为1.
else:
t = targets[0]
offsets = 0
# Define
bc, gxy, gwh, a = t.chunk(4, 1) # (image, class), grid xy, grid wh, anchors
a, (b, c) = a.long().view(-1), bc.long().T # anchors, image, class
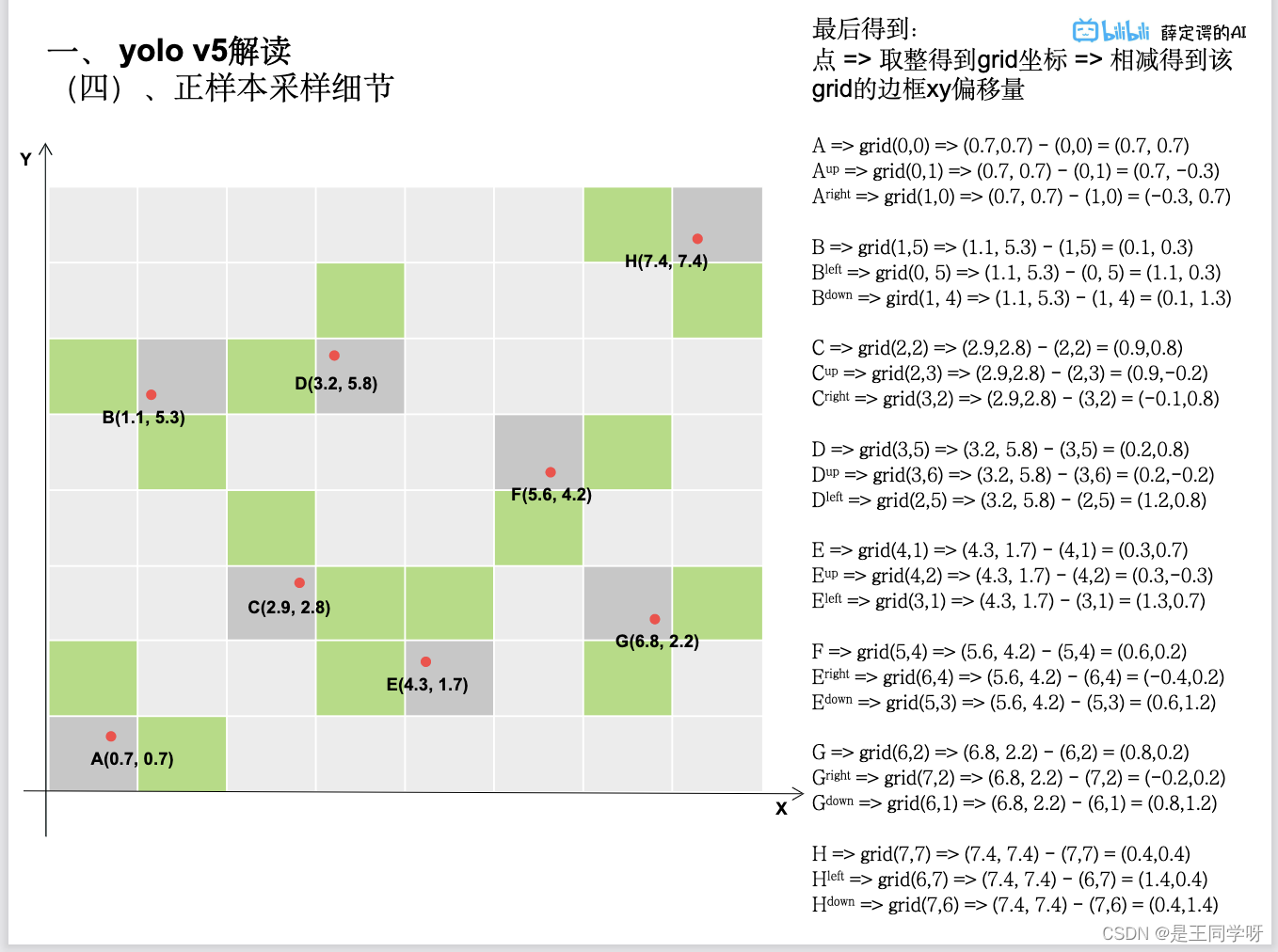
gij = (gxy - offsets).long() #减去偏置,得到更多的正样本所在的网格。
gi, gj = gij.T # grid indices
下面的四张图展示了gij = (gxy - offsets).long() 做了啥。
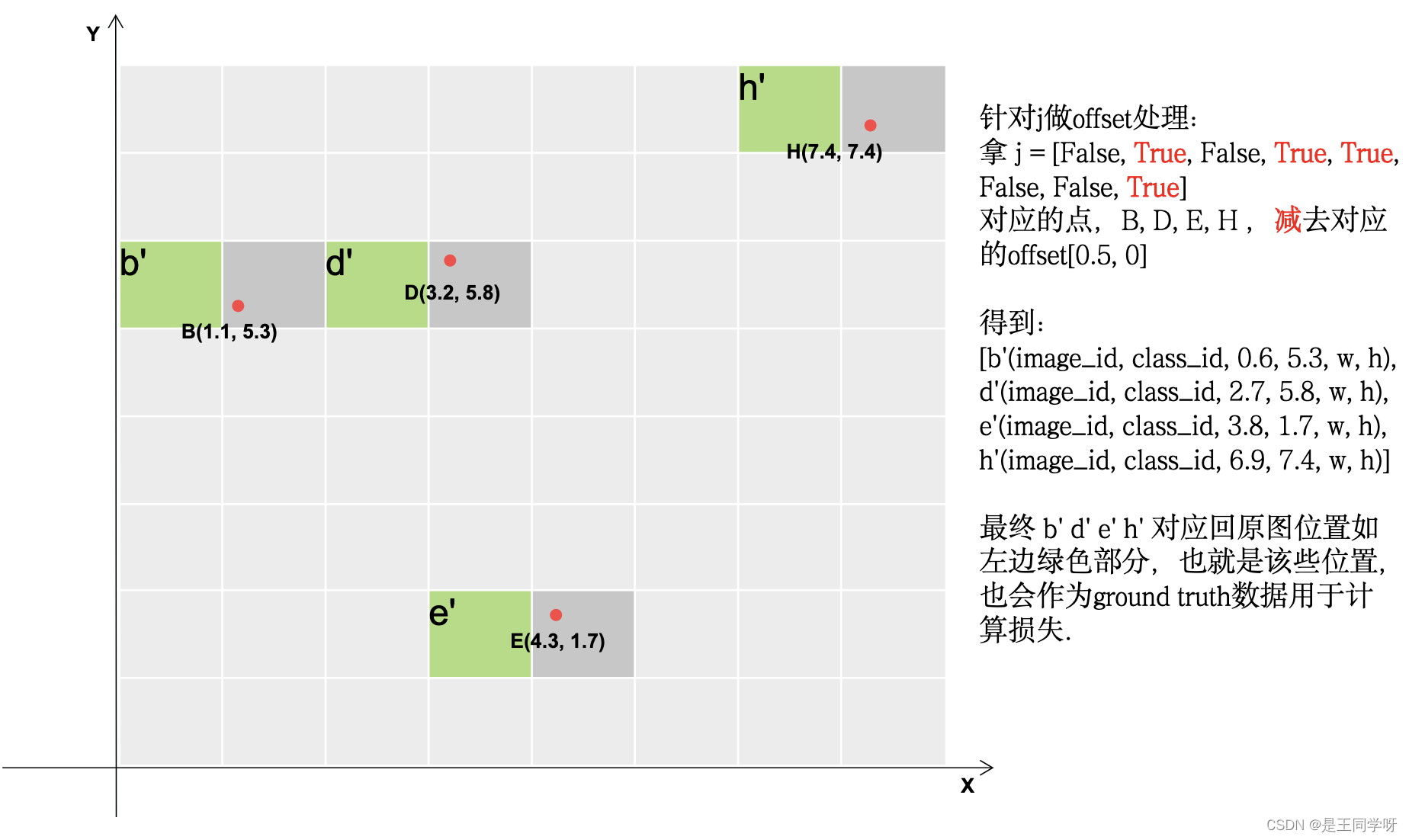
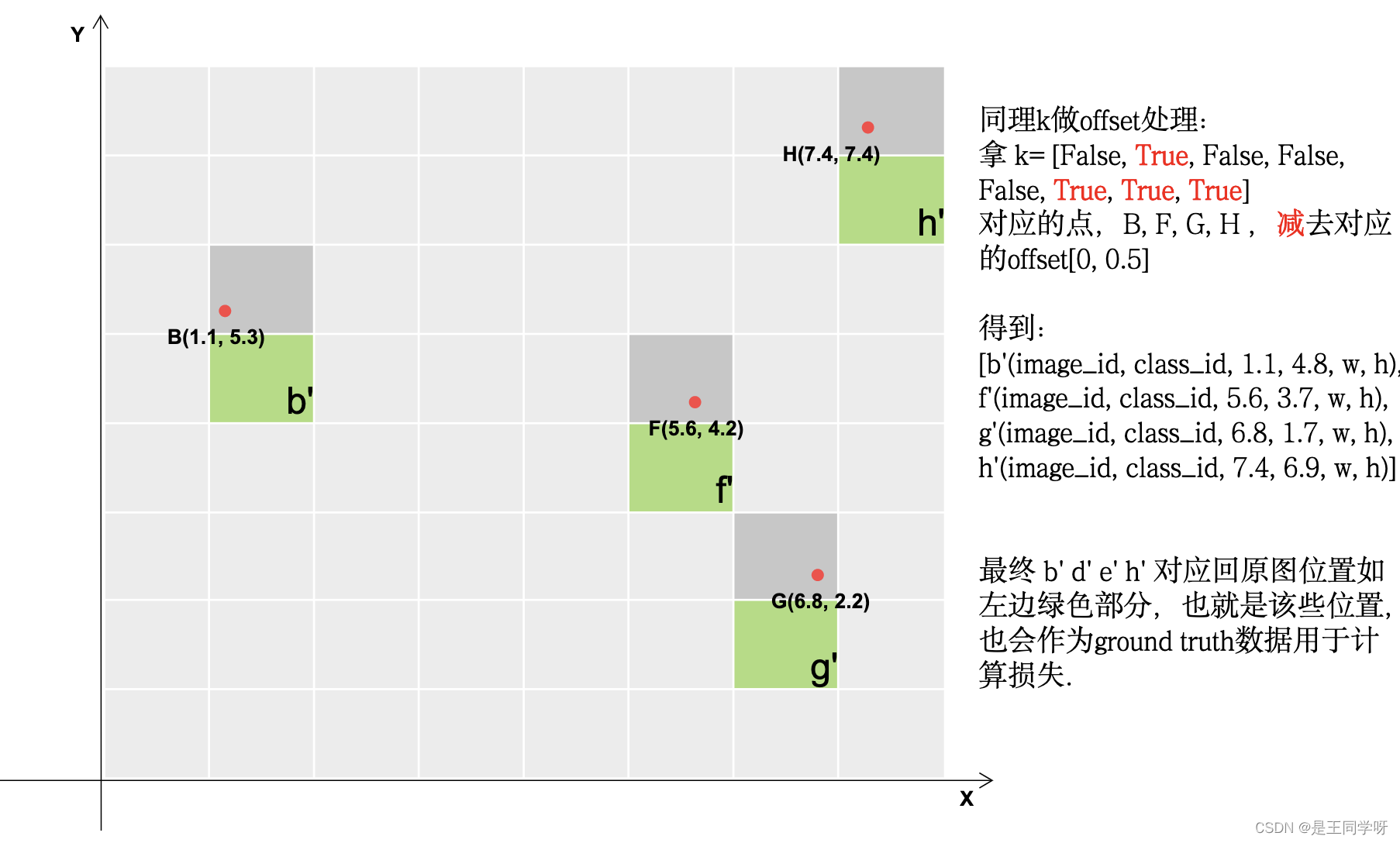
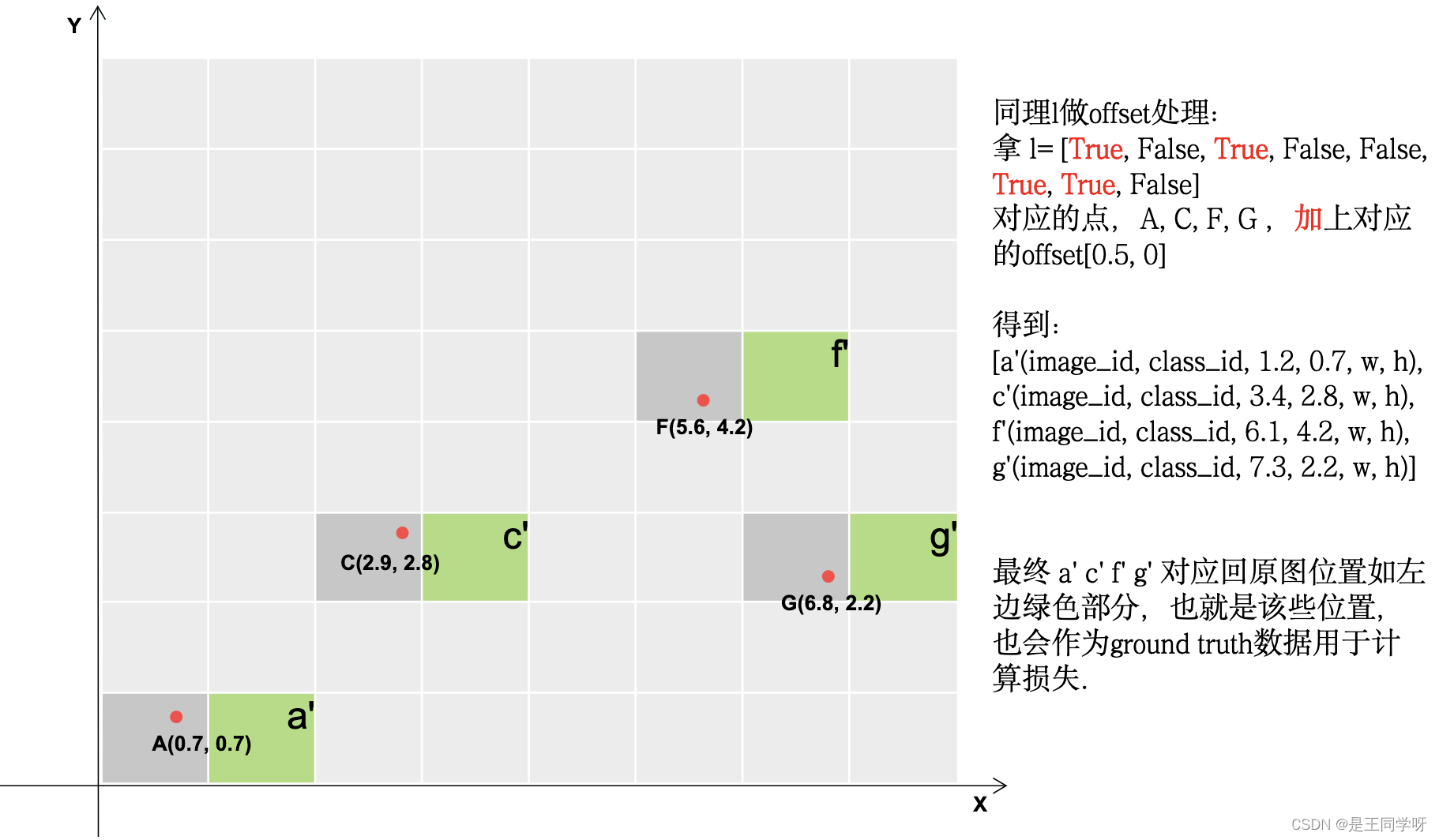
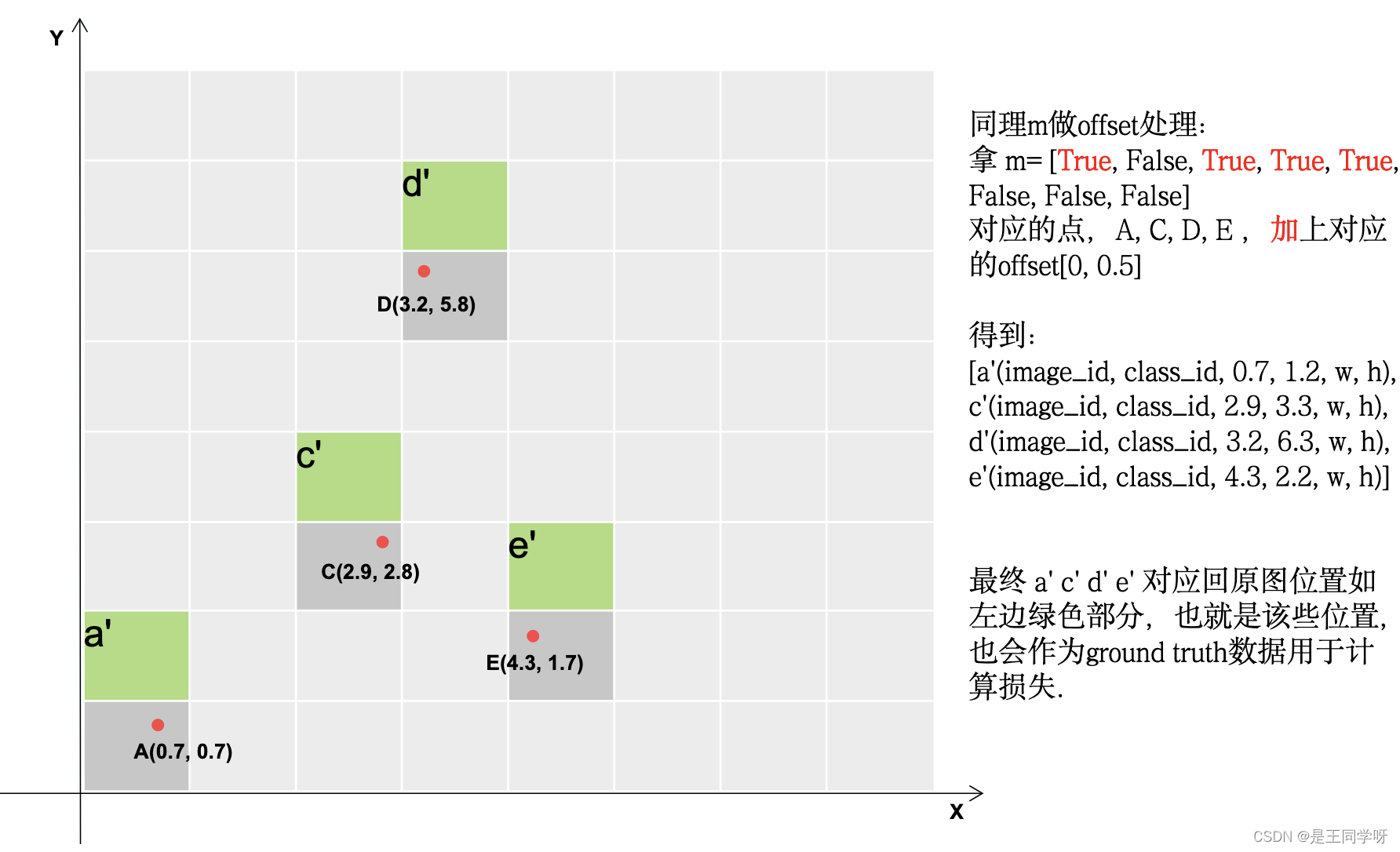
# Append,将对应的结果存储下来。
indices.append((b, a, gj.clamp_(0, gain[3] - 1), gi.clamp_(0, gain[2] - 1))) # image, anchor, grid indices
tbox.append(torch.cat((gxy - gij, gwh), 1)) # box
anch.append(anchors[a]) # anchors
tcls.append(c) # class
tbox.append(torch.cat((gxy - gij, gwh), 1)) # box这句话做的如下:
Reference
- 感谢这位UP主的详细解释,本文的正样本采样细节参考了此UP主的PPT。yolo v5 解读,训练,复现