前言
为了了解模型的泛化能力,即判断模型的好坏,我们需要用某个指标来衡量,有了评价指标,就可以对比不同模型的优劣,并通过这个指标来进一步调参优化模型。对于分类和回归两类监督模型,分别有各自的评判标准。
不同的问题和不同的数据集都会有不同的模型评价指标,比如分类问题,数据集类别平衡的情况下可以使用准确率作为评价指标,但是现实中的数据集几乎都是类别不平衡的,所以一般都是采用 AP 作为分类的评价指标,分别计算每个类别的 AP,再计算mAP。
一,精确率、召回率与F1
1.1,准确率
准确率(精度) – Accuracy,预测正确的结果占总样本的百分比,定义如下:
准确率 = ( T P + T N ) / ( T P + T N + F P + F N ) 准确率 = (TP+TN)/(TP+TN+FP+FN) 准确率=(TP+TN)/(TP+TN+FP+FN)
错误率和精度虽然常用,但是并不能满足所有任务需求。以西瓜问题为例,假设瓜农拉来一车西瓜,我们用训练好的模型对西瓜进行判别,现如精度只能衡量有多少比例的西瓜被我们判断类别正确(两类:好瓜、坏瓜)。但是若我们更加关心的是“挑出的西瓜中有多少比例是好瓜”,或者”所有好瓜中有多少比例被挑出来“,那么精度和错误率这个指标显然是不够用的。
虽然准确率可以判断总的正确率,但是在样本不平衡的情况下,并不能作为很好的指标来衡量结果。举个简单的例子,比如在一个总样本中,正样本占 90%,负样本占 10%,样本是严重不平衡的。对于这种情况,我们只需要将全部样本预测为正样本即可得到 90% 的高准确率,但实际上我们并没有很用心的分类,只是随便无脑一分而已。这就说明了:由于样本不平衡的问题,导致了得到的高准确率结果含有很大的水分。即如果样本不平衡,准确率就会失效。
1.2,精确率、召回率
精确率(查准率)P、召回率(查全率)R 的计算涉及到混淆矩阵的定义,混淆矩阵表格如下:
| 名称 | 定义 |
|---|---|
True Positive(真正例, TP) | 将正类预测为正类数 |
True Negative(真负例, TN) | 将负类预测为负类数 |
False Positive(假正例, FP) | 将负类预测为正类数 → 误报 (Type I error) |
False Negative(假负例子, FN) | 将正类预测为负类数 → 漏报 (Type II error) |
查准率与查全率计算公式:
- 查准率(精确率) P = T P / ( T P + F P ) P = TP/(TP+FP) P=TP/(TP+FP)
- 查全率(召回率) R = T P / ( T P + F N ) R = TP/(TP+FN) R=TP/(TP+FN)
精准率和准确率看上去有些类似,但是完全不同的两个概念。精准率代表对正样本结果中的预测准确程度,而准确率则代表整体的预测准确程度,既包括正样本,也包括负样本。
精确率描述了模型有多准,即在预测为正例的结果中,有多少是真正例;召回率则描述了模型有多全,即在为真的样本中,有多少被我们的模型预测为正例。精确率和召回率的区别在于分母不同,一个分母是预测为正的样本数,另一个是原来样本中所有的正样本数。
1.3,F1 分数
如果想要找到 P P P 和 R R R 二者之间的一个平衡点,我们就需要一个新的指标: F 1 F1 F1 分数。 F 1 F1 F1 分数同时考虑了查准率和查全率,让二者同时达到最高,取一个平衡。 F 1 F1 F1 计算公式如下:
这里的 F 1 F1 F1 计算是针对二分类模型,多分类任务的 F 1 F1 F1 的计算请看下面。
F 1 = 2 × P × R P + R = 2 × T P 样例总数 + T P ? T N F1 = \frac{2\times P\times R}{P+R} = \frac{2\times TP}{样例总数+TP-TN} F1=P+R2×P×R?=样例总数+TP?TN2×TP?
F 1 F1 F1 度量的一般形式: F β F_{\beta} Fβ?,能让我们表达出对查准率/查全率的偏见, F β F_{\beta} Fβ? 计算公式如下:
F β = 1 + β 2 × P × R ( β 2 × P ) + R F_{\beta} = \frac{1+\beta^{2}\times P\times R}{(\beta^{2}\times P)+R} Fβ?=(β2×P)+R1+β2×P×R?
其中 β > 1 \beta >1 β>1 对查全率有更大影响, β < 1 \beta < 1 β<1 对查准率有更大影响。
不同的计算机视觉问题,对两类错误有不同的偏好,常常在某一类错误不多于一定阈值的情况下,努力减少另一类错误。在目标检测中,mAP(mean Average Precision)作为一个统一的指标将这两种错误兼顾考虑。
很多时候我们会有多个混淆矩阵,例如进行多次训练/测试,每次都能得到一个混淆矩阵;或者是在多个数据集上进行训练/测试,希望估计算法的”全局“性能;又或者是执行多分类任务,每两两类别的组合都对应一个混淆矩阵;…总而来说,我们希望能在 n n n 个二分类混淆矩阵上综合考虑查准率和查全率。
一种直接的做法是先在各混淆矩阵上分别计算出查准率和查全率,记为
(
P
1
,
R
1
)
,
(
P
2
,
R
2
)
,
.
.
.
,
(
P
n
,
R
n
)
(P_1,R_1),(P_2,R_2),...,(P_n,R_n)
(P1?,R1?),(P2?,R2?),...,(Pn?,Rn?) 然后取平均,这样得到的是”宏查准率(Macro-P)“、”宏查准率(Macro-R)“及对应的”宏
F
1
F1
F1(Macro-F1)“:
M
a
c
r
o
?
P
=
1
n
∑
i
=
1
n
P
i
Macro\ P = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}P_i
Macro?P=n1?i=1∑n?Pi?
M
a
c
r
o
?
R
=
1
n
∑
i
=
1
n
R
i
Macro\ R = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}R_i
Macro?R=n1?i=1∑n?Ri?
M
a
c
r
o
?
F
1
=
2
×
M
a
c
r
o
?
P
×
M
a
c
r
o
?
R
M
a
c
r
o
?
P
+
M
a
c
r
o
?
R
Macro\ F1 = \frac{2 \times Macro\ P\times Macro\ R}{Macro\ P + Macro\ R}
Macro?F1=Macro?P+Macro?R2×Macro?P×Macro?R?
另一种做法是将各混淆矩阵对应元素进行平均,得到
T
P
、
F
P
、
T
N
、
F
N
TP、FP、TN、FN
TP、FP、TN、FN 的平均值,再基于这些平均值计算出”微查准率“(Micro-P)、”微查全率“(Micro-R)和”微
F
1
F1
F1“(Mairo-F1)
M
i
c
r
o
?
P
=
T
P
 ̄
T
P
 ̄
+
F
P
 ̄
Micro\ P = \frac{\overline{TP}}{\overline{TP}+\overline{FP}}
Micro?P=TP+FPTP?
M
i
c
r
o
?
R
=
T
P
 ̄
T
P
 ̄
+
F
N
 ̄
Micro\ R = \frac{\overline{TP}}{\overline{TP}+\overline{FN}}
Micro?R=TP+FNTP?
M
i
c
r
o
?
F
1
=
2
×
M
i
c
r
o
?
P
×
M
i
c
r
o
?
R
M
a
c
r
o
P
+
M
i
c
r
o
?
R
Micro\ F1 = \frac{2 \times Micro\ P\times Micro\ R}{MacroP+Micro\ R}
Micro?F1=MacroP+Micro?R2×Micro?P×Micro?R?
1.4,PR 曲线
精准率和召回率的关系可以用一个 P-R 图来展示,以查准率 P 为纵轴、查全率 R 为横轴作图,就得到了查准率-查全率曲线,简称 P-R 曲线,PR 曲线下的面积定义为 AP:
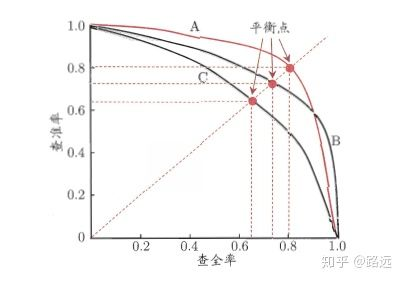
1.4.1,如何理解 P-R 曲线
可以从排序型模型或者分类模型理解。以逻辑回归举例,逻辑回归的输出是一个 0 到 1 之间的概率数字,因此,如果我们想要根据这个概率判断用户好坏的话,我们就必须定义一个阈值 。通常来讲,逻辑回归的概率越大说明越接近 1,也就可以说他是坏用户的可能性更大。比如,我们定义了阈值为 0.5,即概率小于 0.5 的我们都认为是好用户,而大于 0.5 都认为是坏用户。因此,对于阈值为 0.5 的情况下,我们可以得到相应的一对查准率和查全率。
但问题是:这个阈值是我们随便定义的,我们并不知道这个阈值是否符合我们的要求。 因此,为了找到一个最合适的阈值满足我们的要求,我们就必须遍历 0 到 1 之间所有的阈值,而每个阈值下都对应着一对查准率和查全率,从而我们就得到了 PR 曲线。
最后如何找到最好的阈值点呢? 首先,需要说明的是我们对于这两个指标的要求:我们希望查准率和查全率同时都非常高。 但实际上这两个指标是一对矛盾体,无法做到双高。图中明显看到,如果其中一个非常高,另一个肯定会非常低。选取合适的阈值点要根据实际需求,比如我们想要高的查全率,那么我们就会牺牲一些查准率,在保证查全率最高的情况下,查准率也不那么低。。
1.5,ROC 曲线与 AUC 面积
PR曲线是以Recall为横轴,Precision为纵轴;而ROC曲线则是以FPR为横轴,TPR为纵轴**。P-R 曲线越靠近右上角性能越好。PR曲线的两个指标都聚焦于正例PR曲线展示的是Precision vs Recall的曲线,ROC曲线展示的是FPR(x 轴:False positive rate) vsTPR(True positive rate, TPR)曲线。
- ROC 曲线
- AUC 面积
二,AP 与 mAP
2.1,AP 与 mAP 指标理解
AP 衡量的是训练好的模型在每个类别上的好坏,mAP 衡量的是模型在所有类别上的好坏,得到 AP 后 mAP 的计算就变得很简单了,就是取所有 AP 的平均值。AP 的计算公式比较复杂(所以单独作一章节内容),详细内容参考下文。
mAP 这个术语有不同的定义。此度量指标通常用于信息检索、图像分类和目标检测领域。然而这两个领域计算 mAP 的方式却不相同。这里我们只谈论目标检测中的 mAP 计算方法。
mAP 常作为目标检测算法的评价指标,具体来说就是,对于每张图片检测模型会输出多个预测框(远超真实框的个数),我们使用 IoU (Intersection Over Union,交并比)来标记预测框是否预测准确。标记完成后,随着预测框的增多,查全率 R 总会上升,在不同查全率 R 水平下对准确率 P 做平均,即得到 AP,最后再对所有类别按其所占比例做平均,即得到 mAP 指标。
2.2,近似计算AP
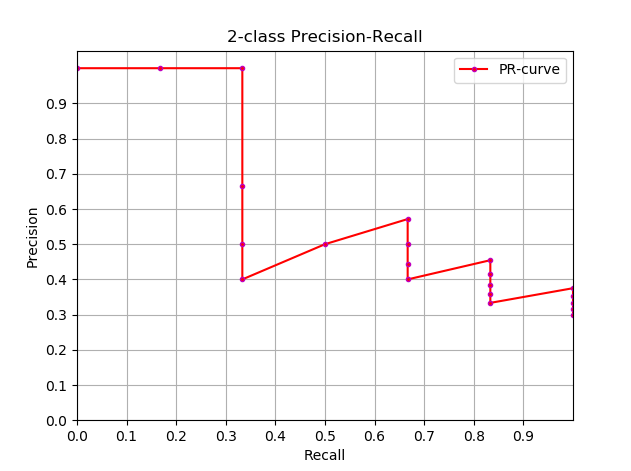
知道了AP 的定义,下一步就是理解AP计算的实现,理论上可以通过积分来计算AP,公式如下:
A
P
=
∫
0
1
P
(
r
)
d
r
AP=\int_0^1 P(r) dr
AP=∫01?P(r)dr
但通常情况下都是使用近似或者插值的方法来计算
A
P
AP
AP。
A P = ∑ k = 1 N P ( k ) Δ r ( k ) AP = \sum_{k=1}^{N}P(k)\Delta r(k) AP=k=1∑N?P(k)Δr(k)
- 近似计算
A
P
AP
AP (
approximated average precision),这种计算方式是approximated形式的; - 很显然位于一条竖直线上的点对计算 A P AP AP 没有贡献;
- 这里 N N N 为数据总量, k k k 为每个样本点的索引, Δ r ( k ) = r ( k ) ? r ( k ? 1 ) Δr(k)=r(k)?r(k?1) Δr(k)=r(k)?r(k?1)。
近似计算 AP 和绘制 PR 曲线代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class_names = ["car", "pedestrians", "bicycle"]
def draw_PR_curve(predict_scores, eval_labels, name, cls_idx=1):
"""calculate AP and draw PR curve, there are 3 types
Parameters:
@all_scores: single test dataset predict scores array, (-1, 3)
@all_labels: single test dataset predict label array, (-1, 3)
@cls_idx: the serial number of the AP to be calculated, example: 0,1,2,3...
"""
# print('sklearn Macro-F1-Score:', f1_score(predict_scores, eval_labels, average='macro'))
global class_names
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, figsize=(15, 10))
# Rank the predicted scores from large to small, extract their corresponding index(index number), and generate an array
idx = predict_scores[:, cls_idx].argsort()[::-1]
eval_labels_descend = eval_labels[idx]
pos_gt_num = np.sum(eval_labels == cls_idx) # number of all gt
predict_results = np.ones_like(eval_labels)
tp_arr = np.logical_and(predict_results == cls_idx, eval_labels_descend == cls_idx) # ndarray
fp_arr = np.logical_and(predict_results == cls_idx, eval_labels_descend != cls_idx)
tp_cum = np.cumsum(tp_arr).astype(float) # ndarray, Cumulative sum of array elements.
fp_cum = np.cumsum(fp_arr).astype(float)
precision_arr = tp_cum / (tp_cum + fp_cum) # ndarray
recall_arr = tp_cum / pos_gt_num
ap = 0.0
prev_recall = 0
for p, r in zip(precision_arr, recall_arr):
ap += p * (r - prev_recall)
# pdb.set_trace()
prev_recall = r
print("------%s, ap: %f-----" % (name, ap))
fig_label = '[%s, %s] ap=%f' % (name, class_names[cls_idx], ap)
ax.plot(recall_arr, precision_arr, label=fig_label)
ax.legend(loc="lower left")
ax.set_title("PR curve about class: %s" % (class_names[cls_idx]))
ax.set(xticks=np.arange(0., 1, 0.05), yticks=np.arange(0., 1, 0.05))
ax.set(xlabel="recall", ylabel="precision", xlim=[0, 1], ylim=[0, 1])
fig.savefig("./pr-curve-%s.png" % class_names[cls_idx])
plt.close(fig)
2.3,插值计算 AP
插值计算(Interpolated average precision)
A
P
AP
AP 的公式的演变过程这里不做讨论,详情可以参考这篇文章,我这里的公式和图也是参考此文章的。11 点插值计算方式计算
A
P
AP
AP 公式如下:
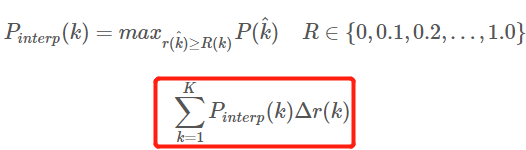
- 这是通常意义上的
11points_Interpolated形式的AP,选取固定的 0 , 0.1 , 0.2 , … , 1.0 {0,0.1,0.2,…,1.0} 0,0.1,0.2,…,1.011个阈值,这个在 PASCAL2007 中使用 - 这里因为参与计算的只有
11个点,所以 K = 11 K=11 K=11,称为 11 points_Interpolated, k k k 为阈值索引 -
P
i
n
t
e
r
p
(
k
)
P_{interp}(k)
Pinterp?(k) 取第
k
k
k 个阈值所对应的样本点之后的样本中的最大值,只不过这里的阈值被限定在了
0
,
0.1
,
0.2
,
…
,
1.0
{0,0.1,0.2,…,1.0}
0,0.1,0.2,…,1.0 范围内。
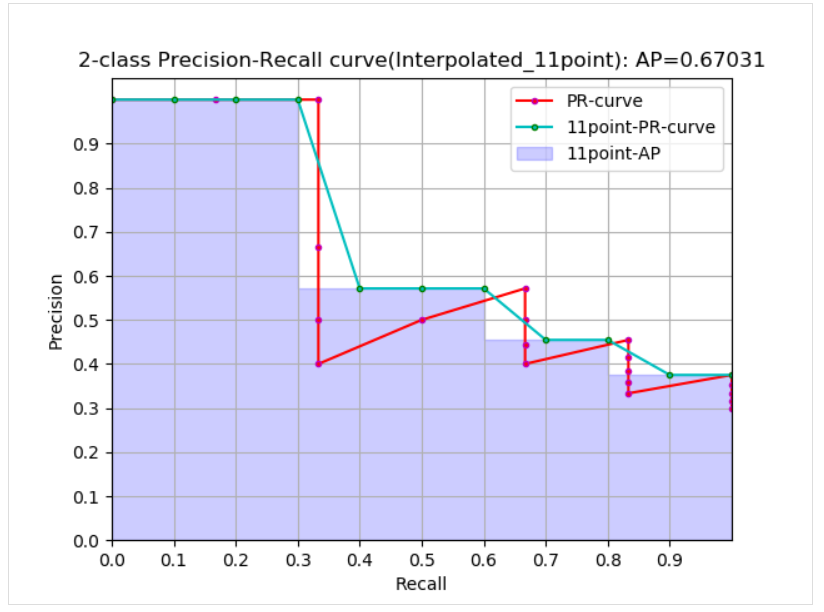
从曲线上看,真实 AP< approximated AP < Interpolated AP,11-points Interpolated AP 可能大也可能小,当数据量很多的时候会接近于 Interpolated AP,与 Interpolated AP 不同,前面的公式中计算 AP 时都是对 PR 曲线的面积估计,PASCAL 的论文里给出的公式就更加简单粗暴了,直接计算11 个阈值处的 precision 的平均值。PASCAL 论文给出的 11 点计算 AP 的公式如下。
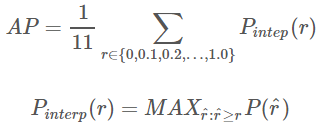
1, 在给定 recal 和 precision 的条件下计算 AP:
def voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric=False):
"""
ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, [use_07_metric])
Compute VOC AP given precision and recall.
If use_07_metric is true, uses the
VOC 07 11 point method (default:False).
"""
if use_07_metric:
# 11 point metric
ap = 0.
for t in np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1):
if np.sum(rec >= t) == 0:
p = 0
else:
p = np.max(prec[rec >= t])
ap = ap + p / 11.
else:
# correct AP calculation
# first append sentinel values at the end
mrec = np.concatenate(([0.], rec, [1.]))
mpre = np.concatenate(([0.], prec, [0.]))
# compute the precision envelope
for i in range(mpre.size - 1, 0, -1):
mpre[i - 1] = np.maximum(mpre[i - 1], mpre[i])
# to calculate area under PR curve, look for points
# where X axis (recall) changes value
i = np.where(mrec[1:] != mrec[:-1])[0]
# and sum (\Delta recall) * prec
ap = np.sum((mrec[i + 1] - mrec[i]) * mpre[i + 1])
return ap
2,给定目标检测结果文件和测试集标签文件 xml 等计算 AP:
def parse_rec(filename):
""" Parse a PASCAL VOC xml file
Return : list, element is dict.
"""
tree = ET.parse(filename)
objects = []
for obj in tree.findall('object'):
obj_struct = {}
obj_struct['name'] = obj.find('name').text
obj_struct['pose'] = obj.find('pose').text
obj_struct['truncated'] = int(obj.find('truncated').text)
obj_struct['difficult'] = int(obj.find('difficult').text)
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
obj_struct['bbox'] = [int(bbox.find('xmin').text),
int(bbox.find('ymin').text),
int(bbox.find('xmax').text),
int(bbox.find('ymax').text)]
objects.append(obj_struct)
return objects
def voc_eval(detpath,
annopath,
imagesetfile,
classname,
cachedir,
ovthresh=0.5,
use_07_metric=False):
"""rec, prec, ap = voc_eval(detpath,
annopath,
imagesetfile,
classname,
[ovthresh],
[use_07_metric])
Top level function that does the PASCAL VOC evaluation.
detpath: Path to detections result file
detpath.format(classname) should produce the detection results file.
annopath: Path to annotations file
annopath.format(imagename) should be the xml annotations file.
imagesetfile: Text file containing the list of images, one image per line.
classname: Category name (duh)
cachedir: Directory for caching the annotations
[ovthresh]: Overlap threshold (default = 0.5)
[use_07_metric]: Whether to use VOC07's 11 point AP computation
(default False)
"""
# assumes detections are in detpath.format(classname)
# assumes annotations are in annopath.format(imagename)
# assumes imagesetfile is a text file with each line an image name
# cachedir caches the annotations in a pickle file
# first load gt
if not os.path.isdir(cachedir):
os.mkdir(cachedir)
cachefile = os.path.join(cachedir, '%s_annots.pkl' % imagesetfile)
# read list of images
with open(imagesetfile, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
imagenames = [x.strip() for x in lines]
if not os.path.isfile(cachefile):
# load annotations
recs = {}
for i, imagename in enumerate(imagenames):
recs[imagename] = parse_rec(annopath.format(imagename))
if i % 100 == 0:
print('Reading annotation for {:d}/{:d}'.format(
i + 1, len(imagenames)))
# save
print('Saving cached annotations to {:s}'.format(cachefile))
with open(cachefile, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(recs, f)
else:
# load
with open(cachefile, 'rb') as f:
try:
recs = pickle.load(f)
except:
recs = pickle.load(f, encoding='bytes')
# extract gt objects for this class
class_recs = {}
npos = 0
for imagename in imagenames:
R = [obj for obj in recs[imagename] if obj['name'] == classname]
bbox = np.array([x['bbox'] for x in R])
difficult = np.array([x['difficult'] for x in R]).astype(np.bool)
det = [False] * len(R)
npos = npos + sum(~difficult)
class_recs[imagename] = {'bbox': bbox,
'difficult': difficult,
'det': det}
# read dets
detfile = detpath.format(classname)
with open(detfile, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
splitlines = [x.strip().split(' ') for x in lines]
image_ids = [x[0] for x in splitlines]
confidence = np.array([float(x[1]) for x in splitlines])
BB = np.array([[float(z) for z in x[2:]] for x in splitlines])
nd = len(image_ids)
tp = np.zeros(nd)
fp = np.zeros(nd)
if BB.shape[0] > 0:
# sort by confidence
sorted_ind = np.argsort(-confidence)
sorted_scores = np.sort(-confidence)
BB = BB[sorted_ind, :]
image_ids = [image_ids[x] for x in sorted_ind]
# go down dets and mark TPs and FPs
for d in range(nd):
R = class_recs[image_ids[d]]
bb = BB[d, :].astype(float)
ovmax = -np.inf
BBGT = R['bbox'].astype(float)
if BBGT.size > 0:
# compute overlaps
# intersection
ixmin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 0], bb[0])
iymin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 1], bb[1])
ixmax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 2], bb[2])
iymax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 3], bb[3])
iw = np.maximum(ixmax - ixmin + 1., 0.)
ih = np.maximum(iymax - iymin + 1., 0.)
inters = iw * ih
# union
uni = ((bb[2] - bb[0] + 1.) * (bb[3] - bb[1] + 1.) +
(BBGT[:, 2] - BBGT[:, 0] + 1.) *
(BBGT[:, 3] - BBGT[:, 1] + 1.) - inters)
overlaps = inters / uni
ovmax = np.max(overlaps)
jmax = np.argmax(overlaps)
if ovmax > ovthresh:
if not R['difficult'][jmax]:
if not R['det'][jmax]:
tp[d] = 1.
R['det'][jmax] = 1
else:
fp[d] = 1.
else:
fp[d] = 1.
# compute precision recall
fp = np.cumsum(fp)
tp = np.cumsum(tp)
rec = tp / float(npos)
# avoid divide by zero in case the first detection matches a difficult
# ground truth
prec = tp / np.maximum(tp + fp, np.finfo(np.float64).eps)
ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric)
return rec, prec, ap
2.4,mAP 计算方法
因为 m A P mAP mAP 值的计算是对数据集中所有类别的 A P AP AP 值求平均,所以我们要计算 m A P mAP mAP,首先得知道某一类别的 A P AP AP 值怎么求。不同数据集的某类别的 A P AP AP 计算方法大同小异,主要分为三种:
(1)在 VOC2007,只需要选取当
R
e
c
a
l
l
>
=
0
,
0.1
,
0.2
,
.
.
.
,
1
Recall >= 0, 0.1, 0.2, ..., 1
Recall>=0,0.1,0.2,...,1 共 11 个点时的 Precision 最大值,然后
A
P
AP
AP 就是这 11 个 Precision 的平均值,
m
A
P
mAP
mAP 就是所有类别
A
P
AP
AP 值的平均。VOC 数据集中计算
A
P
AP
AP 的代码(用的是插值计算方法,代码出自py-faster-rcnn仓库)
(2)在 VOC2010 及以后,需要针对每一个不同的 Recall 值(包括 0 和 1),选取其大于等于这些 Recall 值时的 Precision 最大值,然后计算 PR 曲线下面积作为
A
P
AP
AP 值,
m
A
P
mAP
mAP 就是所有类别
A
P
AP
AP 值的平均。
(3)COCO 数据集,设定多个 IOU 阈值(0.5-0.95, 0.05 为步长),在每一个 IOU 阈值下都有某一类别的 AP 值,然后求不同 IOU 阈值下的 AP 平均,就是所求的最终的某类别的 AP 值。
三,目标检测度量标准汇总
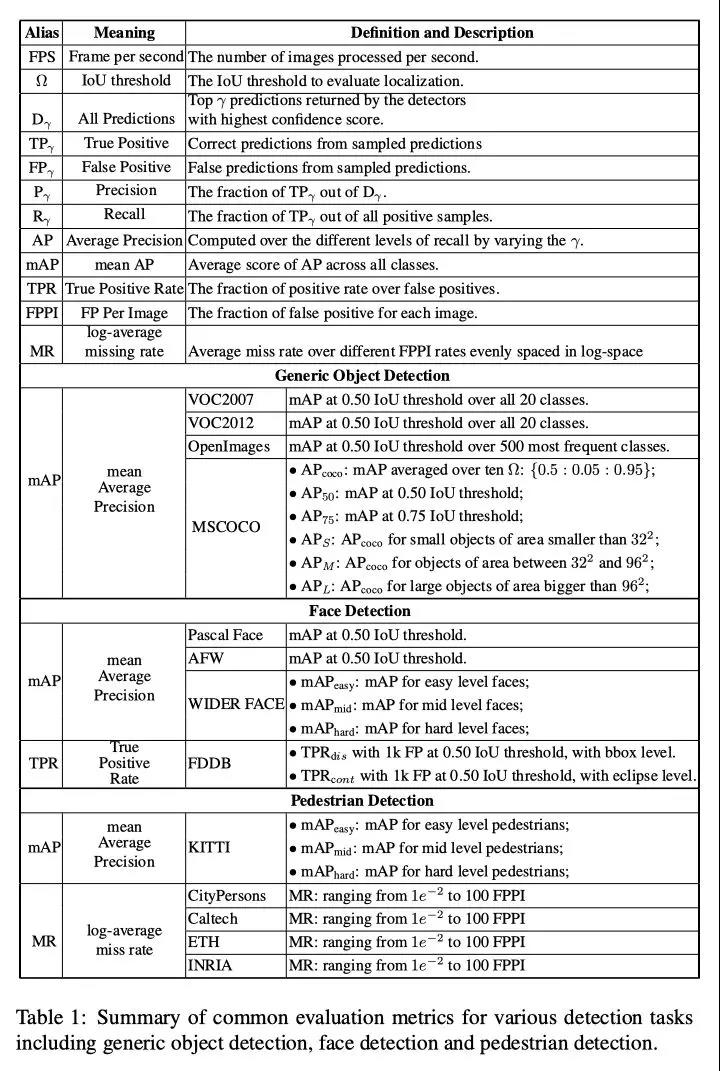
| 评价指标 | 定义及理解 |
|---|---|
mAP | mean Average Precision, 即各类别 AP 的平均值 |
AP | PR 曲线下面积,后文会详细讲解 |
PR 曲线 | Precision-Recall 曲线 |
Precision | T P / ( T P + F P ) TP / (TP + FP) TP/(TP+FP) |
Recall | T P / ( T P + F N ) TP / (TP + FN) TP/(TP+FN) |
TP | IoU>0.5 的检测框数量(同一 Ground Truth 只计算一次,阈值取 0.5) |
FP | IoU<=0.5 的检测框,或者是检测到同一个 GT 的多余检测框的数量 |
FN | 没有检测到的 GT 的数量 |