thegraph
The Graph网络对Web3的查询层和API层进行了去中心化,消除了dApp开发者目前面临的取舍难题:到底是开发一个高性能应用,还是开发一个完全去中心化的应用…
1.创建旧版本子图-浏览器
因为新版收费,且新版至目前只支持以太坊主链
旧版子图地址: https://thegraph.com/hosted-service/
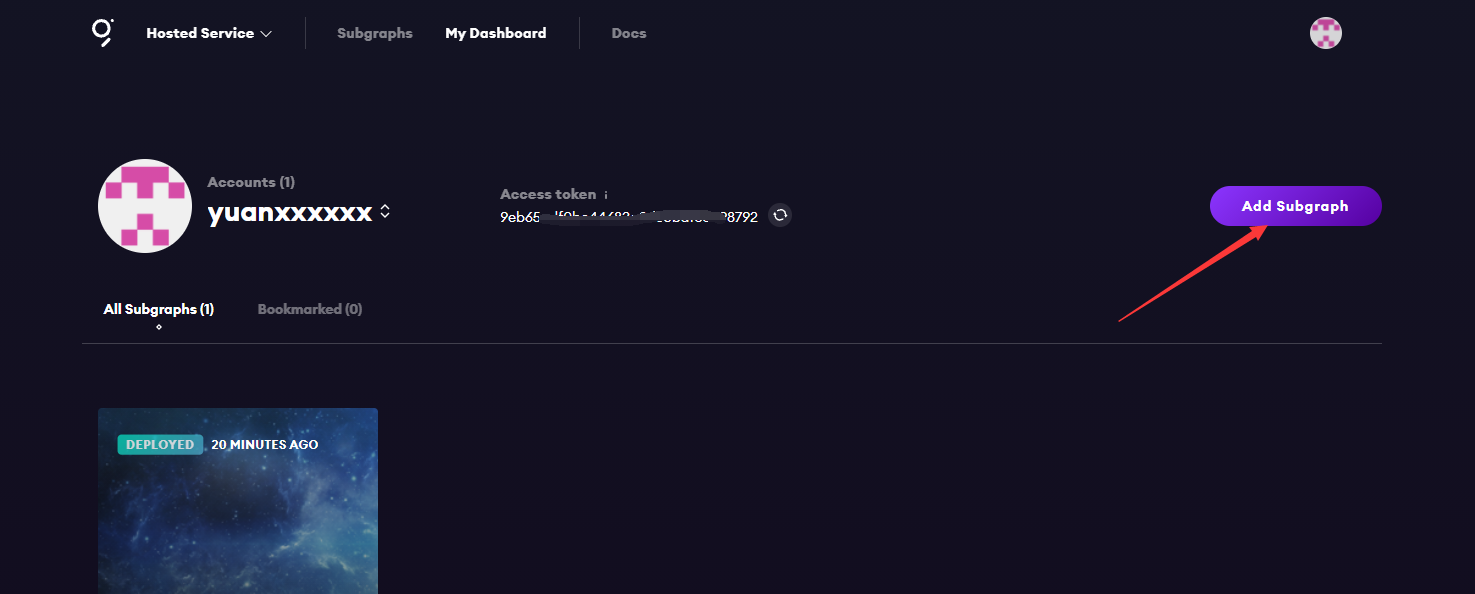
打开地址登录github
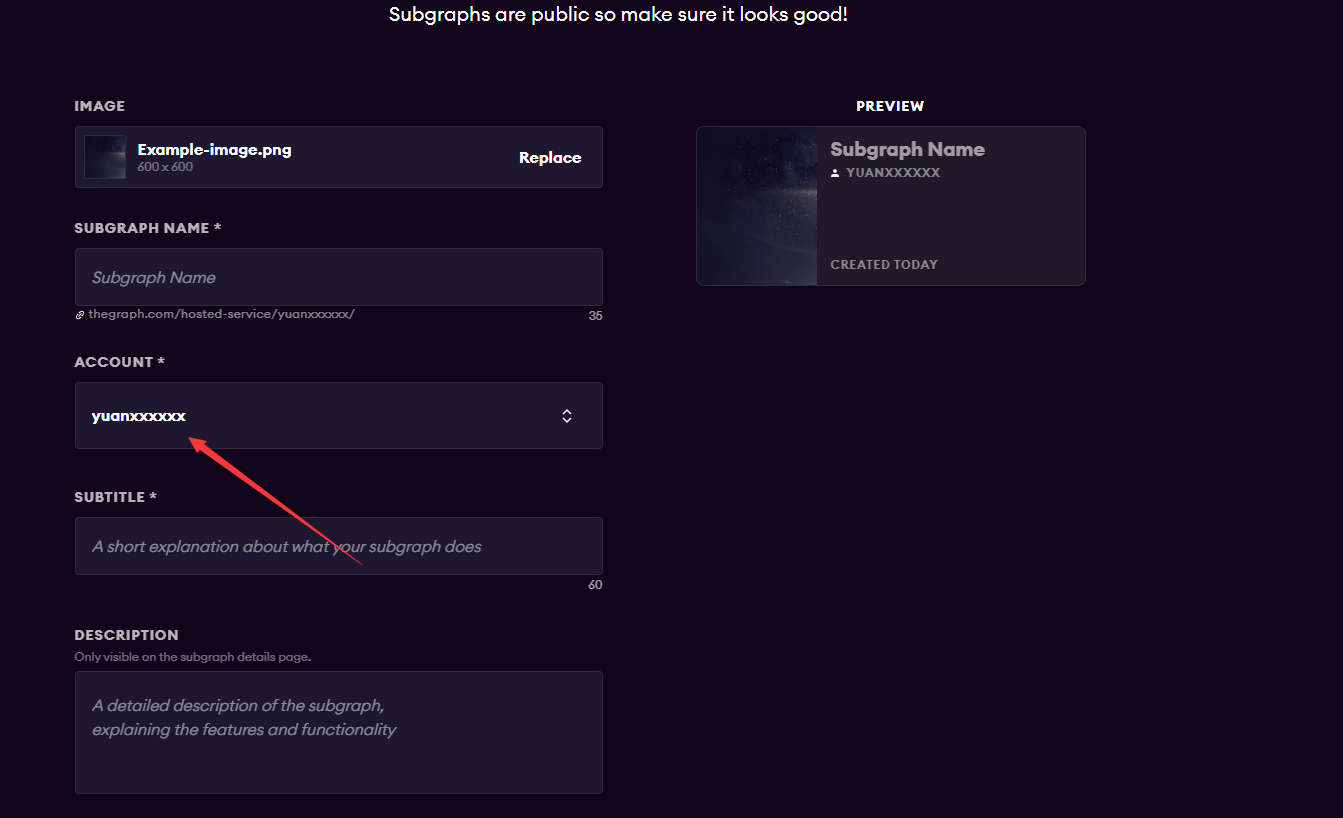
点击Add Subgraph创建子图
此处的名称需要和你的github账号名称对应,否则点击按钮无效,控制台输出报错(可能是bug)
2.创建子图应用
下载graph
// NPM
npm install -g @graphprotocol/graph-cli
// Yarn
yarn global add @graphprotocol/graph-cli
创建项目
graph init
步骤↓
Protocol · ethereum【选择以太坊】
? Product for which to initialize · hosted-service
? Subgraph name · web03/demo【你的graph名称/子图】
? Directory to create the subgraph in · demo
? Ethereum network · bsc【链】
? Contract address · 0x86f447333734052bc3d19858Fe334179eF66bE40【合约地址】
? Fetching ABI from Etherscan
? Contract Name · DuskAllowList【合约名称】
下载依赖
cd 项目地址
npm install
部署
// 构建
npm run codegen
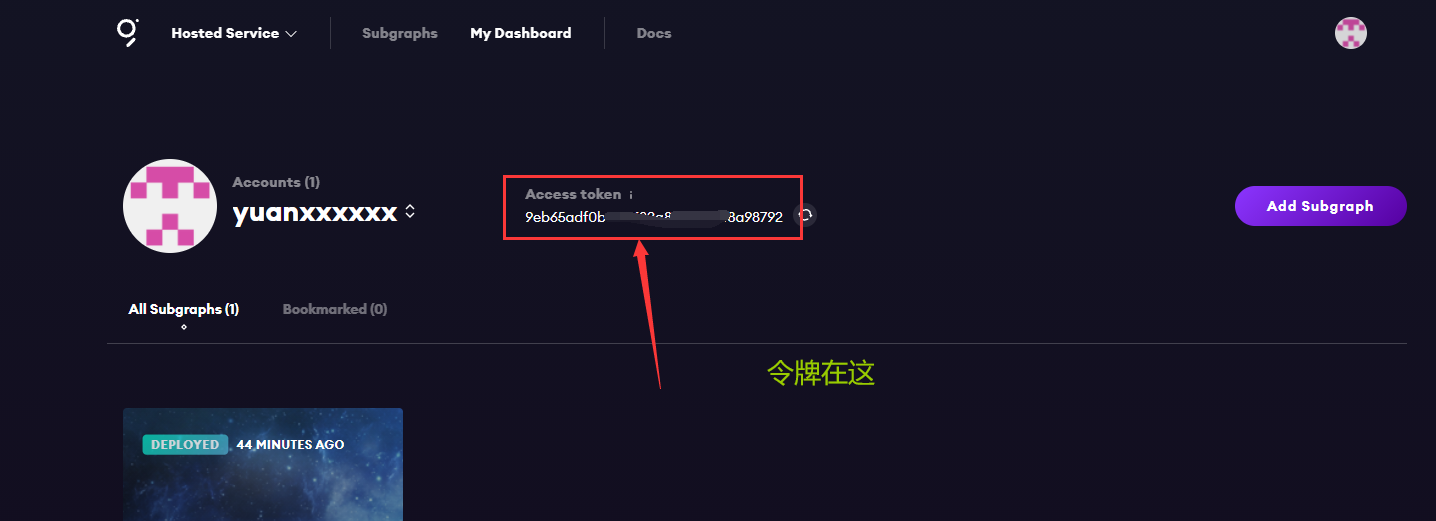
// 添加访问令牌
graph auth --product hosted-service <ACCESS_TOKEN>
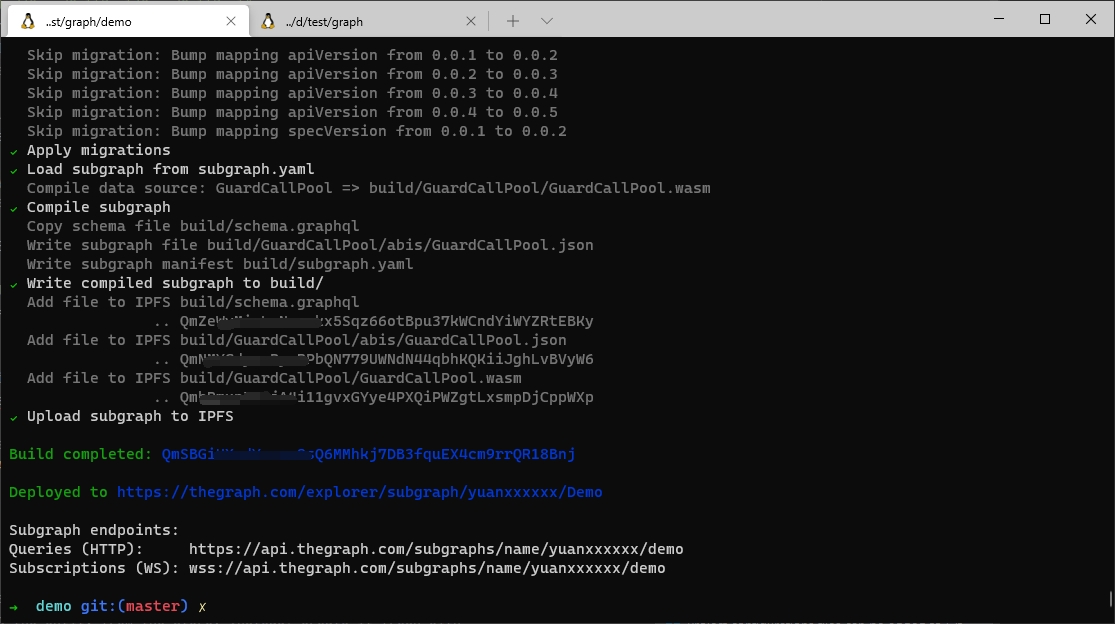
// 部署到线上
graph deploy --product hosted-service <GITHUB_USER>/<SUBGRAPH NAME>
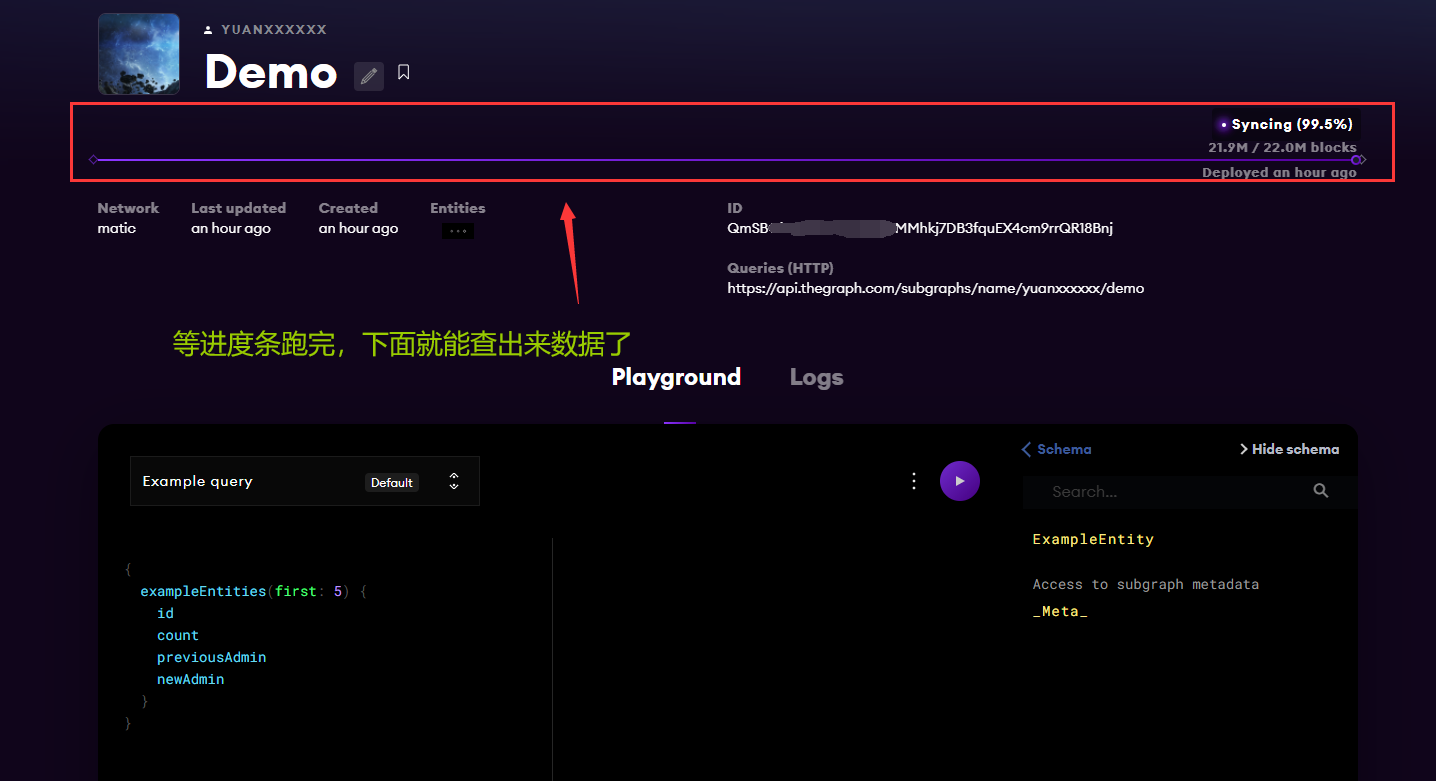
部署完成
配置说明
子图定义由几个文件组成:
-
subgraph.yaml:包含子图清单的 YAML 文件
-
schema.graphql: 一个 GraphQL 模式,它定义了为你的子图存储了什么数据,以及如何通过 GraphQL 查询它
-
AssemblyScript Mappings:从事件数据转换为模式中定义的实体的AssemblyScript代码
建议直接看官方文档:https://thegraph.com/docs/developer/create-subgraph-hosted
查询
{
实体(筛选条件) {
查询返回的字段
}
}
假设schema.graphql
type AccountPool @entity {
id: ID!
accountAddress: Bytes!
poolAddress: String!
amount: BigInt!
createdAt: BigInt!
pool: Pool!
account: Account!
}
查询用户的pool地址
{
AccountPool(first: 1000, skip:0, where:{account: 0x123xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx}) {
id,
poolAddress
}
}
查询说明
排序
// 通过price排序,排序方式为asc【acs升序,desc降序】
{
tokens(orderBy: price, orderDirection: asc) {
id
owner
}
}
分页
first参数可用于从集合的开头进行分页
默认排序顺序是按字母数字升序的 ID,而不是按创建时间
此外,该skip参数可用于跳过实体和分页。例如,first:100 显示前 100 个实体。 first:100, skip:100 显示接下来的 100 个实体
// 查询前10个
{
tokens(first: 10) {
id
owner
}
}
// 查询 10 个Token实体,从集合的开头偏移 10 个位置,获得11~20的Token
{
tokens(first: 10, skip: 10) {
id
owner
}
}
条件过滤-指定值
// 查询前1000个,并且holder字段要等于 用户地址
list(first: 1000, where: { holder: "用户地址" }) {
id
name
holder
}
条件过滤-检索多个实体
// 第一次,它会发送带有 的查询lastID = "",对于后续请求,它将设置lastID为id前一个请求中最后一个实体的属性。这种方法的性能明显优于使用递增skip值
{
query manyTokens($lastID: String) {
tokens(first: 1000, where: { id_gt: $lastID }) {
id
owner
}
}
}
过滤条件-比较
// 查询 amount 字段大于 100 的数据
{
UAmount(where: { amount_gt: "100" }) {
id
amount
}
}
// 查询name字段不等于 mmm 的数据
{
names(where: { name_not: "mmm" }) {
id
name
}
}
| 后缀 | 表现 |
|---|---|
| _not | 不等于 |
| _gt | 大于 |
| _lt | 小于 |
| _gte | 大于等于 |
| _lte | 小于等于 |
| _in | 属于 |
| _not_in | 不属于 |
| _contains | 包含 |
| _not_contains | 不包含 |
| _starts_with | 从 开始 |
| _ends_with | 从 结束 |
| _not_starts_with | 不从 开始 |
| _not_ends_with | 不从 结束 |
请注意,某些后缀仅支持特定类型。例如,Boolean仅支持_not,_in和_not_in。
查询指定区块
// 查询区块号为8000000里面的数据,此查询将返回Challenge实体及其关联 Application实体,因为它们在处理编号为 8000000 的区块后直接存在
{
challenges(block: { number: 8000000 }) {
challenger
outcome
application {
id
}
}
}
查询指定哈希的数据
{
challenges(block: { hash: "0x5a0b54d5dc17e0aadc383d2db43b0a0d3e029c4c" }) {
challenger
outcome
application {
id
}
}
}
运算符
| 运算符 | 表现 |
|---|---|
| & | 和 |
| | | 或 |
| <-> | 指定两个词之间的距离 |
| : * | 前缀(:与*无空格隔开) |
// 检索text值为'a'或者为'b'的数据
{
blogSearch(text: "a | b") {
id
title
body
author
}
}
// 检索text以a在b左边的,如axxxb,xxaxxb,xxaxxbxx【xxaxxb,xxaxxbxx是我的猜测,具体开实际情况】
{
blogSearch(text: "a <-> b") {
id
title
body
author
}
}
// 检索text以a开头的,如axxxb,axxbxx【axxbxx是我的猜测,具体开实际情况】
{
blogSearch(text: "a:* <-> b") {
id
title
body
author
}
}
axios请求graph
axios({
method: 'post',
url:
'https://thegraph.com/explorer/subgraph/xxx/xxx',
data: {
query: `{
dusks(first: 1000, skip:0, where:{holder: "${account}"}) {
id
holder
tokenId
}
}`,
},
}).then(res =>{
})