使用集成学习多数投票分类器对鸢尾花进行分类
本文整理自《Python机器学习》
集成方法中的多数投票
集成方法(ensemble learning)的目标是:将不同的分类器组合成为一个元分类器,与包含于其中的单个分类器相比,元分类器具有更好的泛化能力。
最流行的集成方法使用多数投票原则。多数投票原则是指将大多数分类器预测的结果作为最终的类标即将得票率超过50%的结果作为类标。可将该过程表示为:
y
^
=
m
o
d
e
{
C
1
(
x
)
,
C
2
(
x
)
,
.
.
.
,
C
m
(
x
)
}
\hat y = mode\{C_1(\textbf{x}),C_2(\textbf{x}),...,C_m(\textbf{x})\}
y^?=mode{C1?(x),C2?(x),...,Cm?(x)}
若在二分类中,则可表示为:
C
(
x
)
=
s
i
g
n
{
∑
j
m
C
j
(
x
)
}
=
{
1
i
f
∑
j
C
j
≥
0
?
1
o
t
h
e
r
w
i
s
e
C(\textbf{x})=sign\{\sum_j^mC_j(\textbf{x})\}=\left\{\begin{align} &1 & if \sum_jC_j\geq0\\ &-1&otherwise \end{align}\right.
C(x)=sign{j∑m?Cj?(x)}=?
?
???1?1?ifj∑?Cj?≥0otherwise??
其中
C
j
C_j
Cj?表示单个分类器。
假定二分类别分类中的
n
n
n个成员分类器拥有相同的出错率
?
\epsilon
?,可将成员分类器集成后出错的概率简单地表示为二项分布的概率密度函数:
P
(
y
≥
k
)
=
∑
k
n
<
n
k
>
?
k
(
1
?
?
)
n
?
k
P(y\geq k)=\sum_k^n\left<\begin{aligned}n\\k\end{aligned}\right>\epsilon^k(1-\epsilon)^{n-k}
P(y≥k)=k∑n??nk???k(1??)n?k
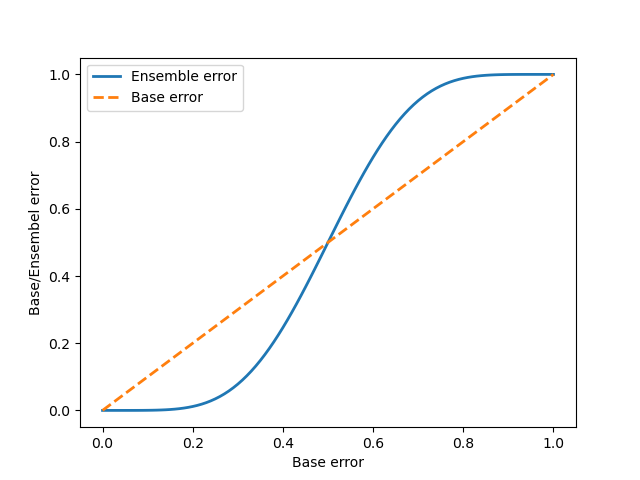
当假设有11个分类器时,可绘制如下的单个分类器与集成分类器的错误率比较图:
代码如下:
from scipy.special import comb # 将misc改为special
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def ensemble_error(n_classifier, error):
k_start = math.ceil(n_classifier/2.0)
probs = [comb(n_classifier, k) * error**k * (1-error)**(n_classifier - k) for k in range(k_start, n_classifier+1)]
return sum(probs)
error_range = np.arange(0.0, 1.01, 0.01)
ens_errors = [ensemble_error(n_classifier=11, error=error) for error in error_range]
plt.plot(error_range, ens_errors, label='Ensemble error', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(error_range, error_range, linestyle='--', label='Base error', linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel('Base error')
plt.ylabel('Base/Ensembel error')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
可见,当成员分类器出错率低于随机猜测时( ? < 0.5 \epsilon<0.5 ?<0.5),集成分类器的出错率要低于单个分类器。
实现一个简单的多数投票分类器
严格数学概念下的加权多数投票记为:
y
^
=
arg
?
max
?
i
∑
j
=
1
m
w
j
χ
A
(
C
j
(
x
)
=
i
)
\hat y = \arg \max_i\sum_{j=1}^mw_j\chi_A(C_j(\textbf{x})=i)
y^?=argimax?j=1∑m?wj?χA?(Cj?(x)=i)
其中
w
j
w_j
wj?是成员分类器
C
j
C_j
Cj?对应的权重,
y
^
\hat y
y^?为集成分类器的预测类标,
χ
A
\chi_A
χA?为特征函数
[
C
j
(
x
)
=
i
∈
A
]
[C_j(x)=i\in A]
[Cj?(x)=i∈A],
A
A
A为类标的集合。若权重相等,则该式可简化为:
y
^
=
m
o
d
e
{
C
1
(
x
)
,
C
2
(
x
)
,
.
.
.
,
C
m
(
x
)
}
\hat y = mode\{C_1(\textbf{x}),C_2(\textbf{x}),...,C_m(\textbf{x})\}
y^?=mode{C1?(x),C2?(x),...,Cm?(x)}
上述公式的理解可由如下例子来说明:
C
1
(
x
)
→
0
,
C
2
(
x
)
→
0
,
C
2
→
1
C_1(x)\rightarrow0, C_2(x)\rightarrow0,C_2\rightarrow1
C1?(x)→0,C2?(x)→0,C2?→1
C
1
(
x
)
,
C
3
(
x
)
,
C
3
(
x
)
C_1(x),C_3(x),C_3(x)
C1?(x),C3?(x),C3?(x)的权重分别为0.2,0.2和0.6。
于是有:
y
^
=
arg
?
max
?
i
[
0.2
×
(
1
0
)
+
0.2
×
(
1
0
)
+
0.6
×
(
0
1
)
]
=
1
\hat y = \arg\max_i[0.2\times\left(\begin{aligned}1\\0\end{aligned}\right)+0.2\times\left(\begin{aligned}1\\0\end{aligned}\right)+0.6\times\left(\begin{aligned}0\\1\end{aligned}\right)]=1
y^?=argimax?[0.2×(10?)+0.2×(10?)+0.6×(01?)]=1
用如上原理,可以用python实现MajorityVoteClassifier类,并对鸢尾花数据集进行分类:
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator
from sklearn.base import ClassifierMixin
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
import six
from sklearn.base import clone
from sklearn.pipeline import _name_estimators
import numpy as np
import operator
class MajorityClassfier(BaseEstimator, ClassifierMixin):
def __init__(self, classifiers, vote='classlabel', weights=None):
"""
:param classifiers:array-like,集成学习中的不同分类器
:param vote:str, {'classlabel', 'probability'},默认为classlabel,classlabel表示使用类标签的argmax,probability表示使用概率和的argmax来预测类标签
:param weights:重要性权重的向量
"""
self.classifiers = classifiers
self.named_classifiers = {key: value for key,value in _name_estimators(classifiers)}
self.vote = vote
self.weights = weights
def fit(self, X, y):
self.lablenc_ = LabelEncoder()
self.lablenc_.fit(y)
self.classes_ = self.lablenc_.classes_
self.classifiers_ = []
for clf in self.classifiers:
fitted_clf = clone(clf).fit(X, self.lablenc_.transform(y))
self.classifiers_.append(fitted_clf)
return self
def predict(self,X):
if self.vote == 'probability':
maj_vote = np.argmax(self.predict_proba(X), axis=1)
else:
predictions = np.asarray([clf.predict(X) for clf in self.classifiers_]).T
maj_vote = np.apply_along_axis(lambda x:np.argmax(np.bincount(x, weights=self.weights)),axis=1,arr=predictions)
maj_vote = self.labelenc_.inverse_transform(maj_vote)
return maj_vote
def predict_proba(self,X):
probas = np.asarray([clf.predict_proba(X) for clf in self.classifiers_])
avg_proba = np.average(probas, axis=0, weights=self.weights)
return avg_proba
def get_params(self, deep=True):
"""
获得梯度搜索的参数名
:param deep:
:return:
"""
if not deep:
return super(MajorityClassfier,self).get_params(deep=False)
else:
out = self.named_classifiers.copy()
for name, step in six.iteritems(self.named_classifiers):
for key, value in six.iteritems(step.get_params(deep=True)):
out['%s__%s' % (name, key)] = value
return out
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X, y = iris.data[50: ,[1,2]], iris.target[50:]
le = LabelEncoder()
y = le.fit_transform(y)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.5,random_state=0)
clf1 = LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', C=0.001, random_state=0)
clf2 = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1, criterion='entropy', random_state=0)
clf3 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1, p=2, metric='minkowski')
pipe1 = Pipeline([['sc', StandardScaler()],['clf', clf1]])
pipe3 = Pipeline([['sc', StandardScaler()],['clf',clf3]])
mv_clf = MajorityClassfier(classifiers=[pipe1, clf2, pipe3])
clf_labels = ['Logistic regression', 'Decision Tree', 'KNN', 'Majority Voting']
print('10-fold cross validation:\n')
for clf, label in zip([pipe1, clf2, pipe3, mv_clf], clf_labels):
scores = cross_val_score(estimator=clf, X=X_train, y=y_train, cv=10, scoring='roc_auc')
print("ROC AUC: %0.2f (+/- %0.2f) [%s]" % (scores.mean(), scores.std(), label))
上述代码比较了Logistic回归,决策树,K近邻和多数投票器的性能,结果如下:
10-fold cross validation:
ROC AUC: 0.97 (+/- 0.07) [Logistic regression]
ROC AUC: 0.97 (+/- 0.07) [Decision Tree]
ROC AUC: 0.98 (+/- 0.05) [KNN]
ROC AUC: 1.00 (+/- 0.00) [Majority Voting]
ROC AUC(Receiver Operator Characteristic Area under the Curve)为受试工作者特征线下区域,能够反映分类器的性能。上述结果表明多数投票器的性能最强。
使用sklearn实现多数投票器
sklearn.ensemble.VotingClassifier类能被简单地实现多数投票器调用。
使用该类对鸢尾花的分类的python代码如下:
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X, y = iris.data[50: ,[1,2]], iris.target[50:]
le = LabelEncoder()
y = le.fit_transform(y)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.5,random_state=0)
clf1 = LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', C=0.001, random_state=0)
clf2 = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1, criterion='entropy', random_state=0)
clf3 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1, p=2, metric='minkowski')
VC = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('Logistic Regression', clf1),('Desicion Tree', clf2),('KNN', clf3)], voting='soft')
# voting为hard时predict_proba不可用
VC.fit(X_train,y_train)
scores = cross_val_score(estimator=VC, X=X_train, y=y_train, cv=10, scoring='roc_auc')
print("ROC AUC: %0.2f (+/- %0.2f) [%s]" % (scores.mean(), scores.std(), 'VC'))
结果如下:
ROC AUC: 1.00 (+/- 0.00) [VC]
= cross_val_score(estimator=VC, X=X_train, y=y_train, cv=10, scoring=‘roc_auc’)
print(“ROC AUC: %0.2f (+/- %0.2f) [%s]” % (scores.mean(), scores.std(), ‘VC’))
结果如下:
ROC AUC: 1.00 (+/- 0.00) [VC]