概述
RabbitMQ是消息队列,消息即请求
一般用来解决应用解耦,异步消息,流量削峰等问题

- 应用解耦:如上图,服务A发送消息之后就不用再去理会后续的消息操作,后续的操作都有MQ来完成,这就有了解耦的效果
- 异步消息:在直接调用服务时,服务A收到请求便会将消息直接发送到服务B,而使用了消息队列,服务A将消息发送到消息队列,消息队列可以自主决定什么时候发送消息,有了异步的效果,以免流量过高,提高了性能
- 流量削峰:消息队列可以将消息按照自己的规划来执行,以免在短时间内面临巨大流量,达到削峰填谷的效果
服务启动
RabbitMQ需要安装erlang,使用set ERLANG_HOME=erlang安装路径来指定erlang的路径,再使用rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management来启用插件,该插件提供了一个网页操作页面,网页访问默认端口为15672,代码访问端口为5672,默认用户名和密码为guest
基本结构

- Producer:生产者,即发送消息的程序
- Connection:表示mq消息代理真实的tcp连接,封装了socket协议相关部分逻辑
- channel:Connection内部建立的逻辑连接
- Exchange:交换机,路由消息到不同的队列
- Queue:消息队列,存放消息
- Virtual Host:虚拟主机,一个rabbitMQ可以有多个虚拟主机
- Consumer:消费者,即接收消息的程序
- routingKey:路由键,交换机路由队列的方式
四种交换机类型
- Direct Exchange(直连交换机):交换机与消息队列的路由键一对一完全匹配,可直接使用队列名作为路由键,当消息发送到直连交换机,交换机会将消息发送到对应完全匹配的路由键的消息队列上
- Fanout Exchange(扇形交换机):不处理路由键,消息被发送到扇形交换机时,交换机会将消息发送到所有绑定的队列上,扇形交换机处理消息是最快的
- Topic Exchange(主题交换机):根据某种匹配模式匹配交换机的路由键(通配符)
1.*:只能匹配一个
2.#:可以匹配0个或多个
3.例如:a.#可以匹配a、a.b、a.b.c,但a.*只能匹配到a.b - Header Exchange(头交换机):不处理路由键,根据发送消息的内容中的头属性进行匹配
五个常用的模式
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.13.0</version>
</dependency>
简单模式(交换机类型:Direct Exchange)

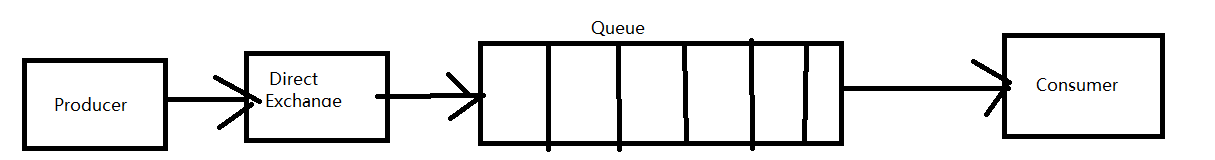
官网的图省略了交换机,但并不是简单模式没有交换机的存在,只是这里使用的是默认交换机,默认交换机是直连交换机
代码演示
- 生产者
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-18
* @Time 13:18
*/
public class ProducerTest {
private ConnectionFactory factory;
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
@Before
public void setUp() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setPort(5672);
connection = factory.newConnection();
channel = connection.createChannel();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testProducer() throws IOException {
//声明队列,没有则创建,参数分别为创建的队列名称、队列的是否需要持久化、是否为独占队列、是否自动删除、队列的其他属性(如最大空间等)
//独占队列表示该队列仅能被创建它的channel访问,当该channel关闭时队列删除
//自动删除队列不是排他的,可以被其他channel访问,当消费者全部断开连接时自动删除
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_1",true,false,false,null);
String message = "hello rabbitmq";
//发布消息,参数分别为交换机、路由键、消息路由标头的其他属性、消息体
channel.basicPublish("","Demo_Queue_1",null,message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
- 消费者
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import com.rabbitmq.client.DeliverCallback;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 13:55
*/
public class ConsumerTest {
private ConnectionFactory factory;
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
@Before
public void setUp() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setPort(5672);
connection = factory.newConnection();
channel = connection.createChannel();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testConsumer() throws IOException {
//声明连接的队列
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_1",true,false,false,null);
//消费消息之后的回调函数
DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag,delivery)->{
String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(message);
};
//接收消息,参数分别为消息名称,是否确认消息,接收完成之后的回调,消费者被取消之后的回调
channel.basicConsume("Demo_Queue_1",true,deliverCallback,consumerTag -> {
System.out.println("cancel");
});
}
}
工作队列模式(交换机类型:Direct Exchange)

工作队列模式与简单模式类似,都使用默认的交换机,这里强调多个消费者共同消费一个队列
发布订阅模式(交换机类型:Fanout Exchange)

发布订阅模式中一个交换机绑定多个队列,使用fanout类型的交换机,消息发布到绑定的所有队列中
代码演示
- 生产者
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-18
* @Time 13:18
*/
public class ProducerTest {
private ConnectionFactory factory;
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
@Before
public void setUp() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setPort(5672);
connection = factory.newConnection();
channel = connection.createChannel();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testProducer() throws IOException {
//声明交换机,参数分别为交换机的名字、交换机的类型
channel.exchangeDeclare("demo_fanout_exchange1", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT);
//声明队列,没有则创建,参数分别为创建的队列名称、队列的是否需要持久化、是否为独占队列、是否自动删除、队列的其他属性(如最大空间等)
//独占队列表示该队列仅能被创建它的channel访问,当该channel关闭时队列删除
//自动删除队列不是排他的,可以被其他channel访问,当消费者全部断开连接时自动删除
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_1",true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_2",true,false,false,null);
//队列绑定交换机,参数分别队列名称、交换机名称、路由键
channel.queueBind("Demo_Queue_1","demo_fanout_exchange1","");
channel.queueBind("Demo_Queue_2","demo_fanout_exchange1","");
String message = "hello rabbitmq";
//发布消息,参数分别为交换机、路由键、消息路由标头的其他属性、消息体
channel.basicPublish("demo_fanout_exchange1","",null,message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
- 消费者
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import com.rabbitmq.client.DeliverCallback;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 13:55
*/
public class ConsumerTest {
private ConnectionFactory factory;
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
@Before
public void setUp() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setPort(5672);
connection = factory.newConnection();
channel = connection.createChannel();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testConsumer() throws IOException {
//声明连接的队列
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_1",true,false,false,null);
//消费消息之后的回调函数
DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag,delivery)->{
String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(message);
};
//接收消息,参数分别为消息名称,是否确认消息,接收完成之后的回调,消费者被取消之后的回调
channel.basicConsume("Demo_Queue_1",true,deliverCallback,consumerTag -> {
System.out.println("cancel");
});
channel.basicConsume("Demo_Queue_2",true,deliverCallback,consumerTag -> {
System.out.println("cancel");
});
}
}
路由模式(交换机类型:Direct Exchange)
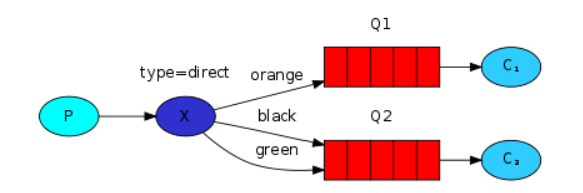
交换机根据路由键绑定不同的队列(亦可一个路由键绑定多个队列),发送消息时通过路由键来指定存放消息的队列
代码演示
- 生产者
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-18
* @Time 13:18
*/
public class ProducerTest {
private ConnectionFactory factory;
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
@Before
public void setUp() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setPort(5672);
connection = factory.newConnection();
channel = connection.createChannel();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testProducer() throws IOException {
//声明交换机,参数分别为交换机的名字、交换机的类型
channel.exchangeDeclare("demo_fanout_exchange1", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT);
channel.exchangeDeclare("demo_direct_exchange1",BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);
//声明队列,没有则创建,参数分别为创建的队列名称、队列的是否需要持久化、是否为独占队列、是否自动删除、队列的其他属性(如最大空间等)
//独占队列表示该队列仅能被创建它的channel访问,当该channel关闭时队列删除
//自动删除队列不是排他的,可以被其他channel访问,当消费者全部断开连接时自动删除
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_1",true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_2",true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_3",true,false,false,null);
//队列绑定交换机,参数分别队列名称、交换机名称、路由键
channel.queueBind("Demo_Queue_1","demo_direct_exchange1","one");
channel.queueBind("Demo_Queue_2","demo_direct_exchange1","two");
channel.queueBind("Demo_Queue_3","demo_direct_exchange1","two");
String message1 = "one";
String message2 = "two";
//发布消息,参数分别为交换机、路由键、消息路由标头的其他属性、消息体
channel.basicPublish("demo_direct_exchange1","one",null,message1.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
channel.basicPublish("demo_direct_exchange1","two",null,message2.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
- 消费者
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import com.rabbitmq.client.DeliverCallback;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 13:55
*/
public class ConsumerTest {
private ConnectionFactory factory;
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
@Before
public void setUp() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setPort(5672);
connection = factory.newConnection();
channel = connection.createChannel();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testConsumer() throws IOException {
//声明连接的队列
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_1",true,false,false,null);
//消费消息之后的回调函数
DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag,delivery)->{
String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(message);
};
//接收消息,参数分别为消息名称,是否确认消息,接收完成之后的回调,消费者被取消之后的回调
channel.basicConsume("Demo_Queue_1",true,deliverCallback,consumerTag -> {
System.out.println("cancel");
});
channel.basicConsume("Demo_Queue_2",true,deliverCallback,consumerTag -> {
System.out.println("cancel");
});
channel.basicConsume("Demo_Queue_3",true,deliverCallback,consumerTag -> {
System.out.println("cancel");
});
}
}

主题模式(交换机类型:Topic Exchange)

主题模式使用topic类型的交换机,特点是路由带有通配符
代码演示
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-18
* @Time 13:18
*/
public class ProducerTest {
private ConnectionFactory factory;
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
@Before
public void setUp() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setPort(5672);
connection = factory.newConnection();
channel = connection.createChannel();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testProducer() throws IOException {
//声明交换机,参数分别为交换机的名字、交换机的类型
channel.exchangeDeclare("demo_exchange_topic1",BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC);
//声明队列,没有则创建,参数分别为创建的队列名称、队列的是否需要持久化、是否为独占队列、是否自动删除、队列的其他属性(如最大空间等)
//独占队列表示该队列仅能被创建它的channel访问,当该channel关闭时队列删除
//自动删除队列不是排他的,可以被其他channel访问,当消费者全部断开连接时自动删除
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_1",true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_2",true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare("Demo_Queue_3",true,false,false,null);
//队列绑定交换机,参数分别队列名称、交换机名称、路由键
channel.queueBind("Demo_Queue_1","demo_exchange_topic1","one.*");
channel.queueBind("Demo_Queue_2","demo_exchange_topic1","one.#");
String message = "one";
//发布消息,参数分别为交换机、路由键、消息路由标头的其他属性、消息体
//只有one.#能匹配
channel.basicPublish("demo_exchange_topic1","one.one.one",null,message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//只有one.#能匹配
channel.basicPublish("demo_exchange_topic1","one",null,message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//one.#和one.*都能匹配
channel.basicPublish("demo_exchange_topic1","one.one",null,message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//one.#和one.*都不能匹配
channel.basicPublish("demo_exchange_topic1","",null,message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
springboot整合rabbitMQ
生产者
- 配置Bean
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 16:58
*/
@Configuration
public class MqConfig {
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("my_topic_exchange");
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("my_direct_exchange");
}
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("my_fanout_exchange");
}
@Bean
public Queue queue(){
return QueueBuilder.durable("my_queue_1").build();
}
@Bean
public Binding binding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue()).to(directExchange()).with("one");
}
/**
* 序列化,rabbitTemplate会自动调用MessageConverter来序列化
* @return
*/
@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter(){
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
}
- 配置文件配置连接参数
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
- 发送消息测试
import com.example.rabbitmq2.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 17:16
*/
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class ProducerTest {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Autowired
private User user;
@Test
public void send1(){
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setAge(13);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("my_direct_exchange","one", user);
}
}
消费者
- 消息队列监听器
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 17:34
*/
@Component
public class ConsumerListener {
//监听器,监听消息队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "my_queue_1")
public void recieve(String msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
- 配置反序列化
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListenerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.listener.RabbitListenerEndpointRegistrar;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.messaging.converter.MappingJackson2MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.support.DefaultMessageHandlerMethodFactory;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.support.MessageHandlerMethodFactory;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description 配置反序列化
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 18:41
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig implements RabbitListenerConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureRabbitListeners(RabbitListenerEndpointRegistrar registrar) {
registrar.setMessageHandlerMethodFactory(messageHandlerMethodFactory());
}
@Bean
public MessageHandlerMethodFactory messageHandlerMethodFactory(){
DefaultMessageHandlerMethodFactory messageHandlerMethodFactory = new DefaultMessageHandlerMethodFactory();
messageHandlerMethodFactory.setMessageConverter(new MappingJackson2MessageConverter());
return messageHandlerMethodFactory;
}
}
消息确认
发送消息和接收消息失败时需要进行下一步的操作,这就需要进行消息确认,并设置回调
生产者
在生产端,当消息发送失败时需要重发或者响应,需要消息确认
- 生产者发送消息到交换机过程
启用消息确认:配置文件spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirm-type=correlated
设置确认消息回调:rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback((CorrelationData correlationData,boolean ack,String cause)->{}),参数ack表示消息是否到达交换机 - 消息从交换机到消息队列过程
启用消息确认:配置文件spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns=true,或者在方法中使用rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true)
设置确认消息回调:rabbitTemplate.setReturnsCallback((ReturnedMessage returned)->{}),参数为路由失败后传回的信息
代码演示
import com.example.rabbitmq2.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ReturnedMessage;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 17:16
*/
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class ProducerTest {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Autowired
private User user;
@Test
public void send1(){
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback((CorrelationData correlationData,boolean ack,String cause)->{
System.out.println(ack);
if(!ack){
System.out.println("消息发送到交换机过程失败");
}
});
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
rabbitTemplate.setReturnsCallback((ReturnedMessage returned)->{
System.out.println("消息从交换机"+returned.getExchange()+"到路由键"+returned.getRoutingKey()+"过程失败");
});
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setAge(13);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("my_direct_exchange","one", user);
}
}
消费者
在消费端,确认消息之后可以进行限流,以及接收消息失败需要重新发送
默认情况下自动签收,通过配置文件设置spring.rabbitmq.listener.direct.acknowledge-mode=manual来手动签收
确认消息:channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),true)
当异常出现,拒签消息:channel basicReject(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),true)
在此基础上,可以使用spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.prefetch=1让消费限流
代码演示
import com.example.rabbitmq2.User;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 17:34
*/
@Component
public class ConsumerListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "my_queue_1")
public void receive(User user, Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
try{
System.out.println(user);
//确认收到消息,第一个参数为消息的标签,第二个参数为是否确认所有消息(false则仅确认消息标签)
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),true);
}catch(Exception e){
//出现异常拒收消息,第二个参数为是否重发,但这里消息已经出现错误,重发基本没有意义,接下来自定义补偿机制
channel.basicReject(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),false);
}
}
}
死信队列
概述
- 创建队列时指定参数x-message-ttl(消息存活时间,单位为毫秒)即为队列添加时效性,在该队列中的消息发布后会具有一个ttl时效性,超过该时间该消息将被队列放弃,不会在该队列中被继续消费;这些超时的消息会转移到一个新的队列,这个队列就是死信队列,这些消息可以在死信队列中被消费
- 创建队列是指定参数x-max-length(队列消息最大容量),队列中消息满后,新来的消息会被路由到死信队列
- 消息拒收后,也会被发送到死信队列
- 消息也可以指定ttl参数,但消息指定时效性后,到时间不会立刻消失,而是等到该消息被消费时会判断该消息是否超时,超时则放弃该消息,路由到死信队列
应用拓展
- 根据时效性队列与死信队列可以相互配合来达到一个延时队列的效果(即消息延时消费)
- 订单超时未支付问题:下订单后商品库存数量需要改动,但此时用户并不是立马支付,于是将订单支付信息发送到消息队列中等待消费,订单支付需要有时间期限,使用时效性的消息队列就能解决超时未支付的问题,超时的订单支付消息被发送到死信队列,死信队列的消费者判断该订单是否被支付,并作后续的业务实现
- 注册发送验证码:验证码具有时效性,超时的验证码被路由到死信队列
- 静态化:延时队列的应用,每隔一段时间对页面进行静态化
代码演示
- 配置
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/***
* @author shaofan
* @Description
* @Date 2021-8-28
* @Time 16:58
*/
@Configuration
public class MqConfig {
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("my_topic_exchange");
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("my_direct_exchange");
}
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("my_fanout_exchange");
}
@Bean
public Queue queue(){
return QueueBuilder.durable("my_queue_1").build();
}
@Bean
public Binding binding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue()).to(directExchange()).with("one");
}
/**
* 序列化,rabbitTemplate会自动调用MessageConverter来序列化
* @return
*/
@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter(){
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
/**
* 死信队列
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue deadQueue(){
return QueueBuilder.durable("my_dead_queue").build();
}
/**
* 死信交换机
* @return
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange deadExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("my_dead_exchange");
}
@Bean
public Binding deadBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(deadQueue()).to(deadExchange()).with("dead");
}
@Bean
public Queue ttlQueue(){
Map<String,Object> args = new HashMap<>();
//消息发送到死信队列是通过交换机和路由键来进行的,所以这里指定的是交换机和路由键
args.put("x-message-ttl",10000);//指定存活时间ttl
args.put("x-dead-letter-exchange","my_dead_exchange");//指定死信交换机
args.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key","dead");//指定死信路由键
return QueueBuilder.durable("my_ttl_queue").withArguments(args).build();
}
@Bean
public Binding binding1(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(ttlQueue()).to(directExchange()).with("ttl");
}
}
- 测试
@Test
public void send2(){
for (int i=0;i<100;i++){
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("my_direct_exchange","ttl","message"+i);
}
}
这一百条消息在ttl队列中存活10秒后,将会被路由到死信队列