QGIS开发入门知识
1. 基础知识
QGIS是一个开源的基础地理信息系统平台软件,是在 GNU 公共许可证 (GPL) 版本 2 或更高版本下发布的,这也意味着用户始终可以免费地获取、修改和使用QGIS。开发技术基于C++和Qt库,具有跨平台的特性,可运行在包括macos、windows等操作系统在内的多个终端平台上。
支持多种矢量、栅格、网格等空间数据格式,优异的插件架构也能很容易地支持新的数据格式。
支持的栅格数据格式:GRASS、USGS DEM、ArcInfo binary grid、 ArcInfo ASCII grid、 ERDAS Imagine 、SDTS、GeoTiff、Tiff with world file 、WMS、WCS。
支持的矢量数据格式:ESRI Shapefiles、PostgreSQL/PostGIS、 GRASS、GeoPackage、SpatiaLite、其他OGR 所支持的格式(http://www.gdal.org/ogr_formats.html)、MSSQL、Oracle、WFS。
支持的网格数据格式:NetCDF、GRIB、2DM、其他MDAL所支持的格式。
软件提供了丰富的地理信息数据编辑、空间分析、数据处理、地图制图等GIS功能。
2. 与ArcGIS的区别
工作中接触到很多GIS从业人员,认为GIS软件就是ArcGIS软件。既不去区分GIS行业基础软件和GIS专题应用软件的区别,也不去思考GIS原理和GIS软件的关系,也没有强烈的版权意识。我认为,ArcGIS能做的事QGIS也能做,有些功能可能还比ArcGIS更好用。实际上QGIS在国外的用户量非常大,国内则少有人用。QGIS与商用GIS软件ArcGIS系列产品相比,根据个人的理解,简单地总结了以下区别:
1) QGIS的接口粒度不如ArcGIS精细。ArcEngine采用接口化编程技术,定义了大量的接口,接口的定义更为细致严谨,接口封装的更为成熟。这表现到二次开发过程中、逻辑严谨性相同的情况下,QGIS的判断条件更多或者处理流程更多,其编码量往往比ArcGIS更大。
2) QGIS采用的是OGC的矢量数据定义标准,而ArcGIS可以支持OGC标准,但又定义了自己的数据标准。空间数据库的存储上表现为WKB结构与OGC定义的标准WKB结构不一致,数据类型表现为QGIS有point、multipoint、linestring、multilinestring、polygon、multipolygon、geometrycollection等几何类型,而ArcGIS简化为point、multipoint、line、polygon这几种类型。这也影响到在开发数据写入、数据处理等相关功能时的代码量,QGIS需要编写更多的代码来进行数据类型一致性判断和数据类型转换。
3) QGIS的数据精度模型和ArcGIS不一致。这是制约QGIS在国内应用最重要因素,相同的作业成本下,生产出符合标准的数据难度更大。一方面是因为QGIS精度模型确实没有ArcGIS完善,另一方面行业内的数据质检软件大多是基于ArcGIS开发的,甚至数据标准中似乎也渗透着ArcGIS的“基因”。但是在空间关系的定义上,两个软件几乎完全一致,都是在九交模型的基础上定义的拓扑规则。
4) 软件体量比ArcGIS小。与ArcGIS动则几个G的安装包相比,QGIS只需要几百M。QGIS只需要C++和python环境即可运行在不同的平台上,而ArcGIS则需要一系列环境部署,特别是令新人头疼的许可。ArcGIS小版本升级都可能伴随着环境的重新部署,而QGIS版本升级很少强制要求环境升级。对比版本升级所带来的部署成本和代码维护成本,QGIS有明显的优势。
5) 性能。这里指的是软件运行时的包含时间、空间、稳定性的综合性能。由于ArcEngine的层层封装,在数据读、写、空间计算上效率极其慢,甚至循环体内会有偶发性的错误,这些问题开发人员又难以从根本上解决。相比而言,QGIS的数据读、写、空间计算效率则快的多,当然内存占有率则取决于开发人员的编码质量,总体上都是自主可控的。在性能上,要显著优于ArcEngine。当然,与ArcGIS Desktop相比,当前版本的渲染效率、稳定性等很多方面还是有一定差距的。
3. 基本的开发技术
工程化:面向地理空间实体对象,依据地理信息数据模型的基本原理,设计软件整体架构;应用github代码托管平台和CMake编译工具,实现跨平台的软件开发技术。
组件化:软件中重要的UI、地理计算模型等都是通过插件注册或者函数注册进行管理,清晰地划分出各个模块,可灵活、快速地搭建专题地理信息软件。
基于已有的开源库:基于Qt库搭建的应用程序以及实现的图形和注记渲染、界面开发等,支持矢量和栅格地理空间数据转换的gdal库,空间几何处理引擎geos库,与影像有关的hdf5、geotiff等,空间索引库spatialindex,空间数据库有关的spatialite、libpq等。
4. 几个入门的基础类
4.1. QgsProject
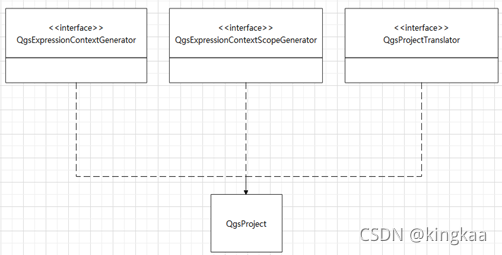
这个类对应于QGIS中的Project,一个应用程序只能有一个QgsProject对象,那么这个类也是单例模式,可以通过QgsProject::instance()获取对象实例。主要功能是记录应用程序中像参考椭球、吸附设置、Layout管理、地图工程文档管理等全局属性信息。
代码样例:遍历当前工程中加载的矢量图层,由于读取的是已加载的图层,不需要重新创建图层对象,可以减少内存消耗,且可以获取到正在编辑的图层中正在编辑的、未commit的图层信息。
QMap<QString, QgsMapLayer*> layers = QgsProject::instance()->mapLayers();
for (QgsMapLayer* layer :layers.values())
{
if (QgsVectorLayer* vlayer=dynamic_cast<QgsVectorLayer*>(layer))
{
qDebug() << vlayer->id();
}
}
4.2. QgsVectorLayer
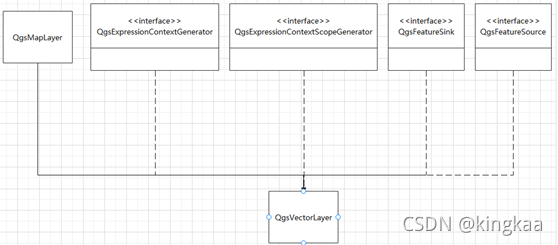
对应一个矢量图层,ArcGIS Engine的IFeatureLayer通过组合IFeatureClass和ITable来构建矢量图层对象,而在QGIS中只用了QgsVectorLayer一个类来管理一个独立的数据源连接和数据渲染。
源码样例:删除当前图层中选中的要素。
void QgisApp::deleteSelected( QgsMapLayer *layer, QWidget *parent, bool checkFeaturesVisible )
{
if ( !layer )
{
layer = mLayerTreeView->currentLayer();//获取图层树选中的图层
}
if ( !parent )
{
parent = this;
}
if ( !layer )
{//如果选中的图层为空,向消息栏推送一条消息
visibleMessageBar()->pushMessage( tr( "No Layer Selected" ),
tr( "To delete features, you must select a vector layer in the legend" ),
Qgis::MessageLevel::Info );
return;
}
//由QgsMapLayer转换为QgsVectorLayer
QgsVectorLayer *vlayer = qobject_cast<QgsVectorLayer *>( layer );
if ( !vlayer )
{//如果选中的非矢量类型的图层
visibleMessageBar()->pushMessage( tr( "No Vector Layer Selected" ),
tr( "Deleting features only works on vector layers" ),
Qgis::MessageLevel::Info );
return;
}
//判断矢量图层是否有删除权限
if ( !( vlayer->dataProvider()->capabilities() & QgsVectorDataProvider::DeleteFeatures ) )
{
visibleMessageBar()->pushMessage( tr( "Provider does not support deletion" ),
tr( "Data provider does not support deleting features" ),
Qgis::MessageLevel::Info );
return;
}
//判断矢量图层是否有编辑权限
if ( !vlayer->isEditable() )
{
visibleMessageBar()->pushMessage( tr( "Layer not editable" ),
tr( "The current layer is not editable. Choose 'Start editing' in the digitizing toolbar." ),
Qgis::MessageLevel::Info );
return;
}
//获取选中要素的数量
const int numberOfSelectedFeatures = vlayer->selectedFeatureCount();
if ( numberOfSelectedFeatures == 0 )
{
visibleMessageBar()->pushMessage( tr( "No Features Selected" ),
tr( "The current layer has no selected features" ),
Qgis::MessageLevel::Info );
return;
}
//display a warning
if ( checkFeaturesVisible )
{
QgsFeature feat;
//遍历选中的矢量要素,且不读取要素的属性信息
QgsFeatureIterator it = vlayer->getSelectedFeatures( QgsFeatureRequest().setNoAttributes() );
bool allFeaturesInView = true;
//将当前显示的地图范围转换为矢量图层地理坐标系所对应的空间范围
QgsRectangle viewRect = mMapCanvas->mapSettings().mapToLayerCoordinates( vlayer, mMapCanvas->extent() );
while ( it.nextFeature( feat ) )
{
if ( allFeaturesInView && !viewRect.intersects( feat.geometry().boundingBox() ) )
{//要素的外接矩形不在画布当前显示的地图范围内
allFeaturesInView = false;
break;
}
}
if ( !allFeaturesInView )
{//当前显示的地图范围内没有选中的要素
// for extra safety to make sure we are not removing geometries by accident
int res = QMessageBox::warning( mMapCanvas, tr( "Delete %n feature(s) from layer \"%1\"", nullptr, numberOfSelectedFeatures ).arg( vlayer->name() ),
tr( "Some of the selected features are outside of the current map view. Would you still like to continue?" ),
QMessageBox::Yes | QMessageBox::No );
if ( res != QMessageBox::Yes )
return;
}
}
//查找其他图层中与当前图层选中要素重复的要素
QgsVectorLayerUtils::QgsDuplicateFeatureContext infoContext;
if ( QgsVectorLayerUtils::impactsCascadeFeatures( vlayer, vlayer->selectedFeatureIds(), QgsProject::instance(), infoContext, QgsVectorLayerUtils::IgnoreAuxiliaryLayers ) )
{
QString childrenInfo;
int childrenCount = 0;
const auto infoContextLayers = infoContext.layers();
for ( QgsVectorLayer *chl : infoContextLayers )
{
childrenCount += infoContext.duplicatedFeatures( chl ).size();
childrenInfo += ( tr( "%1 feature(s) on layer \"%2\", " ).arg( infoContext.duplicatedFeatures( chl ).size() ).arg( chl->name() ) );
}
// for extra safety to make sure we know that the delete can have impact on children and joins
int res = QMessageBox::question( mMapCanvas, tr( "Delete at least %1 feature(s) on other layer(s)" ).arg( childrenCount ),
tr( "Delete %1 feature(s) on layer \"%2\", %3 as well\nand all of its other descendants.\nDelete these features?" ).arg( numberOfSelectedFeatures ).arg( vlayer->name() ).arg( childrenInfo ),
QMessageBox::Yes | QMessageBox::No );
if ( res != QMessageBox::Yes )
return;
}
//开始编辑,创建一个编辑栈
vlayer->beginEditCommand( tr( "Features deleted" ) );
int deletedCount = 0;
QgsVectorLayer::DeleteContext context( true, QgsProject::instance() );
if ( !vlayer->deleteSelectedFeatures( &deletedCount, &context ) )
{
visibleMessageBar()->pushMessage( tr( "Problem deleting features" ),
tr( "A problem occurred during deletion from layer \"%1\". %n feature(s) not deleted.", nullptr, numberOfSelectedFeatures - deletedCount ).arg( vlayer->name() ),
Qgis::MessageLevel::Warning );
}
else
{
const QList<QgsVectorLayer *> contextLayers = context.handledLayers( false );
// if it affects more than one non-auxiliary layer, print feedback for all descendants
if ( contextLayers.size() > 1 )
{
deletedCount = 0;
QString feedbackMessage;
for ( QgsVectorLayer *contextLayer : contextLayers )
{
feedbackMessage += tr( "%1 on layer %2. " ).arg( context.handledFeatures( contextLayer ).size() ).arg( contextLayer->name() );
deletedCount += context.handledFeatures( contextLayer ).size();
}
visibleMessageBar()->pushMessage( tr( "%1 features deleted: %2" ).arg( deletedCount ).arg( feedbackMessage ), Qgis::MessageLevel::Success );
}
showStatusMessage( tr( "%n feature(s) deleted.", "number of features deleted", deletedCount ) );
}
//结束编辑
vlayer->endEditCommand();
}
4.3. QgsMapCanvas
对应于地图画布,负责地图渲染,本质上是在QPainter中生成QImage对象。地图比例尺由QgsMapCanvas对象的物理像素尺寸与抽象的地理空间尺寸所定义。因而,当地图画布大小发生变化时,必将产生比例尺的变化,从而触发地图刷新事件,重新绘制地图。相较于ArcGIS的MapLayout,QGIS目前没有局部刷新功能,当小范围的渲染变化时,相对消耗的资源更多。地图渲染主要用到了缓存和并行计算的方法。
 源码样例:地图刷新
源码样例:地图刷新
void QgsMapCanvas::refreshMap()
{
Q_ASSERT( mRefreshScheduled );
QgsDebugMsgLevel( QStringLiteral( "CANVAS refresh!" ), 3 );
//停止当前正在进行的渲染任务
stopRendering(); // if any...
stopPreviewJobs();
mSettings.setExpressionContext( createExpressionContext() );
mSettings.setPathResolver( QgsProject::instance()->pathResolver() );
if ( !mTheme.isEmpty() )
{
// IMPORTANT: we MUST set the layer style overrides here! (At the time of writing this
// comment) retrieving layer styles from the theme collection gives an XML snapshot of the
// current state of the style. If we had stored the style overrides earlier (such as in
// mapThemeChanged slot) then this xml could be out of date...
// TODO: if in future QgsMapThemeCollection::mapThemeStyleOverrides is changed to
// just return the style name, we can instead set the overrides in mapThemeChanged and not here
mSettings.setLayerStyleOverrides( QgsProject::instance()->mapThemeCollection()->mapThemeStyleOverrides( mTheme ) );
}
// render main annotation layer above all other layers
QgsMapSettings renderSettings = mSettings;
QList<QgsMapLayer *> allLayers = renderSettings.layers();
allLayers.insert( 0, QgsProject::instance()->mainAnnotationLayer() );//主要注记图层
renderSettings.setLayers( allLayers );//渲染图层
// create the renderer job
Q_ASSERT( !mJob );
mJobCanceled = false;
if ( mUseParallelRendering )//多线程并行渲染
mJob = new QgsMapRendererParallelJob( renderSettings );
else //单线程串行渲染
mJob = new QgsMapRendererSequentialJob( renderSettings );
connect( mJob, &QgsMapRendererJob::finished, this, &QgsMapCanvas::rendererJobFinished );//渲染结束后,更新状态信息
mJob->setCache( mCache );//设置缓存对象
mJob->setLayerRenderingTimeHints( mLastLayerRenderTime );
mJob->start();
// from now on we can accept refresh requests again
// this must be reset only after the job has been started, because
// some providers (yes, it's you WCS and AMS!) during preparation
// do network requests and start an internal event loop, which may
// end up calling refresh() and would schedule another refresh,
// deleting the one we have just started.
mRefreshScheduled = false;
mMapUpdateTimer.start();
emit renderStarting();//触发开始渲染的状态
}
源码样例:各个图层绘制的图像合并成一个,并渲染
QImage QgsMapRendererJob::composeImage( const QgsMapSettings &settings,
const std::vector<LayerRenderJob> &jobs,
const LabelRenderJob &labelJob,
const QgsMapRendererCache *cache
)
{
QImage image( settings.deviceOutputSize(), settings.outputImageFormat() );
image.setDevicePixelRatio( settings.devicePixelRatio() );
image.setDotsPerMeterX( static_cast<int>( settings.outputDpi() * 39.37 ) );
image.setDotsPerMeterY( static_cast<int>( settings.outputDpi() * 39.37 ) );
image.fill( settings.backgroundColor().rgba() );
QPainter painter( &image );
#if DEBUG_RENDERING
int i = 0;
#endif
for ( const LayerRenderJob &job : jobs )
{
if ( job.layer && job.layer->customProperty( QStringLiteral( "rendering/renderAboveLabels" ) ).toBool() )
continue; // skip layer for now, it will be rendered after labels
QImage img = layerImageToBeComposed( settings, job, cache );
if ( img.isNull() )
continue; // image is not prepared and not even in cache
painter.setCompositionMode( job.blendMode );
painter.setOpacity( job.opacity );
#if DEBUG_RENDERING
img.save( QString( "/tmp/final_%1.png" ).arg( i ) );
i++;
#endif
painter.drawImage( 0, 0, img );
}
// IMPORTANT - don't draw labelJob img before the label job is complete,
// as the image is uninitialized and full of garbage before the label job
// commences
if ( labelJob.img && labelJob.complete )
{
painter.setCompositionMode( QPainter::CompositionMode_SourceOver );
painter.setOpacity( 1.0 );
painter.drawImage( 0, 0, *labelJob.img );
}
// when checking for a label cache image, we only look for those which would be drawn between 30% and 300% of the
// original size. We don't want to draw massive pixelated labels on top of everything else, and we also don't need
// to draw tiny unreadable labels... better to draw nothing in this case and wait till the updated label results are ready!
else if ( cache && cache->hasAnyCacheImage( LABEL_PREVIEW_CACHE_ID, 0.3, 3 ) )
{
const QImage labelCacheImage = cache->transformedCacheImage( LABEL_PREVIEW_CACHE_ID, settings.mapToPixel() );
painter.setCompositionMode( QPainter::CompositionMode_SourceOver );
painter.setOpacity( 1.0 );
painter.drawImage( 0, 0, labelCacheImage );
}
// render any layers with the renderAboveLabels flag now
for ( const LayerRenderJob &job : jobs )
{
if ( !job.layer || !job.layer->customProperty( QStringLiteral( "rendering/renderAboveLabels" ) ).toBool() )
continue;
QImage img = layerImageToBeComposed( settings, job, cache );
if ( img.isNull() )
continue; // image is not prepared and not even in cache
painter.setCompositionMode( job.blendMode );
painter.setOpacity( job.opacity );
painter.drawImage( 0, 0, img );
}
painter.end();
#if DEBUG_RENDERING
image.save( "/tmp/final.png" );
#endif
return image;
}