贝叶斯分类是一类分类算法的总称,这类算法均以贝叶斯定理为基础,故统称为贝叶斯分类。而朴素贝叶斯分类是贝叶斯分类中最简单,也是常见的一种分类方法。引用一句每篇写到朴素贝叶斯分类文章基本都会介绍的一句话。
对于机器学习和算法之类的,我是个小小白。很多东西都百思不得其解。
写这个也是一个学习的过程,为此专门买了西瓜书等其他算法书籍。emmmm,该看不懂还是看不懂。
我一开始的诉求很简单,就是想做个文本分类,查了一些文章,越看越懵,而且关于此方面的开发,大都是python写的,然后很多python又都是直接调包。。。。
关于朴素贝叶斯分类在看了几篇文章后发现,嗯,最起码我能看懂。所以就照着写了下来。最后的成果的话,我感觉还行,最起码没有太离谱。反正就是一个入门的学习,再深入的话可能要掉头发。
为了实现这个功能,简单的数据处理还是必要的,比如把北京、上海、广州、深圳定义为是城市,张三、李四、赵五定义为人名,长江、黄河、黄浦江定义为河流。这三个层次看起来还是比较好区分,最起码之间干系不大,但也不能绝对,比如有的人名叫长江等,这样的数据多了的话,会影响最终的预测结果。
当然我这里处理的数据不是这些,所以还用到了JiebaNet来对数据进行分词处理。
所以简述下这个流程就很简单,已有数据进行分类->分词处理->调用朴素贝叶斯分类算法->输入数据->预测结果。
最后提一下,虽然说代码写完了,但是是基于怎么简单怎么来的思路来做的,我甚至一度怀疑使用我这个方法来做这件事可能从根本上就是不正确的,所以说,有需要参考下就行,我的思路可能并不正确,不要在这条路上浪费过多时间。
实现功能:
-
-
使用朴素贝叶斯分类实现文本分类
-
开发环境:
开发工具:Visual Studio 2022
.NET Framework版本:4.7.2
实现代码:
/// <summary>
/// 朴素贝叶斯分类
/// </summary>
public class NaiveBayes {
Dictionary<string, string> _types;
List<TrainItem> _trains;
public NaiveBayes(Dictionary<string, string> types
, List<TrainItem> trains) {
_types = types;
_trains = trains;
typesScore = new Dictionary<string, double>();
}
/// <summary>
/// 待分类文本关键词(可重复,重复词有助于分类)
/// </summary>
private List<string> keyList = new List<string>();
/// <summary>
/// 类别分数
/// </summary>
public Dictionary<string, double> typesScore { set; get; }
/// <summary>
/// 计算先验概率
/// </summary>
/// <param name="type"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private double GetPrior(string type) {
/*
* 先验概率P(c)=“类c下的单词总数”/“整个训练样本的单词总数”
*/
int typeCount = GetTrainSetCount(type);
int allCount = GetTrainSetCount();
double result = typeCount * 1.0 / allCount;
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// 计算似然概率
/// </summary>
/// <param name="type"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private double GetLikelihood(string type) {
/*
* P(X|c1)=P(x1|c1)P(x2|c1)...P(xn|c1)
* P(x1|c1)="x1关键字在c1文档中出现过的次数之和+1"/"类c1下单词的总数(单词可重复)+总训练样本的不重复单词数"
* 注:引入Laplace校准,它的思想非常简单,就是对没类别下所有划分的计数加1,解决 P(x1|c1)=0 的情况
*/
int typeTermCount = GetTrainSetCount(type);
int allTermCount = GetTrainSetCount();
int sum = typeTermCount + allTermCount;
double result = 1.0;
int count = 0;
//遍历待分类文本的关键字集合
keyList.ForEach(x => {
//计算 P(x1|c1)
count = GetTrainSetCountForKey(type, x) + 1;
result *= (count * 1.0 / sum);
});
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取训练集中的关键字数量
/// </summary>
/// <param name="type">类别名称,为空则获取全部</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int GetTrainSetCount(string type = null) {
if(!string.IsNullOrEmpty(type)) {
return _trains.Where(s => s.type == type).Count();
}
else {
return _trains.Count();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取训练集中某类别下某关键字数量
/// </summary>
/// <param name="type">类别</param>
/// <param name="key">关键字</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int GetTrainSetCountForKey(string type, string key) {
int count = 0;
//在可重复集合中寻找
_trains.FindAll(s => s.type == type).ForEach(s => {
count += s.textList.FindAll(t => t.Contains(key)).Count;
});
return count;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取最终分类结果
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public string GetClassify(string content) {
// _tempTermList = GetTermSegment(content);//分词
var segmenter = new JiebaSegmenter();
keyList = segmenter.CutForSearch(content).ToList();
/*
* P(C|X)=P(X|C)P(C)/P(X);后验概率=似然概率(条件概率)*先验概率/联合概率
*
* 其中,P(X)联合概率,为常量,所以只需要计算 P(X|C)P(C)
*
* 公式:P(X|C)P(C)
* 其中:
* P(X|C)=P(x1|c1)P(x2|c1)...P(xn|c1)
* P(x1|c1)="x1关键字在c1文档中出现过的次数之和 +1"/"类c1下单词的总数(单词可重复)+总训练样本的不重复单词数"
* P(c1)=类c1下总共有单词个数(可重复)/训练样本单词总数(可重复),
*/
double likelihood = 0f;//似然概率
double prior = 0f;//先验概率
double probability = 0f; //后验概率
//1 计算每个列别的概率值
foreach(var type in _types.Keys) {
//计算似然概率 P(X|c1)=P(x1|c1)P(x2|c1)...P(xn|c1)
likelihood = GetLikelihood(type);
//计算先验概率 P(c1)
prior = GetPrior(type);
//计算最中值:P(X|C)P(C)
probability = likelihood * prior;
//保存类的最终概率值
NoteTypeScore(type, probability);
}
//2 获取最大概率的类型code
string typeCode = GetMaxSoreType();
if(string.Equals(typeCode, string.Empty))
return "-1";
return typeCode;
}
private string GetMaxSoreType() {
//对字典中的值进行排序
Dictionary<string, double> soretDic = typesScore
.OrderByDescending(x => x.Value)
.ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Value);
//返回第一个分数最高的类型code
return soretDic.First().Key;
}
/// <summary>
/// 记录类型得分
/// </summary>
/// <param name="type"></param>
/// <param name="sore"></param>
private void NoteTypeScore(string type, double sore) {
typesScore[type] = sore;
}
}
public class TrainItem {
public string type { get; set; }
public List<string> textList { get; set; }
// public SortedSet<string> textDistinctList = new SortedSet<string>();
public TrainItem(string _type, List<string> _textList) {
type = _type;
textList = _textList;
//textList.ForEach(s => textDistinctList.Add(s));
}
}Console.WriteLine("正在加载模型...");
var split_kindname = Properties.Resource.品种.Split(new string[] { "\r\n" }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
var split_specname = Properties.Resource.规格.Split(new string[] { "\r\n" }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
var split_areaname = Properties.Resource.产地.Split(new string[] { "\r\n" }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
Dictionary<string, string> types = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
{"0","品种" },
{"1","规格" },
{"2","产地" },
};
List<TrainItem> trainSet = new List<TrainItem>
{
new TrainItem("0",split_kindname.ToList()),
new TrainItem("1",split_specname.ToList()),
new TrainItem("2",split_areaname.ToList()),
};
Console.WriteLine("模型加载完毕...\n");
while(true) {
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.WriteLine("\n请输入要检测的文本:\n");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
string input = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine($"输入文本:{input}\n");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.WriteLine("正在预测结果...\n");
NaiveBayes naiveBayes = new NaiveBayes(types, trainSet);
string type = naiveBayes.GetClassify(input);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
if(naiveBayes.typesScore.Values.Distinct().Count() == 1) {
Console.WriteLine($"预测结果:未知数据");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine($"预测结果:{types[type]}");
}
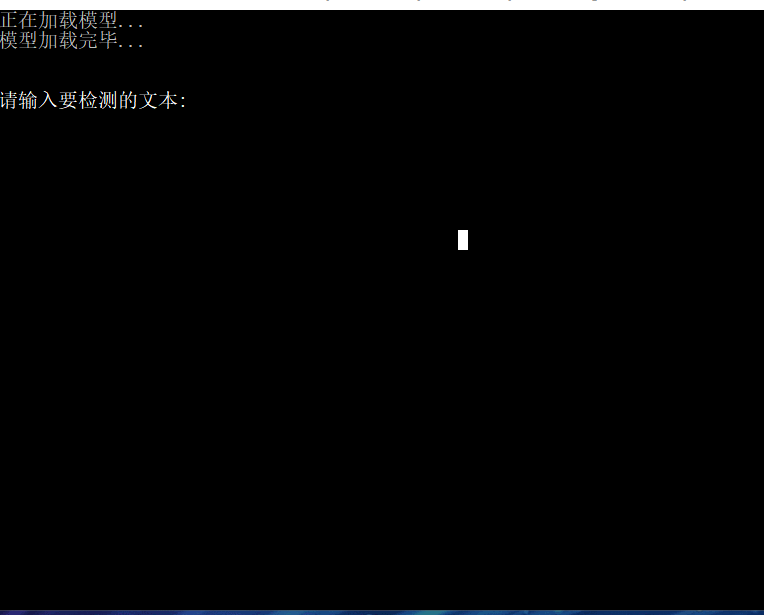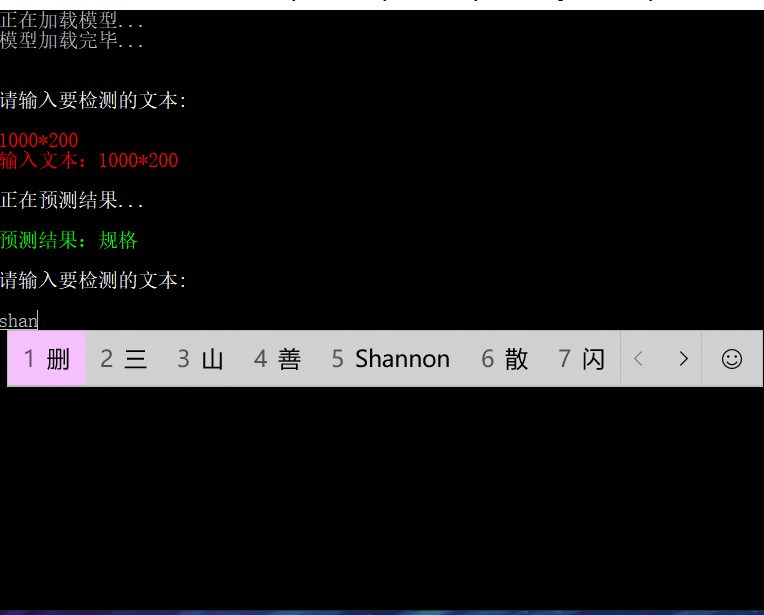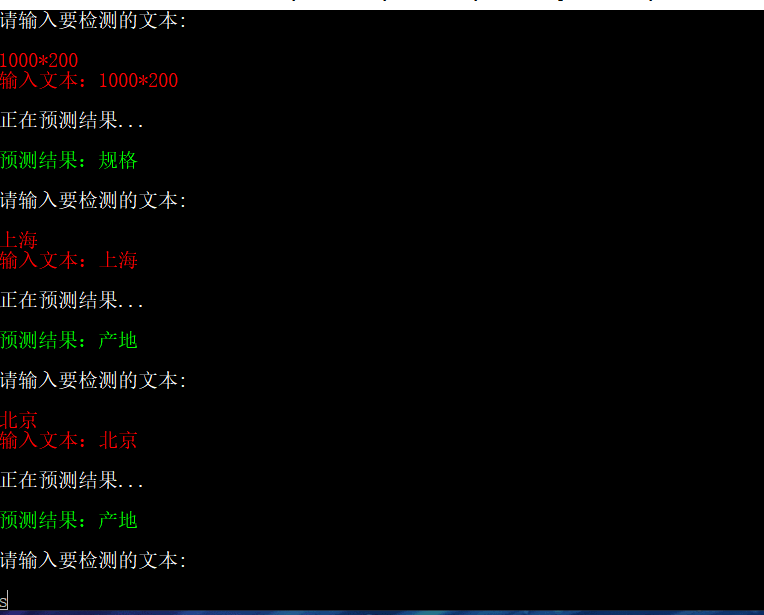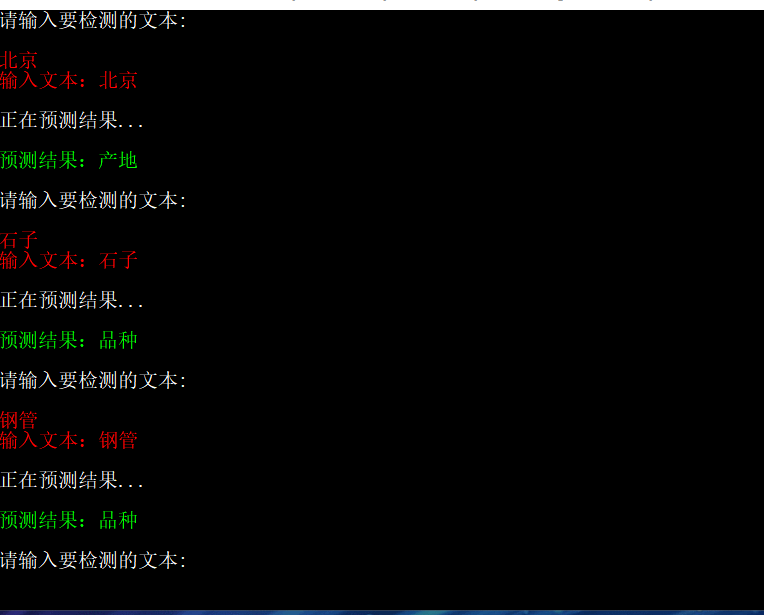
}实现效果:
?