文章目录
Spark核心编程
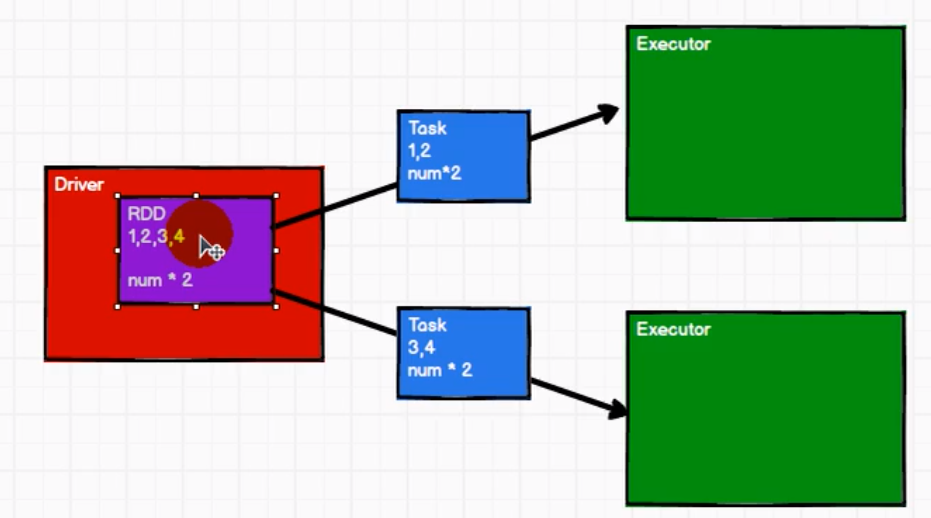
分布式计算就是将Driver封装好的计算逻辑和数据(数据结构)交给拆分为多个任务在不同机器交给Executor上并发处理。其中的计算逻辑并不是写死,而是可以大量扩展的,这样就低耦合,核心不变,在原来的功能上扩展。(装饰者设计模式)
Spark 计算框架为了能够进行高并发和高吞吐的数据处理,封装了三大数据结构,用于处理不同的应用场景。三大数据结构分别是:
? RDD : 弹性分布式数据集
? 累加器:分布式共享只写变量
? 广播变量:分布式共享只读变量
RDD
RDD概述
RDD(Resilient Distributed Dataset)叫做弹性分布式数据集,是 Spark 中最基本的数据处理模型代码中是一个抽象类,它代表一个弹性的、不可变、可分区、里面的元素可并行计算的集合。
? 弹性
? 存储的弹性:内存与磁盘的自动切换;
? 容错的弹性:数据丢失可以自动恢复;
? 计算的弹性:计算出错重试机制;
? 分片的弹性:可根据需要重新分片。
? 分布式:数据存储在大数据集群不同节点上
? 数据集:RDD 封装了计算逻辑,并不保存数据
? 数据抽象:RDD 是一个抽象类,需要子类具体实现? 不可变:RDD 封装了计算逻辑,是不可以改变的,想要改变,只能产生新的 RDD,在新的 RDD 里面封装计算逻辑
? 可分区、并行
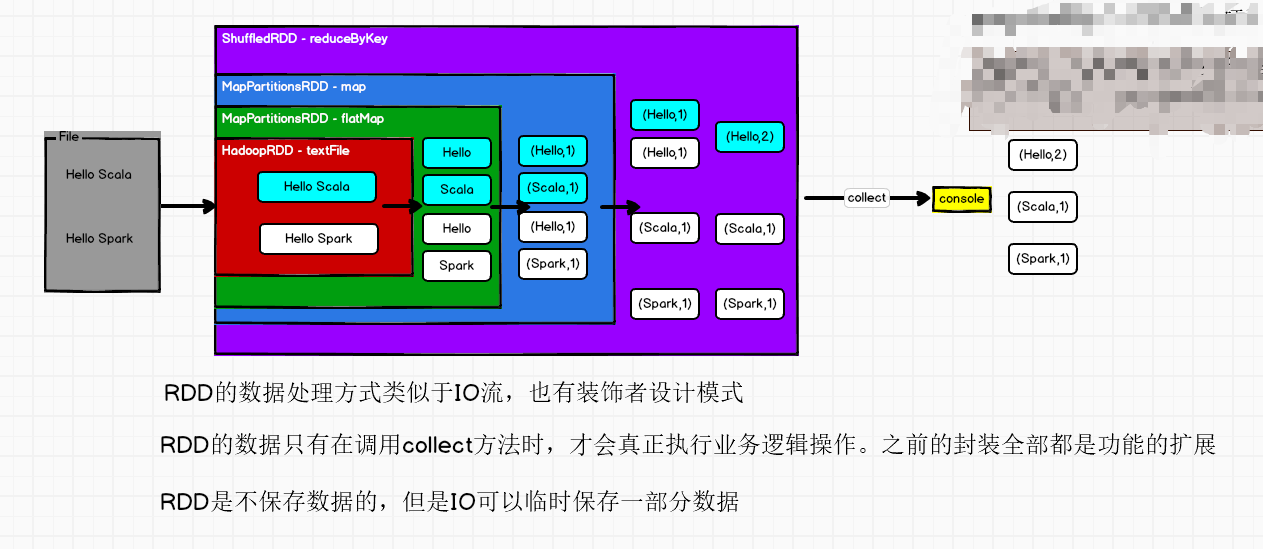
wordcount的rdd底层执行图
RDD核心属性(五大属性)
? 分区列表
RDD 数据结构中存在分区列表,用于执行任务时并行计算,是实现分布式计算的重要属性
? 分区计算函数
Spark 在计算时,是使用分区函数对每一个分区进行计算
? RDD 之间的依赖关系
RDD 是计算模型的封装,当需求中需要将多个计算模型进行组合时,就需要将多个 RDD 建立依赖关系
? 分区器(可选)
当数据为 KV 类型数据时,可以通过设定分区器自定义数据的分区
? 首选位置(可选)
计算数据时,可以根据计算节点的状态选择不同的节点位置进行计算
执行原理
从计算的角度来讲,数据处理过程中需要计算资源(内存 & CPU)和计算模型(逻辑)。执行时,需要将计算资源和计算模型进行协调和整合。
Spark 框架在执行时,先申请资源,然后将应用程序的数据处理逻辑分解成一个一个的计算任务。然后将任务发到已经分配资源的计算节点上, 按照指定的计算模型进行数据计算。最后得到计算结果。
Yarn 环境中,RDD 的工作原理:
- 启动 Yarn 集群环境
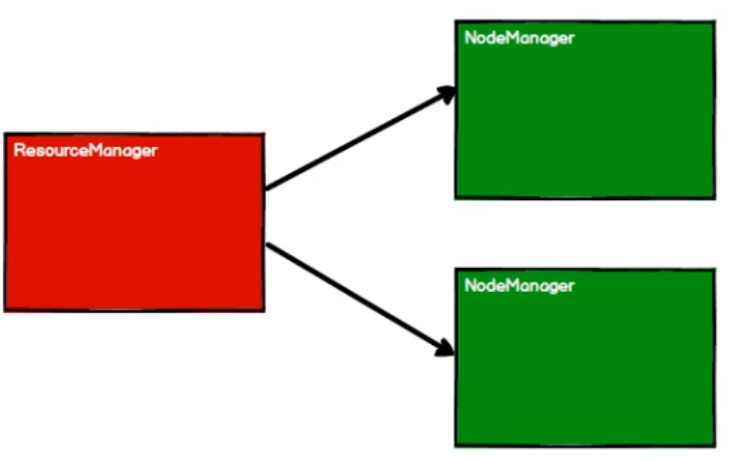
- Spark 通过申请资源创建调度节点和计算节点
? 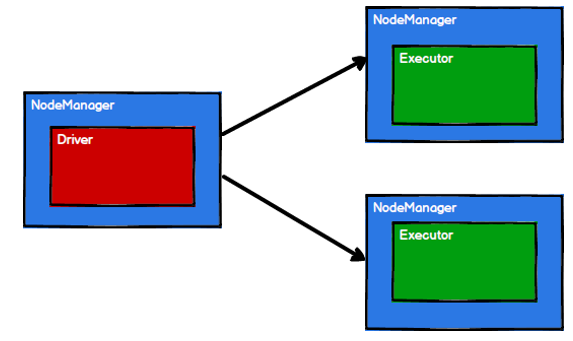
- Spark 框架根据需求将计算逻辑根据分区划分成不同的任务
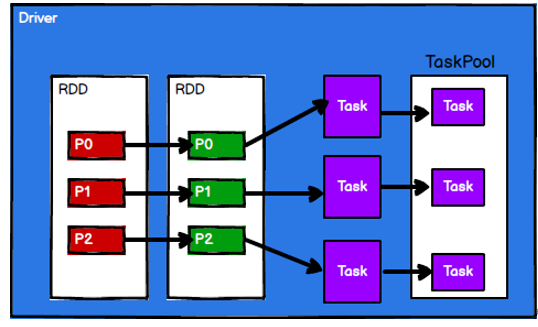
- 调度节点将任务根据计算节点状态发送到对应的计算节点进行计算
? 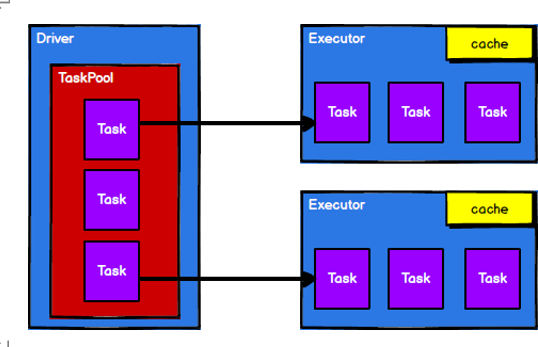
从以上流程可以看出 RDD 在整个流程中主要用于将逻辑进行封装,并生成 Task 发送给Executor 节点执行计算,接下来我们就一起看看 Spark 框架中RDD 是具体是如何进行数据处理的。
RDD基础编程
在 Spark 中创建RDD 的创建方式可以分为四种:
从集合(内存)中创建 RDD
从集合中创建RDD,Spark 主要提供了两个方法:parallelize 和 makeRDD
object Spark01_RDD_Memory {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1.准备环境
// setmaster设置运行环境+[*]模拟本机的最大核数,不加是单线程,setAPPName设置数据结构
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// 2.创建RDD
// 从内存中创建RDD,将内存中的集合的数据作为处理数据的数据源
val seq = Seq[Int](1,2,3,4)
// paralleize:并行
// val rdd: RDD[Int] = sc.parallelize(seq)
val rdd: RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(seq)
rdd.collect().foreach(println)
// 3.关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
}
从底层代码实现来讲,makeRDD 方法其实就是parallelize 方法
从外部存储(文件)创建RDD
由外部存储系统的数据集创建RDD 包括:本地的文件系统,所有Hadoop 支持的数据集, 比如HDFS、HBase 等
TextFile
object Spark02_RDD_File {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1.准备环境
var conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
// 2.创建RDD
// 从文件中创建RDD,将文件中读取的数据当做数据源
// path路径默认以当前的根路径为基准,可以写绝对路径也可以写相对路径
// val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/1.txt")
// path路径既可以是文件也可以是文件夹
val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas")
// path路径可以将相同文件添加通配符*
// val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/1*.txt")
// path路径还可以是hdfs的路径
// val rdd2: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("hdfs://master:9000/test.txt")
rdd.collect().foreach(println)
}
}
读取文件另一个方法wholeTextFiles
ef main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// TODO 准备环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 创建RDD
// 从文件中创建RDD,将文件中的数据作为处理的数据源
// textFile : 以行为单位来读取数据,读取的数据都是字符串
// wholeTextFiles : 以文件为单位读取数据
// 读取的结果表示为元组,第一个元素表示文件路径,第二个元素表示文件内容
val rdd = sc.wholeTextFiles("datas")
rdd.collect().foreach(println)
// TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
从其他 RDD 创建
主要是通过一个RDD 运算完后,再产生新的RDD。
直接创建 RDD(new)
使用 new 的方式直接构造RDD,一般由Spark 框架自身使用。
RDD并行度和分区
默认情况下,Spark 可以将一个作业切分多个任务后,发送给 Executor 节点并行计算,而能够并行计算的任务数量我们称之为并行度。这个数量可以在构建RDD 时指定。记住,这里的并行执行的任务数量,并不是指的切分任务的数量,不要混淆了
指定分区数
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1.准备环境
// setmaster设置运行环境+[*]模拟本机的最大核数,不加是单线程,setAPPName设置数据结构
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
// sparkConf.set("spark.default.parallelism", "5")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// 2.创建RDD
// 并行度和分区
// makerdd第二个参数可以不传递的,那么makeRDD方法会使用默认值 : defaultParallelism(默认并行度)
// scheduler.conf.getInt("spark.default.parallelism", totalCores)
// spark在默认情况下,从配置对象中获取配置参数:spark.default.parallelism
// 如果获取不到,那么使用totalCores属性,这个属性取值为当前运行环境的最大可用核数
//val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),2)
// val rdd = sc.makeRDD(
// List(1,2,3,4),2
// )
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(
List(1,2,3,4)
)
rdd.saveAsTextFile("output")
// 3.关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
数据的存放如何存放
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 准备环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// 创建RDD
// 【1,2】,【3,4】
//val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4), 2)
// 【1】,【2】,【3,4】
//val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4), 3)
// 【1】,【2,3】,【4,5】
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5), 3)
// 将处理的数据保存成分区文件
rdd.saveAsTextFile("output")
// 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
文件的分区
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// TODO 准备环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 创建RDD
// textFile可以将文件作为数据处理的数据源,默认也可以设定分区。
// minPartitions : 最小分区数量
// math.min(defaultParallelism, 2)
//val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/1.txt")
// 如果不想使用默认的分区数量,可以通过第二个参数指定分区数
// Spark读取文件,底层其实使用的就是Hadoop的读取方式
// 分区数量的计算方式:
// totalSize = 7
// goalSize = 7 / 2 = 3(byte)
// 7 / 3 = 2...1 (1.1) + 1 = 3(分区)
//
val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/1.txt", 2)
rdd.saveAsTextFile("output")
// TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
文件的分区如何存储的
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// TODO 准备环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 创建RDD
// 14byte / 2 = 7byte
// 14 / 7 = 2(分区)
/*
1234567@@ => 012345678
89@@ => 9101112
0 => 13
[0, 7] => 1234567
[7, 14] => 890
*/
// 如果数据源为多个文件,那么计算分区时以文件为单位进行分区
val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/word.txt", 2)
rdd.saveAsTextFile("output")
// TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
RDD算子介绍

RDD方法又叫做算子

RDD 根据数据处理方式的不同将算子整体上分为Value 类型、双 Value 类型和Key-Value类型
RDD 转换算子(value类型)
map
def map[U: ClassTag](f: T => U): RDD[U]
将处理的数据逐条进行映射转换,这里的转换可以是类型的转换,也可以是值的转换
map
object Spark01_RDD_Operator_Transform {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - map
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4))
// 1,2,3,4
// 2,4,6,8
// 转换函数
def mapFunction(num:Int): Int = {
num * 2
}
//val mapRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.map(mapFunction)
//val mapRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.map((num:Int)=>{num*2})
//val mapRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.map((num:Int)=>num*2)
//val mapRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.map((num)=>num*2)
//val mapRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.map(num=>num*2)
val mapRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.map(_*2)
mapRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
rdd并行执行的情况
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - map
// 1. rdd的计算一个分区内的数据是一个一个执行逻辑
// 只有前面一个数据全部的逻辑执行完毕后,才会执行下一个数据。
// 分区内数据的执行是有序的。
// 2. 不同分区数据计算是无序的。
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),2)
val mapRDD = rdd.map(
num => {
println(">>>>>>>> " + num)
num
}
)
val mapRDD1 = mapRDD.map(
num => {
println("######" + num)
num
}
)
mapRDD1.collect()
sc.stop()
}
处理小案例
从服务器日志数据 apache.log 中获取用户请求URL 资源路径
数据格式如下:
83.149.9.216 - - 17/05/2015:10:05:03 +0000 GET /presentations/logstash-monitorama-2013/images/kibana-search.png
83.149.9.216 - - 17/05/2015:10:05:43 +0000 GET /presentations/logstash-monitorama-2013/images/kibana-dashboard3.png
83.149.9.216 - - 17/05/2015:10:05:47 +0000 GET /presentations/logstash-monitorama-2013/plugin/highlight/highlight.js
83.149.9.216 - - 17/05/2015:10:05:12 +0000 GET /presentations/logstash-monitorama-2013/plugin/zoom-js/zoom.js
83.149.9.216 - - 17/05/2015:10:05:07 +0000 GET /presentations/logstash-monitorama-2013/plugin/notes/notes.js
可以一行行的读,每行以空格分隔开去url路径的index
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - map
val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/apache.log")
// 长的字符串
// 短的字符串
val mapRDD: RDD[String] = rdd.map(
line => {
val datas = line.split(" ")
datas(6)
}
)
mapRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
mapPartitions
def mapPartitions[U:
ClassTag]( f: Iterator[T] =>
Iterator[U],
preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false): RDD[U]
将待处理的数据以分区为单位发送到计算节点进行处理,这里的处理是指可以进行任意的处理,哪怕是过滤数据。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - mapPartitions
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4), 2)
// mapPartitions : 可以以分区为单位进行数据转换操作
// 但是会将整个分区的数据加载到内存进行引用
// 如果处理完的数据是不会被释放掉,存在对象的引用。
// 在内存较小,数据量较大的场合下,容易出现内存溢出。
val mpRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.mapPartitions(
iter => {
println(">>>>>>>>>>")
iter.map(_ * 2)
}
)
mpRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
Map 算子是分区内一个数据一个数据的执行,类似于串行操作。而 mapPartitions 算子是以分区为单位进行批处理操作。
Map 算子因为类似于串行操作,所以性能比较低,而是 mapPartitions 算子类似于批处
理,所以性能较高。但是mapPartitions 算子会长时间占用内存,那么这样会导致内存可能不够用,出现内存溢出的错误。所以在内存有限的情况下,不推荐使用。使用 map 操作。
案例获得每个分区的最大值
bject Spark02_RDD_Operator_Transform_Test {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - mapPartitions
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4), 2)
// 【1,2】,【3,4】
// 【2】,【4】
val mpRDD = rdd.mapPartitions(
iter => {
List(iter.max).iterator
}
)
mpRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
mapPartitionsWithIndex
将待处理的数据以分区为单位发送到计算节点进行处理,这里的处理是指可以进行任意的处理,哪怕是过滤数据,在处理时同时可以获取当前分区索引。
获取想要分区的数据
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - mapPartitions
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4), 2)
// 【1,2】,【3,4】
val mpiRDD = rdd.mapPartitionsWithIndex(
(index, iter) => {
if ( index == 1 ) {
iter
} else {
Nil.iterator
}
}
)
mpiRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
列出数据所在分区
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - mapPartitions
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4))
val mpiRDD = rdd.mapPartitionsWithIndex(
(index, iter) => {
// 1, 2, 3, 4
//(0,1)(2,2),(4,3),(6,4)
iter.map(
num => {
(index, num)
}
)
}
)
mpiRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
flatMap
def flatMap[U: ClassTag](f: T => TraversableOnce[U]): RDD[U]
将处理的数据进行扁平化后再进行映射处理,所以算子也称之为扁平映射
将大集合拆分为小集合
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - mapPartitions
val rdd: RDD[List[Int]] = sc.makeRDD(List(
List(1, 2), List(3, 4)
))
val flatRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.flatMap(
list => {
list
}
)
flatRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
模式匹配判断数据
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - flatMap
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(List(1,2),3,List(4,5)))
val flatRDD = rdd.flatMap(
data => {
data match {
case list:List[_] => list
case dat => List(dat)
}
}
)
flatRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
glom
def glom(): RDD[Array[T]]
以分区划分元数据为集合,有几个分区就有几个集合
将同一个分区的数据直接转换为相同类型的内存数组进行处理,分区不变
将不同区的数据求最大值,并对最大值相加
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - glom
val rdd : RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4), 2)
// 【1,2】,【3,4】
// 【2】,【4】
// 【6】
val glomRDD: RDD[Array[Int]] = rdd.glom()
val maxRDD: RDD[Int] = glomRDD.map(
array => {
array.max
}
)
println(maxRDD.collect().sum)
sc.stop()
}
groupBy
def groupBy[K](f: T => K)(implicit kt: ClassTag[K]): RDD[(K, Iterable[T])]
将数据根据指定的规则进行分组, 分区默认不变,但是数据会被打乱重新组合,我们将这样的操作称之为shuffle。极限情况下,数据可能被分在同一个分区中
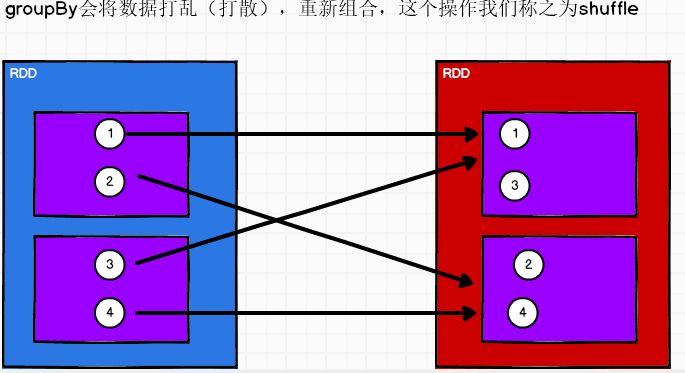
一个组的数据在一个分区中,但是并不是说一个分区中只有一个组
奇偶数分组
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - groupBy
val rdd : RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4), 2)
// groupBy会将数据源中的每一个数据进行分组判断,根据返回的分组key进行分组
// 相同的key值的数据会放置在一个组中
def groupFunction(num:Int) = {
num % 2
}
val groupRDD: RDD[(Int, Iterable[Int])] = rdd.groupBy(groupFunction)
groupRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
以首字母进行分组
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - groupBy
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello", "Spark", "Scala", "Hadoop"), 2)
// 分组和分区没有必然的关系
val groupRDD = rdd.groupBy(_.charAt(0))
groupRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
以每个时间段对Apache服务器日志点击量进行分组
81.220.24.207 - - 17/05/2015:10:05:44 +0000 GET /reset.css
81.220.24.207 - - 17/05/2015:10:05:26 +0000 GET /images/jordan-80.png
81.220.24.207 - - 17/05/2015:10:05:39 +0000 GET /style2.css
71.212.224.97 - - 17/05/2015:11:05:05 +0000 GET /projects/xdotool/
71.212.224.97 - - 17/05/2015:11:05:15 +0000 GET /reset.css
50.16.19.13 - - 17/05/2015:12:05:58 +0000 GET /blog/tags/puppet?flav=rss20
82.193.99.33 - - 17/05/2015:12:05:56 +0000 GET /blog/geekery/ssl-latency.html
111.199.235.239 - - 17/05/2015:13:05:14 +0000 GET /presentations/logstash-puppetconf-2012/images/logs.jpg
111.199.235.239 - - 17/05/2015:13:05:23 +0000 GET /presentations/logstash-puppetconf-2012/
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - groupBy
val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/apache.log")
val timeRDD: RDD[(String, Iterable[(String, Int)])] = rdd.map(
line => {
val datas = line.split(" ")
val time = datas(3)
//time.substring(0, )
val sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss")
val date: Date = sdf.parse(time)
val sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("HH")
val hour: String = sdf1.format(date)
(hour, 1)
}
).groupBy(_._1)
timeRDD.map{
case ( hour, iter ) => {
(hour, iter.size)
}
}.collect.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
filter
def filter(f: T => Boolean): RDD[T]
将数据根据指定的规则进行筛选过滤,符合规则的数据保留,不符合规则的数据丢弃。
当数据进行筛选过滤后,分区不变,但是分区内的数据可能不均衡,生产环境下,可能会出现数据倾斜
过滤掉偶数
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - filter
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4))
val filterRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.filter(num=>num%2!=0)
filterRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
获得服务器xx年xx月xx日的数据
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - filter
val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/apache.log")
rdd.filter(
line => {
val datas = line.split(" ")
val time = datas(3)
time.startsWith("17/05/2015")
}
).collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
sample
def sample( withReplacement:
Boolean, fraction: Double,
seed: Long = Utils.random.nextLong): RDD[T]
根据指定的规则从数据集中抽取数据
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - filter
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10))
// sample算子需要传递三个参数
// 1. 第一个参数表示,抽取数据后是否将数据返回 true(放回),false(丢弃)
// 2. 第二个参数表示,
// 如果抽取不放回的场合:数据源中每条数据被抽取的概率,基准值的概念
// 如果抽取放回的场合:表示数据源中的每条数据被抽取的可能次数
// 3. 第三个参数表示,抽取数据时随机算法的种子
// 如果不传递第三个参数,那么使用的是当前系统时间
// println(rdd.sample(
// false,
// 0.4
// //1
// ).collect().mkString(","))
println(rdd.sample(
true,
2
//1
).collect().mkString(","))
sc.stop()
}
distinct
def distinct()(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T]
def distinct(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T]
将数据集中重复的数据去重
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - filter
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,1,2,3,4))
// map(x => (x, null)).reduceByKey((x, _) => x, numPartitions).map(_._1)
// (1, null),(2, null),(3, null),(4, null),(1, null),(2, null),(3, null),(4, null)
// (1, null)(1, null)(1, null)
// (null, null) => null
// (1, null) => 1
val rdd1: RDD[Int] = rdd.distinct()
rdd1.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
coalesce
根据数据量缩减分区,用于大数据集过滤后,提高小数据集的执行效率
当 spark 程序中,存在过多的小任务的时候,可以通过 coalesce 方法,收缩合并分区,减少分区的个数,减小任务调度成本
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - filter
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6), 3)
// coalesce方法默认情况下不会将分区的数据打乱重新组合
// 这种情况下的缩减分区可能会导致数据不均衡,出现数据倾斜
// 如果想要让数据均衡,可以进行shuffle处理,默认是false,改为true即可
//val newRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.coalesce(2)
val newRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.coalesce(2,true)
newRDD.saveAsTextFile("output")
sc.stop()
}
repartition
def repartition(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T]
该操作内部其实执行的是 coalesce 操作,参数 shuffle 的默认值为 true。无论是将分区数多的RDD 转换为分区数少的RDD,还是将分区数少的 RDD 转换为分区数多的RDD,repartition 操作都可以完成,因为无论如何都会经 shuffle 过程,
扩大分区
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - filter
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6), 2)
// coalesce算子可以扩大分区的,但是如果不进行shuffle操作,是没有意义,不起作用。
// 所以如果想要实现扩大分区的效果,需要使用shuffle操作
// spark提供了一个简化的操作
// 缩减分区:coalesce,如果想要数据均衡,可以采用shuffle
// 扩大分区:repartition, 底层代码调用的就是coalesce,而且肯定采用shuffle
//val newRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.coalesce(3, true)
val newRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.repartition(3)
newRDD.saveAsTextFile("output")
sc.stop()
}
sortBy
操作用于排序数据。在排序之前,可以将数据通过 f 函数进行处理,之后按照 f 函数处理的结果进行排序,默认为升序排列。排序后新产生的 RDD 的分区数与原RDD 的分区数一致。中间存在 shuffle 的过程
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - sortBy
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(6,2,4,5,3,1), 2)
val newRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.sortBy(num=>num)
newRDD.saveAsTextFile("output")
sc.stop()
}
排序
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - sortBy
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(("1", 1), ("11", 2), ("2", 3)), 2)
// sortBy方法可以根据指定的规则对数据源中的数据进行排序,默认为升序,第二个参数可以改变排序的方式
// sortBy默认情况下,不会改变分区。但是中间存在shuffle操作
val newRDD = rdd.sortBy(t=>t._1.toInt, false)
newRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
RDD转换算子(双value类型)
intersection
函数签名
def intersection(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T]
对源RDD 和参数RDD 求交集后返回一个新的RDD
union
def union(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T]
对源RDD 和参数RDD 求并集后返回一个新的RDD
subtract
def subtract(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T]
以一个 RDD 元素为主,去除两个 RDD 中重复元素,将其他元素保留下来。求差集
zip
def zip[U: ClassTag](other: RDD[U]): RDD[(T, U)]
将两个 RDD 中的元素,以键值对的形式进行合并。其中,键值对中的Key 为第 1 个 RDD
中的元素,Value 为第 2 个 RDD 中的相同位置的元素。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - 双Value类型
// 交集,并集和差集要求两个数据源数据类型保持一致
// 拉链操作两个数据源的类型可以不一致
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4))
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(3,4,5,6))
val rdd7 = sc.makeRDD(List("3","4","5","6"))
// 交集 : 【3,4】
val rdd3: RDD[Int] = rdd1.intersection(rdd2)
//val rdd8 = rdd1.intersection(rdd7)
println(rdd3.collect().mkString(","))
// 并集 : 【1,2,3,4,3,4,5,6】
val rdd4: RDD[Int] = rdd1.union(rdd2)
println(rdd4.collect().mkString(","))
// 差集 : 【1,2】
val rdd5: RDD[Int] = rdd1.subtract(rdd2)
println(rdd5.collect().mkString(","))
// 拉链 : 【1-3,2-4,3-5,4-6】
val rdd6: RDD[(Int, Int)] = rdd1.zip(rdd2)
val rdd8 = rdd1.zip(rdd7)
println(rdd6.collect().mkString(","))
sc.stop()
}
zip要求两个数据源分区数量保持一致,分区里的数据也要保持一致
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - 双Value类型
// Can't zip RDDs with unequal numbers of partitions: List(2, 4)
// 两个数据源要求分区数量要保持一致
// Can only zip RDDs with same number of elements in each partition
// 两个数据源要求分区中数据数量保持一致
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6),2)
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(3,4,5,6),2)
val rdd6: RDD[(Int, Int)] = rdd1.zip(rdd2)
println(rdd6.collect().mkString(","))
sc.stop()
}
RDD转换算子(key-value类型)
partitionBy
def partitionBy(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, V)]
将数据按照指定Partitioner 重新进行分区。Spark 默认的分区器是HashPartitioner
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),2)
val mapRDD:RDD[(Int, Int)] = rdd.map((_,1))
// RDD => PairRDDFunctions
// 隐式转换(二次编译)
// partitionBy根据指定的分区规则对数据进行重分区
val newRDD = mapRDD.partitionBy(new HashPartitioner(2))
newRDD.partitionBy(new HashPartitioner(2))
newRDD.saveAsTextFile("output")
sc.stop()
}
reduceByKey
def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)]
def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) => V, numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, V)]
可以将数据按照相同的Key 对Value 进行聚合
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("a", 3), ("b", 4)
))
// reduceByKey : 相同的key的数据进行value数据的聚合操作
// scala语言中一般的聚合操作都是两两聚合,spark基于scala开发的,所以它的聚合也是两两聚合
// 【1,2,3】
// 【3,3】
// 【6】
// reduceByKey中如果key的数据只有一个,是不会参与运算的。
val reduceRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = rdd.reduceByKey( (x:Int, y:Int) => {
println(s"x = ${x}, y = ${y}")
x + y
} )
reduceRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
groupByKey
将数据源的数据根据 key 对 value 进行分组
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("a", 3), ("b", 4)
))
// groupByKey : 将数据源中的数据,相同key的数据分在一个组中,形成一个对偶元组
// 元组中的第一个元素就是key,
// 元组中的第二个元素就是相同key的value的集合
val groupRDD: RDD[(String, Iterable[Int])] = rdd.groupByKey()
groupRDD.collect().foreach(println)
val groupRDD1: RDD[(String, Iterable[(String, Int)])] = rdd.groupBy(_._1)
sc.stop()
}
groupByKey和reduceByKey的区别
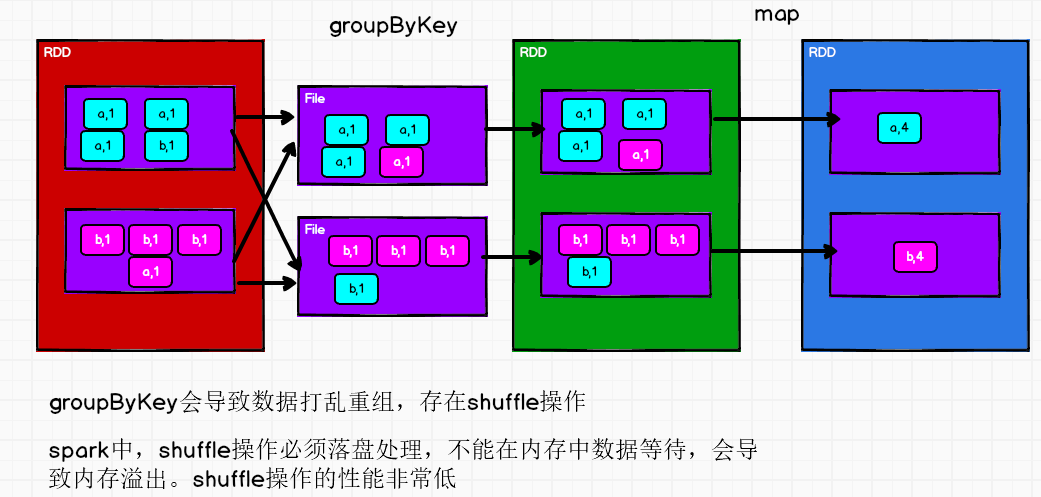
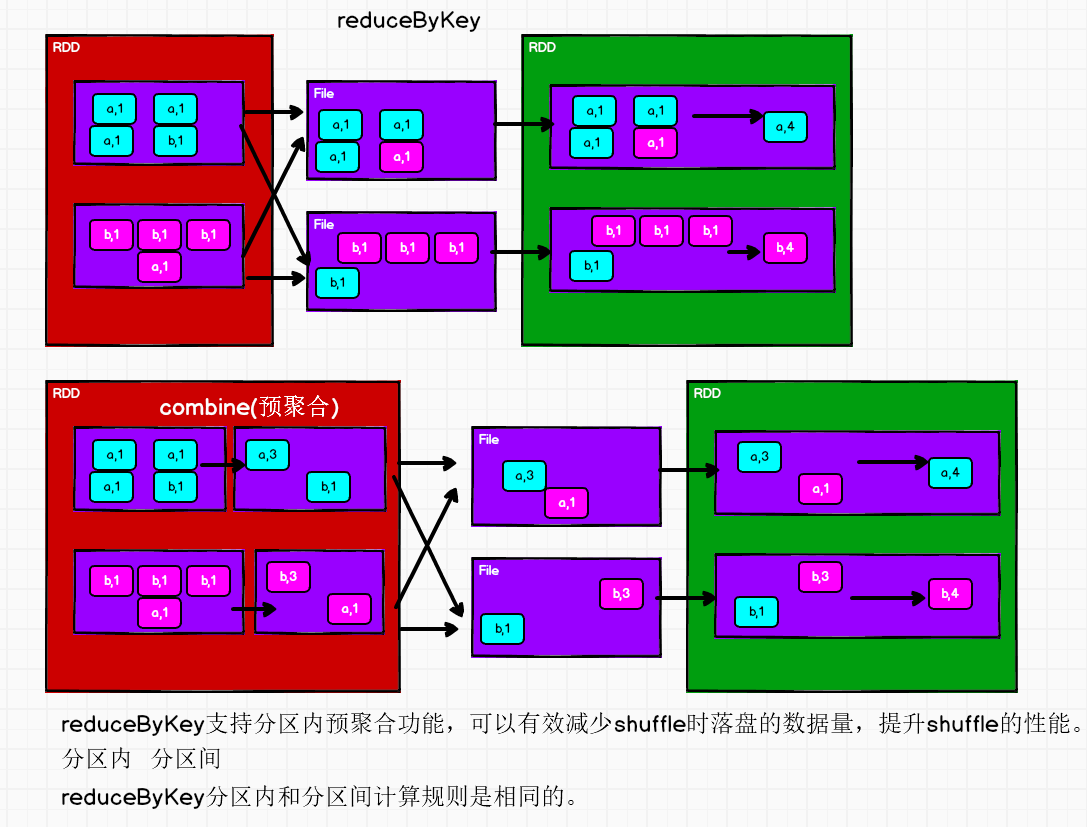
从 shuffle 的角度:reduceByKey 和 groupByKey 都存在 shuffle 的操作,但是reduceByKey 可以在 shuffle 前对分区内相同 key 的数据进行预聚合(combine)功能,这样会减少落盘的数据量,而groupByKey 只是进行分组,不存在数据量减少的问题,reduceByKey 性能比较高。
从功能的角度:reduceByKey 其实包含分组和聚合的功能。GroupByKey 只能分组,不能聚合,所以在分组聚合的场合下,推荐使用 reduceByKey,如果仅仅是分组而不需要聚合。那么还是只能使用groupByKey
aggregateByKey
将数据根据不同的规则进行分区内计算和分区间计算
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("a", 3), ("a", 4)
),2)
// (a,【1,2】), (a, 【3,4】)
// (a, 2), (a, 4)
// (a, 6)
// aggregateByKey存在函数柯里化,有两个参数列表
// 第一个参数列表,需要传递一个参数,表示为初始值
// 主要用于当碰见第一个key的时候,和value进行分区内计算
// 第二个参数列表需要传递2个参数
// 第一个参数表示分区内计算规则
// 第二个参数表示分区间计算规则
// math.min(x, y)
// math.max(x, y)
rdd.aggregateByKey(0)(
(x, y) => math.max(x, y),
(x, y) => x + y
).collect.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("b", 3),
("b", 4), ("b", 5), ("a", 6)
),2)
// (a,【1,2】), (a, 【3,4】)
// (a, 2), (a, 4)
// (a, 6)
// aggregateByKey存在函数柯里化,有两个参数列表
// 第一个参数列表,需要传递一个参数,表示为初始值
// 主要用于当碰见第一个key的时候,和value进行分区内计算
// 第二个参数列表需要传递2个参数
// 第一个参数表示分区内计算规则
// 第二个参数表示分区间计算规则
// math.min(x, y)
// math.max(x, y)
rdd.aggregateByKey(5)(
(x, y) => math.max(x, y),
(x, y) => x + y
).collect.foreach(println)
rdd.aggregateByKey(0)(
(x, y) => x + y,
(x, y) => x + y
).collect.foreach(println)
rdd.aggregateByKey(0)(_+_, _+_).collect.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
求平均值
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("b", 3),
("b", 4), ("b", 5), ("a", 6)
),2)
// aggregateByKey最终的返回数据结果应该和初始值的类型保持一致
//val aggRDD: RDD[(String, String)] = rdd.aggregateByKey("")(_ + _, _ + _)
//aggRDD.collect.foreach(println)
// 获取相同key的数据的平均值 => (a, 3),(b, 4)
val newRDD : RDD[(String, (Int, Int))] = rdd.aggregateByKey( (0,0) )(
( t, v ) => {
(t._1 + v, t._2 + 1)
},
(t1, t2) => {
(t1._1 + t2._1, t1._2 + t2._2)
}
)
val resultRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = newRDD.mapValues {
case (num, cnt) => {
num / cnt
}
}
resultRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
foldByKey
当分区内计算规则和分区间计算规则相同时,aggregateByKey 就可以简化为foldByKey
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("b", 3),
("b", 4), ("b", 5), ("a", 6)
),2)
//rdd.aggregateByKey(0)(_+_, _+_).collect.foreach(println)
// 如果聚合计算时,分区内和分区间计算规则相同,spark提供了简化的方法
rdd.foldByKey(0)(_+_).collect.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
combineByKey
最通用的对key-value 型 rdd 进行聚集操作的聚集函数(aggregation function)。类似于aggregate(),combineByKey()允许用户返回值的类型与输入不一致。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("b", 3),
("b", 4), ("b", 5), ("a", 6)
),2)
// combineByKey : 方法需要三个参数
// 第一个参数表示:将相同key的第一个数据进行结构的转换,实现操作
// 第二个参数表示:分区内的计算规则
// 第三个参数表示:分区间的计算规则
val newRDD : RDD[(String, (Int, Int))] = rdd.combineByKey(
v => (v, 1),
( t:(Int, Int), v ) => {
(t._1 + v, t._2 + 1)
},
(t1:(Int, Int), t2:(Int, Int)) => {
(t1._1 + t2._1, t1._2 + t2._2)
}
)
val resultRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = newRDD.mapValues {
case (num, cnt) => {
num / cnt
}
}
resultRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
reduceByKey、foldByKey、aggregateByKey、combineByKey 的区别?
reduceByKey: 相同 key 的第一个数据不进行任何计算,分区内和分区间计算规则相同
FoldByKey: 相同 key 的第一个数据和初始值进行分区内计算,分区内和分区间计算规则相同
AggregateByKey:相同 key 的第一个数据和初始值进行分区内计算,分区内和分区间计算规则可以不相
CombineByKey:当计算时,发现数据结构不满足要求时,可以让第一个数据转换结构。分区内和分区间计算规则不相同。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("b", 3),
("b", 4), ("b", 5), ("a", 6)
),2)
/*
reduceByKey:
combineByKeyWithClassTag[V](
(v: V) => v, // 第一个值不会参与计算
func, // 分区内计算规则
func, // 分区间计算规则
)
aggregateByKey :
combineByKeyWithClassTag[U](
(v: V) => cleanedSeqOp(createZero(), v), // 初始值和第一个key的value值进行的分区内数据操作
cleanedSeqOp, // 分区内计算规则
combOp, // 分区间计算规则
)
foldByKey:
combineByKeyWithClassTag[V](
(v: V) => cleanedFunc(createZero(), v), // 初始值和第一个key的value值进行的分区内数据操作
cleanedFunc, // 分区内计算规则
cleanedFunc, // 分区间计算规则
)
combineByKey :
combineByKeyWithClassTag(
createCombiner, // 相同key的第一条数据进行的处理函数
mergeValue, // 表示分区内数据的处理函数
mergeCombiners, // 表示分区间数据的处理函数
)
*/
rdd.reduceByKey(_+_) // wordcount
rdd.aggregateByKey(0)(_+_, _+_) // wordcount
rdd.foldByKey(0)(_+_) // wordcount
rdd.combineByKey(v=>v,(x:Int,y)=>x+y,(x:Int,y:Int)=>x+y) // wordcount
sc.stop()
}
sortByKey
def sortByKey(ascending: Boolean = true, numPartitions: Int = self.partitions.length): RDD[(K, V)]
在一个(K,V)的 RDD 上调用,K 必须实现 Ordered 接口(特质),返回一个按照 key 进行排序
join
def join[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (V, W))]
在类型为(K,V)和(K,W)的RDD 上调用,返回一个相同 key 对应的所有元素连接在一起的(K,(V,W))的RDD
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("c", 3)
))
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 5), ("c", 6),("a", 4)
))
// join : 两个不同数据源的数据,相同的key的value会连接在一起,形成元组
// 如果两个数据源中key没有匹配上,那么数据不会出现在结果中
// 如果两个数据源中key有多个相同的,会依次匹配,可能会出现笛卡尔乘积,数据量会几何性增长,会导致性能降低。
val joinRDD: RDD[(String, (Int, Int))] = rdd1.join(rdd2)
joinRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
leftOuterJoin
def leftOuterJoin[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (V, Option[W]))]
类似于 SQL 语句的左外连接
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("b", 2)//, ("c", 3)
))
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 4), ("b", 5),("c", 6)
))
//val leftJoinRDD = rdd1.leftOuterJoin(rdd2)
val rightJoinRDD = rdd1.rightOuterJoin(rdd2)
//leftJoinRDD.collect().foreach(println)
rightJoinRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ZNCRUQbb-1626336375450)(https://gitee.com/sgxmr/image/0raw/master/image-20210714215950975.png)]
cogroup
def cogroup[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W]))]
在类型为(K,V)和(K,W)的RDD 上调用,返回一个(K,(Iterable<V>,Iterable<W>))类型的 RDD
join、leftOuterJoin只能返回key相同的一个v,而cogroup一次全部返回
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// TODO 算子 - (Key - Value类型)
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("b", 2)//, ("c", 3)
))
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 4), ("b", 5),("c", 6),("c", 7)
))
// cogroup : connect + group (分组,连接)
val cgRDD: RDD[(String, (Iterable[Int], Iterable[Int]))] = rdd1.cogroup(rdd2)
cgRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}

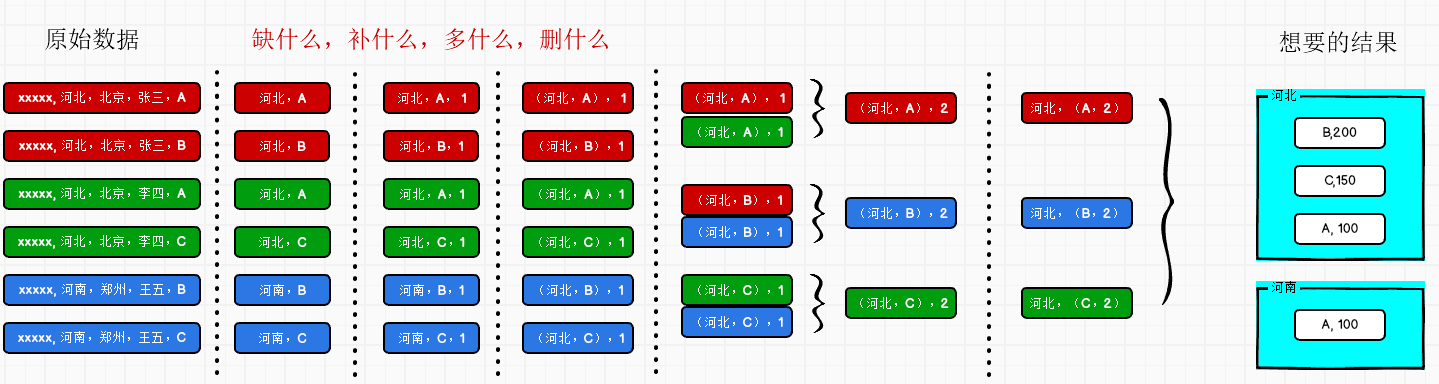
RDD算子综合练习
数据准备
agent.log:时间戳,省份,城市,用户,广告,中间字段使用空格分隔。
1516609143869 0 1 18 24
1516609143869 1 4 44 15
1516609143869 1 3 54 13
1516609143869 1 3 30 3
1516609143871 9 6 65 11
1516609143871 0 9 9 19
1516609143871 4 0 32 20
1516609143871 2 1 28 26
1516609143871 5 2 68 24
1516609143871 8 6 58 3
需求描述
统计出每一个省份每个广告被点击数量排行的 Top3
需求分析
功能实现
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
object RDD_sort {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1.获取原始数据局,时间戳,省份,城市,用户,广告
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("SORT")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val dataRdd = sc.textFile("datas/agent.log")
// 2.将原始的数据进行结构的转换,方便解决问题
// 时间戳,省份,城市,用户,广告 ==> ((省份,广告),1)
val mapRdd =dataRdd.map(
line =>{
val datas = line.split(" ")
((datas(1),datas(4)),1)
}
)
// 3.将转换后的数据结构,进行分组聚合
// ((省份,广告),1) => ((省份,广告),sum)
val reduceRDD: RDD[((String, String), Int)] = mapRdd.reduceByKey(_+_)
// 4.将聚合的结果进行结构的转变 ((省份,广告),sum) => (省份,(广告,sum))
val newMapRdd =reduceRDD.map{
case ((prv,ad),sum)=>{
(prv,(ad,sum))
}
}
// 5.将转换后的数据根据省份进行分组
// (省份,[(广告a,suma),(广告,sumb),....])
val groupRdd: RDD[(String, Iterable[(String, Int)])] = newMapRdd.groupByKey()
// 6.将分组后的数据以sum进行排序并取前3
val result: RDD[(String, List[(String, Int)])] = groupRdd.mapValues(
item =>
item.toList.sortBy(_._2)(Ordering.Int.reverse).take(3)
)
// 7.采集数据打印到控制台
result.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
wordcount不同实现方式
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
wordcount91011(sc)
sc.stop()
}
// groupBy
def wordcount1(sc : SparkContext): Unit = {
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark"))
val words = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val group: RDD[(String, Iterable[String])] = words.groupBy(word=>word)
val wordCount: RDD[(String, Int)] = group.mapValues(iter=>iter.size)
}
// groupByKey
def wordcount2(sc : SparkContext): Unit = {
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark"))
val words = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordOne = words.map((_,1))
val group: RDD[(String, Iterable[Int])] = wordOne.groupByKey()
val wordCount: RDD[(String, Int)] = group.mapValues(iter=>iter.size)
}
// reduceByKey
def wordcount3(sc : SparkContext): Unit = {
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark"))
val words = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordOne = words.map((_,1))
val wordCount: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordOne.reduceByKey(_+_)
}
// aggregateByKey
def wordcount4(sc : SparkContext): Unit = {
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark"))
val words = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordOne = words.map((_,1))
val wordCount: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordOne.aggregateByKey(0)(_+_, _+_)
}
// foldByKey
def wordcount5(sc : SparkContext): Unit = {
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark"))
val words = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordOne = words.map((_,1))
val wordCount: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordOne.foldByKey(0)(_+_)
}
// combineByKey
def wordcount6(sc : SparkContext): Unit = {
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark"))
val words = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordOne = words.map((_,1))
val wordCount: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordOne.combineByKey(
v=>v,
(x:Int, y) => x + y,
(x:Int, y:Int) => x + y
)
}
// countByKey
def wordcount7(sc : SparkContext): Unit = {
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark"))
val words = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordOne = words.map((_,1))
val wordCount: collection.Map[String, Long] = wordOne.countByKey()
}
// countByValue
def wordcount8(sc : SparkContext): Unit = {
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark"))
val words = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordCount: collection.Map[String, Long] = words.countByValue()
}
// reduce, aggregate, fold
def wordcount91011(sc : SparkContext): Unit = {
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark"))
val words = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
// 【(word, count),(word, count)】
// word => Map[(word,1)]
val mapWord = words.map(
word => {
mutable.Map[String, Long]((word,1))
}
)
val wordCount = mapWord.reduce(
(map1, map2) => {
map2.foreach{
case (word, count) => {
val newCount = map1.getOrElse(word, 0L) + count
map1.update(word, newCount)
}
}
map1
}
)
println(wordCount)
}
RDD行动算子
所谓的行动算子,其实就是触发作业(Job)执行的方法
底层代码调用的是环境对象的runJob方法
底层代码中会创建ActiveJob,并提交执行
reduce
def reduce(f: (T, T) => T): T
聚集RDD 中的所有元素,先聚合分区内数据,再聚合分区间数据
collect
def collect(): Array[T]
在驱动程序中,以数组Array 的形式返回数据集的所有元素
count
def count(): Long
返回RDD元素的个数
first
def first(): T
返回RDD第一个元素
take
def take(num: Int): Array[T]
返回一个由RDD 的前 n 个元素组成的数组
takeOrdered
def takeOrdered(num: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T]): Array[T]
返回一个由RDD排序后 的前 n 个元素组成的数组
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4))
// TODO - 行动算子
// reduce
//val i: Int = rdd.reduce(_+_)
//println(i)
// collect : 方法会将不同分区的数据按照分区顺序采集到Driver端内存中,形成数组
//val ints: Array[Int] = rdd.collect()
//println(ints.mkString(","))
// count : 数据源中数据的个数
val cnt = rdd.count()
println(cnt)
// first : 获取数据源中数据的第一个
val first = rdd.first()
println(first)
// take : 获取N个数据
val ints: Array[Int] = rdd.take(3)
println(ints.mkString(","))
// takeOrdered : 数据排序后,取N个数据
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(4,2,3,1))
val ints1: Array[Int] = rdd1.takeOrdered(3)
println(ints1.mkString(","))
sc.stop()
}
aggregate
def aggregate[U: ClassTag](zeroValue: U)(seqOp: (U, T) => U, combOp: (U, U) => U): U
分区的数据通过初始值和分区内的数据进行聚合,然后再和初始值进行分区间的数据聚合
fold
def fold(zeroValue: T)(op: (T, T) => T): T
折叠操作,aggregate 的简化版操作,分区间分区内规则相同时
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),2)
// TODO - 行动算子
//10 + 13 + 17 = 40
// aggregateByKey : 初始值只会参与分区内计算
// aggregate : 初始值会参与分区内计算,并且和参与分区间计算
//val result = rdd.aggregate(10)(_+_, _+_)
val result = rdd.fold(10)(_+_)
println(result)
sc.stop()
}
countByKey
def countByKey(): Map[K, Long]
统计每种key的个数
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,1,1,4),2)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1),("a", 2),("a", 3)
))
// TODO - 行动算子
//val intToLong: collection.Map[Int, Long] = rdd.countByValue()
//println(intToLong)
val stringToLong: collection.Map[String, Long] = rdd.countByKey()
println(stringToLong)
sc.stop()
}
save相关算子
def saveAsTextFile(path: String): Unit def saveAsObjectFile(path: String): Unit def saveAsSequenceFile(
path: String,
codec: Option[Class[_ <: CompressionCodec]] = None): Unit
将数据保存到不同格式的文件中
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,1,1,4),2)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1),("a", 2),("a", 3)
))
// TODO - 行动算子
rdd.saveAsTextFile("output")
rdd.saveAsObjectFile("output1")
// saveAsSequenceFile方法要求数据的格式必须为K-V类型
rdd.saveAsSequenceFile("output2")
sc.stop()
}
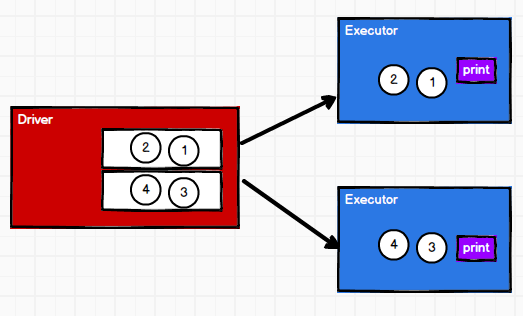
foreach
def foreach(f: T => Unit): Unit = withScope { val cleanF = sc.clean(f)
sc.runJob(this, (iter: Iterator[T]) => iter.foreach(cleanF))
}
分布式遍历RDD 中的每一个元素,调用指定函数
RDD的方法和Scala集合对象的方法不一样
RDD的方法可以将计算逻辑发送到Executor端(分布式节点)执行
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4))
// foreach 其实是Driver端内存集合的循环遍历方法
rdd.collect().foreach(println)
println("******************")
// foreach 其实是Executor端内存数据打印
rdd.foreach(println)
// 算子 : Operator(操作)
// RDD的方法和Scala集合对象的方法不一样
// 集合对象的方法都是在同一个节点的内存中完成的。
// RDD的方法可以将计算逻辑发送到Executor端(分布式节点)执行
// 为了区分不同的处理效果,所以将RDD的方法称之为算子。
// RDD的方法外部的操作都是在Driver端执行的,而方法内部的逻辑代码是在Executor端执行。
sc.stop()
}
RDD序列化
闭包检查
从计算的角度,算子以外的代码都是在Driver 端执行, 算子里面的代码都是在 Executor 端执行。那么在 scala 的函数式编程中,就会导致算子内经常会用到算子外的数据,这样就形成了闭包的效果,如果使用的算子外的数据无法序列化,就意味着无法传值给Executor 端执行,就会发生错误,所以需要在执行任务计算前,检测闭包内的对象是否可以进行序列化,这个操作我们称之为闭包检测。Scala2.12 版本后闭包编译方式发生了改变
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List[Int]())
val user = new User()
// SparkException: Task not serializable
// NotSerializableException: com.atguigu.bigdata.spark.core.rdd.operator.action.Spark07_RDD_Operator_Action$User
// RDD算子中传递的函数是会包含闭包操作,那么就会进行检测功能
// 闭包检测
rdd.foreach(
num => {
println("age = " + (user.age + num))
}
)
sc.stop()
}
//class User extends Serializable {
// 样例类在编译时,会自动混入序列化特质(实现可序列化接口)
//case class User() {
class User {
var age : Int = 30
}
序列化
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.makeRDD(Array("hello world", "hello spark", "hive", "atguigu"))
val search = new Search("h")
//search.getMatch1(rdd).collect().foreach(println)
search.getMatch2(rdd).collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
// 查询对象
// 类的构造参数其实是类的属性, 构造参数需要进行闭包检测,其实就等同于类进行闭包检测
class Search(query:String){
def isMatch(s: String): Boolean = {
s.contains(this.query)
}
// 函数序列化案例
def getMatch1 (rdd: RDD[String]): RDD[String] = {
rdd.filter(isMatch)
}
// 属性序列化案例
def getMatch2(rdd: RDD[String]): RDD[String] = {
val s = query
rdd.filter(x => x.contains(s))
}
}
Kryo 序列化框架
参考地址: https://github.com/EsotericSoftware/kryo
Java 的序列化能够序列化任何的类。但是比较重(字节多),序列化后,对象的提交也比较大。Spark 出于性能的考虑,Spark2.0 开始支持另外一种Kryo 序列化机制。Kryo 速度是 Serializable 的 10 倍。当 RDD 在 Shuffle 数据的时候,简单数据类型、数组和字符串类型已经在 Spark 内部使用 Kryo 来序列化。
注意:即使使用Kryo 序列化,也要继承Serializable 接口
bject serializable_Kryo {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf()
.setAppName("SerDemo")
.setMaster("local[*]")
// 替换默认的序列化机制
.set("spark.serializer", "org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer")
// 注册需要使用 kryo 序列化的自定义类
.registerKryoClasses(Array(classOf[Searcher])) val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.makeRDD(Array("hello world", "hello atguigu", "atguigu", "hahah"), 2)
val searcher = new Searcher("hello")
val result: RDD[String] = searcher.getMatchedRDD1(rdd)
result.collect.foreach(println)
}
}
case class Searcher(val query: String) {
def isMatch(s: String) = { s.contains(query)
}
def getMatchedRDD1(rdd: RDD[String]) = { rdd.filter(isMatch)
}
def getMatchedRDD2(rdd: RDD[String]) = { val q = query rdd.filter(_.contains(q))}
RDD依赖关系
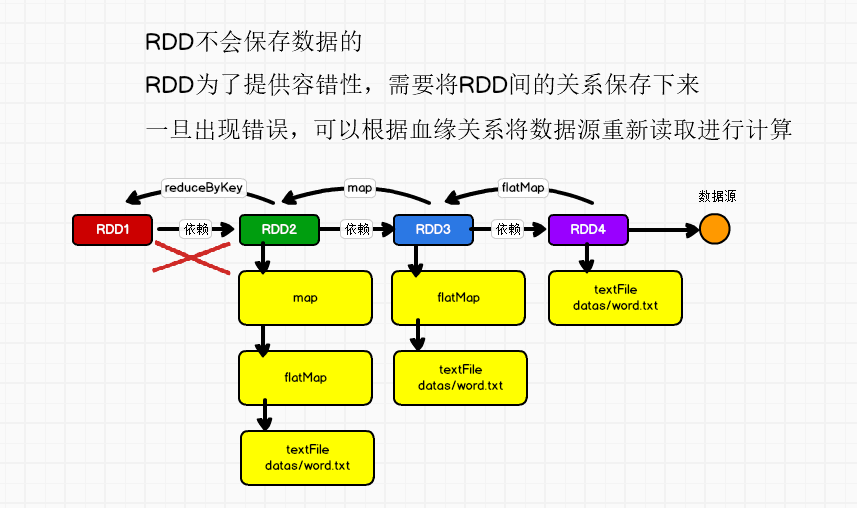
RDD血缘关系
RDD 只支持粗粒度转换,即在大量记录上执行的单个操作。将创建 RDD 的一系列Lineage(血统)记录下来,以便恢复丢失的分区。RDD 的Lineage 会记录RDD 的元数据信息和转换行为,当该RDD 的部分分区数据丢失时,它可以根据这些信息来重新运算和恢复丢失的数据分区。
object Spark01_RDD_Dep {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val lines: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/word.txt")
println(lines.toDebugString)
println("*************************")
val words: RDD[String] = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
println(words.toDebugString)
println("*************************")
val wordToOne = words.map(word=>(word,1))
println(wordToOne.toDebugString)
println("*************************")
val wordToSum: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordToOne.reduceByKey(_+_)
println(wordToSum.toDebugString)
println("*************************")
val array: Array[(String, Int)] = wordToSum.collect()
array.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
RDD依赖关系
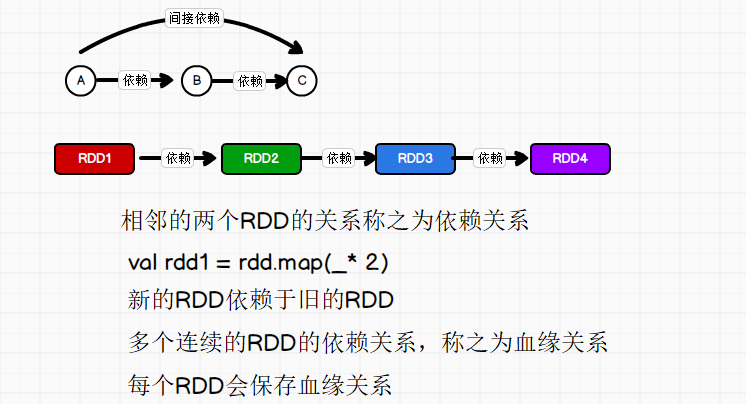
这里所谓的依赖关系,其实就是两个相邻 RDD 之间的关系
object Spark02_RDD_Dep {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("Dep")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val lines: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/word.txt")
println(lines.dependencies)
println("*************************")
val words: RDD[String] = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
println(words.dependencies)
println("*************************")
val wordToOne = words.map(word=>(word,1))
println(wordToOne.dependencies)
println("*************************")
val wordToSum: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordToOne.reduceByKey(_+_)
println(wordToSum.dependencies)
println("*************************")
val array: Array[(String, Int)] = wordToSum.collect()
array.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
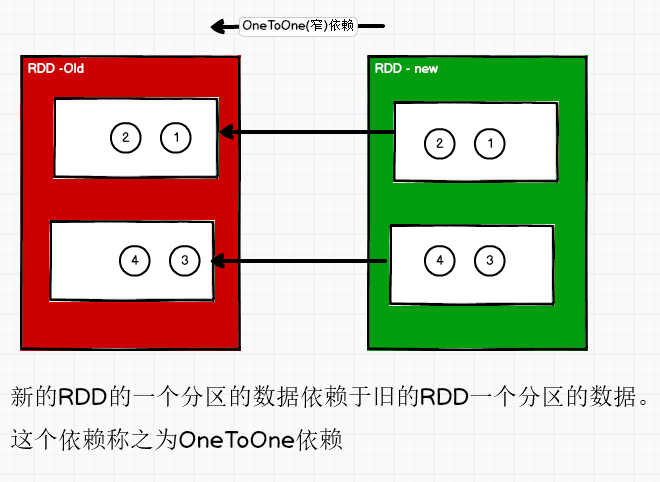
RDD 窄依赖
窄依赖表示每一个父(上游)RDD 的 Partition 最多被子(下游)RDD 的一个 Partition 使用, 窄依赖我们形象的比喻为独生子女
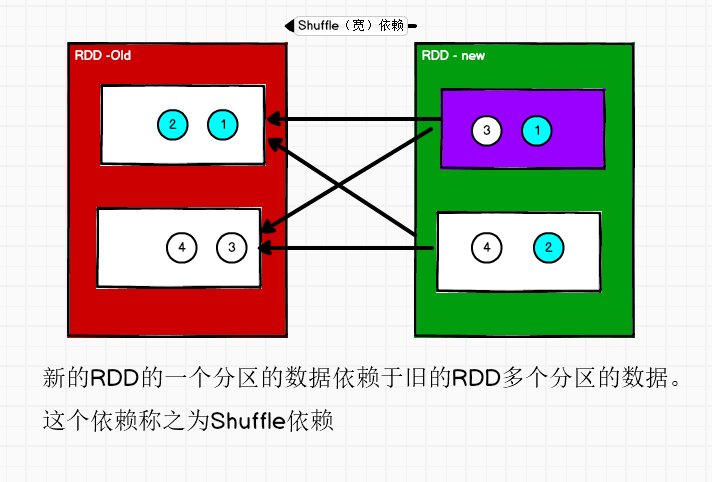
RDD 宽依赖
依赖表示同一个父(上游)RDD 的 Partition 被多个子(下游)RDD 的 Partition 依赖,会引起 Shuffle,总结:宽依赖我们形象的比喻为多生。
RDD持久化
RDD Cache缓存
RDD 通过Cache 或者 Persist 方法将前面的计算结果缓存,默认情况下会把数据以缓存在 JVM 的堆内存中。但是并不是这两个方法被调用时立即缓存,而是触发后面的 action 算子时,该RDD 将会被缓存在计算节点的内存中,并后面重用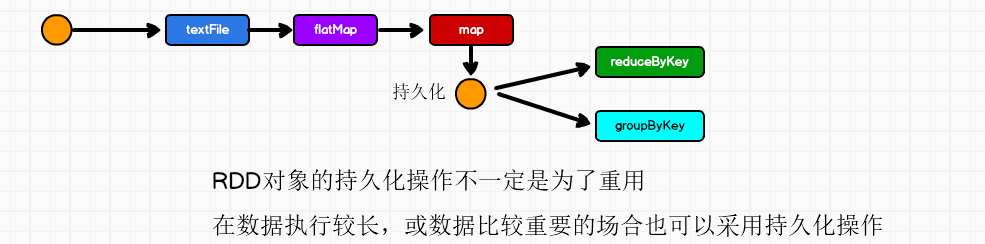
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("Persist")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val list = List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark")
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(list)
val flatRDD = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val mapRDD = flatRDD.map(word=>{
println("@@@@@@@@@@@@")
(word,1)
})
// cache默认持久化的操作,只能将数据保存到内存中,如果想要保存到磁盘文件,需要更改存储级别
//mapRDD.cache()
// 持久化操作必须在行动算子执行时完成的。
mapRDD.persist(StorageLevel.DISK_ONLY)
val reduceRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = mapRDD.reduceByKey(_+_)
reduceRDD.collect().foreach(println)
println("**************************************")
val groupRDD = mapRDD.groupByKey()
groupRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
RDD CheckPoint检查点
所谓的检查点其实就是通过将RDD 中间结果写入磁盘由于血缘依赖过长会造成容错成本过高,这样就不如在中间阶段做检查点容错,如果检查点之后有节点出现问题,可以从检查点开始重做血缘,减少了开销。对 RDD 进行 checkpoint 操作并不会马上被执行,必须执行 Action 操作才能触发
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("Persist")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
sc.setCheckpointDir("cp")
val list = List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark")
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(list)
val flatRDD = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val mapRDD = flatRDD.map(word=>{
println("@@@@@@@@@@@@")
(word,1)
})
// checkpoint 需要落盘,需要指定检查点保存路径
// 检查点路径保存的文件,当作业执行完毕后,不会被删除
// 一般保存路径都是在分布式存储系统:HDFS
mapRDD.checkpoint()
val reduceRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = mapRDD.reduceByKey(_+_)
reduceRDD.collect().foreach(println)
println("**************************************")
val groupRDD = mapRDD.groupByKey()
groupRDD.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
缓存和检查点区别
1) Cache 缓存只是将数据保存起来,不切断血缘依赖。Checkpoint 检查点切断血缘依赖。
2) Cache 缓存的数据通常存储在磁盘、内存等地方,可靠性低。Checkpoint 的数据通常存储在HDFS 等容错、高可用的文件系统,可靠性高。
3) 建议对checkpoint()的RDD 使用Cache 缓存,这样 checkpoint 的 job 只需从 Cache 缓存中读取数据即可,否则需要再从头计算一次RDD。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// cache : 将数据临时存储在内存中进行数据重用
// 会在血缘关系中添加新的依赖。一旦,出现问题,可以重头读取数据
// persist : 将数据临时存储在磁盘文件中进行数据重用
// 涉及到磁盘IO,性能较低,但是数据安全
// 如果作业执行完毕,临时保存的数据文件就会丢失
// checkpoint : 将数据长久地保存在磁盘文件中进行数据重用
// 涉及到磁盘IO,性能较低,但是数据安全
// 为了保证数据安全,所以一般情况下,会独立执行作业
// 为了能够提高效率,一般情况下,是需要和cache联合使用
// 执行过程中,会切断血缘关系。重新建立新的血缘关系
// checkpoint等同于改变数据源
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("Persist")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
sc.setCheckpointDir("cp")
val list = List("Hello Scala", "Hello Spark")
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(list)
val flatRDD = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val mapRDD = flatRDD.map(word=>{
(word,1)
})
//mapRDD.cache()
mapRDD.checkpoint()
println(mapRDD.toDebugString)
val reduceRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = mapRDD.reduceByKey(_+_)
reduceRDD.collect().foreach(println)
println("**************************************")
println(mapRDD.toDebugString)
sc.stop()
}
RDD分区器
Spark 目前支持Hash 分区和 Range 分区,和用户自定义分区。Hash 分区为当前的默认分区。分区器直接决定了RDD 中分区的个数、RDD 中每条数据经过Shuffle 后进入哪个分区,进而决定了Reduce 的个数。
? 只有Key-Value 类型的RDD 才有分区器,非 Key-Value 类型的RDD 分区的值是 None
? 每个RDD 的分区 ID 范围:0 ~ (numPartitions - 1),决定这个值是属于那个分区的。
-
Hash 分区:对于给定的 key,计算其hashCode,并除以分区个数取余
-
Range分区将一定范围内的数据映射到一个分区中,尽量保证每个分区数据均匀,而且分区间有序
自定义分区案例
object Spark01_RDD_Part {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("nba", "xxxxxxxxx"),
("cba", "xxxxxxxxx"),
("wnba", "xxxxxxxxx"),
("nba", "xxxxxxxxx"),
),3)
val partRDD: RDD[(String, String)] = rdd.partitionBy( new MyPartitioner )
partRDD.saveAsTextFile("output")
sc.stop()
}
/**
* 自定义分区器
* 1. 继承Partitioner
* 2. 重写方法
*/
class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner{
// 分区数量
override def numPartitions: Int = 3
// 根据数据的key值返回数据所在的分区索引(从0开始)
override def getPartition(key: Any): Int = {
key match {
case "nba" => 0
case "wnba" => 1
case _ => 2
}
}
}
}
RDD文件读取和保存
Spark 的数据读取及数据保存可以从两个维度来作区分:文件格式以及文件系统。
文件格式分为:
text 文件、csv 文件、sequence 文件以及Object 文件;
文件系统分为:
本地文件系统、HDFS、HBASE 以及数据库。
保存
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(
List(
("a", 1),
("b", 2),
("c", 3)
)
)
rdd.saveAsTextFile("output1")
rdd.saveAsObjectFile("output2")
rdd.saveAsSequenceFile("output3")
sc.stop()
}
读取
object Spark01_RDD_IO_Load {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val rdd = sc.textFile("output1")
println(rdd.collect().mkString(","))
val rdd1 = sc.objectFile[(String, Int)]("output2")
println(rdd1.collect().mkString(","))
val rdd2 = sc.sequenceFile[String, Int]("output3")
println(rdd2.collect().mkString(","))
sc.stop()
}
累加器
分布式共享只写变量
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("Acc")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4))
// reduce : 分区内计算,分区间计算
//val i: Int = rdd.reduce(_+_)
//println(i)
var sum = 0
rdd.foreach(
num => {
sum += num
}
)
println("sum = " + sum) //0 按说应该是10
}
没有累加器的话Executor无法返回数据给Driver,计算的时候是分布式的
累加器的作用
累加器用来把Executor 端变量信息聚合到Driver 端。在Driver 程序中定义的变量,在Executor 端的每个Task 都会得到这个变量的一份新的副本,每个 task 更新这些副本的值后, 传回Driver 端进行 merge。
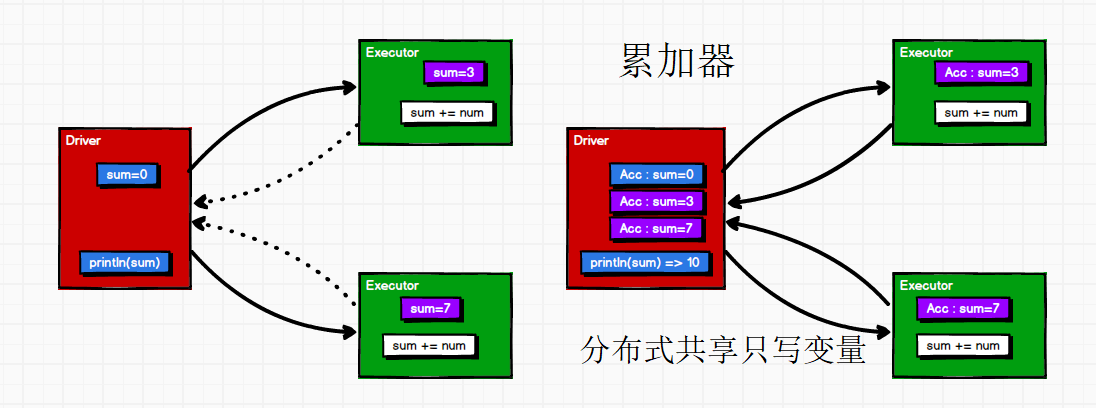
系统累加器
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("Acc")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4))
// 获取系统累加器
// Spark默认就提供了简单数据聚合的累加器
val sumAcc = sc.longAccumulator("sum")
//sc.doubleAccumulator
//sc.collectionAccumulator
rdd.foreach(
num => {
// 使用累加器
sumAcc.add(num)
}
)
// 获取累加器的值
println(sumAcc.value)
sc.stop()
}
转换算子和累加器
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("Acc")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4))
// 获取系统累加器
// Spark默认就提供了简单数据聚合的累加器
val sumAcc = sc.longAccumulator("sum")
//sc.doubleAccumulator
//sc.collectionAccumulator
val mapRDD = rdd.map(
num => {
// 使用累加器
sumAcc.add(num)
num
}
)
// 获取累加器的值
// 少加:转换算子中调用累加器,如果没有行动算子的话,那么不会执行
// 多加:转换算子中调用累加器,如果没有行动算子的话,那么不会执行
// 一般情况下,累加器会放置在行动算子进行操作
mapRDD.collect()
mapRDD.collect()
println(sumAcc.value)
sc.stop()
}
自定义累加器
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("Acc")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("hello", "spark", "hello"))
// 累加器 : WordCount
// 创建累加器对象
val wcAcc = new MyAccumulator()
// 向Spark进行注册
sc.register(wcAcc, "wordCountAcc")
rdd.foreach(
word => {
// 数据的累加(使用累加器)
wcAcc.add(word)
}
)
// 获取累加器累加的结果
println(wcAcc.value)
sc.stop()
}
/*
自定义数据累加器:WordCount
1. 继承AccumulatorV2, 定义泛型
IN : 累加器输入的数据类型 String
OUT : 累加器返回的数据类型 mutable.Map[String, Long]
2. 重写方法(6)
*/
class MyAccumulator extends AccumulatorV2[String, mutable.Map[String, Long]] {
private var wcMap = mutable.Map[String, Long]()
// 判断是否初始状态
override def isZero: Boolean = {
wcMap.isEmpty
}
override def copy(): AccumulatorV2[String, mutable.Map[String, Long]] = {
new MyAccumulator()
}
override def reset(): Unit = {
wcMap.clear()
}
// 获取累加器需要计算的值
override def add(word: String): Unit = {
val newCnt = wcMap.getOrElse(word, 0L) + 1
wcMap.update(word, newCnt)
}
// Driver合并多个累加器
override def merge(other: AccumulatorV2[String, mutable.Map[String, Long]]): Unit = {
val map1 = this.wcMap
val map2 = other.value
map2.foreach{
case ( word, count ) => {
val newCount = map1.getOrElse(word, 0L) + count
map1.update(word, newCount)
}
}
}
// 累加器结果
override def value: mutable.Map[String, Long] = {
wcMap
}
}
广播变量
分布式共享只读变量
广播变量用来高效分发较大的对象。向所有工作节点发送一个较大的只读值,以供一个或多个 Spark 操作使用。比如,如果你的应用需要向所有节点发送一个较大的只读查询表, 广播变量用起来都很顺手。在多个并行操作中使用同一个变量,但是 Spark 会为每个任务分别发送。
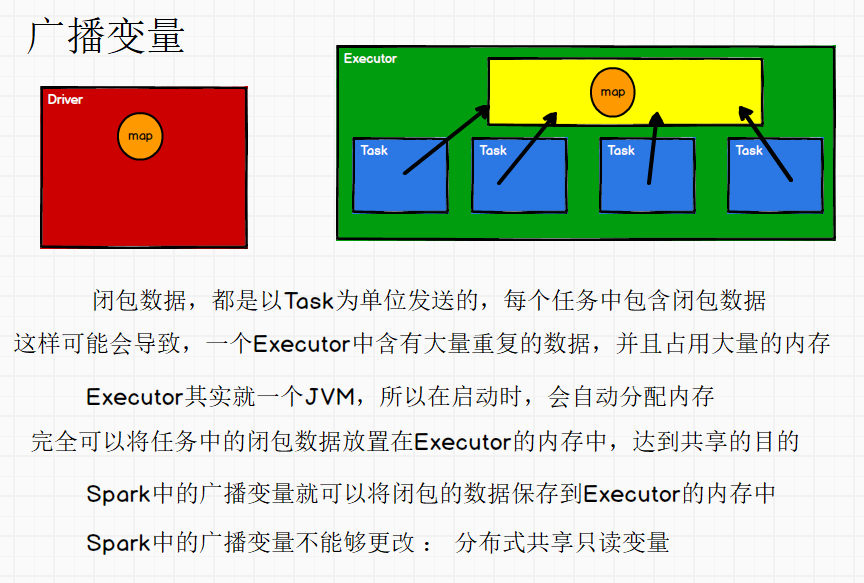
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("Acc")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1),("b", 2),("c", 3)
))
val map = mutable.Map(("a", 4),("b", 5),("c", 6))
// 封装广播变量
val bc: Broadcast[mutable.Map[String, Int]] = sc.broadcast(map)
rdd1.map {
case (w, c) => {
// 方法广播变量
val l: Int = bc.value.getOrElse(w, 0)
(w, (c, l))
}
}.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}