HBase 简介
HBase 的全称是 Hadoop Database,是一个分布式的,可扩展,面向列簇的数据库。HDFS 为 Hbase 提供了可靠的底层数据存储服务,Zookeeper 为 Hbase 元数据管理和协调服务,Hbase 是一个通过大量廉价的机器解决海量数据的高速存储和读取的分布式数据库解决方案。HBase 的原型是谷歌的分布式存储系统 BigTable,是谷歌 BigTable 的开源实现。

HBase 基本概念
- Table:表,一个表包含多行数据。
- Rowkey:行的主键,唯一标识一行数据,用于检索记录。
- Column family:列簇,同一个列簇的所有成员具有相同的列簇前缀,通常将同一类型的列存放在一个列簇下。
- Qualifier:列,以列簇作为前缀,格式为 Column family:Qualifier。
- Timestamp:时间戳,插入单元格时的时间戳,默认作为单元格的版本号。不同版本的数据按照时间戳倒序排序,即最新的数据排在最前面。
- Cell:单元格,在 HBase 中,值作为一个单元保存在单元格中。要定位一个单元,需要满足 “rowkey + column family + qualifier + timestamp” 四个要素。每个 cell 保存着同一份数据的多个版本。cell 中没有数据类型,完全是字节存储。
- Master:主要负责 HBase 系统的各种管理工作:
- 处理用户的各种管理请求,包括建表、修改表、权限操作、切分表、合并数据分片以及 Compaction 等。
- 管理集群中所有 RegionServer,包括 RegionServe r中 Region 的负载均衡、RegionServer 的宕机恢复以及 Region 的迁移等。
- 清理过期日志以及文件,Master 会每隔一段时间检查 HDFS 中 HLog 是否过期、HFile 是否已经被删除,并在过期之后将其删除。
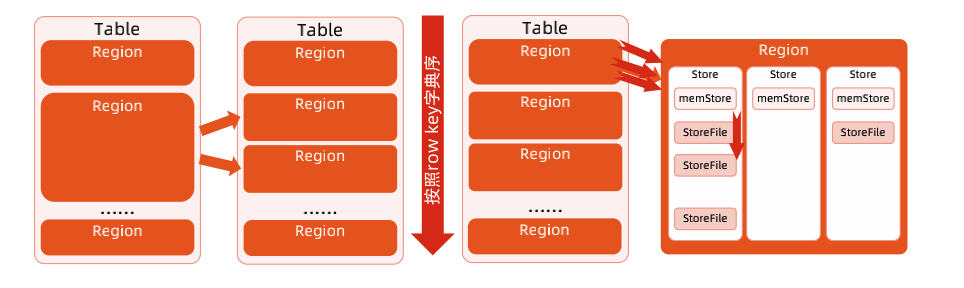
- RegionServer: RegionServer 主要用来响应用户的 IO 请求,是 HBase 中最核心的模块,由 WAL(HLog)、BlockCache 以及多个 Region 构成。
-
Region: 数据表的一个分片,当数据表大小超过一定阈值就会“水平切分”,Region 是集群负载均衡的基本单位。一个 Region 由一个或者多个 Store 构成, Store 的个数取决于表中列簇(column family)的个数,有多少个列簇就有多少个 Store。
- Store:由两部分组成:MemStore 和 StoreFile。MemStore 称为写缓存,用户写入数据时首先会写到 MemStore,当 MemStore 写满之后(缓存数据超过阈值,默认 128M)系统会异步地将数据 flush成一个 HFile 文件。显然,随着数据不断写入,HFile 文件会越来越多,当 HFile 文件数超过一定阈值之后系统将会执行 Compact 操作,将这些小文件通过一定策略合并成一个或多个大文件。
- StoreFile(HFile): HBase 的数据最终是存放在 HDFS 上的,StoreFile 在 HDFS 上称为 HFile。
-
HLog:Write ahead log(WAL),HLog 在 HBase 中有两个核心作用:其一,用于实现数据的高可靠性,HBase 数据随机写入时,并非直接写入 HFile 数据文件,而是先写入缓存,再异步刷新落盘。为了防止缓存数据丢失,数据写入缓存之前需要首先顺序写入 HLog,这样,即使缓存数据丢失,仍然可以通过 HLog 日志恢复;其二,用于实现 HBase 集群间主从复制,通过回放主集群推送过来的 HLog 日志实现主从复制。
-
BlockCache:HBase系统中的读缓存。客户端从磁盘读取数据之后通常会将数据缓存到系统内存中,后续访问同一行数据可以直接从内存中获取而不需要访问磁盘。
-
- HBase 客户端:提供了 Shell 命令行接口、原生 Java API 编程接口、Thrift/REST API 编程接口以及 MapReduce 编程接口。
整体示意图:

HBase 视图
逻辑视图
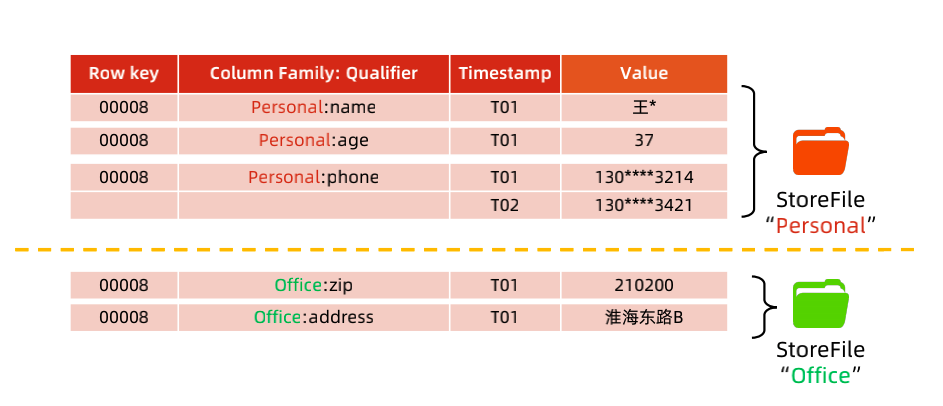
从逻辑视图来看,HBase 中的数据是以表形式进行组织的,而且和关系型数据库中的表一样,HBase 中的表也由行和列构成。
在下图中有两个列簇: Personal 和 Office,Personal 列簇中存放了和个人信息相关的三个列:name,age,phone。Office 列簇中存放了和办公地点相关的两个列:zip,address。rowkey 为 00008 的 personal:phone 的 cell 存放了两个版本的数据。
HBase 将数据按照 rowkey 字典序排序存储,访问 Hbase 表有三种方式:
- 1.通过单个row key访问
- 2.通过row key的range
- 3.全表扫描

物理视图
从物理视图来看,HBase 是一个 Map,由键值 KV 构成,不过与普通的 Map 不同,HBase 是一个稀疏的、分布式的、多维排序的 Map。
HBase 中 Map 的 key 是一个复合键,由 rowkey、column family、qualifier 以及 timestamp 组成,value 即为 cell 的值。
稀疏性是 HBase 中的一个突出的特点,在其他数据库中,对于空值的处理一般都会填充 null,对于成百上千万列的表来说,通常会存在大量的空值,如果使用填充 null 的策略,势必会造成大量空间的浪费。而对于 HBase 空值不需要任何填充,因此稀疏性是 HBase 的列可以无限扩展的一个重要的条件。
行式存储、列式存储、列簇式存储
与大多数数据库系统不同,HBase 中的数据是按照列簇存储的,即将数据按照列簇分别存储在不同的目录中。为什么 HBase 要将数据按照列簇分别存储?回答这个问题之前需要先了解两个非常常见的概念:行式存储、列式存储,这是数据存储领域比较常见的两种数据存储方式。
行式存储:行式存储系统会将一行数据存储在一起,一行数据写完之后再接着写下一行,最典型的如 MySQL 这类关系型数据库。

行式存储在获取一行数据时是很高效的,但是如果某个查询只需要读取表中指定列对应的数据,那么行式存储会先取出一行行数据,再在每一行数据中截取待查找目标列。这种处理方式在查找过程中引入了大量无用列信息,从而导致大量内存占用。因此,这类系统仅适合于处理OLTP 类型的负载,对于 OLAP 这类分析型负载并不擅长。
列式存储:列式存储理论上会将一列数据存储在一起,不同列的数据分别集中存储,最典型的如Kudu、Parquet on HDFS 等系统。
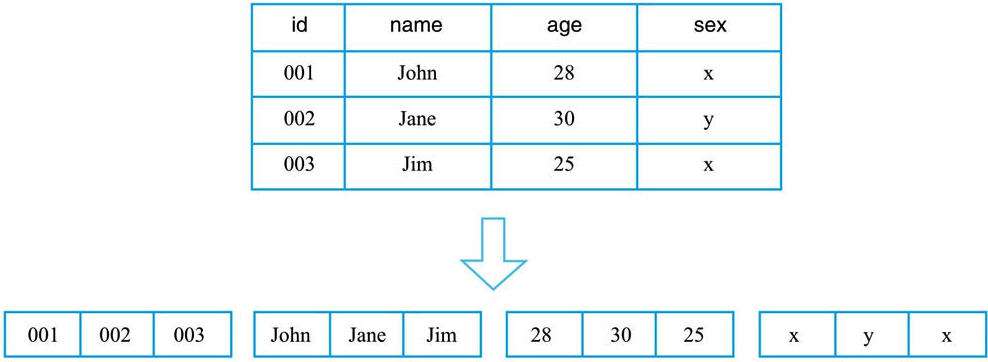
列式存储对于只查找某些列数据的请求非常高效,只需要连续读出所有待查目标列,然后遍历处理即可;但是反过来,列式存储对于获取一行的请求就不那么高效了,需要多次 IO 读多个列数据,最终合并得到一行数据。另外,因为同一列的数据通常都具有相同的数据类型,因此列式存储具有天然的高压缩特性。
列簇式存储:从概念上来说,列簇式存储介于行式存储和列式存储之间,可以通过不同的设计思路在行式存储和列式存储两者之间相互切换。比如,一张表只设置一个列簇,这个列簇包含所有用户的列。HBase 中一个列簇的数据是存储在一起的,因此这种设计模式就等同于行式存储。再比如,一张表设置大量列簇,每个列簇下仅有一列,很显然这种设计模式就等同于列式存储。上面两例当然是两种极端的情况,在当前体系中不建议设置太多列簇,但是这种架构为HBase将来演变成 HTAP(Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing)系统提供了最核心的基础。
HBase 架构
- HBase 是典型的 Master-Slave 模型,系统中有一个管理集群的 Master 节点以及大量实际服务用户读写的 RegionServer 节点。
- HBase 中所有数据最终都存储在 HDFS 系统中,为数据提供了高可靠的保障。
- Zookeeper 节点为 HBase 集群提供了协调管理的作用。
- 实现 Master 高可用:通常情况下系统中只有一个 Master 工作,一旦 ActiveMaster 由于异常宕机,ZooKeeper 会检测到该宕机事件,并通过一定机制选举出新的 Master,保证系统正常运转。
- 管理系统核心元数据:比如,管理当前系统中正常工作的 RegionServer 集合,保存系统元数据表 hbase:meta 所在的 RegionServer 地址等。
- 参与 RegionServer 宕机恢复:ZooKeeper 通过心跳可以感知到 RegionServer 是否宕机,并在宕机后通知 Master 进行宕机处理。
- 实现分布式表锁:HBase 中对一张表进行各种管理操作(比如 alter 操作)需要先加表锁,防止其他用户对同一张表进行管理操作,造成表状态不一致。和其他 RDBMS 表不同,HBase 中的表通常都是分布式存储,ZooKeeper 可以通过特定机制实现分布式表锁。

HBase 读写流程
Client 在读写数据的过程中,不会和 Master 节点进行交互,当处理管理请求时:包括建表、修改表、权限操作、切分表、合并数据分片以及 Compaction 等,才会和 Master 节点通信。
写流程
- 1.Client 先访问 Zookeeper 的 /hbase/meta-region-server 节点,获取 hbase:meta 表位于哪个 RegionServer。
- 2.Client 访问对应的 RegionServer,获取 hbase:meta 表,将 hbase:meta 表信息缓存在客户端的 MetaCache,方便下次访问。从 hbase:meta 表中找到相应 rowkey 需要访问的 RegionServer。
- 3.Client 的 Put 操作会将数据先写入 HLog(WAL)。
- 4.当数据写入 HLog 后,再将数据写入 MemStore(内存),数据会在 MemStore 进行排序。
- 5.一旦数据成功写入到 MemStore,Client 将收到 ACK。
- 6.当 MemStore 中的数据达到阈值,数据会刷写入 HFile(磁盘)。
HBase 服务端并没有提供 update、delete 接口,HBase 中队数据的更新、删除操作在服务端也认为是写入操作,不同的是,更新操作会写入一个最新版本的数据,删除操作会写入一条标记为 deleted 的 KV 数据。
MemStore Flush 触发条件:
- MemStore 级别限制:当 Region 中任意一个 MemStore 大小达到上限(默认是 128M),触发 MemStore 刷新。
- Region 级别限制:当 Region 中所有 MemStore 大小总和达到了上限,会触发 MemStore 刷新。
- RegionServer 级别限制:当 RegionServer 中 MemStore 的大小总和超过低水位阈值,RegionServer 开始强制执行 flush,先 flush MemStore 最大的 Region,再 flush 次大的,依次执行。如果此时的写入吞吐量依然很高,导致总 MemStore 大小超过高水位阈值,RegionServer 会阻塞更新并强制执行 flush,直至总 MemStore 大小降到低水位阈值。
- 当一个 RegionServer 的 HLog 数量达到上限,系统会选取最早的 HLog 对应的一个或多个 Region 进行 flush。
- HBase 定期 1 小时刷新 MemStore。
- 手动执行 flush:用户可以通过 shell 命令 flush ‘tablename’ 或者 flush ‘regionname’ 分别对一个表或者一个 Region 进行 flush。
HBase 系统内部设计了一张特殊的表 — hbase:meta 表,专门用来存放整个集群所有的 Region 信息,该表存放在 Zookeeper 中。hbase:meta 中的 hbase 指的是 namespace,HBase 允许针对不同的业务设计不同的 namespace,系统表采用统一的 namespace,即 hbase;meta 指的是 hbase 这个 namespace 下的表名。
读流程
- 1、2.前两步和写入流程相同,如果本地没有 hbase:meta 表的缓存或者根据缓存没有在 RegionServer 上查到数据,那么会去请求 Zookeeper。
- 3.分别在 BlockCache(读缓存),MemStore 和 StoreFile(HFile)中查询目标数据,并将查到的所有数据进行合并。数据合并指的同一条数据的不同版本(timestamp)或者不同的类型(put/delete)。
- 4.将从文件中查询到的数据块(Block,HFile 数据存储单元,默认大小为 64KB)缓存到 BlockCache。
- 5.将合并后的最终结果返回给客户端。
LSM 树
Hbase 的一个列簇(Column Family)本质上就是一颗 LSM 树(Log-Structured Merge Tree),
LSM 树分为内存部分和磁盘部分。内存部分是一个维护有序数据集合的数据结构。一般来讲,内存数据结构可以选择平衡二叉树、红黑树、跳跃表(SkipList) 等维护有序集的数据结构。这里由于考虑到并发性能,HBase 选择了表现更优秀的跳跃表。磁盘部分是由一个个独立的文件组成,每一个文件又是由一个个数据块组成。
LSM 树的索引结构本质是将写入操作全部转化成磁盘的顺序写入,极大地提高了写入操作的性能。
HBase Compaction
HBase 的 MemStore 在满足阈值的情况下会将内存中的数据刷写成 HFile,一个 MemStore 刷写就会形成一个 Hfile。随着时间的推移,同一个 Store 下的 HFile 会越来越多,文件太多会影响 HBase 查询性能,主要体现在查询数据的 IO 次数增加。为了优化查询性能,HBase 会合并小的 HFile 以减少文件数量,这种合并 HFile 的操作称为 Compaction。
- Minor Compaction:会将邻近的若干个 HFile 合并,在合并过程中会清理 TTL 的数据,但不会清理被删除的数据。Minor Compaction 消耗的资源较少,通过少量的 IO 减少文件的个数,提升读取操作的性能,适合高频率地跑。
- Major Compaction:会将一个 Store 下的所有 HFile 进行合并,并且会清理掉过期的和被删除的数据,即在 Major Compaction 会删除全部需要删除的数据。一般情况下,Major Compaction 时间会持续比较长,整个过程会消耗大量系统资源,对上层业务有比较大的影响。因此,生产环境下通常关闭自动触发 Major Compaction 功能,改为手动在业务低峰期触发。

Hbase 集群搭建
安装前提
节点规划
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 角色 |
|---|---|---|
| hadoop1 | 192.168.1.117 | Master,RegionServer |
| hadoop2 | 192.168.1.117 | Backup Master,RegionServer |
| hadoop3 | 192.168.1.117 | Backup Master,RegionServer |
Hosts 配置
编辑 /etc/hosts 文件,添加以下内容,3 台机器都要配置:
192.168.1.117 hadoop1
192.168.1.118 hadoop2
192.168.1.119 hadoop3
下载安装包
wget https://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.lua/hbase/2.4.4/hbase-2.4.4-bin.tar.gz
tar -xzvf hbase-2.4.4-bin.tar.gz
mv hbase-2.4.4 /software/hbase
配置环境变量
添加环境变量,修改 /etc/profile,添加以下两行:
export HBASE_HOME=/software/hbase
export PATH=$PATH:$HBASE_HOME/bin
保存退出后,使用下面命令使环境变量生效:
source /etc/profile
修改配置文件
编辑 conf/hbase-env.sh:
#配置JAVA_HOME
export JAVA_HOME=/software/jdk
#使用的外置的 zookeeper
export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=false
编辑 conf/hbase-site.xml:
<configuration>
//设置将数据写入hdfs的目录
<property>
<name>hbase.rootdir</name>
<value>hdfs://hadoop1:8020/hbase</value>
</property>
//设置hbase模式为集群模式
<property>
<name>hbase.cluster.distributed</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
//设置zookeeper的连接地址
<property>
<name>hbase.zookeeper.quorum</name>
<value>hadoop1,hadoop2,hadoop3</value>
</property>
</configuration>
编辑 conf/regionservers,配置 RegionServer 地址:
hadoop1
hadoop2
hadoop3
编辑 conf/backup-masters,配置 Backup Master 地址:
hadoop2
hadoop3
复制 hadoop1 中的 hbase 文件夹到 hadoop2、hadoop3 中,在hadoop1 中执行如下命令:
scp -r /software/hbase hadoop2:/software/
scp -r /software/hbase hadoop3:/software/
复制 hadoop1中的 /etc/profile 到 hadoop2、hadoop3 中,然后在hadoop2、hadoop3 上执行 source /etc/profile。
scp /etc/profile hadoop2:/etc/
scp /etc/profile hadoop3:/etc/
启动 Hbase 集群
在 Hadoop1 节点上启动 Hbase 集群:
start-hbase.sh
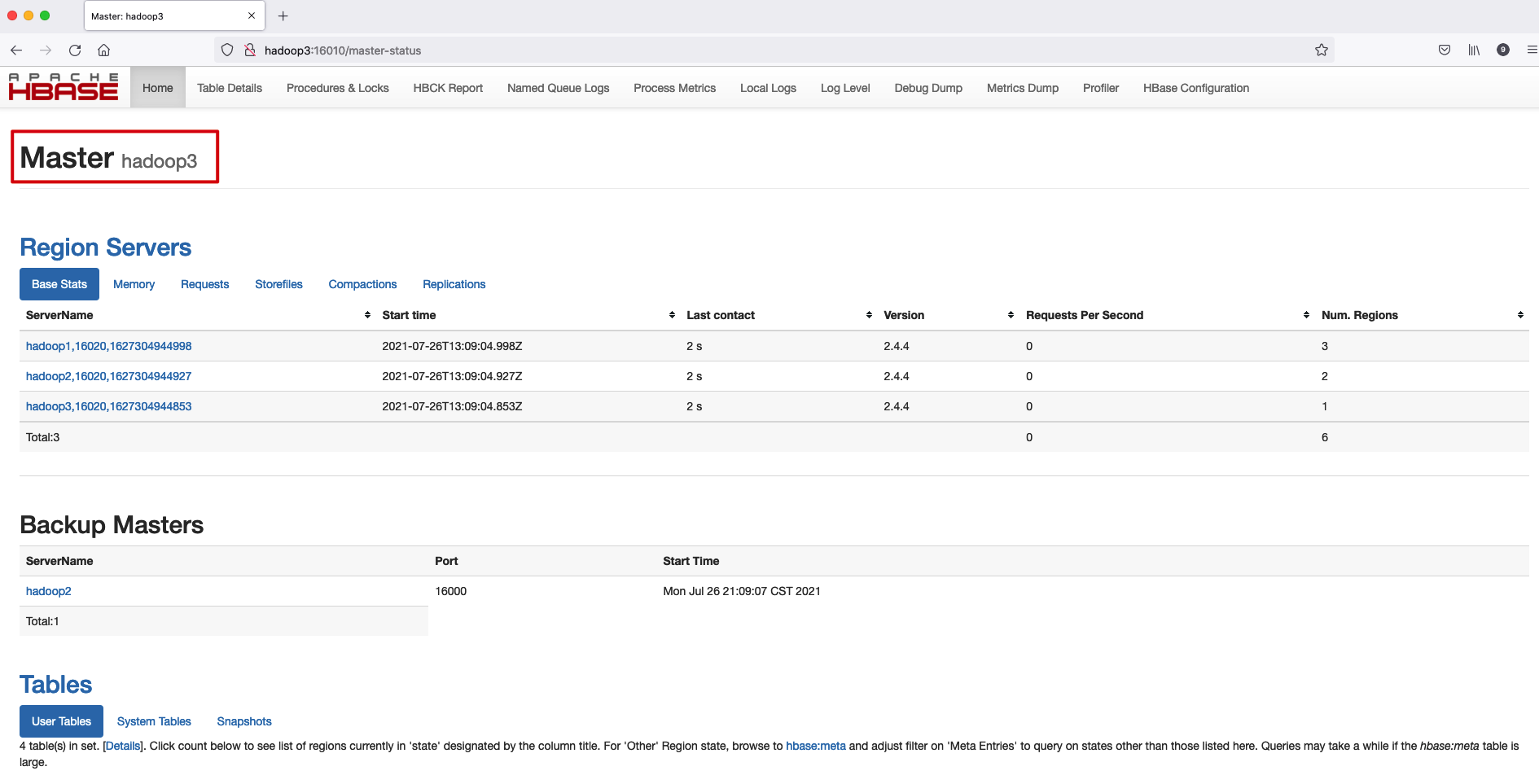
浏览器输入 http://hadoop1:16010 访问 Hbase WebUI 界面。可以看到我们运行了 3 个 RegionServer,Hadoop1 是 HMaster,Hadoop2 和 Hadoop3 是 Backup Master。

高可用测试
在 Hadoop1 上 kill 掉 HMaster 进程。

此时 HMaster 节点变为 Hadoop3。
测试完毕后重新在 Hadoop1 上启动 Hbase。
Hbase Shell 操作
连接 Hbase:
hbase shell
查看节点相关信息
hbase:001:0> zk_dump
HBase is rooted at /hbase
Active master address: hadoop3,16000,1627304946697
Backup master addresses:
hadoop2,16000,1627304947104
hadoop1,16000,1627305210616
Region server holding hbase:meta: hadoop2,16020,1627304944927
Region servers:
hadoop1,16020,1627304944998
hadoop2,16020,1627304944927
hadoop3,16020,1627304944853
Quorum Server Statistics:
hadoop1:2181
stat is not executed because it is not in the whitelist.
hadoop2:2181
stat is not executed because it is not in the whitelist.
hadoop3:2181
stat is not executed because it is not in the whitelist.
Took 0.2593 seconds
创建命名空间
hbase:007:0> create_namespace 'chengzw'
Took 0.1970 seconds
列出命名空间
hbase:020:0> list_namespace
NAMESPACE
chengzw #刚刚创建的命名空间
default
hbase
school
4 row(s)
Took 0.0150 seconds
创建表
在 chengzw 命名空间内创建 student 表,一张表的所有 row 按照 rowkey 的字典序由小到大排序,rowkey 为 name,有 2 个列簇 info,score,表结构如下所示:

使用以下命令创建表:
hbase:003:0> create 'chengzw:student','info','score'
Created table chengzw:student
Took 0.6718 seconds
=> Hbase::Table - chengzw:student
判断表是否存在
hbase:012:0> exists 'chengzw:student'
Table chengzw:student does exist
Took 0.0230 seconds
=> true
列出表
hbase:023:0> list
TABLE
chengzw:student #刚刚创建的表
kylin_metadata
member
new_help_keyword
student
5 row(s)
Took 0.0109 seconds
=> ["chengzw:student", "kylin_metadata", "member", "new_help_keyword", "student"]
查看表结构
hbase:005:0> describe 'chengzw:student'
Table chengzw:student is ENABLED
chengzw:student
COLUMN FAMILIES DESCRIPTION
{NAME => 'info', BLOOMFILTER => 'ROW', IN_MEMORY => 'false', VERSIONS => '1', KEEP_DELETED_CELLS => 'FALSE', DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING => 'NONE', COMPRESSI
ON => 'NONE', TTL => 'FOREVER', MIN_VERSIONS => '0', BLOCKCACHE => 'true', BLOCKSIZE => '65536', REPLICATION_SCOPE => '0'}
{NAME => 'score', BLOOMFILTER => 'ROW', IN_MEMORY => 'false', VERSIONS => '1', KEEP_DELETED_CELLS => 'FALSE', DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING => 'NONE', COMPRESS
ION => 'NONE', TTL => 'FOREVER', MIN_VERSIONS => '0', BLOCKCACHE => 'true', BLOCKSIZE => '65536', REPLICATION_SCOPE => '0'}
2 row(s)
Quota is disabled
Took 0.0654 seconds
插入数据
插入 5 行数据,put 后面从左往右依次有 4 个参数:
- 1.表名
- 2.rowkey
- 3.列名,使用
Column Family:Qualifier表示。 - 4.值
put 'chengzw:student','Tom','info:student_id','20210000000001'
put 'chengzw:student','Tom','info:class',1
put 'chengzw:student','Tom','score:understanding',75
put 'chengzw:student','Tom','score:programming',82
put 'chengzw:student','Jerry','info:student_id','20210000000002'
put 'chengzw:student','Jerry','info:class',1
put 'chengzw:student','Jerry','score:understanding',85
put 'chengzw:student','Jerry','score:programming',67
put 'chengzw:student','Jack','info:student_id','20210000000003'
put 'chengzw:student','Jack','info:class',2
put 'chengzw:student','Jack','score:understanding',80
put 'chengzw:student','Jack','score:programming',80
put 'chengzw:student','Rose','info:student_id','20210000000004'
put 'chengzw:student','Rose','info:class',2
put 'chengzw:student','Rose','score:understanding',60
put 'chengzw:student','Rose','score:programming',61
put 'chengzw:student','程治玮','info:student_id','G20210735010497'
put 'chengzw:student','程治玮','info:class',5
put 'chengzw:student','程治玮','score:understanding',100
put 'chengzw:student','程治玮','score:programming',100
扫描表查看数据
默认情况下,通过 hbase shell 的 scan 或 get 等命令获取的中文内容都是 16 进制的,无法直观的查看数据。通过 {FORMATTER => 'toString'} 可以将 16 进制中文转换成 utf-8 格式的中文的。
获取全表数据:
hbase:093:0> scan 'chengzw:student',{FORMATTER => 'toString'}
ROW COLUMN+CELL
Jack column=info:class, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.469, value=2
Jack column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.442, value=20210000000003
Jack column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.532, value=80
Jack column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.510, value=80
Jerry column=info:class, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.362, value=1
Jerry column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.338, value=20210000000002
Jerry column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.409, value=67
Jerry column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.387, value=85
Rose column=info:class, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.587, value=2
Rose column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.565, value=20210000000004
Rose column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.632, value=61
Rose column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.609, value=60
Tom column=info:class, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.203, value=1
Tom column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.175, value=20210000000001
Tom column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.298, value=82
Tom column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.243, value=75
程治玮 column=info:class, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.685, value=5
程治玮 column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.663, value=G20210735010497
程治玮 column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:11.518, value=100
程治玮 column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.707, value=100
5 row(s)
Took 0.0378 seconds
扫描 rowkey 从 Jack 到 Rose 中的行,这是左闭右开的区间,返回的结果包括 Jack,不包括 Rose:
hbase:094:0> scan 'chengzw:student',{STARTROW => 'Jack',STOPROW => 'Rose'}
ROW COLUMN+CELL
Jack column=info:class, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.469, value=2
Jack column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.442, value=20210000000003
Jack column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.532, value=80
Jack column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.510, value=80
Jerry column=info:class, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.362, value=1
Jerry column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.338, value=20210000000002
Jerry column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.409, value=67
Jerry column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.387, value=85
2 row(s)
Took 0.0188 seconds
扫描到 rowkey 为 Tom 的行,获取 score 和 info:student_id 的值,返回的结果不包括 Tom 这一行:
hbase:101:0> scan 'chengzw:student',{COLUMNS => ['score','info:student_id'],STOPROW => 'Tom'}
ROW COLUMN+CELL
Jack column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.442, value=20210000000003
Jack column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.532, value=80
Jack column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.510, value=80
Jerry column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.338, value=20210000000002
Jerry column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.409, value=67
Jerry column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.387, value=85
Rose column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.565, value=20210000000004
Rose column=score:programming, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.632, value=61
Rose column=score:understanding, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.609, value=60
3 row(s)
Took 0.0175 seconds
获取 info:student_id 这列的数据:
hbase:100:0> scan 'chengzw:student', {COLUMNS => 'info:student_id',FORMATTER => 'toString'}
ROW COLUMN+CELL
Jack column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.442, value=20210000000003
Jerry column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.338, value=20210000000002
Rose column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.565, value=20210000000004
Tom column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.175, value=20210000000001
程治玮 column=info:student_id, timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.663, value=G20210735010497
5 row(s)
Took 0.0112 seconds
获取数据
获取 rowkey 为 Tom 的行:
hbase:105:0> get 'chengzw:student','Tom'
COLUMN CELL
info:class timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.203, value=1
info:student_id timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.175, value=20210000000001
score:programming timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.298, value=82
score:understanding timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.243, value=75
1 row(s)
获取 rowkey 为 Tom 的行 score 列簇的值:
hbase:106:0> get "chengzw:student",'Tom','score'
COLUMN CELL
score:programming timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.298, value=82
score:understanding timestamp=2021-07-31T12:16:10.243, value=75
1 row(s)
Took 0.0068 seconds
获取行数
hbase:007:0> count 'chengzw:student'
5 row(s)
Took 0.0885 seconds
=> 5
删除某列的数据
删除 rowkey 为 Tom 的行 score:programming 的值。
hbase:015:0> delete 'chengzw:student','Tom','score:programming'
Took 0.0078 seconds
删除整行的值
删除 rowkey 为 Tom 这行的值。
hbase:109:0>deleteall 'chengzw:student','Tom'
Took 0.0047 seconds
添加列簇
添加一个列簇 group。
hbase:008:0> alter 'chengzw:student','group'
Updating all regions with the new schema...
1/1 regions updated.
Done.
Took 2.2075 seconds
删除列簇
删除列簇 group。
hbase:010:0> alter 'chengzw:student',{NAME => 'group',METHOD => 'delete'}
Updating all regions with the new schema...
1/1 regions updated.
Done.
Took 1.7310 seconds
清空表
hbase:029:0> truncate 'chengzw:student'
Truncating 'chengzw:student' table (it may take a while):
Disabling table...
Truncating table...
Took 1.3207 seconds
#此时再查表就没有数据了
hbase:030:0> scan 'chengzw:student'
ROW COLUMN+CELL
0 row(s)
Took 0.1715 seconds
删除表
#删除表之前先要禁用表
hbase:076:0> disable 'chengzw:student'
Took 0.3411 seconds
#删除表
hbase:077:0> drop 'chengzw:student'
Took 0.1496 seconds
删除命名空间
hbase:018:0> drop_namespace 'chengzw'
Took 0.1203 seconds
Hbase Java API
引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>2.4.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-endpoint</artifactId>
<version>2.4.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
编写代码
package com.chengzw;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.coprocessor.AggregationClient;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.coprocessor.LongColumnInterpreter;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author chengzw
* @description
* @since 2021/7/29
*/
public class HbaseOperate {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
//创建命名空
System.out.println("===========创建命名空间===========");
createNamespace("chengzw");
//获取命名空间
System.out.println("===========获取命名空间===========");
String[] namespaces = listNamespace();
for (String namespace : namespaces) {
System.out.println(namespace);
}
//检查表是否存在
System.out.println("===========检查表是否存在===========");
System.out.println(isTableExist("chengzw:student"));
//创建表
System.out.println("===========创建表===========");
createTable("chengzw:student","name","info","score");
//列出表
System.out.println("===========列出表===========");
TableName[] tableNames = listTable();
for (TableName tableName : tableNames) {
System.out.println(tableName);
}
//插入数据
System.out.println("===========插入数据===========");
addData("chengzw:student","1","name","","Tom");
addData("chengzw:student","1","info","student_id","20210000000001");
addData("chengzw:student","1","info","class","1");
addData("chengzw:student","1","score","understanding","75");
addData("chengzw:student","1","score","programming","82");
addData("chengzw:student","2","name","","Jerry");
addData("chengzw:student","2","info","student_id","20210000000002");
addData("chengzw:student","2","info","class","1");
addData("chengzw:student","2","score","understanding","85");
addData("chengzw:student","2","score","programming","67");
addData("chengzw:student","3","name","","Jack");
addData("chengzw:student","3","info","student_id","20210000000003");
addData("chengzw:student","3","info","class","2");
addData("chengzw:student","3","score","understanding","80");
addData("chengzw:student","3","score","programming","80");
addData("chengzw:student","4","name","","Rose");
addData("chengzw:student","4","info","student_id","20210000000004");
addData("chengzw:student","4","info","class","2");
addData("chengzw:student","4","score","understanding","60");
addData("chengzw:student","4","score","programming","61");
addData("chengzw:student","5","name","","程治玮");
addData("chengzw:student","5","info","student_id","G20210735010497");
addData("chengzw:student","5","info","class","5");
addData("chengzw:student","5","score","understanding","100");
addData("chengzw:student","5","score","programming","100");
//扫描表所有数据
System.out.println("===========扫描表所有数据===========");
scanAllData("chengzw:student");
//扫描指定列
System.out.println("===========扫描指定列===========");
scanQualifierData("chengzw:student","score","programming");
//扫描指定列在指定行键范围的值
System.out.println("===========扫描指定列在指定行范围的值===========");
scanQualifierRowData("chengzw:student","info","student_id","1","4");
//按行键读取行
System.out.println("===========按行键读取行===========");
getDataByRowkey("chengzw:student","3");
//获取某行指定列的值
System.out.println("===========获取某行指定列的数据===========");
getRowQualifierData("chengzw:student","1","score","programming");
//获取行数
System.out.println("===========获取行数===========");
countRows("chengzw:student");
//获取某列的值
System.out.println("===========删除一行或多行===========");
deleteRowsData("chengzw:student", "1","3");
//删除表
System.out.println("===========删除表===========");
dropTable("chengzw:student");
//删除命名空间
System.out.println("===========删除命名空间===========");
dropNamespace("chengzw");
}
//获取Configuration对象
public static Configuration conf;
public static Connection connection;
//HBaseAdmin: HBase系统管理员的角色,对数据表进行操作或者管理
public static HBaseAdmin admin;
static {
//使用HBaseConfiguration的单例方法实例化
//HBaseConfiguration:封装了hbase集群所有的配置信息(最终代码运行所需要的各种环境)
conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop1:2181,hadoop2:2181,hadoop3:2181");
try {
//创建连接
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
//创建HBaseAdmin对象,用于对表进行create,delete,list等操作
admin = (HBaseAdmin) connection.getAdmin();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 创建命名空间
*
* @param namespace
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void createNamespace(String namespace) throws IOException {
//创建namespace
NamespaceDescriptor descriptor = NamespaceDescriptor.create(namespace).build();
admin.createNamespace(descriptor);
}
/**
* 列出命名空间
*
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String[] listNamespace() throws IOException {
return admin.listNamespaces();
}
/**
* 创建表,String... columnFamily 是不定长参数
*
* @param tableName
* @param columnFamily
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void createTable(String tableName, String... columnFamily) throws Exception {
//判断表是否存在
if (isTableExist(tableName)) {
System.out.println("table: " + tableName + " 表已存在");
} else {
//创建表属性对象,表名需要转字节类型
//HTableDescriptor:所有列簇的信息(一到多个HColumnDescriptor)
HTableDescriptor descriptor = new HTableDescriptor(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
//建表的时候要添加这行,否则下面统计行数的时候会报错:
//org.apache.hadoop.hbase.exceptions.UnknownProtocolException: No registered coprocessor service found for name AggregateService in region
descriptor.addCoprocessor("org.apache.hadoop.hbase.coprocessor.AggregateImplementation");
//创建多个列簇
for (String cf : columnFamily) {
descriptor.addFamily(new HColumnDescriptor(cf));
}
//根据对表的配置,创建表
admin.createTable(descriptor);
System.out.println("table: " + tableName + " 表创建成功!");
}
}
/**
* 判断表是否存在
*
* @param tableName
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static boolean isTableExist(String tableName) throws Exception {
return admin.tableExists(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
}
/**
* 列出表
*
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static TableName[] listTable() throws IOException {
return admin.listTableNames();
}
/**
* 插入数据
*
* @param tableName
* @param rowKey
* @param columnFamily
* @param qualifier
* @param value
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void addData(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamily, String qualifier, String value) throws IOException {
//获取table对象,对表的数据进行增删改查操作
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
//插入一行数据
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier), Bytes.toBytes(value));
table.put(put);
System.out.println("插入数据成功: 行键:" + rowKey + ", 列簇:" + columnFamily + ", 列:" + qualifier + ", 值:" + value);
}
/**
* 扫描表查看数据
*
* @param tableName
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void scanAllData(String tableName) throws IOException {
//获取table对象,对表的数据进行增删改查操作
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Scan scan = new Scan();
//使用HTable得到resultcanner实现类的对象
ResultScanner resultScanner = table.getScanner(scan);
for (Result result : resultScanner) {
//Cell:封装了Column的所有的信息:Rowkey、column qualifier、value、时间戳
Cell[] cells = result.rawCells();
for (Cell cell : cells) {
System.out.println("行键:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneRow(cell)) +
", 列簇:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell)) +
", 列:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)) +
", 值:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)));
}
}
}
/**
* 扫描指定列
*
* @param tableName
* @param columnFamily
* @param qualifier
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void scanQualifierData(String tableName, String columnFamily, String qualifier) throws IOException {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Scan scan = new Scan();
//扫描指定的列
scan.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier));
ResultScanner resultScanner = table.getScanner(scan);
for (Result result : resultScanner) {
//Cell:封装了Column的所有的信息:Rowkey、column qualifier、value、时间戳
Cell[] cells = result.rawCells();
for (Cell cell : cells) {
System.out.println("行键:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneRow(cell)) +
", 列簇:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell)) +
", 列:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)) +
", 值:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)));
}
}
}
/**
* 扫描指定列在指定行键范围的值
*
* @param tableName
* @param columnFamily
* @param qualifier
* @param startRow
* @param stopRow
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void scanQualifierRowData(String tableName, String columnFamily, String qualifier, String startRow, String stopRow) throws IOException {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
//指定起始行键和结束行键
Scan scan = new Scan(Bytes.toBytes(startRow), Bytes.toBytes(stopRow));
//扫描指定的列
scan.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier));
ResultScanner resultScanner = table.getScanner(scan);
for (Result result : resultScanner) {
//Cell:封装了Column的所有的信息:Rowkey、column qualifier、value、时间戳
Cell[] cells = result.rawCells();
for (Cell cell : cells) {
System.out.println("行键:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneRow(cell)) +
", 列簇:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell)) +
", 列:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)) +
", 值:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)));
}
}
}
/**
* 按行键读取行
*
* @param tableName
* @param rowKey
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void getDataByRowkey(String tableName, String rowKey) throws IOException {
//获取table对象,对表的数据进行增删改查操作
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Result result = table.get(new Get(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey)));
for (Cell cell : result.rawCells()) {
System.out.println("行键:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneRow(cell)) +
", 列簇:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell)) +
", 列:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)) +
", 值:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)));
}
}
/**
* 获取某行指定列的值
*
* @param tableName
* @param rowKey
* @param columnFamily
* @param qualifier
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void getRowQualifierData(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamily, String qualifier) throws IOException {
//获取table对象,对表的数据进行增删改查操作
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
//获取某行指定列的值
get.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier));
Result result = table.get(get);
for (Cell cell : result.rawCells()) {
System.out.println("行键:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneRow(cell)) +
", 列簇:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell)) +
", 列:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)) +
", 值:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)));
}
}
/**
* 获取行数
*
* @param tableName
* @throws Throwable
*/
public static void countRows(String tableName) throws Throwable {
//TableName name=TableName.valueOf(tableName);
//HTableDescriptor descriptor = admin.getTableDescriptor(name);
//String coprocessorClass = "org.apache.hadoop.hbase.coprocessor.AggregateImplementation";
//if (! descriptor.hasCoprocessor(coprocessorClass)) {
// descriptor.addCoprocessor(coprocessorClass);
//}
//admin.modifyTable(name, descriptor);
//admin.enableTable(name);
//
计时
//StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
//stopWatch.start();
Scan scan = new Scan();
AggregationClient aggregationClient = new AggregationClient(conf);
System.out.println("RowCount: " + aggregationClient.rowCount(TableName.valueOf(tableName), new LongColumnInterpreter(), scan));
//stopWatch.stop();
//System.out.println("统计耗时:" +stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis());
}
/**
* 删除一行或多行数据
*
* @param tableName
* @param rows
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void deleteRowsData(String tableName, String... rows) throws IOException{
//获取table对象,对表的数据进行增删改查操作
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
List<Delete> deleteList = new ArrayList<Delete>();
//根据行键循环
for(String row : rows){
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(row));
deleteList.add(delete);
}
table.delete(deleteList);
table.close();
}
/**
* 删除表
*
* @param tableName
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void dropTable(String tableName) throws IOException {
//删除前先要禁用表
admin.disableTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
admin.deleteTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
}
/**
* 删除命名空间
*
* @param namespace
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void dropNamespace(String namespace) throws IOException {
admin.deleteNamespace(namespace);
}
}
参考资料
- https://hbase.apache.org
- https://blog.csdn.net/u011974797/article/details/81531490
- https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1006043
- https://www.cnblogs.com/bbgs-xc/p/13070724.html
- https://juejin.cn/post/6844903777347043336#heading-41
- https://www.cnblogs.com/bbgs-xc/p/13070724.html
- HBase 原理与实践
- 极客时间大数据训练营
欢迎关注
