论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.06434.pdf
一 文章介绍
1.1 Abstract
CNN在无监督学习方面受到的关注较少,作者希望通过此项工作弥合CNN在有监督与无监督学习方面的成功。作者提出了DCGAN的结构并证明了其是无监督学习的有力候选工具。通过对各种图像数据集的训练以及检验,证明了DCGAN中的生成器(G)与判别器(D)可以学习到从对象部分到场景的表示层次。此外,作者将学习到的特征用于新任务,证明了其作为一般图像表示的适用性。
1.2 本文贡献
1.提出并评估了DCGAN拓扑上的一组约束,使其在大多数情况下都能稳定训练。
2.将经过训练的判别器用于图像分类任务,显示出与其他无监督算法的对比结果。
3.将GAN学习的过滤器可视化,并通过经验证明特定的滤波器已经学会绘制特定的图像。
4.展示了生成器具有有趣的向量算术特性,允许对生成样本的许多语义质量进行操作(没懂这句)。
1.3 方法核心
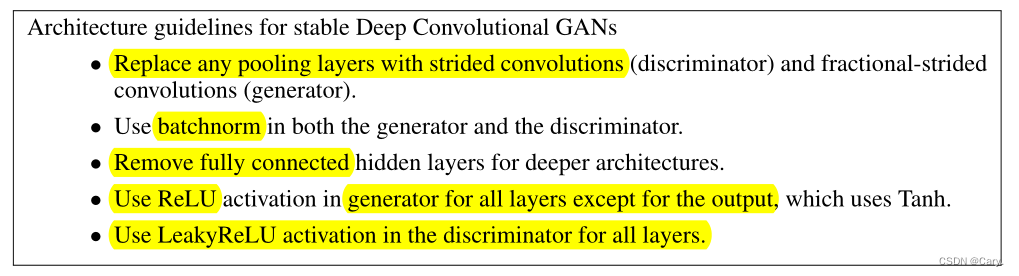
作者经过反复试验以及尝试,对已有的CNN架构做了以下几个方面的修改:
1.全卷积网络:
用步幅卷积(strided convolutions)替代确定性空间池化函数(常见的均值池化及最大池化操作)。让网络自己学习空间下采样(spatial downsampling)。
2.在卷积特征之上消除全连接层
使用全局平均池化(global average pooling)替代全连接层。虽然全局平均池化会降低收敛速度,但是可以提高模型稳定性。
GAN的输入采用均匀分布初始化,对于生成器,开始会使用全连接层(矩阵相乘),然后得到的结果可以reshape成一个4维张量,然后在后面堆叠卷积层即可;对于判别器,最后的卷积层结束后先flatten,再接上sigmoid函数。
3.批归一化(Batch Normalization)
BN是深度学习中十分重要的加速收敛和减缓过拟合的手段。
通过将每一层的输入变换为0均值单位方差,有助于改善初始化不足问题并帮助梯度流向更深的网络。
实践结果表明:将所有层都加上BN操作,对导致样本震荡与模型不稳定,因此只对生成器G和判别器D的输入层使用BN操作。
4.LeakyRelu激活函数
G输出层使用tanh激活函数,其余层使用relu;
D均使用Leaky Relu函数。
1.4 实验及训练
- 作者在三个数据集上进行了实验(LSUN、Imagenet-1k以及一个新建的人脸数据集)。
- 训练中,除了将训练图像缩放到tanh激活函数的[-1,1]的范围内之外,没有对其进行其他操作。
- model采用mini-batch随机梯度下降训练。(mini_batch=128)
- 所有权重均用0均值,0.02的真态分布初始化。
- Leaky Relu激活函数的斜率设置为0.2。
- 使用Adam优化器。
- 调整了超参数,将学习率从原来的0.001改为0.0002。
- 动量项0.9会导致训练过程振动且不稳定,将其降为0.5有助于稳定训练。
二 实验代码
2.1 代码
参考:GitHub - eriklindernoren/PyTorch-GAN: PyTorch implementations of Generative Adversarial Networks.
重点是对于网络的修改:
判别器:
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
def discriminator_block(in_filters, out_filters, bn=True):
block = [nn.Conv2d(in_filters, out_filters, 3, 2, 1), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True), nn.Dropout2d(0.25)]
if bn:
block.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_filters, 0.8))
return block
self.model = nn.Sequential(
*discriminator_block(opt.channels, 16, bn=False),
*discriminator_block(16, 32),
*discriminator_block(32, 64),
*discriminator_block(64, 128),
)
# The height and width of downsampled image
ds_size = opt.img_size // 2 ** 4
self.adv_layer = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128 * ds_size ** 2, 1), nn.Sigmoid())
def forward(self, img):
out = self.model(img)
out = out.view(out.shape[0], -1)
validity = self.adv_layer(out)
return validity生成器:
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.init_size = opt.img_size // 4
self.l1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(opt.latent_dim, 128 * self.init_size ** 2))
self.conv_blocks = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128, 0.8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64, 0.8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, opt.channels, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.Tanh(),
)
def forward(self, z):
out = self.l1(z)
out = out.view(out.shape[0], 128, self.init_size, self.init_size)
img = self.conv_blocks(out)
return img全部代码:
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import math
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torchvision.utils import save_image
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
os.makedirs("images", exist_ok=True)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--n_epochs", type=int, default=200, help="number of epochs of training")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=64, help="size of the batches")
parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=0.0002, help="adam: learning rate")
parser.add_argument("--b1", type=float, default=0.5, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--b2", type=float, default=0.999, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--n_cpu", type=int, default=8, help="number of cpu threads to use during batch generation")
parser.add_argument("--latent_dim", type=int, default=100, help="dimensionality of the latent space")
parser.add_argument("--img_size", type=int, default=32, help="size of each image dimension")
parser.add_argument("--channels", type=int, default=1, help="number of image channels")
parser.add_argument("--sample_interval", type=int, default=400, help="interval between image sampling")
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
cuda = True if torch.cuda.is_available() else False
def weights_init_normal(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__
if classname.find("Conv") != -1:
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02)
elif classname.find("BatchNorm2d") != -1:
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.init_size = opt.img_size // 4
self.l1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(opt.latent_dim, 128 * self.init_size ** 2))
self.conv_blocks = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128, 0.8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64, 0.8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, opt.channels, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.Tanh(),
)
def forward(self, z):
out = self.l1(z)
out = out.view(out.shape[0], 128, self.init_size, self.init_size)
img = self.conv_blocks(out)
return img
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
def discriminator_block(in_filters, out_filters, bn=True):
block = [nn.Conv2d(in_filters, out_filters, 3, 2, 1), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True), nn.Dropout2d(0.25)]
if bn:
block.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_filters, 0.8))
return block
self.model = nn.Sequential(
*discriminator_block(opt.channels, 16, bn=False),
*discriminator_block(16, 32),
*discriminator_block(32, 64),
*discriminator_block(64, 128),
)
# The height and width of downsampled image
ds_size = opt.img_size // 2 ** 4
self.adv_layer = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128 * ds_size ** 2, 1), nn.Sigmoid())
def forward(self, img):
out = self.model(img)
out = out.view(out.shape[0], -1)
validity = self.adv_layer(out)
return validity
# Loss function
adversarial_loss = torch.nn.BCELoss()
# Initialize generator and discriminator
generator = Generator()
discriminator = Discriminator()
if cuda:
generator.cuda()
discriminator.cuda()
adversarial_loss.cuda()
# Initialize weights
generator.apply(weights_init_normal)
discriminator.apply(weights_init_normal)
# Configure data loader
os.makedirs("../../data/mnist", exist_ok=True)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(
"../../data/mnist",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(opt.img_size), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5])]
),
),
batch_size=opt.batch_size,
shuffle=True,
)
# Optimizers
optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
Tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if cuda else torch.FloatTensor
# ----------
# Training
# ----------
dloss_real_list = []
dloss_fake_list = []
d_loss_list = []
g_loss_list = []
for epoch in range(opt.n_epochs):
for i, (imgs, _) in enumerate(dataloader):
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = Variable(Tensor(imgs.shape[0], 1).fill_(1.0), requires_grad=False)
fake = Variable(Tensor(imgs.shape[0], 1).fill_(0.0), requires_grad=False)
# Configure input
real_imgs = Variable(imgs.type(Tensor))
# -----------------
# Train Generator
# -----------------
optimizer_G.zero_grad()
# Sample noise as generator input
z = Variable(Tensor(np.random.normal(0, 1, (imgs.shape[0], opt.latent_dim))))
# Generate a batch of images
gen_imgs = generator(z)
# Loss measures generator's ability to fool the discriminator
g_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs), valid)
g_loss_list.append(g_loss.item())
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_G.step()
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
optimizer_D.zero_grad()
# Measure discriminator's ability to classify real from generated samples
real_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(real_imgs), valid)
dloss_real_list.append(real_loss.item())
fake_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs.detach()), fake)
dloss_fake_list.append(fake_loss.item())
d_loss = (real_loss + fake_loss) / 2
d_loss_list.append(d_loss.item())
d_loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
print(
"[Epoch %d/%d] [Batch %d/%d] [D loss: %f] [G loss: %f]"
% (epoch, opt.n_epochs, i, len(dataloader), d_loss.item(), g_loss.item())
)
batches_done = epoch * len(dataloader) + i
if batches_done % opt.sample_interval == 0:
save_image(gen_imgs.data[:25], "images/%d.png" % batches_done, nrow=5, normalize=True)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(2,2,1)
plt.plot(dloss_real_list)
plt.ylabel("dloss_real")
plt.subplot(2,2,2)
plt.plot(dloss_fake_list)
plt.ylabel("dloss_fake")
plt.subplot(2,2,3)
plt.plot(d_loss_list)
plt.ylabel("dloss(real+fake)/2")
plt.subplot(2,2,4)
plt.plot(g_loss_list)
plt.ylabel("gloss")
plt.savefig('./loss_image/loss.jpg')
plt.show()输出:
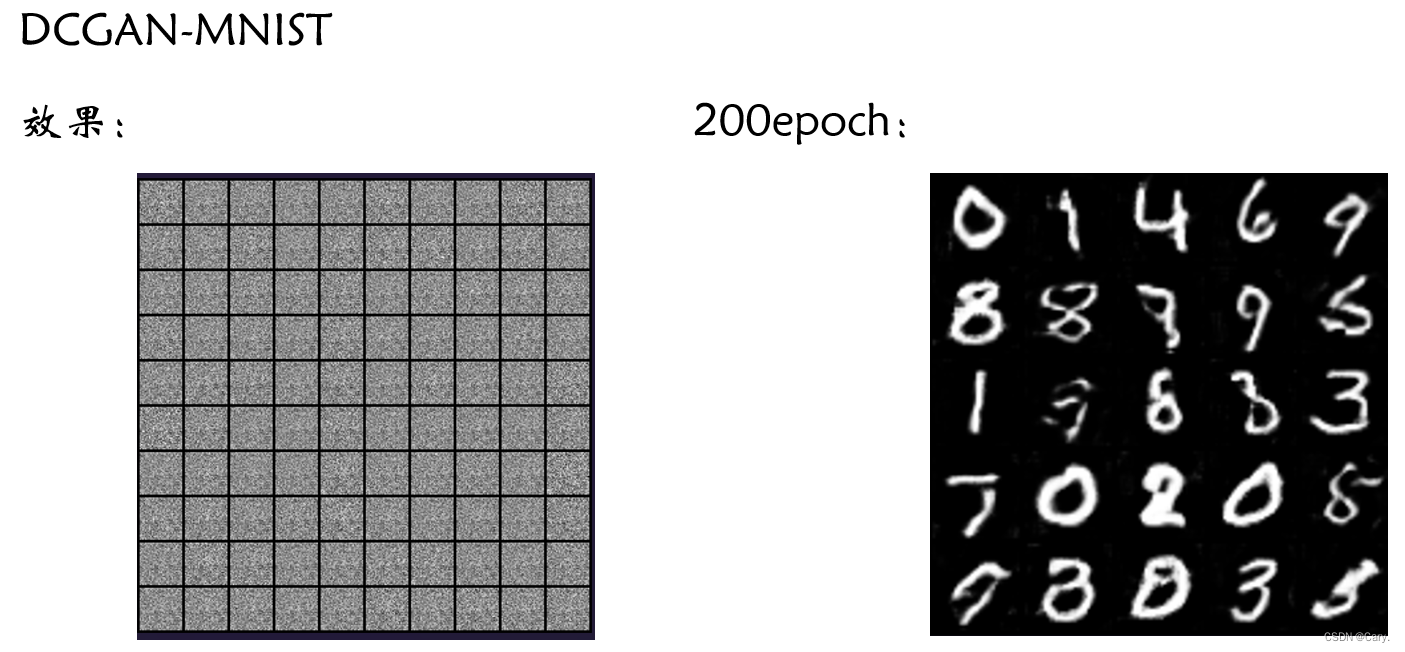
2.2 代码阅读
主要是一些生成器判别器中出现的函数:
1 torch.nn.BatchNorm2d()
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True, device=None, dtype=None)
如论文 Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift 中所述,在 4D 输入(具有附加通道维度的小批量 2D 输入)上应用 Batch Normalization。
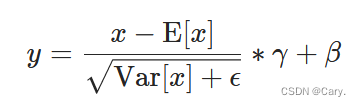
均值和标准差是在 mini-batch 上按维度计算的,γ 和 β 是大小为 C 的可学习参数向量(其中 C 是输入大小)。默认情况下,γ的元素设置为 1,β的元素设置为 0。标准偏差通过有偏估计器计算,相当于 torch.var(input, unbiased=False)。?
同样默认情况下,在训练期间,该层会继续对其计算的均值和方差进行估计,然后在评估期间将其用于归一化。运行估计保持默认动量 0.1。
如果 track_running_stats 设置为 False,则该层不会继续运行估计,并且在评估期间也会使用批处理统计信息。
因为批量归一化是在 C 维度上完成的,计算 (N, H, W) 切片的统计信息,所以将其称为空间批量归一化。
参数:
- num_features:C 来自大小为 (N,C,H,W)的预期输入。
- eps:加到分母上的值,以保证数值稳定性。默认值:1e-5。
- momentum:用于 running_mean 和 running_var 计算的值。对于累积移动平均(即简单平均),可以设置为无。默认值:0.1。
- affine:一个布尔值,当设置为 True 时,此模块具有可学习的仿射参数。默认值:True。
- track_running_stats:一个布尔值,当设置为 True 时,此模块跟踪运行均值和方差,当设置为 False 时,此模块不跟踪此类统计信息,并将统计缓冲区 running_mean 和 running_var 初始化为 None。当这些缓冲区为 None 时,此模块始终使用批处理统计信息。在训练和评估模式下。默认值:True。
shape:
input:(N,C,H,W)
output:(N,C,H,W)
example:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 具有可学习的参数
m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100)
# 无可学习的参数
m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100, affine=False)
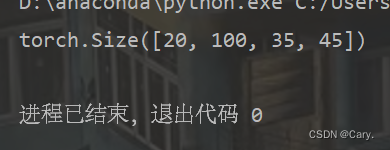
input = torch.randn(20, 100, 35, 45)
output = m(input)
print(output.size())输出:
其他函数下一篇再写,该干饭了~
?
?